数据结构之排序算法--C#实现 (下)
上一篇和大家一起学习了基本的排序算法,这一篇写一些高级的排序算法,
1.希尔排序(Shell‘s Sort)又称“缩小增量排序”(Diminshing Increment Sort)是一种对插入排序的改进算法。
基本思想为:
设待排序记录序列有n个记录,首先取一个整数gap<n作为间隔,将全部记录分为gap个子序列,所有间隔为gap的记录放在同一子序列中,在每一子序列中分别执行直接插入排序。
重复上述的子序列划分和排序工作,直到gap==1将所有记录放在同一个序列中排序为止。
C#实现代码如下:
 Shell's Sort Code
Shell's Sort Code
1 public static void ShellSort(int[] arr) 2 { 3 int inner, temp; 4 int h = 3; 5 while (h > 0) 6 { 7 for (int outer = h; outer <= arr.Length - 1; outer ++) 8 9 { 10 temp = arr[outer]; 11 inner = outer; 12 while ((inner > h - 1) && arr[inner - h] >= temp) 13 { 14 arr[inner] = arr[inner - h]; 15 inner -= h; 16 } 17 arr[inner] = temp; 18 } 19 Console.WriteLine(); 20 Console.WriteLine("h="+h.ToString()); 21 DisplayArray(arr); 22 h = (h - 1) % 3; 23 } 24 }
2.归并排序算法(Merge Sort)
归并排序法是将两个(或多个)有序集合合并成一个新的有序集合。即把待排序集合分为若干个子集合,对每个集合进行排序,然后再把这些有序的子集合合并为整体集合。是分治法(Divide and COnquer)的典型应用。
若将两个集合合并成一个集合称为2-路归并。
百度百科关于归并排序算法的介绍,非常的详细,请参阅:http://baike.baidu.com/view/19000.htm
本处以2-路归并算法为例给出C#源代码,供大家学习。
 Merge Sort Code
Merge Sort Code
1 public static void MergeSort(int[] arr) 2 { 3 int arrLength1, arrLength2; 4 arrLength1 = arr.Length / 2; 5 if (arr.Length % 2 == 0) 6 { 7 arrLength2 = arrLength1; 8 } 9 else 10 { 11 arrLength2 = arrLength1 + 1; 12 } 13 int[] arr1 = new int[arrLength1]; 14 int[] arr2 = new int[arrLength2]; 15 Array.Copy(arr, 0, arr1, 0, arrLength1); 16 Array.Copy(arr, arrLength1, arr2, 0, arrLength2); 17 Console.WriteLine("\narr1 Before Sort:"); 18 DisplayArray(arr1); 19 Console.WriteLine("\narr2 Before Sort:"); 20 DisplayArray(arr2); 21 //应用冒泡排序法为其排序 22 BubbleSort(arr1); 23 BubbleSort(arr2); 24 Console.WriteLine("\narr1 After Sort:"); 25 DisplayArray(arr1); 26 Console.WriteLine("\narr2 After Sort:"); 27 DisplayArray(arr2); 28 //合并操作arr作为目标数组 29 int arrIndex = 0; 30 int arr1Index =0,arr2Index = 0; 31 while(arr1Index<arrLength1 && arr2Index < arrLength2) 32 { 33 //选择较小项存入arr 34 if (arr1[arr1Index] < arr2[arr2Index]) 35 { 36 arr[arrIndex] = arr1[arr1Index]; 37 arr1Index++; 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 arr[arrIndex] = arr2[arr2Index]; 42 arr2Index++; 43 } 44 arrIndex++; 45 } 46 //对arr1或者arr2中的没有存入arr中的元素进行追加 47 if (arr1Index != arrLength1 ) 48 { 49 while (arr1Index < arrLength1) 50 { 51 arr[arrIndex] = arr1[arr1Index]; 52 arrIndex++; 53 arr1Index++; 54 } 55 } 56 else if (arr2Index != arrLength2 ) 57 { 58 while (arr2Index < arrLength2) 59 { 60 arr[arrIndex] = arr2[arr2Index]; 61 arrIndex++; 62 arr2Index++; 63 } 64 } 65 DisplayArray(arr); 66 }
如果需要可以运行的代码,请到后面下载。
归并排序算法的时间复杂度为O(nlogn),空间复杂度为O(n).
