二叉树题目合集(C++)
二叉树题目合集
-
- 1.二叉树创建字符串(简单)
- 2.二叉树的分层遍历(中等)
- 3.二叉树的最近公共祖先(中等)
- 4.二叉树搜索树转换成排序双向链表(中等)
- 5.根据树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树(中等)
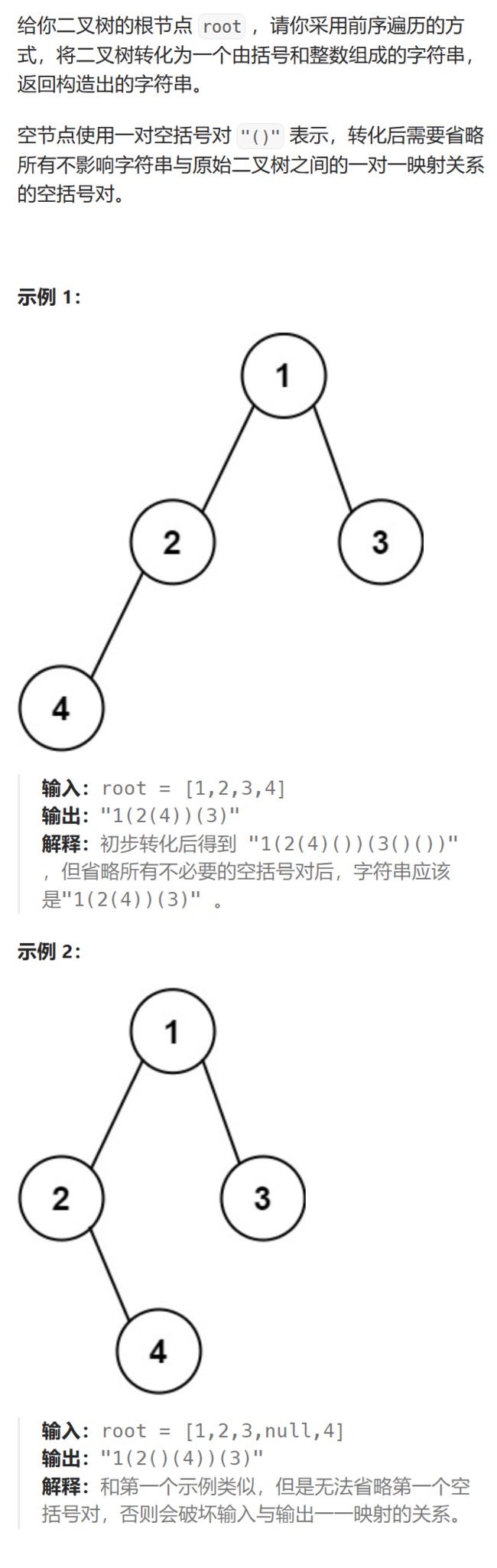
1.二叉树创建字符串(简单)
链接:二叉树创建字符串
PS:题目描述的不是特别清楚,其实就是前序遍历树,然后用括号分别包含左子树和右子树遍历结果。
基础思路:
(1)不考虑括号去重的话,其实只要访问完当前节点后递归访问左右子树即可,并且在访问前加左括号,访问完毕后加右括号,当前节点为空时返回即可。代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
string ret;
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ret;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return;
ret += to_string(root->val);
ret += '(', dfs(root->left), ret += ')';
ret += '(', dfs(root->right), ret += ')';
}
};
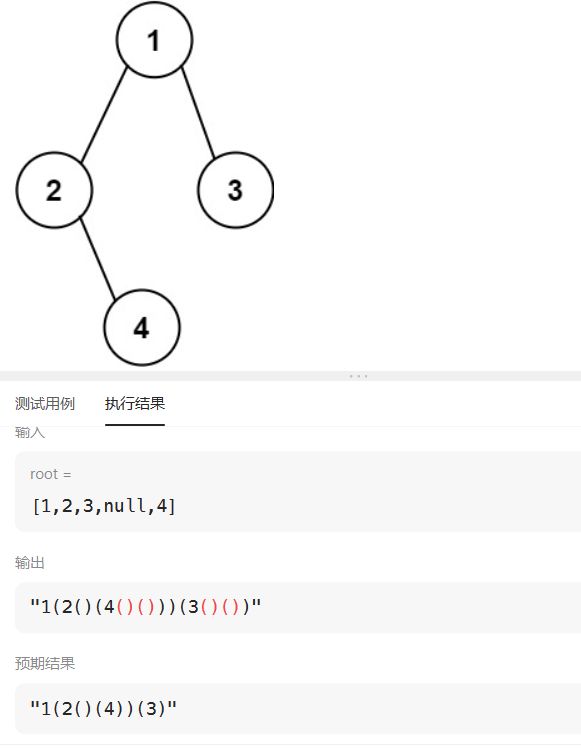
