并查集C++实现——算法设计与分析,含代码解释
文章目录
-
-
- 什么是并查集
- quick-find并查集
- quick-union并查集
- 优化一:增加权重比较使树变的平衡
- 优化二:路径压缩
- 优化过后的代码
-
什么是并查集
并查集简单来说是集合的集合,其中里层集合表示的节点都是可互相联通的,并查集有两种操作:
- union连接(并):合并两个集合
- find查询(查):查询两个元素是否在同一个集合
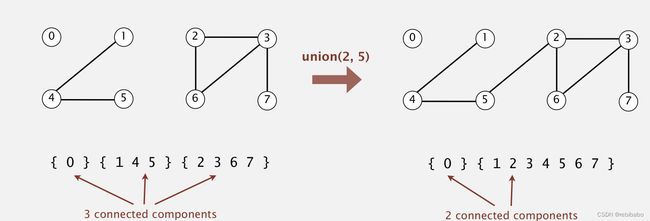
如下图所示,原来的并查集为 { { 0 } , { 1 , 4 , 5 } , { 2 , 3 , 6 , 7 } } \{\{0\},\{1,4,5\},\{2,3,6,7\}\} {{0},{1,4,5},{2,3,6,7}}, { 1 , 4 , 5 } \{1,4,5\} {1,4,5}集合表示节点1、4、5可互相连通,经过合并2,5节点后,变成了右边的并查集,即 { 1 , 4 , 5 } \{1,4,5\} {1,4,5}和 { 2 , 3 , 6 , 7 } \{2,3,6,7\} {2,3,6,7}合并成了一个集合 { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 } \{1,2,3,4,5,6,7\} {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
并查集的节点个数N可以很大,查询操作个数M也可能很大,并且合并和查询操作可以是混合在一起的。
接下来将介绍几种类型的并查集,最终将介绍一个优化的并查集,它只增加了几行代码就可以让性能提高很多。
quick-find并查集
我们用一个数组id来表示并查集,如果节点p和节点q是连接的,当且仅当它们的id相同,例如0,5,6是相连的,它们有共同的id = 0。
- union操作:将节点q和p合并,则需要遍历一遍整个id数组,将q所在集合的所有节点id改成p所在集合的id,时间复杂度为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
- find操作:判断p和q是否相连只需要判断它们的id是否一样,时间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),所以是quick-find并查集。
上述并查集的代码如下:
#include quick-union并查集
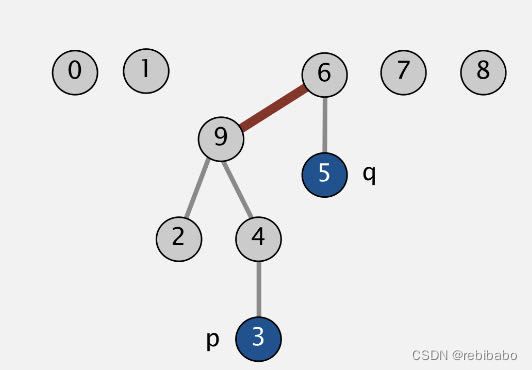
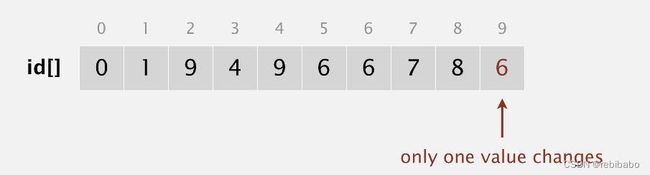
和quick-find的id数组表示含义不一样,quick-union的id数组表示它的父节点,根节点为 i d [ i d [ i d [ . . . i d [ i ] ] . . . ] ] ] id[id[id[...id[i]]...]]] id[id[id[...id[i]]...]]],如下图所示,3号节点的父节点,即id为4,根节点为 i d [ i d [ i d [ 3 ] ] ] = i d [ i d [ 4 ] ] = i d [ 9 ] = 9 id[id[id[3]]] = id[id[4]]=id[9]=9 id[id[id[3]]]=id[id[4]]=id[9]=9。

union操作:合并p和q两个节点只需要将p的根节点id设置成q的根节点id即可,例如,将3和5合并,只需要将3的根节点id设置成5的根节点id即可,时间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),下图展示了Union操作
- find操作:查询p和q是否相连只需要判断p和q的根节点是否相同,最坏的情况查询根节点花费 O ( N ) O(N) O(N),也就是节点连成一条线的情况
代码表示如下:
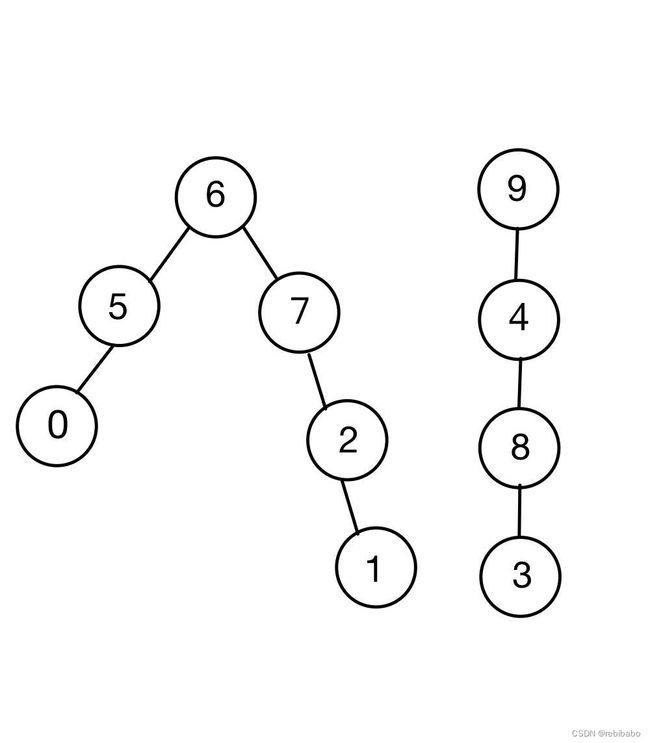
#include 最后的id图和并查集(两棵树)如下两幅图所示,可以看出来深度还是挺大的,例如查询1和3节点的根节点需要查询3次,比较耗时。