3.堆排序(Heap Sort)
首先介绍堆的概念,如果有一个关键字集合{k0,k1,k2,...,kn-1},把其所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储在一个一维数组中,当且仅当ki<=K2i并且ki<=k(2i+1)称为最小堆。相反称为最大堆。
堆性质1:大顶堆的堆顶关键字肯定是所有关键字中最大的,小顶堆的堆顶关键字是所有关键字中最小的。
堆排序的思想:
堆排序的思想:利用如上堆的性质1为基础,使每次从无序中选择最大记录(或最小记录)变得简单。
构建初始堆和调整堆是堆排序的两个最重要的过程。并且初始堆也是对堆中所有元素的调整过程。所以算法的核心也正是堆的调整。
如下摘自海子的园子(http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/archive/2011/10/06/2199741.html)
下面举例说明:
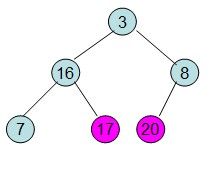
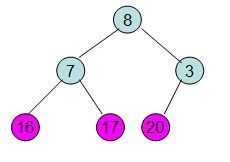
给定一个整形数组a[]={16,7,3,20,17,8},对其进行堆排序。
首先根据该数组元素构建一个完全二叉树,得到
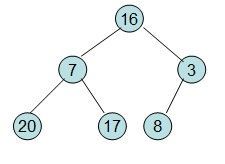
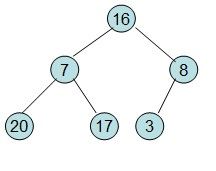
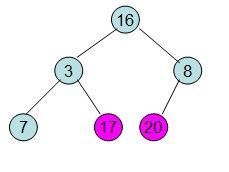
 20和16交换后导致16不满足堆的性质,因此需重新调整
20和16交换后导致16不满足堆的性质,因此需重新调整
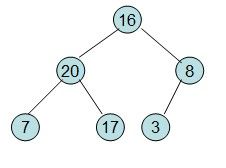
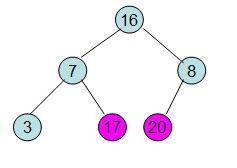
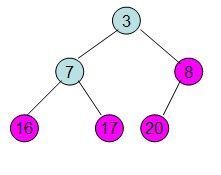
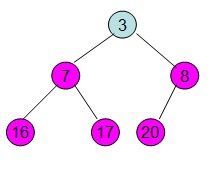
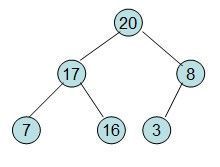 这样就得到了初始堆。
这样就得到了初始堆。
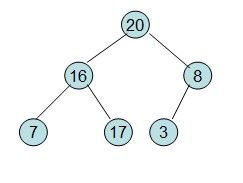
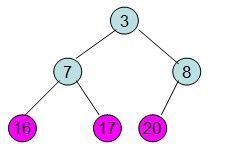
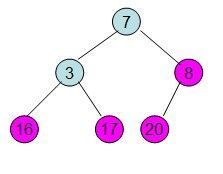
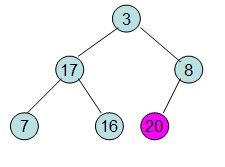 此时3位于堆顶不满堆的性质,则需调整继续调整
此时3位于堆顶不满堆的性质,则需调整继续调整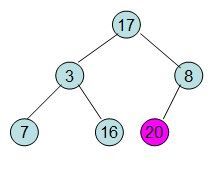
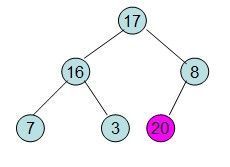
 Heap Sort Code
Heap Sort Code
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace HeapSort { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = {53,17,78,09,45,65,87,23}; //调整初始数据为最小堆(或者最大堆) Heap.MinHeapAdjust(arr,0, arr.Length); //交换首尾数字输出排序结果 for (int i = arr.Length-1; i >= 0; i--) { //交换首尾 int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[0]; arr[0] = temp; //调整除尾部之后的特定的堆 Heap.MinHeapAdjust(arr, 0, i); } Heap.DisplayHeap(arr); Console.ReadLine(); } } public static class Heap { /// <summary> /// 将传入的数组调节为最小堆 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr">待调解数组</param> /// <param name="maxIndex">待调节的最大索引,最大索引之后的数据将不会调节</param> public static void MinHeapAdjust(int[] arr,int startIndex, int maxIndex) { //Console.WriteLine("Before Adjust"); //DisplayHeap(arr); //首先需要获得倒数第一个分枝节点 int currentBranchIndex = maxIndex / 2-1; //调整分枝节点及其子节点 for (; currentBranchIndex >= startIndex; currentBranchIndex--) { AdjustSubHeap(arr, currentBranchIndex, maxIndex); } //Console.WriteLine("After Adjust"); //DisplayHeap(arr); } /// <summary> /// FliterDown算法,调整以startIndex为要的子树为最小堆 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> /// <param name="currentIndex"></param> /// <param name="maxIndex"></param> public static void AdjustSubHeap(int[] arr, int