《剑指Offer》链表全题——妙解思路,难度由浅入深
目录
JZ6 从尾到头打印链表
JZ24 反转链表
JZ25 合并两个排序的链表
JZ52 两个链表的第一个公共结点
JZ23 链表中环的入口结点
JZ22 链表中倒数最后k个结点
JZ35 复杂链表的复制
JZ76 删除链表中重复的结点
JZ6 从尾到头打印链表
思路:建立一个顺序表,用一个指针遍历链表并每次插入在顺序表的0位置处,最后得到的就是逆序。
public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
//可以设置每次从顺序表的0下标位置插入,得到的就是逆序
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode cur = listNode;
while(cur != null){
list.add(0,cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
return list;
} JZ24 反转链表
解法一(辅助栈):建立一个辅助栈,将链表元素全部入栈,最后在一个一个出栈并从到尾修改链表值
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
//通过辅助栈来反转
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = head;
//入栈
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
//出栈进入链表
cur = head;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
cur.val = stack.pop();
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
} 解法二思路(新链表头插法):建立一个新链表,遍历需要反转的链表,同时每次头插新链表即可
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode list = null;
ListNode listHead = null;
ListNode cur = head;
//每次头插
while(cur != null){
if(listHead == null){
list = new ListNode(cur.val);
listHead = list;
}else{
listHead = new ListNode(cur.val);
listHead.next = list;
