LeetCode——数组(Java)
移除元素
- 简介
- 二分查找
- 移除元素
-
- [简单] 27. 移除元素
- [简单] 26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
- [简单] 283. 移动零
- [简单] 844. 比较含退格的字符串
- [简单] 977. 有序数组的平方
- [中等] 209.长度最小的子数组
- [中等] 59. 螺旋矩阵 II
简介
记录一下自己刷题的历程以及代码。写题过程中参考了 代码随想录。会附上一些个人的思路,如果有错误,可以在评论区提醒一下。
二分查找
数组——二分查找
移除元素
一旦设计到数组移除元素,就可以首先考虑一下双指针法解题。
双指针中的快慢指针法经常可以比较高效的对数组做一遍处理,把需要删除的元素删掉进行压缩。
[简单] 27. 移除元素
原题链接
(注意:这样的方法是一种不保留原先顺序的方法)
方法①:其实也是一种双指针的思路。设置一个下标指向数组最右边,从头开始遍历,一旦遍历到有元素需要移除,就把他往最后放,并将下标左移,右边区域不再参与遍历,记住一旦有元素被置换到后面,需要将当前循环下标做i--处理,因为你换过来的元素依然可能是一个需要移除的元素。
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int length = nums.length;
int right = nums.length - 1; //替换指针
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++){
if(nums[i] == val){
int temp = nums[right];
nums[right] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
right--;
length--; //相当于舍弃末尾的部分长度
i--; //置换之后当前位置可能还是一个需要置换的元素,继续检查
}
}
return length;
}
}
(注意:该方法保留了原数组的顺序)
方法②:快慢指针法,相当于慢指针负责对快指针指向的元素进行复制,而快指针则会跳过那些不需要复制的元素。
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int fastIndex = 0;
int slowIndex = 0;
int count = 0;
while(fastIndex < nums.length && slowIndex < nums.length - count){
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
if(nums[fastIndex] == val){
count++;
}else{
slowIndex++;
}
fastIndex++;
}
return nums.length - count;
}
}
[简单] 26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
原题链接
方法①:根据有序数组的条件,对上面的双指针法进行一定的改造,定义一个tag标记目前碰到的数,之后碰到相同的则快指针跳过,碰到不同的则标记新的tag。
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
int fastIndex = 1;
int slowIndex = 1;
int count = 0;
int tag = nums[1]; //题目为有序数组
while(fastIndex < nums.length && slowIndex < nums.length - count){
nums[slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
if(nums[fastIndex] == tag){
count++;
}else{
tag = nums[fastIndex];
slowIndex++;
}
fastIndex++;
}
return nums.length - count;
}
}
方法②:直接省去标记的问题,因为数组是有序的,慢指针和快指针所指向的元素只有nums[fastIndex] > nums[slowIndex]以及nums[fastIndex] == nums[slowIndex]两种情况,相等的时候快指针即可跳过,一旦不相等即可做赋值操作。
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
//题目为有序数组
int fastIndex = 0;
int slowIndex = 0;
while(fastIndex < nums.length){
if(nums[fastIndex] > nums[slowIndex]){
nums[++slowIndex] = nums[fastIndex];
}else{
fastIndex++;
}
}
return slowIndex + 1;
}
方法①与方法②速度差距:
[简单] 283. 移动零
原题链接
经典的双指针法。因为末尾要保留0,所以使用对换的swap方式来做。但这样时间效率不是最高的,直接覆盖,然后在末尾使用Arrays.fill(nums,count,nums.length,0);直接填充0能够更高效。
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int fastIndex = 0;
int slowIndex = 0;
while(fastIndex < nums.length){
if(nums[fastIndex] != 0){
int temp = nums[fastIndex];
nums[fastIndex] = nums[slowIndex];
nums[slowIndex] = temp;
slowIndex++;
}
fastIndex++;
}
}
}
[简单] 844. 比较含退格的字符串
原题链接
方法①:也可以用快慢指针法,把两个字符串该删的删了对最后的结果作比较,这里就不重复实现了。
方法②:看到退格操作'#'就想到使用栈,用两个栈保存s和t经过退格操作之后的值,然后再出栈进行比较。
class Solution {
public boolean backspaceCompare(String s, String t) {
Stack<Character> sStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Character> tStack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(s.charAt(i) == '#' && !sStack.empty()){
sStack.pop();
}else if(s.charAt(i) != '#'){
sStack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
//System.out.println(sStack.toString());
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
