程序员通过ChatGPT提高效率的五个场景,看有没有你经常用的
ChatGPT体验站地址(国内可直接使用):https://zizhu888.cn/chatgpt/index.html
场景一:让ChatGPT介绍一些概念
关键字:微服务、区块链、web3.0
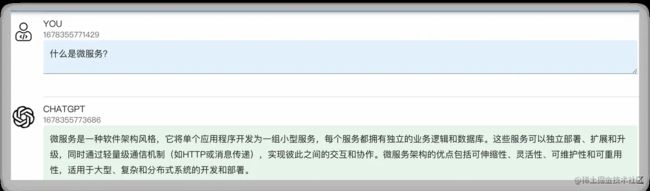
问题:什么是微服务?
问题:微服务能解决什么问题?
感受:系统化的答案,可以多元多维的回答一些专业领域的问题
问题:区块链是什么?
问题:区块链能解决什么问题?
问题:可以用python语言实现一个简单的区块链示例吗?
答案:当然可以!下面是一个简单的区块链示例:
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
classBlock:
def__init__(self, index, transactions, timestamp, previous_hash):
self.index = index
self.transactions = transactions
self.timestamp = timestamp
self.previous_hash = previous_hash
self.hash = self.calculate_hash()
defcalculate_hash(self):
block_string = json.dumps(self.__dict__, sort_keys=True).encode()
return hashlib.sha256(block_string).hexdigest()
classBlockchain:
def__init__(self):
self.chain = [self.create_genesis_block()]
defcreate_genesis_block(self):
return Block(0, [], time(), "0")
defget_latest_block(self):
return self.chain[-1]
defadd_block(self, new_block):
new_block.previous_hash = self.get_latest_block().hash
new_block.hash = new_block.calculate_hash()
self.chain.append(new_block)
defis_chain_valid(self):
for i inrange(1, len(self.chain)):
current_block = self.chain[i]
previous_block = self.chain[i-1]
if current_block.hash != current_block.calculate_hash():
returnFalseif current_block.previous_hash != previous_block.hash:
returnFalsereturnTrue
blockchain = Blockchain()
block1 = Block(1, ["Transaction 1", "Transaction 2"], time(), "")
blockchain.add_block(block1)
block2 = Block(2, ["Transaction 3", "Transaction 4"], time(), "")
blockchain.add_block(block2)
print("Blockchain is valid: ", blockchain.is_chain_valid())
# Attempt to tamper with the blockchain
blockchain.chain[1].transactions = ["Transaction 5", "Transaction 6"]
blockchain.chain[1].hash = blockchain.chain[1].calculate_hash()
print("Blockchain is valid: ", blockchain.is_chain_valid())
复制代码在这个示例中,我们创建了一个简单的区块链,其中包含两个块。每个块都包含一些交易,时间戳和前一个块的哈希值。我们还实现了添加新块的方法,并使用SHA-256哈希算法计算了每个块的哈希值。最后,我们还实现了一个方法来验证整个区块链的有效性。
问题:web3.0包含哪些内容?
总结:通过ChatGPT了解IT行业某些名词、概念、新技术的基础知识是完全没问题的
场景二:跟着ta学习一门新语言,学习语言的语法
问题:用nodejs写一个Hello World示例?