list = listHead;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return listHead;
}JZ25 合并两个排序的链表
解法一思路(不够优化,易理解):创建一个新链表,用两个指针遍历要合并的两个链表,两链表结点值谁小,谁就尾插如新链表中,往复以上操作,最后返回新链表头节点即可。
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
//严防有一方为空
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode start1 = list1;
ListNode start2 = list2;
ListNode head = null;
ListNode cur = null;
ListNode pd = null;
//有一方为空就停下来
while(start1 != null && start2 != null){
if(start1.val < start2.val){
if(head == null){
head = new ListNode(start1.val);
cur = head;
pd = head;
}else{
cur = new ListNode(start1.val);
pd.next = cur;
pd = cur;
}
start1 = start1.next;
}else{
if(head == null){
head = new ListNode(start2.val);
cur = head;
pd = head;
}else{
cur = new ListNode(start2.val);
pd.next = cur;
pd = cur;
}
start2 = start2.next;
}
}
//检测还有哪一方没有完
if(start1 != null){
cur.next = start1;
}
if(start2 != null){
cur.next = start2;
}
return head;
}解法二思路(虚拟链表,优化时间复杂度为O(1)):创建一个虚拟的头节点,比较待合并的两链表的结点值大小,虚拟新结点的下一个next就是他,往复以上操作(相当于不断在待合并的两链表之间建立联系),最后返回虚拟头结点的next即可。
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
//优化空间复杂度为O(1)
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);//虚拟结点