if(t.charAt(i) == '#' && !tStack.empty()){
tStack.pop();
}else if(t.charAt(i) != '#'){
tStack.push(t.charAt(i));
}
//System.out.println(tStack.toString());
}
if(sStack.size() != tStack.size()) return false;
while(!sStack.empty() && !tStack.empty()){
if(sStack.pop() != tStack.pop()) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
方法③:两个指针从后往前遍历,效率高,但是对边界的控制比较麻烦,没有栈写起来简单
class Solution {
public boolean backspaceCompare(String s, String t) {
int sIndex = s.length() - 1;
int tIndex = t.length() - 1;
int sCount = 0;
int tCount = 0;
while(sIndex >= 0 || tIndex >= 0){
//让sIndex指向s中接下来要比较的字符(能够确定最后不被删除
while (sIndex >= 0){
if (s.charAt(sIndex) == '#') {
sCount++;
sIndex--;
} else if (sCount > 0) {
sCount--;
sIndex--;
} else{
break;
}
}
while (tIndex >= 0){
if (t.charAt(tIndex) == '#') {
tCount++;
tIndex--;
} else if (tCount > 0) {
tCount--;
tIndex--;
} else{
break;
}
}
if(sIndex < 0 || tIndex < 0) break;
if (s.charAt(sIndex) != t.charAt(tIndex)){
return false;
}
sIndex--;
tIndex--;
}
if(sIndex >=0 || tIndex >= 0) return false;
return true;
}
}
[简单] 977. 有序数组的平方
原题链接
题目中没有强调在原数组上修改,返回值也是int[],就可以思考是不是创建一个新的数组更方便一些。
找到数组中正负值的分界点,然后从分界点向两边遍历,按照绝对值的大小挨个平方计算后加入到新的数组中。正数或者负数用完之后无法继续进行绝对值比较的循环。然后再将左边或者右边剩下的数依次放入答案数组中。
时间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int[] answer = new int[nums.length];
int zeroIndex = 0;
//找到正负分界点
while(zeroIndex < nums.length && nums[zeroIndex] < 0){
zeroIndex++;
}
int negativeIndex = zeroIndex - 1;
int positiveIndex = zeroIndex;
int i = 0;
while(negativeIndex >= 0 && positiveIndex < nums.length){
if (Math.abs(nums[negativeIndex]) < Math.abs(nums[positiveIndex])) {
answer[i++] = nums[negativeIndex] * nums[negativeIndex];
negativeIndex--;
continue;
} else {
answer[i++] = nums[positiveIndex] * nums[positiveIndex];
positiveIndex++;
continue;
}
}
while(negativeIndex >= 0){
answer[i++] = nums[negativeIndex] * nums[negativeIndex];
negativeIndex--;
}
while(positiveIndex < nums.length){
answer[i++] = nums[positiveIndex] * nums[positiveIndex];
positiveIndex++;
}
return answer;
}
}
[中等] 209.长度最小的子数组
原题链接
还是类似双指针的思路:滑动窗口
最朴素的思路就是二重循环,二重循环中一般第一重循环找起始点i,第二重循环找结束点j,判断i到j相加的所有情况。滑动窗口其实类似,但是第一重循环标记的是结束点j,这种方法下,i和j都不需要回退,时间复杂度为O(n)。
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
int min = nums.length + 1;
for(int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++){
sum += nums[j];
if(sum >= target){
while(sum >= target){
int newLength = j - i + 1;
min = newLength < min ? newLength: min;
sum -= nums[i++];
}
}
}
if(min < nums.length + 1) return min;
return 0;
}
}
[中等] 59. 螺旋矩阵 II
原题链接
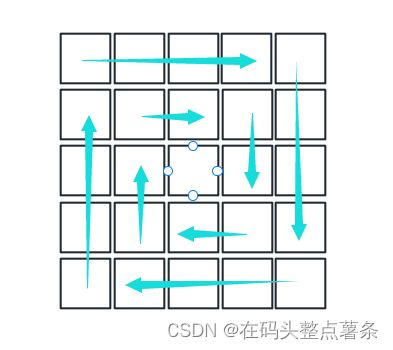
将下图这样算作画一圈,如果n是偶数,需要画n/2圈,如果n是奇数,则需要画n/2圈外额外填充中间一格

当n为6:

当n为5
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
//转 n / 2 圈,奇数要额外补上一个
int [][] answer = new int[n][n];
int count = 1; //填充计数
int flag = 0; //循环圈数
while(flag < n / 2) {
for (int i = flag; i < n - 1 - flag; i++) {
answer[flag][i] = count++;
}
for (int i = flag; i < n - 1 - flag; i++) {
answer[i][n - 1 - flag] = count++;
}
for (int i = n - 1 - flag; i > flag; i--) {
answer[n - 1 - flag][i] = count++;
}
for (int i = n - 1 - flag; i > flag; i--) {
answer[i][flag] = count++;
}
flag++;
}
if(n%2 != 0){
answer[n / 2][n / 2] = count;
}
return answer;
}
}