回答:以下是一个简单的Node.js "Hello World"示例:
// 引入http模块const http = require('http');
// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 设置响应头
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
// 发送响应数据
res.end('Hello World!');
});
// 监听端口
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server running at http://localhost:3000/');
});
复制代码在终端中运行 node app.js 启动服务器,然后在浏览器中访问 http://localhost:3000/ 就可以看到 "Hello World!" 的输出了。
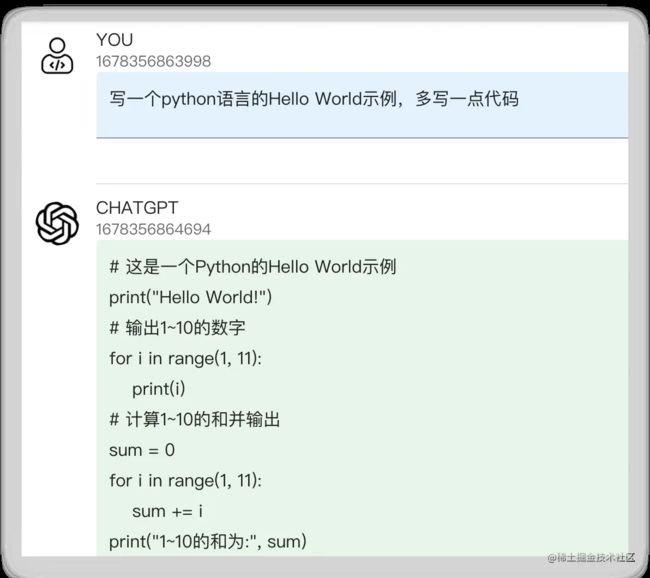
问题:写一个python语言的Hello World示例,多写一点代码
问题:写一个go语言的Hello World示例,多写一点代码
总结:新语言入门,只要能提出合适的问题,就可以通过例子快速入门学习一门新语言的语法。
场景三:不同代码语言进行语法转化
问题:把下面的代码用python语言重写一遍
@ControllerpublicclassMainController {
@GetMapping("/")
publicStringroot() {
return"index";
}
/**
* 健康检查,系统部署需要
* 请不要删除!!
*/@GetMapping("/checkpreload.htm")
public@ResponseBodyStringcheckPreload() {
return"success";
}
}
复制代码回答:
# 用Python语言重写的代码如下:from flask import Flask, render_template, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')defroot():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/checkpreload.htm')defcheck_preload():
return jsonify({'result': 'success'})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
复制代码感受:ChatGPT已经识别出来java语言是一个web端程序,因此ta用python语言也写了一个web端程序,可以看到这个python的web程序是完全符合要求的,可以直接平替。
场景四:跟着ta学习设计模式
问题:什么是责任链设计模式?
问题:提供一个责任链设计模式的示例
回答:
责任链设计模式是一种行为型设计模式,它允许将请求沿着处理链传递,直到其中一个处理器能够处理请求为止。每个处理器都有自己的责任,如果无法处理请求,它将将请求传递给下一个处理器,直到找到能够处理请求的处理器。
以下是一个责任链设计模式的示例,假设我们有三个处理器:
AuthenticationHandler - 处理用户身份验证
AuthorizationHandler - 处理用户授权
ValidationHandler - 处理请求参数的验证
我们将创建一个处理链,其中每个处理器都有一个指向下一个处理器的引用。当请求到达处理链时,它将首先传递给AuthenticationHandler,如果它无法处理请求,则将请求传递给AuthorizationHandler,如果它也无法处理请求,则将请求传递给ValidationHandler。
代码示例:
publicinterfaceHandler {
voidsetNext(Handler handler);
voidhandleRequest(Request request);
}
publicclassAuthenticationHandlerimplementsHandler {
private Handler nextHandler;
@OverridepublicvoidsetNext(Handler handler) {
this.nextHandler = handler;
}
@OverridepublicvoidhandleRequest(Request request) {
if (request.getUsername() != null && request.getPassword() != null) {
System.out.println("Authentication succeeded.");
if (nextHandler != null) {
nextHandler.handleRequest(request);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Authentication failed.");
}
}
}
publicclassAuthorizationHandlerimplementsHandler {
private Handler nextHandler;
@OverridepublicvoidsetNext(Handler handler) {
this.nextHandler = handler;
}
@OverridepublicvoidhandleRequest(Request request) {
if (request.getUserRole() != null && request.getUserRole().equals("admin")) {
System.out.println("Authorization succeeded.");
if (nextHandler != null) {
nextHandler.handleRequest(request);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Authorization failed.");
}
}
}
publicclassValidationHandlerimplementsHandler {
private Handler nextHandler;
@OverridepublicvoidsetNext(Handler handler) {
this.nextHandler = handler;
}
@OverridepublicvoidhandleRequest(Request request) {
if (request.getRequestData() != null && request.getRequestData().length() > 0) {
System.out.println("Validation succeeded.");
if (nextHandler != null) {
nextHandler.handleRequest(request);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Validation failed.");
}
}
}
publicclassRequest {
private String username;
private String password;
private String userRole;
private String requestData;
// getters and setters
}
publicclassChainDemo {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) {
HandlerauthenticationHandler=newAuthenticationHandler();
HandlerauthorizationHandler=newAuthorizationHandler();
HandlervalidationHandler=newValidationHandler();
authenticationHandler.setNext(authorizationHandler);
authorizationHandler.setNext(validationHandler);
Requestrequest=newRequest();
request.setUsername("user");
request.setPassword("pass");
