PCL系列笔记——Octree
目录
-
- 八叉树原理
- 八叉树的存储结构
- 八叉树的可视化
- 八叉树的应用举例
-
- 点云压缩
- 近邻搜索
八叉树原理
与KD树一样,八叉树(octree)也是一种高效的组织点云数据的办法,它可以从原始点云数据建树状数据结构。八叉树可以有效实现对点云的空间分区、下采样、搜索操作(如近邻搜索)等。每个八叉树要么有8个节点,要么没有节点。根节点是一个包含所有点云数据的立方体包围盒
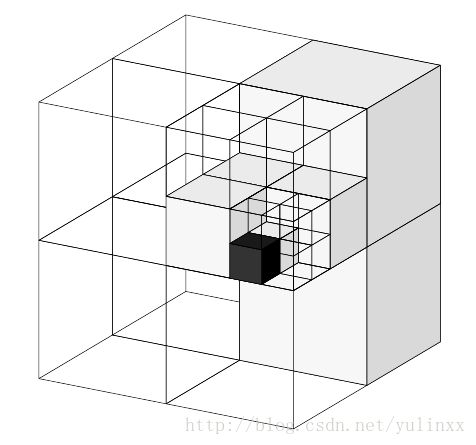
八叉树结构是由 Hunter博士于1978年首次提出的一种数据模型。八叉树结构通过对三维空间的几何实体进行体元剖分,每个体元具有相同的时间和空间复杂度,通过循环递归的划分方法对大小为 (2n∗2n∗2n)(2n∗2n∗2n) 的三维空间的几何对象进行剖分,从而构成一个具有根节点的方向图。在八叉树结构中如果被划分的体元具有相同的属性,则该体元构成一个叶节点;否则继续对该体元剖分成8个子立方体,依次递剖分,对于 (2n∗2n∗2n)(2n∗2n∗2n)大小的空间对象,最多剖分 nn 次,如下示意图所示。
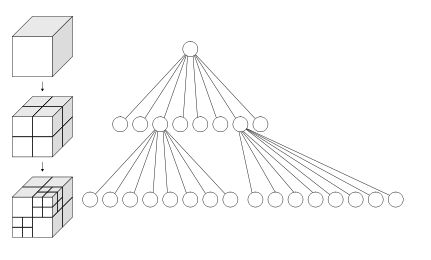
上图中最大的正方体就是八叉树的根节点,然后不断的进行划分。八叉树叶子节点代表了分辨率最高的情况。例如分辨率设成0.01m,那么最小叶子就是一个1cm见方的小方块。为什么要这么划分呢?想象一个立方体,我们最少可以切成多少个相同等分的小立方体?答案就是8个。再想象我们有一个房间,房间里某个角落藏着一枚金币,我们想很快的把金币找出来,聪明的你会怎么做?我们可以把房间当成一个立方体,先切成八个小立方体,然后排除掉没有放任何东西的小立方体,再把有可能藏金币的小立方体继续切八等份….如此下去,平均在Log8(房间内的所有物品数)的时间内就可找到金币。因此,Octree就是用在3D空间中的场景管理,可以很快地知道物体在3D场景中的位置,或侦测与其它物体是否有碰撞以及是否在可视范围内(摘自百度百科)。
八叉树的实现流程如下:
- 设定最大递归深度
- 找出场景的最大尺寸,并以此尺寸建立第一个立方体
- 依序将单位元元素丢入能被包含且没有子节点的立方体
- 若没有达到最大递归深度,就进行细分八等份,再将该立方体所装的单位元元素全部分担给八个子立方体
- 若发现子立方体所分配到的单位元元素数量不为零且跟父立方体是一样的,则该子立方体停止细分,因为跟据空间分割理论,细分的空间所得到的分配必定较少,若是一样数目,则再怎么切数目还是一样,会造成无穷切割的情形
- 重复3,直到达到最大递归深度
八叉树的存储结构
八叉树有三种不同的存贮结构,分别是规则方式、线性方式以及一对八方式。相应的八叉树也分别称为规则八叉树、线性八叉树以及一对八式八叉树。不同的存贮结构的空间利用率及运算操作的方便性是不同的。分析表明,一对八式八叉树优点更多一些。
