数据结构-图详解(最小生成树 Kruskal、 Prim算法-C++)
图基本概念与基本遍历
文章目录
- 1.生成树
-
- 生成树定义:
- 2. 构造最小生成树
-
- Kruskal算法
- Prim算法
1.生成树
生成树定义:
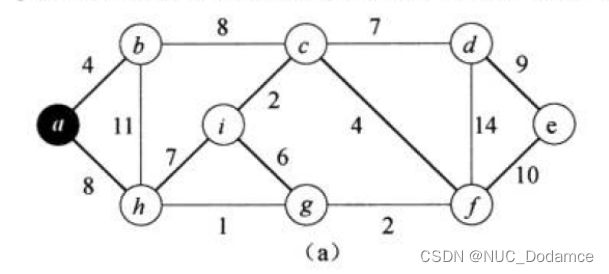
无向图中一个连通图的最小连通子图称为生成树。(用最少的边把所有顶点连接起来)。n个顶点的连通图的生成树有n-1条边。
路径长度:对于不带权图为路径的边个数。带权图为路径所有边权值的和
最小生成树:所有生成树中,路径长度最小的生成树。
所以生成树一定是连通图。这个定义是在无向图的基础上开展的。
连通图:无向图中,若顶点A、B存在路径,称为A、B连通。若图中的任意两点都是连通的,则称此图为连通图。
2. 构造最小生成树
若连通图由n个顶点组成,则其生成树必含n个顶点和n-1条边。因此构造最小生成树的准则有三条:
- 只能使用图中的权值最小的边来构造最小生成树
- 只能使用恰好n-1条边来连接图中的n个顶点
- 选用的n-1条边不能构成回路
构造最小生成树的方法:Kruskal算法和Prim算法。这两个算法都采用了逐步求解的贪心策略。
Kruskal算法
克鲁斯卡尔算法查找最小生成树的方法是:将连通网中所有的边按照权值大小做升序排序,从权值最小的边开始选择,只要此边不和已选择的边一起构成环路,就可以选择它组成最小生成树。对于 N 个顶点的连通网,挑选出 N-1 条符合条件的边,这些边组成的生成树就是最小生成树。
判断图是否产生闭环,可以采用并查集的方式。如果这个边的顶点在并查集中,则说明如果添加这条边的话就构成环。
参考文章及算法流程
这里权值从小到大排序使用C++优先级队列完成。默认大顶堆,我们这里要使用小顶堆。
引入之前博客介绍的并查集:
#pragma once
#pragma once
#include#include
#include测试代码:
void TestGraphMinTree()
{
std::vector<char>vet{ 'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i' };
matrix::Graph<char, int> g(vet);
g.AddEdge('a', 'b', 4);
g.AddEdge('a', 'h', 8);
//g.AddEdge('a', 'h', 9);
g.AddEdge('b', 'c', 8);
g.AddEdge('b', 'h', 11);
g.AddEdge('c', 'i', 2);
g.AddEdge('c', 'f', 4);
g.AddEdge('c', 'd', 7);
g.AddEdge('d', 'f', 14);
g.AddEdge('d', 'e', 9);
g.AddEdge('e', 'f', 10);
g.AddEdge('f', 'g', 2);
g.AddEdge('g', 'h', 1);
g.AddEdge('g', 'i', 6);
g.AddEdge('h', 'i', 7);
matrix::Graph<char, int> kminTree;
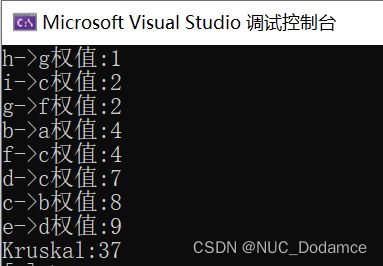
std::cout << "Kruskal:" << g.Kruskal(kminTree) << std::endl;
kminTree.Print();
}
int main() {
TestGraphMinTree();
}
Prim算法
与Kruskal算法类似,Prim算法也是通用最小生成树算法的一个特例。
Prim算法的工作原理与Dijkstra最短路径算法类似,也是使用局部贪心。
Prim算法:
开始指出一个起点,从起点开始找最小生成树。Prim算法将所有顶点分成两部分:已经选入的点,未选入的点。算法思路是从未选入部分顶点中选出一个点,再从选入的点中选择一个。这两个点的关系是:直接相连构成边,且这条边是所有选择中权值最小的。将选则的点添加到已经选择部分顶点集合中。
开始将顶点分成两部分X、Y
X={a} Y={b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i}
X集合中选一个点a
Y中选一个点,两个点要直接相连。Y中只能选b、h。又要选权值最小的边,所以这个点只能选择b
此后
X={a,b}
Y={c,d,e,f,g,h,i}
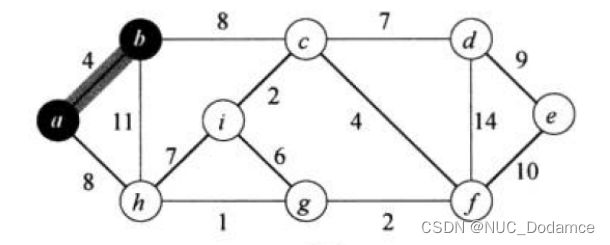
特殊:如果权值相同任意选择点即可。
后序重复这个过程即可,第二步选择的顶点组入下:
X=a Y=h 权值:8
或者
X=b Y=c 权值:8
这两个条权值相同,任意选择即可。
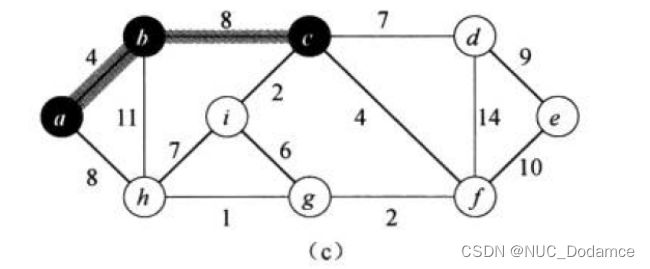
此时X={a,b,c} Y={d,e,f,g,h,i}
知道把Y集合所有点选择完毕即可。这样就可以避免选择成环。不需要并查集来判断成环。
但是:
这里处理时使用优先级队列,因为优先级队列开始时把顶点周围的所有边添加进去,而优先级队列又不支持指定删除元素。所以当优先级队列弹出最小权值边的时候,还需要判断这条边的两个顶点是不是在同一个集合X中,如果在集合X,说明这条边构成环。