ListNode cur = head;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val < list2.val){
cur.next = list1;
cur = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
cur.next = list2;
cur = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if(list1 != null){
cur.next = list1;
}
if(list2 != null){
cur.next = list2;
}
return head.next;
}JZ52 两个链表的第一个公共结点
思路:先分别遍历两个链表求出各自长度,再比较大小求出差值,让链表较长的一方先走完差值,两链表就可以同步往后走,找到公共结点,若有一方为空,则说明没有公共结点。
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
if(head1 == null && head2 == null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur1 = head1;
ListNode cur2 = head2;
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
//先求出链表的长度差
while(cur1 != null){
count1++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != null){
count2++;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
//比较大小,谁长谁就先走长度的差值,使其同步
cur1 = head1;
cur2 = head2;
if(count1 > count2){
int D_value = count1 - count2;
while(D_value > 0){
D_value--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
}else{
int D_value = count2 - count1;
while(D_value > 0){
D_value--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}
//同步后两个一起走,相遇后停下,cur1 == null是防止对null解引用,并且说明没有公共结点
while(cur1 != null && cur1.val != cur2.val){
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
//若为空说明没有公共点
if(cur1 == null){
return null;
}else{
return cur1;
}
}JZ23 链表中环的入口结点
解法一(哈希法):创建一个哈希表来来记录用cur指针遍历的每一个元素,一旦发现重复,立刻return。
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
Set set = new HashSet();
ListNode cur = pHead;
while(cur != null){
//一旦发现重复,立刻返回
if(set.contains(cur.val)){
return cur;
}
set.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
} 解法二(快慢指针+数学推理),博主已经整理出文章,快来看看吧~
http://t.csdn.cn/x9E1w
JZ22 链表中倒数最后k个结点
此题给出了进阶要求:时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度O(1);
以下两种方法皆符合
解法一(差值法):通过cur指针遍历链表计算出长度,再计算与K的差值,若差值小于0,则返回null;否则重置cur,让cur走差值步即可,
最后返回cur;
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = pHead;
//计数
while(cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = pHead;
//求差值,确定走的步数
int D_value = count - k;
if(D_value < 0){
return null;
}
while(D_value > 0){
D_value--;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
} 解法二(快慢指针法):让快指针先走K步,然后快慢指针一起走,直到fast为空时返回慢指针,注意K值大于链表的情况。
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
ListNode fast = pHead;
ListNode slow = pHead;
//快指针先走k步
while(k > 0 && fast != null){
