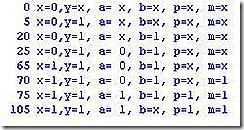【原创】The solutional manual of the Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis (2nd)—ch07-III
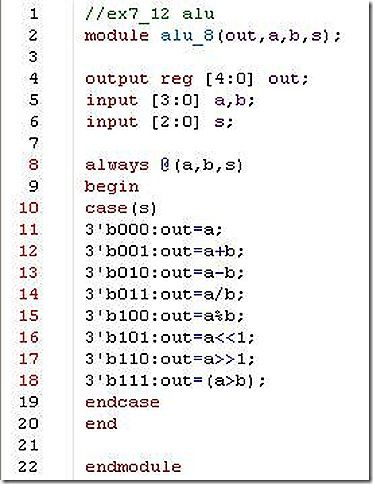
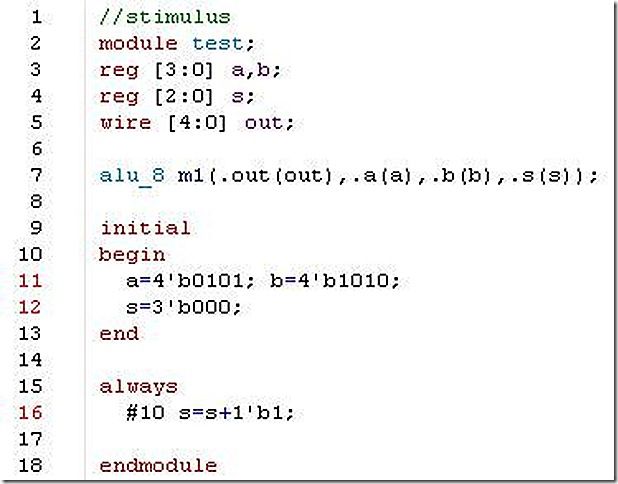
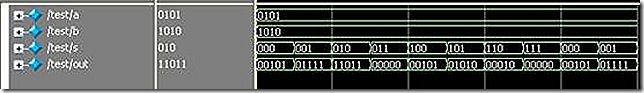
12. Using a case statement, design an 8-function ALU that takes 4-bit inputs a and b and a 3-bit input signal select, and gives a 5-bit output out. The ALU implements the following functions based on a 3-bit input signal select. Ignore any overflow or underflow bits.
| Select Signal |
Function |
| 3’b000 |
Out=a |
| 3’b001 |
Out=a+b |
| 3’b010 |
Out=a-b |
| 3’b011 |
Out=a/b |
| 3’b100 |
Out=a%b(remainder) |
| 3’b101 |
Out=a<<1 |
| 3’b110 |
Out=a>>1 |
| 3’b111 |
Out=(a>b)(magnitude compare) |
my answer:
13. Using a while loop, design a clock generator. Initial value of clock is 0. Time period for the clock is 10.
my answer:
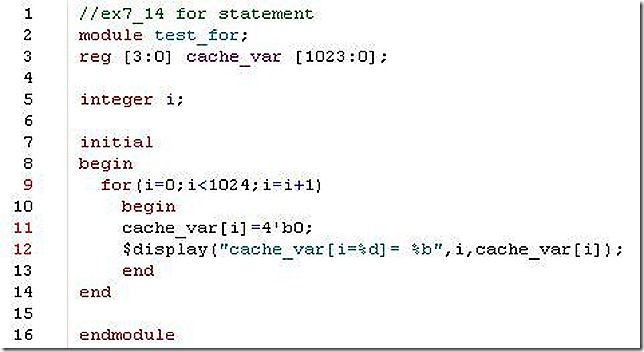
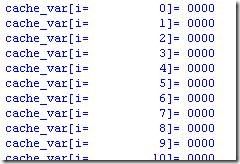
14. Using the for loop, initialize locations 0 to 1023 of a 4-bit register array cache_var to 0.
my answer:
15. Using forever statement, design a clock with time period =10 and duty cycl = 40%. Initial value of clock is 0.
my answer:
16. Using the repeat loop, delay the statement a= a+1 by 20 positive edges of clock.
my answer:
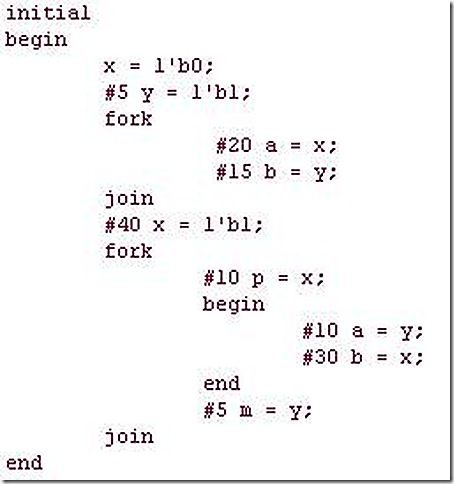
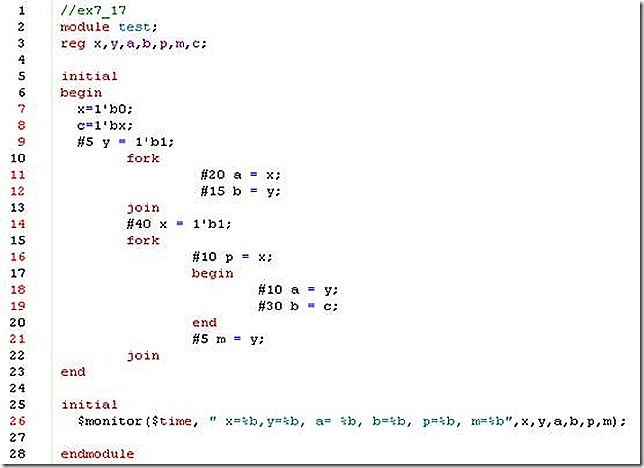
17. Below is a block with nested sequential and parallel blocks. When does the block finish and what is the order of execution of events? At what simulation times does each statement finish execution?
my answer:
(p.s, I made a change at line 19).
18. Design an 8-bit counter by using forever loop, named block, and disabling of named block. The counter starts counting at count=5 and finishes at count=67. The count is incremented at positive edge of clock. The clock has a time period of 10. The counter counts through the loop only once and then is disabled.(Hint: Use the disable statement).
my answer:
0 count= 5
# 5 count= 6
# 15 count= 7
# 25 count= 8
# 35 count= 9
# 45 count= 10
# 55 count= 11
# 65 count= 12
# 75 count= 13
# 85 count= 14
# 95 count= 15
# 105 count= 16
# 115 count= 17
# 125 count= 18
# 135 count= 19
# 145 count= 20
# 155 count= 21
# 165 count= 22
# 175 count= 23
# 185 count= 24
# 195 count= 25
# 205 count= 26
# 215 count= 27
# 225 count= 28
# 235 count= 29
# 245 count= 30
# 255 count= 31
# 265 count= 32
# 275 count= 33
# 285 count= 34
# 295 count= 35
# 305 count= 36
# 315 count= 37
# 325 count= 38
# 335 count= 39
# 345 count= 40
# 355 count= 41
# 365 count= 42
# 375 count= 43
# 385 count= 44
# 395 count= 45
# 405 count= 46
# 415 count= 47
# 425 count= 48
# 435 count= 49
# 445 count= 50
# 455 count= 51
# 465 count= 52
# 475 count= 53
# 485 count= 54
# 495 count= 55
# 505 count= 56
# 515 count= 57
# 525 count= 58
# 535 count= 59
# 545 count= 60
# 555 count= 61
# 565 count= 62
# 575 count= 63
# 585 count= 64
# 595 count= 65
# 605 count= 66
# 615 count= 67
Reference
Smair Palnitkar, <Verilog HDL: A Guide to Digital Design and Synthesis (2nd) >