(2) 对于括号去重,主要围绕左右子树为空,我们需要分情况讨论:
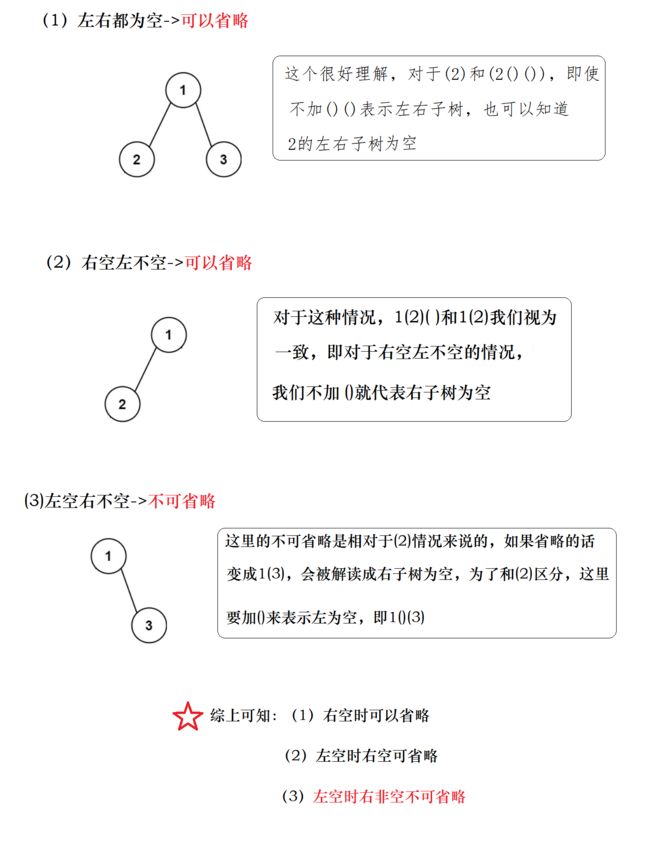
代码:
class Solution {
public:
string ret;
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ret;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == nullptr) return;
ret += to_string(root->val);
if(root->left || root->right) ret += '(', dfs(root->left), ret += ')';
if(root->right) ret += '(', dfs(root->right), ret += ')';
}
};
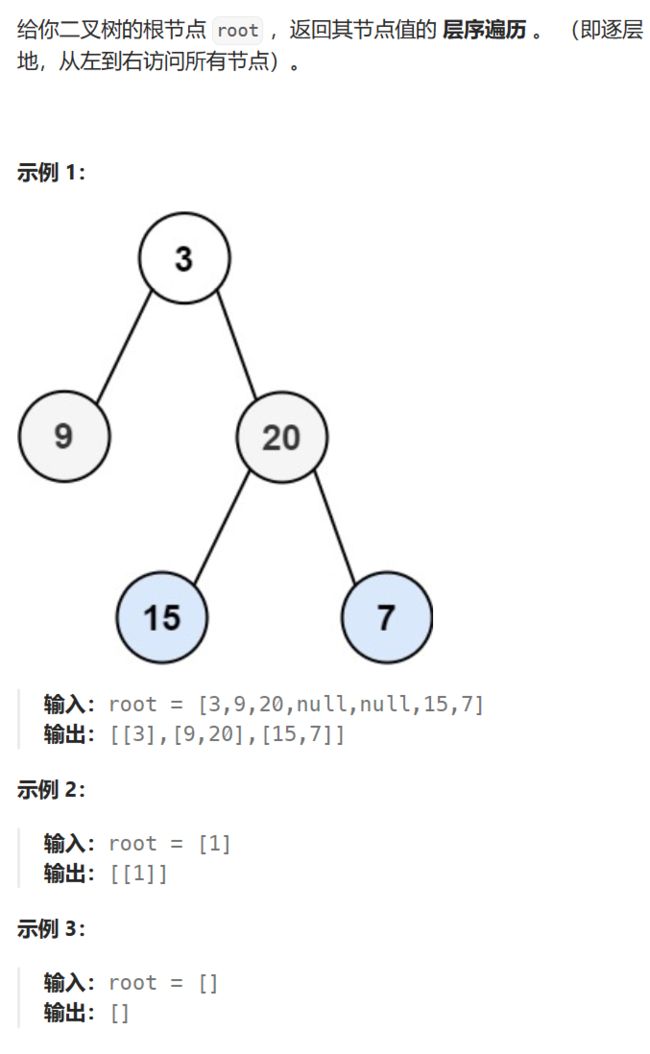
2.二叉树的分层遍历(中等)
链接:二叉树的分层遍历
基础思路:
(1) 二叉树层序遍历的思想其实很简单,就是借助队列,父节点带出子节点,依靠队列先进先出的特点控制访问顺序。
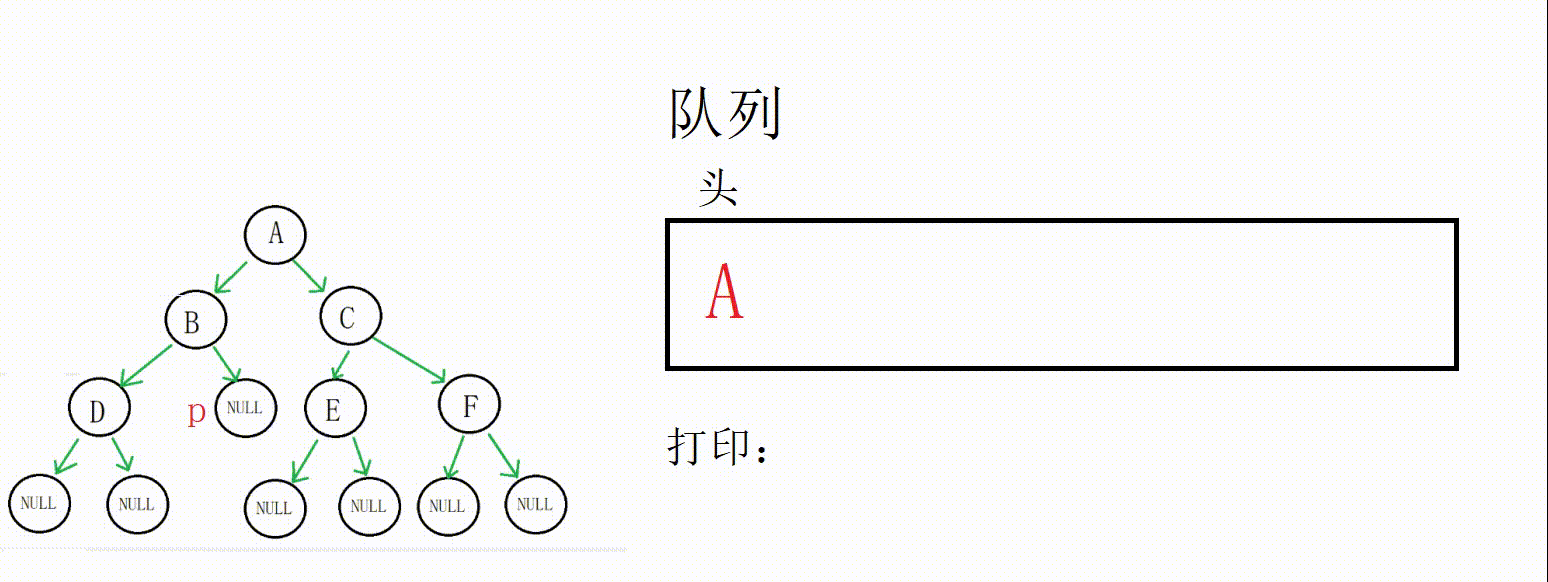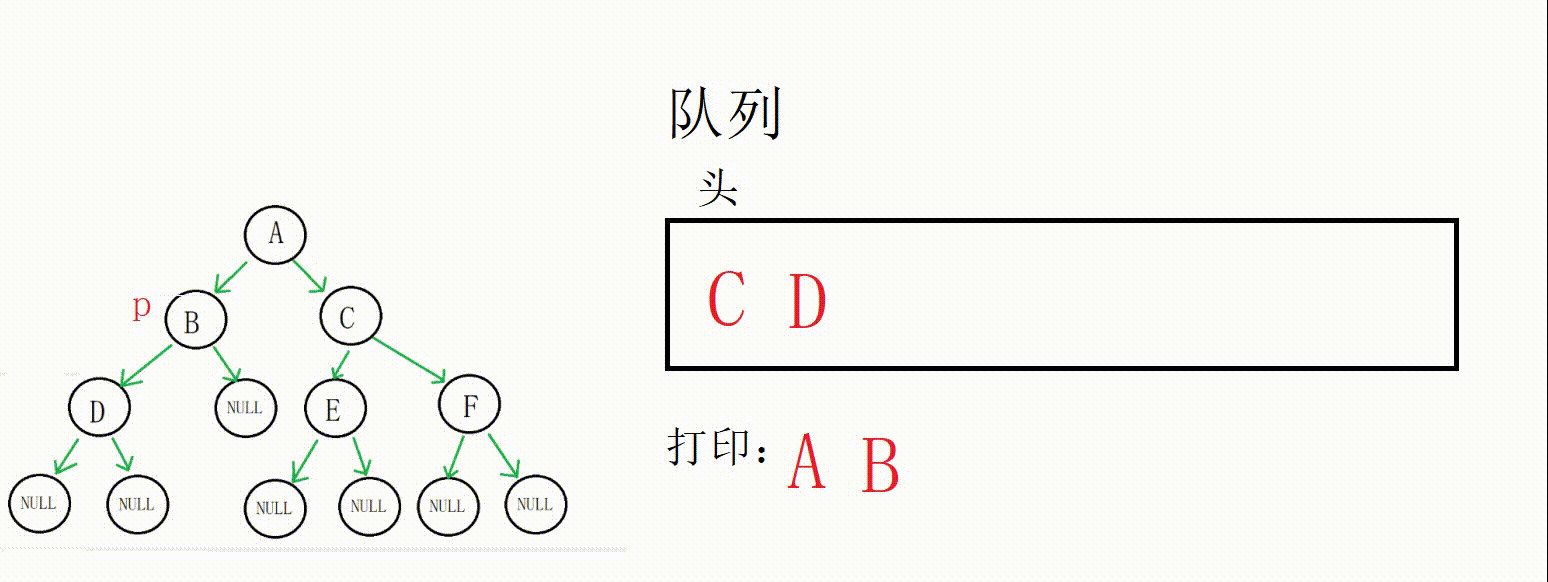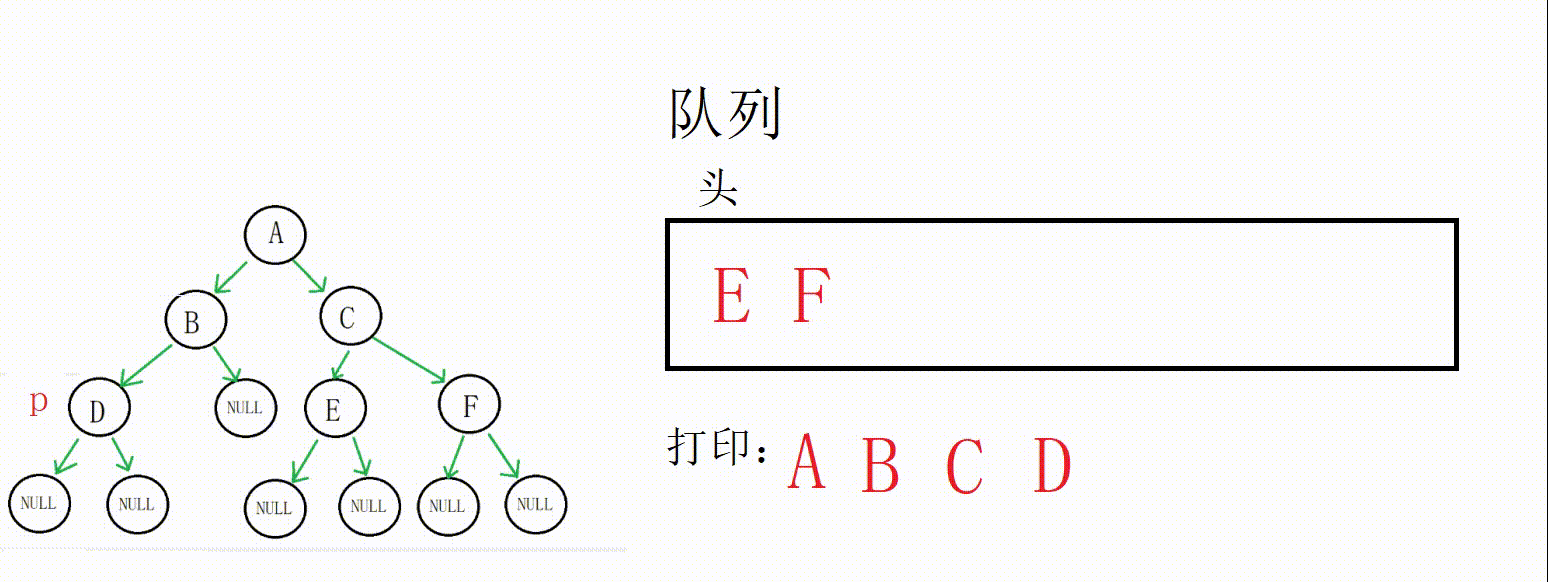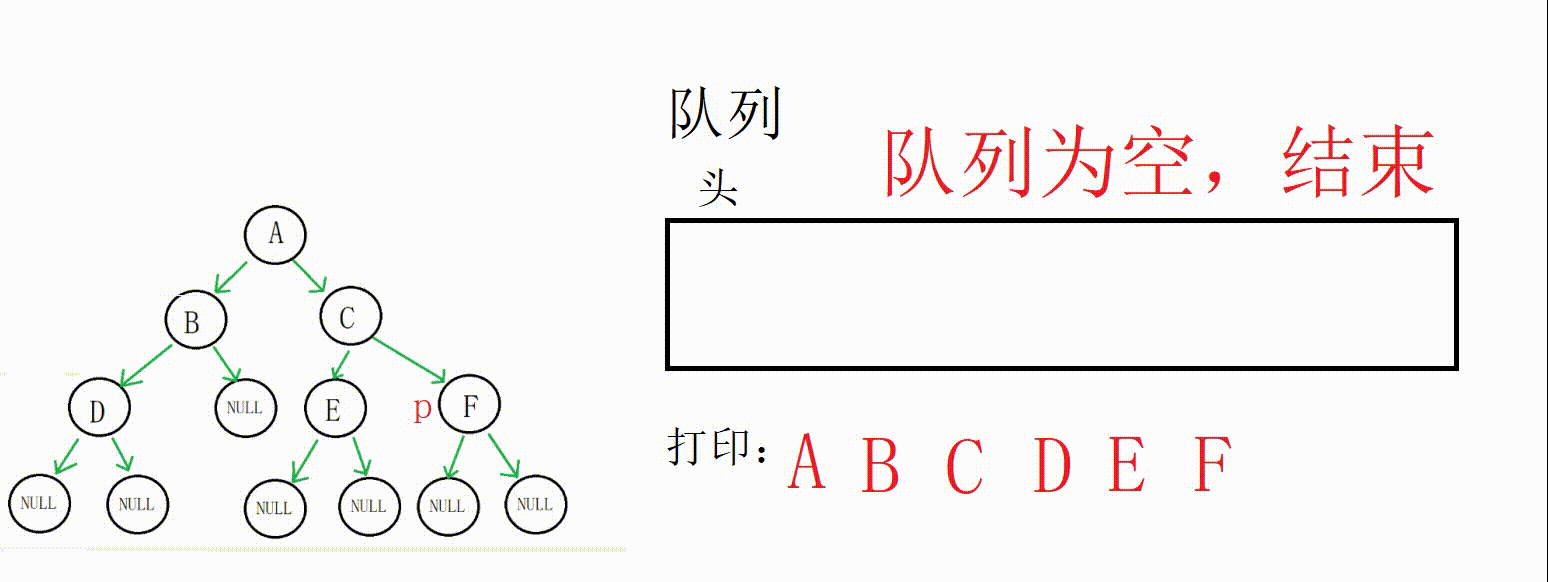
(2) 这个题目的关键点在于如何得知当前层和下一层的节点数,因为我们需要每一层都构建一个数组来存储结果。这里采用的解决方案是用一个next变量记录下一层的节点数,count(count初始为1)记录当前层的节点数,当前层访问完把next赋给count即可。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int count = 1; //每一层的节点数
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> tmp;
int next = 0; //用一个变量记录下一层的节点
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left) q.push(node->left), next++;
if(node->right) q.push(node->right), next++;
}
count = next;
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};
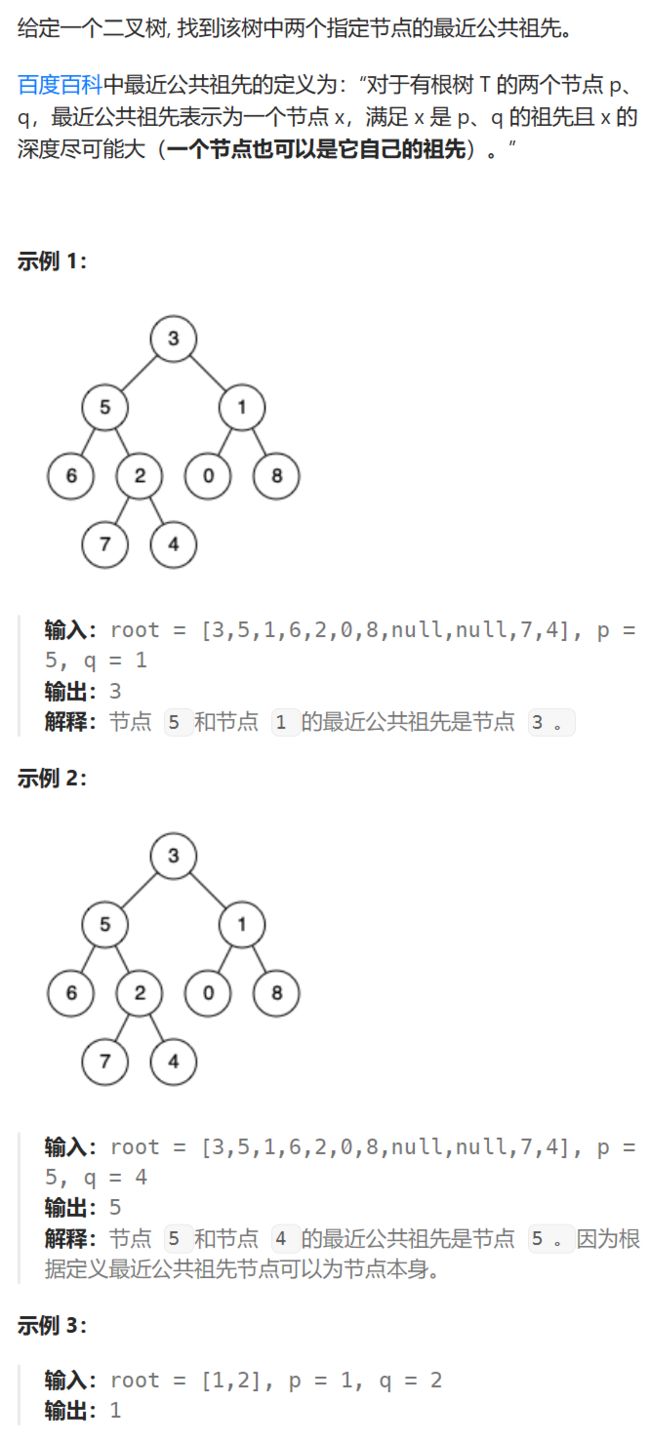
3.二叉树的最近公共祖先(中等)
解法一代码:
//理想是N*logN,对于退化成链表的情况变成O(N ^ N)
class Solution {
public:
bool isTree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x)
{
if(root == nullptr) return false;