namespace matrix {
//邻接矩阵保存边关系
template<class v, class w, w max_w = INT_MAX, bool Direction = false>
class Graph {
typedef Graph<v, w, max_w, Direction>Self;
private:
std::vector<v>_vertexs;//顶点集合
std::map<v, int>_indexMap;//顶点与下标的映射
std::vector<std::vector<w>>_matrix;//邻接矩阵
//获取顶点下标
size_t GetPointIndex(const v& point) {
auto ptr = _indexMap.find(point);
if (ptr != _indexMap.end()) {
return ptr->second;
}
else {
throw std::invalid_argument("顶点不存在");
return -1;
}
}
public:
//图的创建
Graph() = default;
Graph(std::vector<v>& points) {
_vertexs.resize(points.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
_vertexs[i] = points[i];
_indexMap[points[i]] = i;
}
_matrix.resize(points.size());
//邻接矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); i++) {
_matrix[i].resize(points.size(), max_w);
}
}
//添加边关系,输入两个点,以及这两个点连线边的权值。
private:
void _AddEdge(size_t posSrc, size_t posDst, const w& weight) {
//区分有向图与无向图
_matrix[posSrc][posDst] = weight;
if (Direction == false) {
//无向图,添加两条边关系
_matrix[posDst][posSrc] = weight;
}
}
public:
void AddEdge(const v& src, const v& dst, const w& weight) {
size_t posSrc = GetPointIndex(src);
size_t posDst = GetPointIndex(dst);
_AddEdge(posSrc, posDst, weight);
}
public:
struct Edge {
size_t posSrc;
size_t posDst;
w weight;
Edge(size_t _posSrc, size_t _posDst, const w& _weight)
:posSrc(_posSrc), posDst(_posDst), weight(_weight)
{}
};
struct rules {
bool operator()(const Edge& left, const Edge& right) {
return left.weight > right.weight;//从小到大
}
};
//最小生成树,返回最小生成树权值,传入一个图,这个参数是输入输出参数,函数结束后,minTree是图的最小生成树
//Src:Prim算法传入的起始点
w Prim(Self& minTree, const v& Src) {
size_t posSrc = GetPointIndex(Src);
//初始化minTree
size_t size = _vertexs.size();
minTree._vertexs = _vertexs;
minTree._indexMap = _indexMap;
minTree._matrix.resize(size);
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
minTree._matrix[i].resize(size, max_w);
}
std::vector<bool>X(size,false);//已经加入的顶点的集合
std::vector<bool>Y(size, true);//未加入的顶点的集合
X[posSrc] = true; Y[posSrc] = false;
//从两个集合中选择两个点,构成权值最小的边
std::priority_queue<Edge, std::vector<Edge>, rules> minQueue;
//将这个顶点连接的边入队列
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (_matrix[posSrc][i] != max_w) {
minQueue.push(Edge(posSrc, i, _matrix[posSrc][i]));
}
}
//选择权值最小的边,添加到最小生成树
size_t edgeSize = 0;
w weight = w();
while (!minQueue.empty()) {
Edge minEdge = minQueue.top();
minQueue.pop();
//如果这条边的两个顶点在一个集合X中,说明构成环
if (X[minEdge.posDst]) {
//构成环
continue;
}
std::cout << _vertexs[minEdge.posSrc] << "->" << _vertexs[minEdge.posDst] << "权值:" << minEdge.weight << endl;
minTree._AddEdge(minEdge.posSrc, minEdge.posDst, minEdge.weight);
X[minEdge.posDst] = true;
Y[minEdge.posDst] = false;
edgeSize++;
weight += minEdge.weight;
//size个点,选size-1条边就可以结束循环了
if (edgeSize == size - 1) {
break;
}
//posSrc---posDst,把posDst点所有边(除了posSrc---posDst)加入优先级队列
//所以posDst的另一个点不在集合X即可。
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (_matrix[minEdge.posDst][i] != max_w && X[i] == false) {
minQueue.push(Edge(minEdge.posDst, i, _matrix[minEdge.posDst][i]));
}
}
}
if (edgeSize == size - 1) {
return weight;
}
else {
return w();
}
}
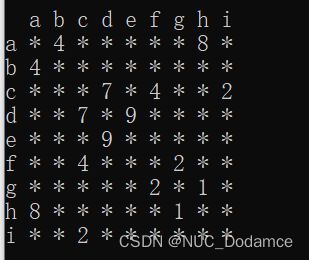
void Print() {
//打印顶点对应坐标
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++) {
std::cout << "[" << i << "]" << "->" << _vertexs[i] << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
}
//打印边
std::cout << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++) {
std::cout << _vertexs[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//打印矩阵
for (size_t i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); i++) {
std::cout << _vertexs[i] << " ";
for (size_t j = 0; j < _matrix[i].size(); j++) {
if (_matrix[i][j] == max_w) {
std::cout << "*" << " ";
}
else {
std::cout << _matrix[i][j] << " ";
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
};
}
测试代码
void TestGraphMinTree()
{
std::vector<char>vet{ 'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i' };
matrix::Graph<char, int> g(vet);
g.AddEdge('a', 'b', 4);
g.AddEdge('a', 'h', 8);
//g.AddEdge('a', 'h', 9);
g.AddEdge('b', 'c', 8);
g.AddEdge('b', 'h', 11);
g.AddEdge('c', 'i', 2);
g.AddEdge('c', 'f', 4);
g.AddEdge('c', 'd', 7);
g.AddEdge('d', 'f', 14);
g.AddEdge('d', 'e', 9);
g.AddEdge('e', 'f', 10);
g.AddEdge('f', 'g', 2);
g.AddEdge('g', 'h', 1);
g.AddEdge('g', 'i', 6);
g.AddEdge('h', 'i', 7);
/*matrix::Graph kminTree;
std::cout << "Kruskal:" << g.Kruskal(kminTree) << std::endl;*/
matrix::Graph<char, int> primTree;
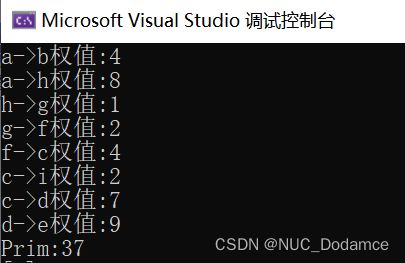
std::cout << "Prim:" << g.Prim(primTree,'a') << std::endl;
primTree.Print();
}
int main() {
TestGraphMinTree();
}