currentIndex, int maxIndex) { var temp = arr[currentIndex]; if(2 * currentIndex + 1<maxIndex) if (temp > arr[2 * currentIndex + 1]) { arr[currentIndex] = arr[2 * currentIndex + 1]; arr[2 * currentIndex + 1] = temp; temp = arr[currentIndex]; //若本子树顶部的键值已经改变,则将此键值存入临时区 AdjustSubHeap(arr, 2 * currentIndex + 1, maxIndex); } if (2 * currentIndex + 2 < maxIndex) //如果有最后一个节点有两个子节点 { if (temp > arr[2 * currentIndex + 2]) { arr[currentIndex] = arr[2 * currentIndex + 2]; arr[2 * currentIndex + 2] = temp; } AdjustSubHeap(arr, 2 * currentIndex + 2, maxIndex); } } /// <summary> /// 显示Heap /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> public static void DisplayHeap(int[] arr) { foreach(int val in arr) { Console.WriteLine(val + " "); } } } }
4.快速排序(quick sort)
快速排序也是分治法的一个实例,其主要思想为,选取一个值,将大于其的值放在其后,小于其的值放在其前。并对其前和其后的数据段进行迭代,直至分到数据段为一个数字。
【它的基本思想是:通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列。】(如上括号里面的为引用自别处,人家写的比俺写的好多了。)
其具体做法如下:
设要排序的数组是A[0]……A[N-1],首先任意选取一个数据(通常选用第一个数据)作为关键数据,然后将所有比它小的数都放到它前面,所有比它大的数都放到它后面,这个过程称为一趟快速排序。值得注意的是,快速排序不是一种稳定的排序算法,也就是说,多个相同的值的相对位置也许会在算法结束时产生变动。
 Quick Sort Code
Quick Sort Code
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace QuickSort 7 { 8 class Program 9 { 10 static void Main(string[] args) 11 { 12 int[] arr = { 97,76,13,27,20,10,9,90,49,65}; 13 QuickSort.sort(arr, 0, arr.Length-1); 14 QuickSort.DisplayArr(arr, 0, arr.Length); 15 Console.ReadLine(); 16 } 17 } 18 public static class QuickSort 19 { 20 public static void sort(int[] arr,int lowIndex,int upperIndex) 21 { 22 if (lowIndex >= upperIndex) return; 23 int key,i,j,temp; 24 i = lowIndex; 25 key = arr[lowIndex]; 26 j = upperIndex; 27 bool leftToRight = false; 28 while (i< j) 29 { 30 //从右向左检索,查找右边第一个小于key的元素 31 if(!leftToRight) 32 if (arr[j] < key) 33 { 34 temp = arr[i]; 35 arr[i] = arr[j]; 36 arr[j] = temp; 37 leftToRight = true; 38 i = lowIndex; 39 } 40 else 41 { 42 j--; 43 } 44 //从左向右检索,查找左边第一个大于key的元素 45 if (leftToRight) 46 if (arr[i] > key) 47 { 48 temp = arr[i]; 49 arr[i] = arr[j]; 50 arr[j] = temp; 51 j = upperIndex; 52 leftToRight = false; 53 } 54 else 55 { 56 i++; 57 } 58 } 59 if (lowIndex < upperIndex) 60 { 61 sort(arr, lowIndex, i-1); 62 sort(arr, i + 1, upperIndex); 63 } 64 } 65 //输出数组 66 public static void DisplayArr(int[] arr, int lowindex, int upperindex) 67 { 68 Console.WriteLine(); 69 for (int i = lowindex; i < upperindex; i++) 70 { 71 Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 }
算法咱就先讲这么多,把源代码作为附件放在这里。大家有需要的自己下载。
(唉,没有找到在哪里上传附件。只好放在微软的SkyDriver里面,大家可以通过如下链接下载。)
最后增加个链接,提高点排名:
