oracle _hash partition,深入解析partition-hash分区
依据惯例,先看官网对hash partition的解释
Hash partitioning enables easy partitioning of data that does not lend itself to range or list partitioning. It does this with a simple syntax and is easy to implement. It is a better choice than range partitioning when:
■ You do not know beforehand how much data maps into a given range
■ The sizes of range partitions would differ quite substantially or would be difficult to balance manually
■ Range partitioning would cause the data to be undesirably clustered
■ Performance features such as parallel DML, partition pruning, and partition-wise
joins are important
The concepts of splitting, dropping or merging partitions do not apply to hash partitions. Instead, hash partitions can be added and coalesced.
1、创建hash partition
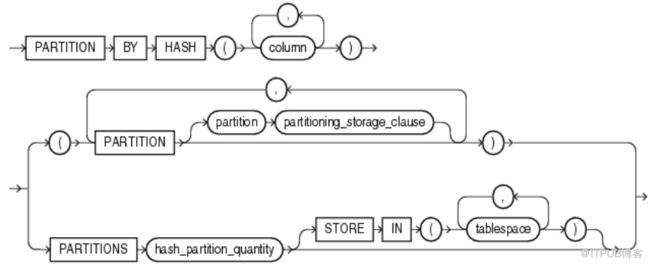
语法如下:
语法看起来比range partition复杂,实际要简单的多。
column: 分区依赖列 ( 支持多个,中间以逗号分隔 );
partition: 指定分区,有两种方式:
直接指定分区名,分区所在表空间等信息。
只指定分区数量,和可供使用的表空间。
例:
--创建hash分区表
SQL> create table t_partition_hash(id number,name varchar2(20))
2 partition by hash(id)(
3 partition t_hash_p1 tablespace tbs01,
4 partition t_hash_p2 tablespace tbs02,
5 partition t_hash_p3 tablespace tbs03);
表已创建。
--查看hash分区表分区信息
SQL> edit
已写入 file afiedt.buf
1 select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name from user_tab_partitions
2* where table_name='T_PARTITION_HASH'
SQL> /
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME
------------------------------ ---------------------------------------------------------------------
T_HASH_P1 TBS01
T_HASH_P2 TBS02
T_HASH_P3 TBS03
--指定分区数量及表空间,创建相同的hash分区表
SQL> drop table t_partition_hash;
表已删除。
SQL> edit
已写入 file afiedt.buf
1 create table t_partition_hash(id number,name varchar2(20))
2 partition by hash(id)
3* partitions 3 store in(tbs01,tbs02,tbs03)
SQL> /
表已创建。
SQL> select partition_name,tablespace_name from user_tab_partitions
2 where table_name='T_PARTITION_HASH';
PARTITION_NAME TABLESPACE_NAME
------------------------------ ------------------------------
SYS_P21 TBS01
SYS_P22 TBS02
SYS_P23 TBS03
提示: 这里分区数量和可供使用的表空间数量之间没有直接对应关系。 分区数并不一定要等于表 空间数。
例如:
--指定分区数量
SQL> edit
已写入 file afiedt.buf
1 create table t_partition_hash(id number,name varchar2(20))
2 partition by hash(id)
3* partitions 3 store in(tbs01,tbs02,tbs03,jjjg)
SQL> /
表已创建。
SQL> select partition_name,tablespace_name from user_tab_partitions
2 where table_name='T_PARTITION_HASH';
PARTITION_NAME TABLESPACE_NAME
------------------------------ ------------------------------
SYS_P24 TBS01
SYS_P25 TBS02
SYS_P26 TBS03
--指定分区数量>指定表空间数量
SQL> edit
已写入 file afiedt.buf
1 create table t_partition_hash(id number,name varchar2(20))
2 partition by hash(id)
3* partitions 3 store in(tbs01,tbs02)
SQL> /
表已创建。
SQL> select partition_name,tablespace_name from