k--;
fast = fast.next;
}
//严防K值大于链表长度
if(k > 0 && fast == null){
return null;
}
//快慢指针一起走,fast为空时,返回即可
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}JZ35 复杂链表的复制
思路(HashMap法):注意此题需要进行深拷贝,先用虚拟头节点尾插复制一份原链表的val,同时将待复制和复制的结点地址同时存入HashMap中(key为待复制结点的地址,val为复制的结点的地址),最后通过HashMap其中的对应关系即可深拷贝Random指针,此题用画图理解会更加容易,此题也是百度的面试题,博主已经整理出了画图理解的思路,快来看看吧!
http://t.csdn.cn/FGVly
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
//通过HashMap来确定随机指针
Map map = new HashMap<>();
//虚拟头结点
RandomListNode head = new RandomListNode(-1);
RandomListNode cur = head;
//拷贝val值,并创建新链表
RandomListNode pCur = pHead;
while(pCur != null){
cur.next = new RandomListNode(pCur.label);
cur = cur.next;
map.put(pCur, cur);
pCur = pCur.next;
}
cur = head.next;
pCur = pHead;
//随机指针的复制
while(pCur != null){
cur.random = map.get(pCur.random);
pCur = pCur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return head.next;
} JZ76 删除链表中重复的结点
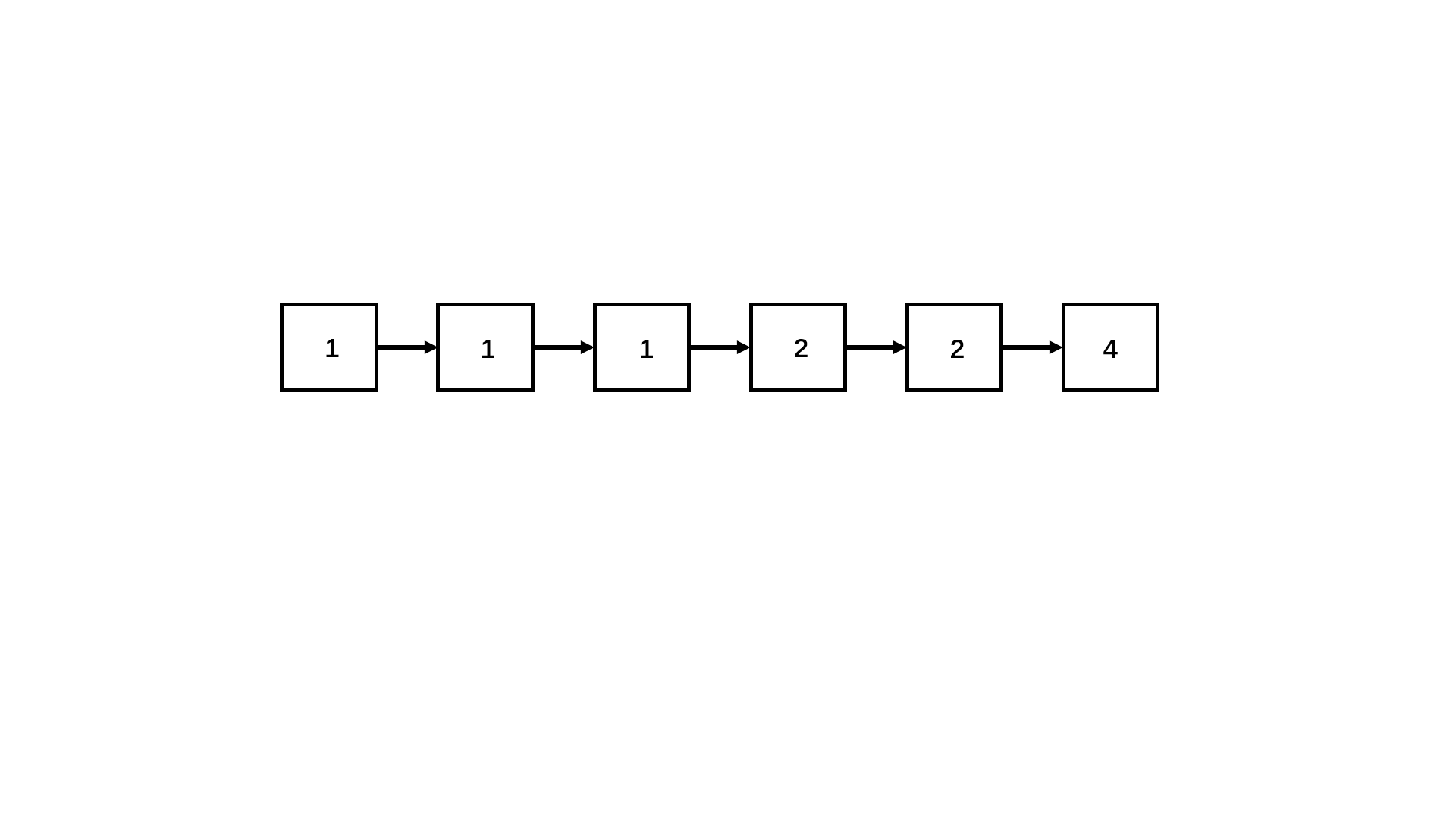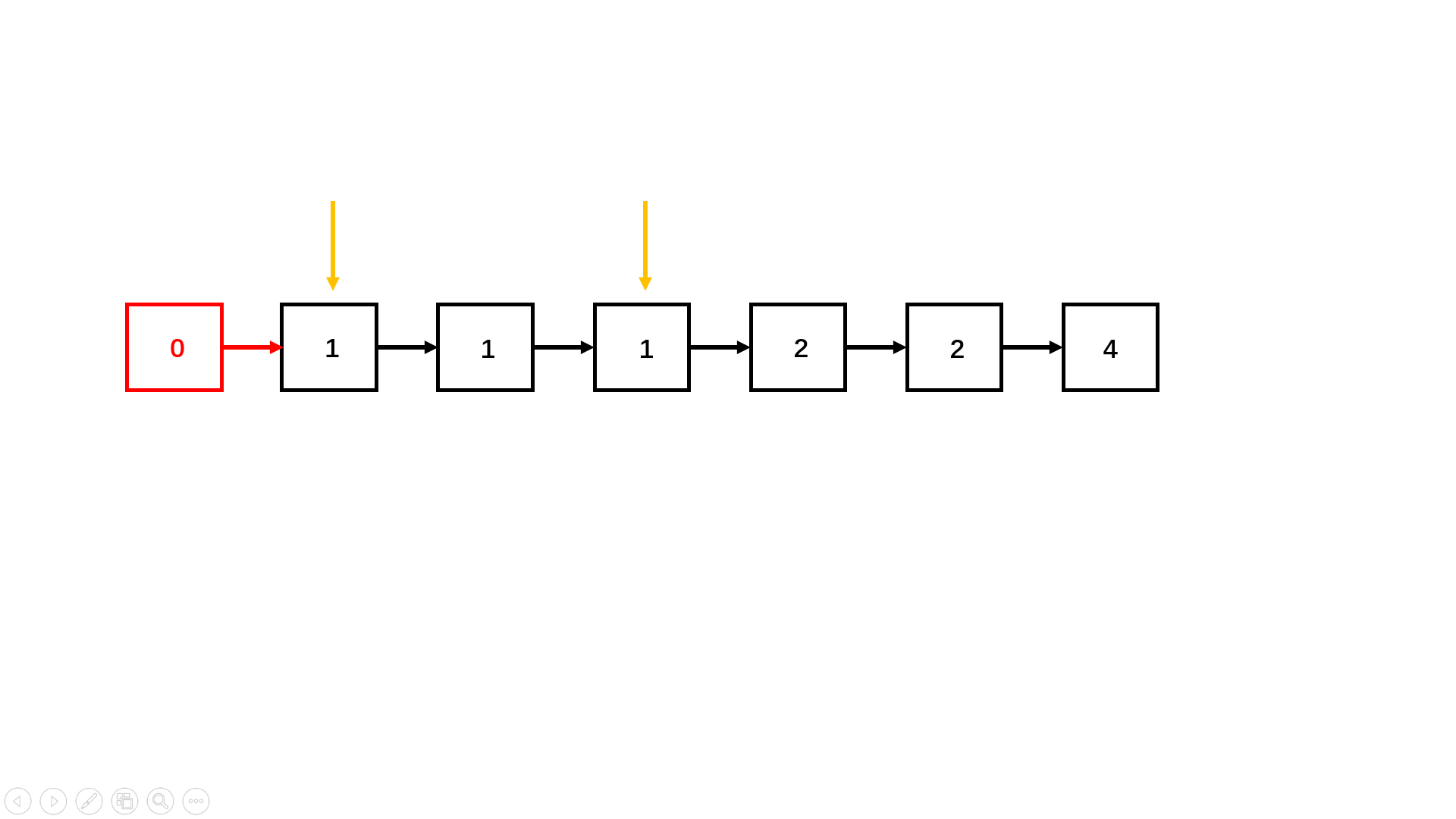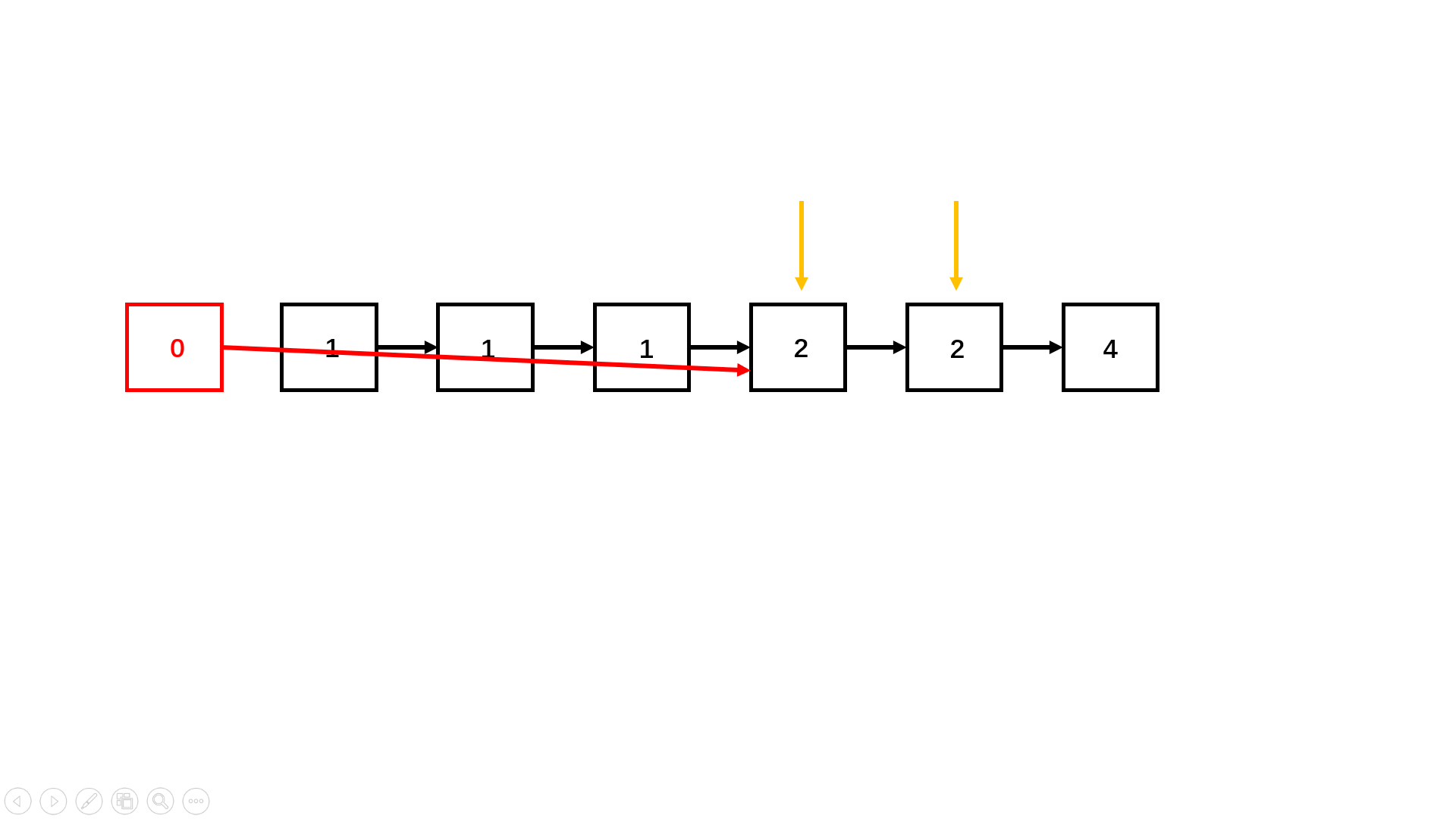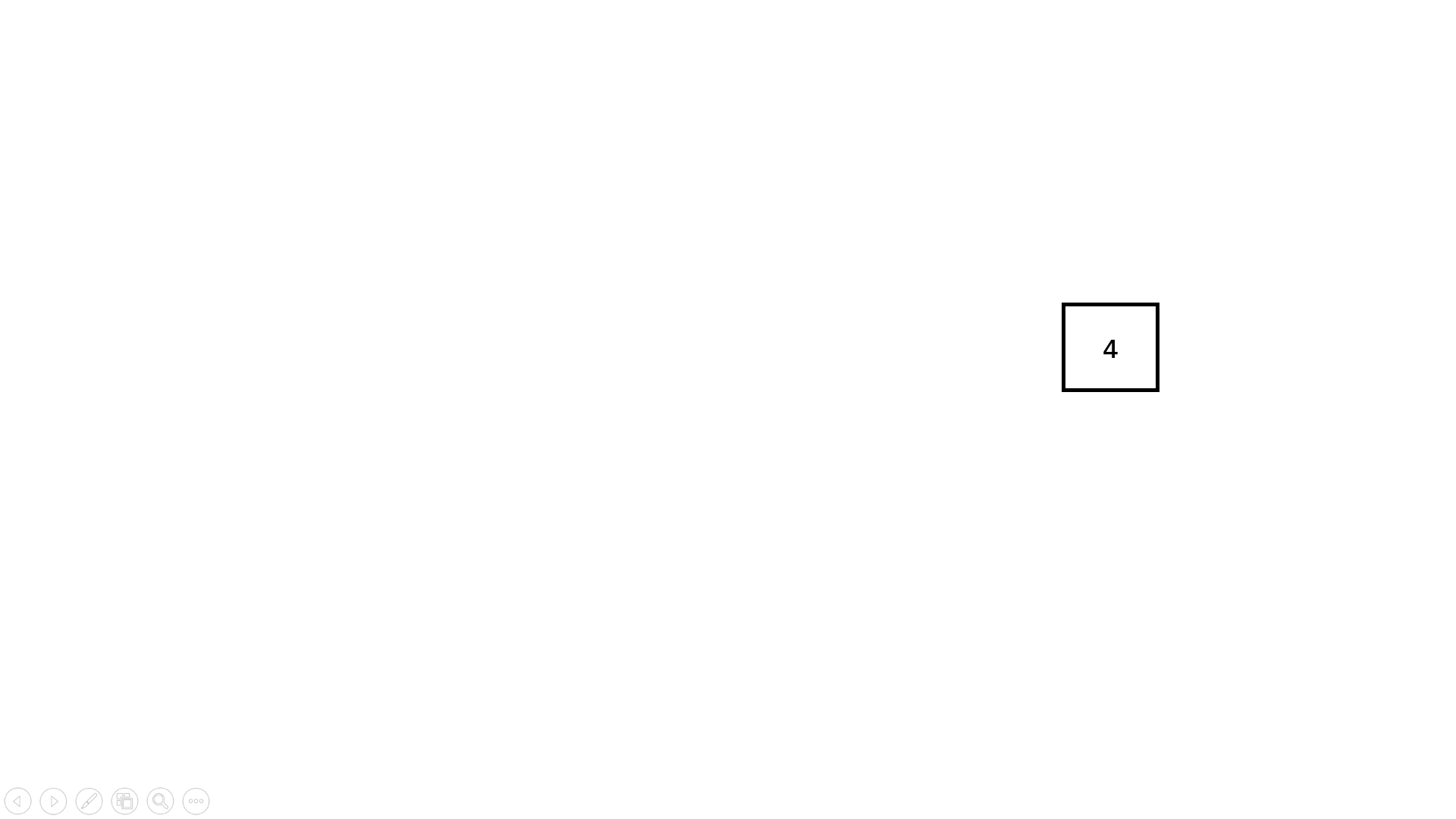
写法一(三指针法,不够优化,但便于理解):此题与普通的删除链表中重复的结点不同,一旦重复,则全部删除;
可以先创建一个虚拟结点,这个虚拟结点是为了方便三个指针分别位于前中后以及避免{1,1}情况,造成空指针异常,接着让这三个指针遍历链表,一旦发现前指针和中指针重复,就让前指针继续走下去,直到值不同,停下来,若为空,将后指针的next置为空返回头指针即可,若不为空,将后指针的next指向他,继续向后调整即可(如下图):
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null){
return null;
}
//创建一个虚拟头节点
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
head.next = pHead;
ListNode cur = pHead;
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode prevPrev = null;
while(cur != null){
//找到了
if(prev.val == cur.val){
//继续找有没有重复的
while(cur != null && prev.val == cur.val){
cur = cur.next;
}
if(cur == null){
prevPrev.next = null;
return head.next;
}else{
prevPrev.next = cur;
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}else{
prevPrev = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head.next;
}写法二(单个指针):与思路一的思想是相同的,不易看懂,但是更优化
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null){
return null;
}
//创建一个虚拟头节点
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
head.next = pHead;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){
//发现重复
if(cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val){
int tmp = cur.next.val;
//继续向后找出所有相同的,注意while条件的先后顺序不能变
while(cur.next != null && cur.next.val == tmp){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head.next;
}