优化一:增加权重比较使树变的平衡
这里的trick是把矮一点的树拼接到高一点的树,这样树的高度就不会增加,查询根节点就会更快

我们增加一个数组contain,contain[i]表示以i为根节点的子树的节点个数,初始条件下contain值全为1。
当我们拼接两棵树时,我们比较两棵树的contain值,将contain值小的树拼接到contain值大的树上,并且大树的contain值要加上小树的contain值,用代码表示如下:
int pRoot = getRoot(p);
int qRoot = getRoot(q);
if (qRoot == pRoot) {
return false; // 已经在同一个set里面了,已经在同一个连通分量里面了
}
else {
if(contain[p] >= contain[q]) {
id[qRoot] = pRoot;
contain[pRoot] += contain[qRoot];
}
else {
id[pRoot] = qRoot;
contain[qRoot] += contain[pRoot];
}
}
这样修改以后,树的深度最多是 l o g N log\ N log N,也就是说find操作的时间复杂度为 O ( l o g N ) O(log\ N) O(log N),union操作也为 O ( l o g N ) O(log\ N) O(log N),因为union需要寻找根节点,这样union操作和find操作的复杂度得到了中和。
优化二:路径压缩
当我们查询了一次节点p之后,我们求出了它的根节点root,我们可以p直接和root相连,这样我们下一次查找p的根节点就只要 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)的时间了,我们就只需要在find操作里加两行代码即可,表示将当前节点与其父节点相连,直到与其根节点相连。
int getRoot(int p) {//采用递归的方式
if (id[p] == p) { //自己就是根节点
return p;
}
else {
int d = id[p];
int root = getRoot(d);
if (d != root) {
id[p] = root; //将当前节点的id设置成根节点
contain[d] -= contain[p]; //因为d的子树移到了根节点,所以要将d的contain减去p的contain
}
return root;
}
}
初始的树如下所示:
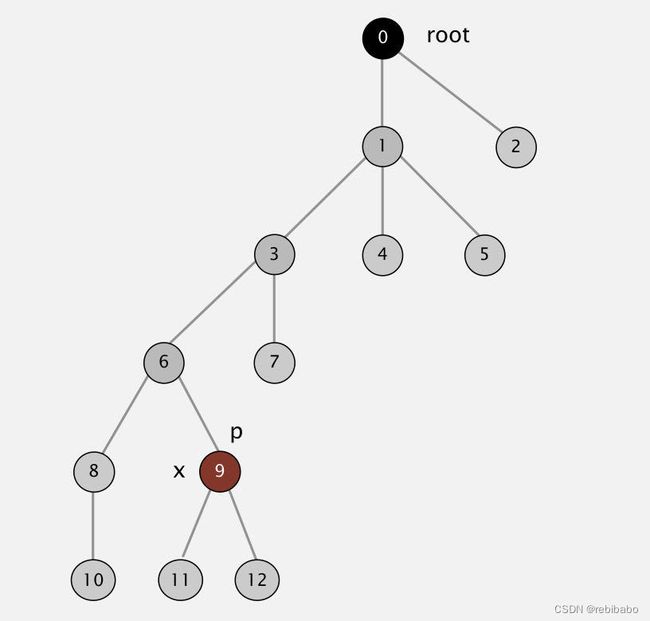
依次查询节点9,6,3以后,将它们移到根节点下,整棵树的高度就比之前少了很多,变得更平坦了。
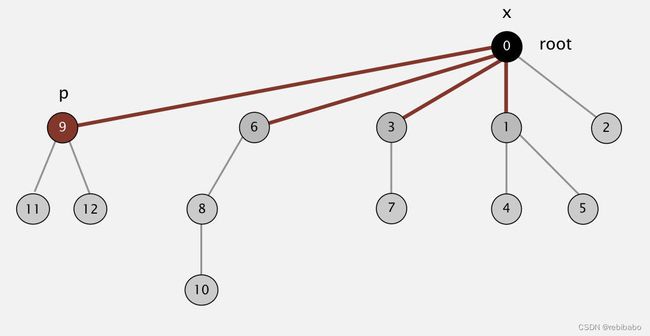
可以验证当有 1 0 9 10^9 109次union操作和 1 0 9 10^9 109次find操作,最普通的并查集需要花费30多年,而仅加上几行代码的优化过的并查集只需要6秒,由此可见一个性能好的算法是多么重要。
优化过后的代码
#include