- 规则八叉树:
规则八叉树的存贮结构用一个有九个字段的记录来表示树中的每个结点。其中一个字段用来描述该结点的特性,其余的八个字段用来作为存放指向其八个子结点的指针。这是最普遍使用的表示树形数据的存贮结构方式。规则八叉树缺陷较多,最大的问题是指针占用了大量的空间 - 线性八叉树:线性八叉树注重考虑如何提高空间利用率。用某一预先确定的次序遍历八叉树(例如以深度第一的方式),将八叉树转换成一个线性表,表的每个元素与一个结点相对应。对于结点的描述可以丰富一点,例如用适当的方式来说明它是否为叶结点,如果不是叶结点时还可用其八个子结点值的平均值作为非叶结点的值等等。这样,可以在内存中以紧凑的方式来表示线性表,可以不用指针或者仅用一个指针表示即可。线性八叉树不仅节省存贮空间,对某些运算也较为方便。但是为此付出的代价是丧失了一定的灵活性。例如为了存取属于原图形右下角的子图形对应的结点,那么必须先遍历了其余七个子图形对应的所有结点后才能进行;不能方便地以其它遍历方式对树的结点进行存取,导致了许多与此相关的运算效率变低。因此尽管不少文章讨论了这种八叉树的应用,但是仍很难令人满意。
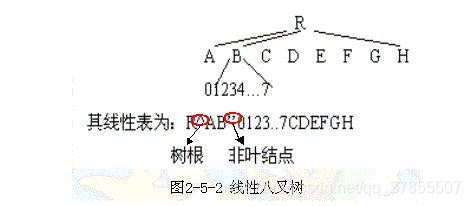
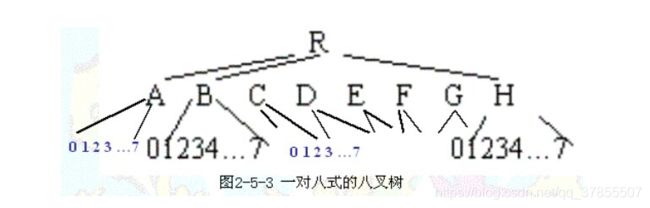
- 一对八八叉树:一个非叶结点有八个子结点,为了确定起见,将它们分别标记为0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7。从上面的介绍可以看到,如果一个记录与一个结点相对应,那么在这个记录中描述的是这个结点的八个子结点的特性值。而指针给出的则是该八个子结点所对应记录的存放处,而且还隐含地假定了这些子结点记录存放的次序。也就是说,即使某个记录是不必要的(例如,该结点已是叶结点),那么相应的存贮位置也必须空闲在那里(图2-5-3),以保证不会错误地存取到其它同辈结点的记录。这样当然会有一定的浪费,除非它是完全的八叉树,即所有的叶结点均在同一层次出现,而在该层次之上的所有层中的结点均为非叶结点
八叉树的可视化
octree可视化基于的是VTK库,可视化可以更好理解OCtree的数据结构,斯坦福兔子的可视化结果如下:
#include 八叉树的应用举例
点云压缩
点云数据较为庞大,如果要实现两个设备之间进行点云数据传输,会占用较大的传输资源,同时传输速率可能受限,因而进行点云压缩是十分有必要的,PCL中,基于OCtree可以实现高效的点云压缩(实现点云压缩的办法就是是相同的存储空间,比如1字节尽可能存储多的信息)。
#include 近邻搜索
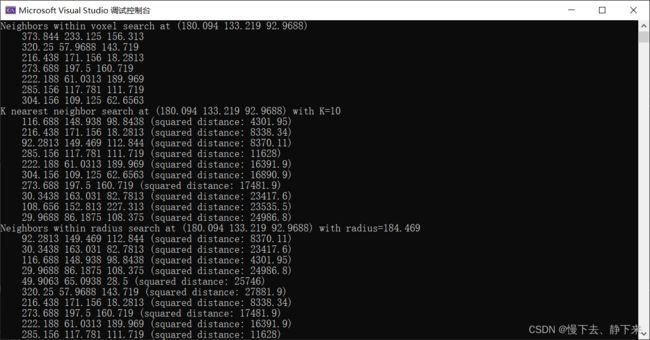
Octree树建立的过程其实就是对空间进行划分的过程,其中最小的划分单元叫体素。故而相比于KDtree,除了K近邻与半径搜索外,Octree还有体素邻域搜索,具体如下代码所示:
#include