if(root->val == x->val) return true;
return isTree(root->left, x) || isTree(root->right, x);
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == p || root == q) return root;
bool pInLeft = isTree(root->left, p);
bool pInRight = !pInLeft; //不在左树就在右树
bool qInLeft = isTree(root->left, q);
bool qInRight = !qInLeft;
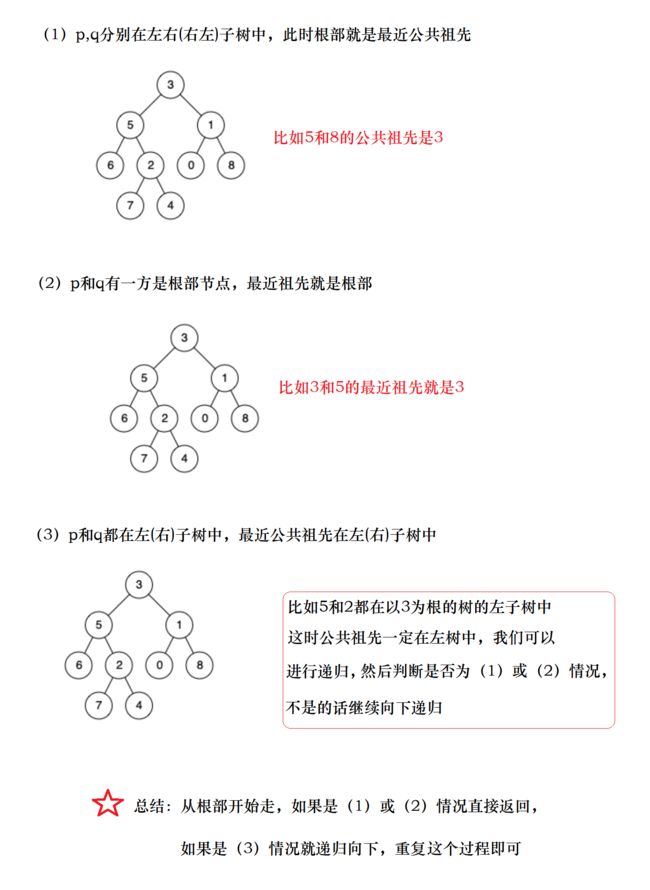
if((pInLeft && qInRight) || (pInRight && qInLeft)) //p,q分别在左右子树
return root;
if(pInLeft && qInLeft) return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); //pq都在左树
else return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); //pq都在右树
}
};
解法二代码:
//找路径,转换为链表交点,用栈来存储路径,O(N)
class Solution {
public:
bool FindPath(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x, stack<TreeNode*>& path)
{
if(root == nullptr) return false;
path.push(root); //不管怎么说,先入栈
if(root == x) return true;
if(FindPath(root->left, x, path)) return true; //递归走左找到了,直接返回
if(FindPath(root->right, x, path)) return true; //递归走右找到了,直接返回
//左右子树都没有,当前这个节点出栈
path.pop();
return false;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
{
stack<TreeNode*> path1;
stack<TreeNode*> path2;
FindPath(root, p, path1);
FindPath(root, q, path2);
while(path1.size() != path2.size()) //长路径先走
{
if(path1.size() > path2.size()) path1.pop();
else path2.pop();
}
while(path1.top() != path2.top())
{
path1.pop(), path2.pop();
}
return path1.top(); //随便返回一个即可
}
};
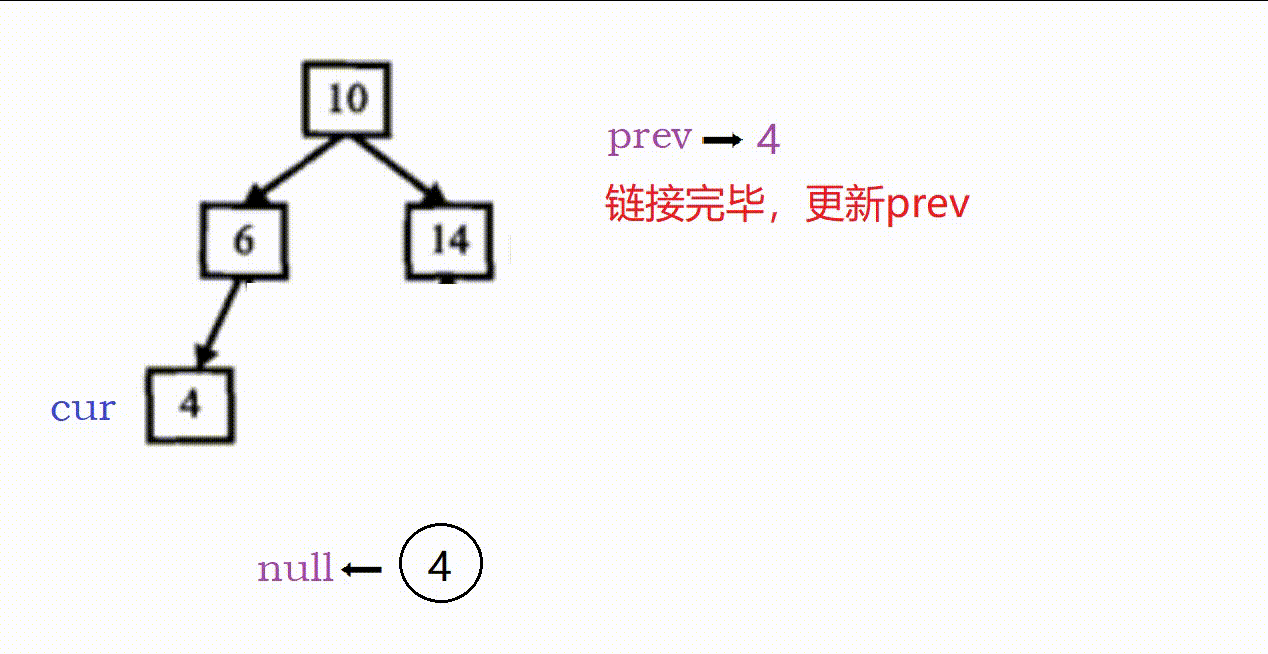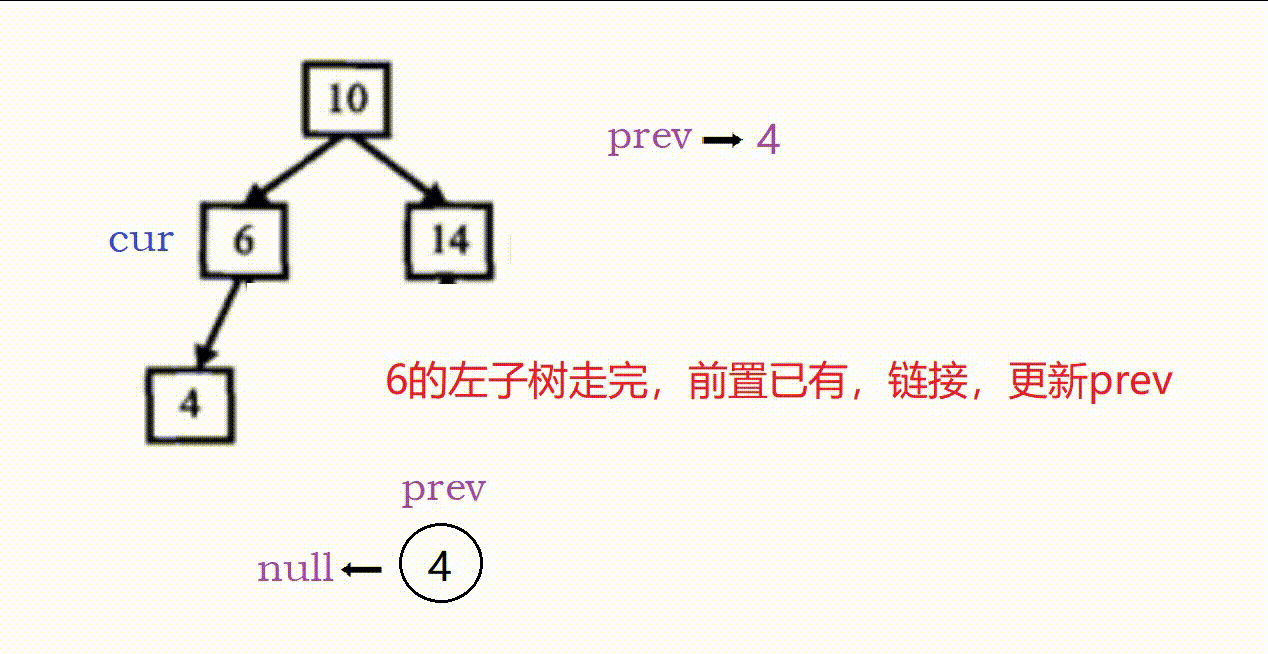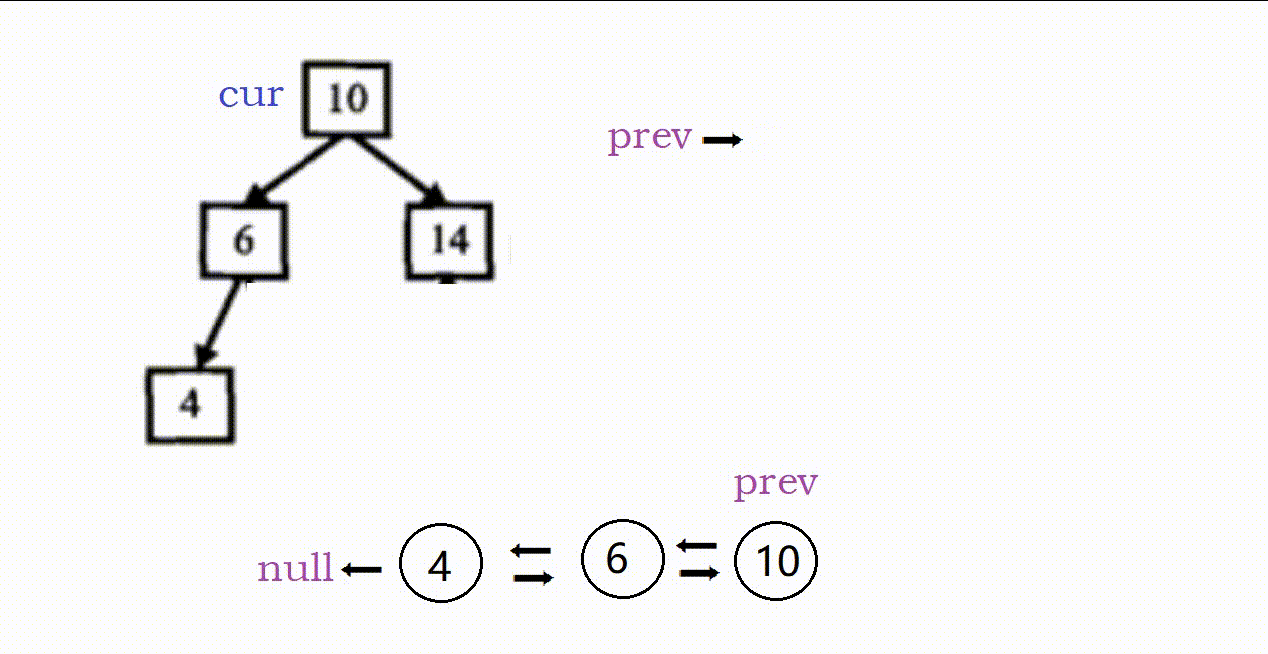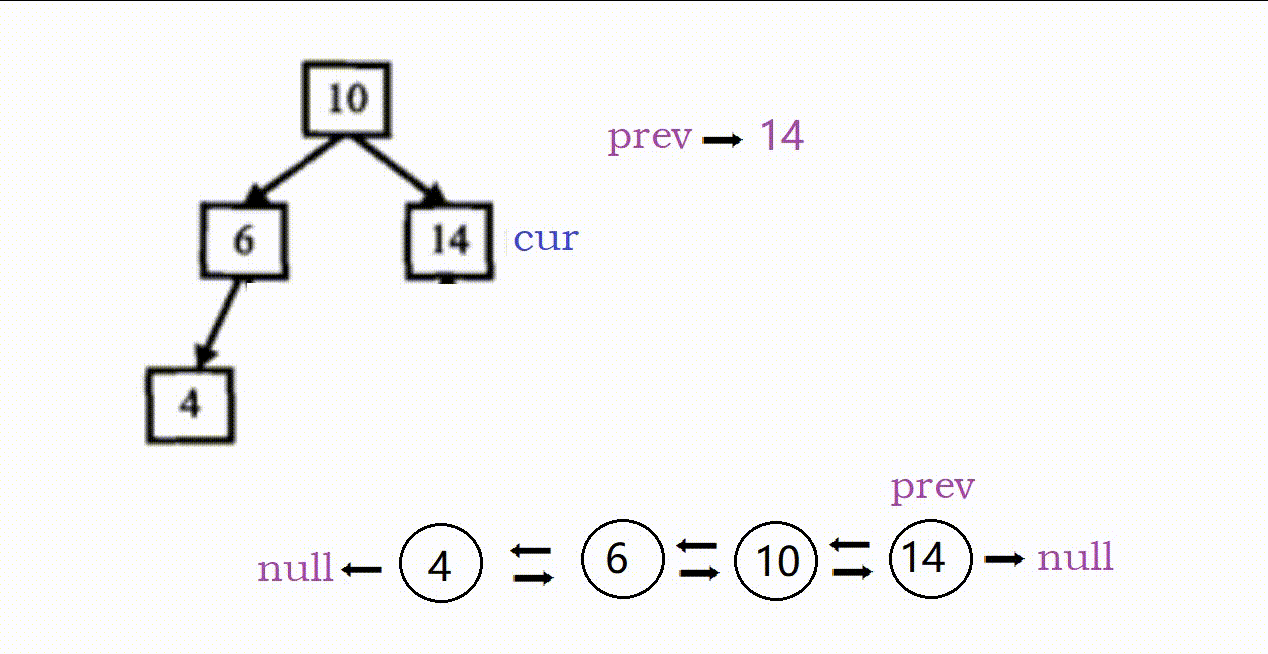
4.二叉树搜索树转换成排序双向链表(中等)
链接:二叉树搜索树转换成排序双向链表
基础思路:
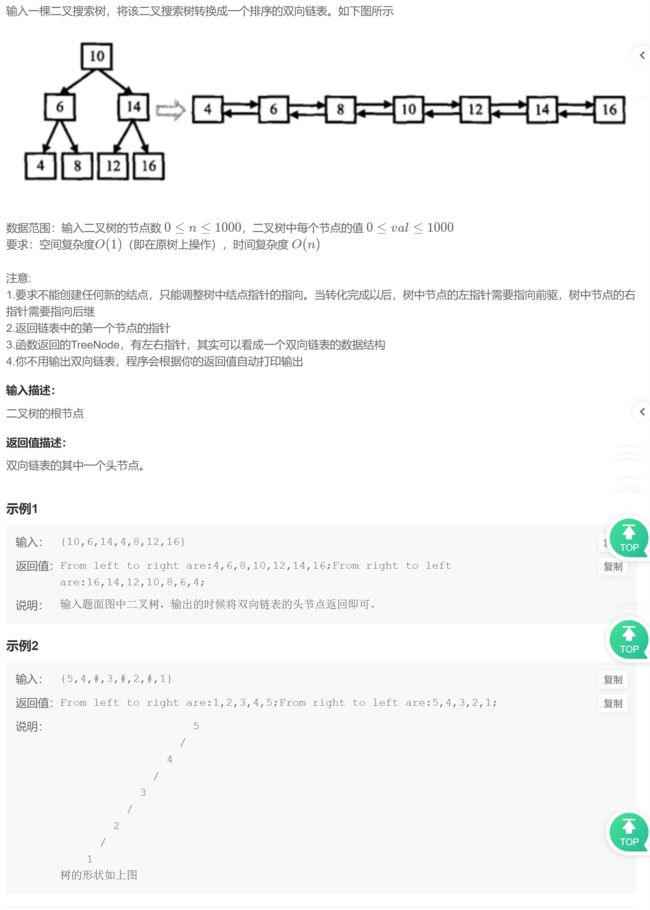
(1)因为是搜索树,我们采用类似中序遍历的方式解题。
(2)这个题的关键在于找前置节点,只要找到当前节点的前置就可以进行链接。
具体过程如下:
- 两个指针,prev记录前置,cur记录当前,prev初始为空
- cur为空,返回。
- (1)cur非空,先递归走左;
(2)左走完后prev就是前置,链接:cur->left = prev,prev->right = cur(这里prev非空)。
(3)链接完毕后更新前置,prev = cur。
(4)左走完,递归右,链接右子树。 - 最后需要确定链表头节点,这个可以
①转换前找:树的最左下角的节点。
②转换后找:从原根部节点一直向左即可。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
void _Convert_order(TreeNode* cur, TreeNode*& prev)
{
if(cur == nullptr) return;
_Convert_order(cur->left, prev);
cur->left = prev;
if(prev) prev->right = cur;
prev = cur;
_Convert_order(cur->right, prev);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree)
{
TreeNode* cur = pRootOfTree, *prev = nullptr;
_Convert_order(cur, prev);
TreeNode* ret = pRootOfTree;
while(ret && ret->left) //(1)有空树的情况(2)先链接好再向左找目标节点即可
{
ret = ret->left;
}
return ret;
}
};
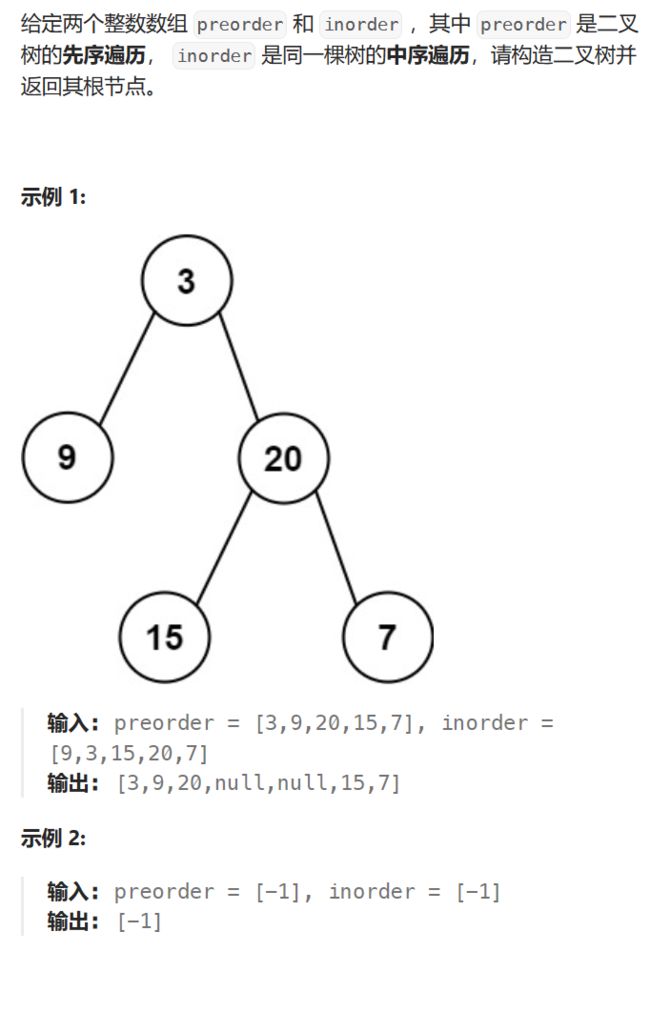
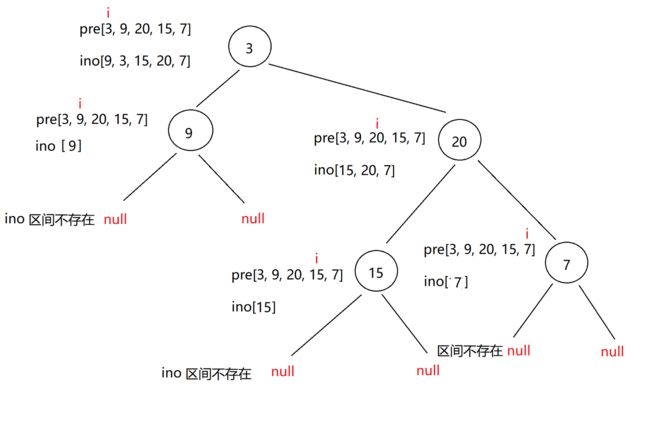
5.根据树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树(中等)
链接:构造二叉树
基础思路:
(1)前序定根,中序定左右。
(2)先构造根,然后找到当前节点在中序数组的位置,把左右子树的节点划分出来。
(3)依据划分出的中序区间递归走左和右,区间不存在说明这个位置为空,返回空。
左右走完后链接起来即可。左右链接好了返回该树的根部节点。
处理细节:
(1)怎么找到当前节点在中序数组的位置:
①一种方式是遍历中序区间,这样每一层都需要遍历,时间复杂度高
②一种是用哈希表进行存储,用值映射中序下标,时间复杂度低。
本文选择方式②。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, int> ord;
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int& prei, int inbegin, int inend)
{
if(inbegin > inend) return nullptr; //区间不存在返回空
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);
int rooti = ord[preorder[prei++]];
//划分出三段区间:[inbegin, rooti - 1] rooti [rooti + 1, inend]
root->left = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, inbegin, rooti - 1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, rooti + 1, inend);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++)
{
ord[inorder[i]] = i;
}
int i = 0;
return _buildTree(preorder, inorder, i, 0, inorder.size() - 1);
}
};