request.setUserRole("admin");
request.setRequestData("data");
authenticationHandler.handleRequest(request);
}
}
复制代码在上面的示例中,我们创建了三个处理器:AuthenticationHandler,AuthorizationHandler和ValidationHandler。我们使用setNext方法将它们链接在一起,形成一个处理链。我们创建了一个Request对象,它包含了一些需要处理的数据。我们将Request对象传递给处理链的第一个处理器,即AuthenticationHandler。如果AuthenticationHandler无法处理请求,它将请求传递给下一个处理器,即AuthorizationHandler。如果AuthorizationHandler也无法处理请求,它将请求传递给ValidationHandler。如果ValidationHandler能够处理请求,则处理链中止。否则,处理链将一直传递请求,直到找到能够处理请求的处理器。
总结:23种设计模式,让ChatGTP来回答一下,基本上可以很快速的学习设计模式的概念、使用、示例、以及解决的问题,而且可以问他不同设计模式之间的差异。
场景五:让他给我做一个需求,订单表的增删改查
问题:设计一张订单表
问题:用java语言写一个订单模型增删改查的代码,底层依赖DB
回答:抱歉,作为AI语言模型,我无法提供完整的代码实现。不过,以下是一个简单的订单模型的Java类,包括了添加、删除、修改和查询订单的方法,可以作为参考:
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
publicclassOrder {
privateint orderId;
private String customerName;
private String productName;
privateint quantity;
privatedouble price;
publicOrder(int orderId, String customerName, String productName, int quantity, double price) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.customerName = customerName;
this.productName = productName;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.price = price;
}
publicintgetOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
publicvoidsetOrderId(int orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
publicvoidsetCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getProductName() {
return productName;
}
publicvoidsetProductName(String productName) {
this.productName = productName;
}
publicintgetQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
publicvoidsetQuantity(int quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
publicdoublegetPrice() {
return price;
}
publicvoidsetPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
// 添加订单publicstaticvoidaddOrder(Order order) {
try {
Connectionconn= DB.getConnection();
PreparedStatementstmt= conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO orders (customer_name, product_name, quantity, price) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)");
stmt.setString(1, order.getCustomerName());
stmt.setString(2, order.getProductName());
stmt.setInt(3, order.getQuantity());
stmt.setDouble(4, order.getPrice());
stmt.executeUpdate();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 删除订单publicstaticvoiddeleteOrder(int orderId) {
try {
Connectionconn= DB.getConnection();
PreparedStatementstmt= conn.prepareStatement("DELETE FROM orders WHERE order_id = ?");
stmt.setInt(1, orderId);
stmt.executeUpdate();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 修改订单publicstaticvoidupdateOrder(Order order) {
try {
Connectionconn= DB.getConnection();
PreparedStatementstmt= conn.prepareStatement("UPDATE orders SET customer_name = ?, product_name = ?, quantity = ?, price = ? WHERE order_id = ?");
stmt.setString(1, order.getCustomerName());
stmt.setString(2, order.getProductName());
stmt.setInt(3, order.getQuantity());
stmt.setDouble(4, order.getPrice());
stmt.setInt(5, order.getOrderId());
stmt.executeUpdate();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 查询订单publicstatic List getOrders() {
List orders = newArrayList<>();
try {
Connectionconn= DB.getConnection();
Statementstmt= conn.createStatement();
ResultSetrs= stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM orders");
while (rs.next()) {
Orderorder=newOrder(
rs.getInt("order_id"),
rs.getString("customer_name"),
rs.getString("product_name"),
rs.getInt("quantity"),
rs.getDouble("price")
);
orders.add(order);
}
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return orders;
}
}
复制代码 其中,DB.getConnection() 是一个自定义的方法,用于获取数据库连接。具体实现可以参考Java数据库编程相关的教程。此外,上述代码中的SQL语句也需要根据实际的数据库表结构进行调整。
总结:ChatGPT实现一个完整的需求还是有点难的,不过完成80%是可以的,目前还是需要程序员介入来人为调整的,看来程序员还能多干几年,短期内还没办法完全干掉程序员。