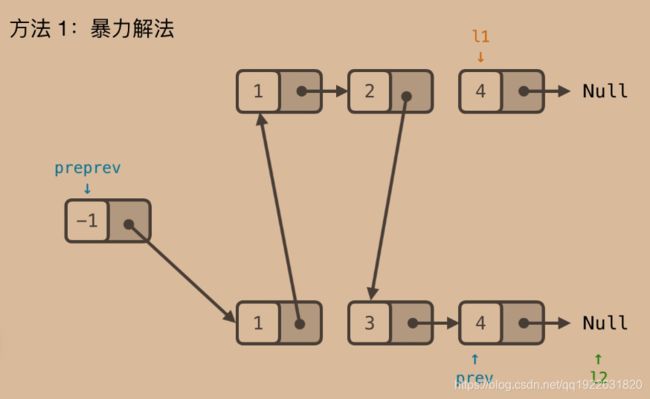
- 动态规划算法--找零方式
大王算法
数据结构和算法实战宝典算法动态规划c++
一、问题介绍给定数组arr,arr中所有的值都为正数且不重复。每个值代表一种面值的货币,每种面值的货币可以使用任意张,再给定一个整数aim,代表要找的钱数,求所有的找零方法有多少种。二、算法思路枚举法,列出使用某张钞票n次的所有可能。1、暴力递归intprocess1(intn,intarr[],intindex,intrest){if(index==n)returnrest==0?1:0;int
- leetcode29. 两数相除-medium
智趣代码实验室
Leetcodeleetcodec++
1题目:两数相除官方标定难度:中给你两个整数,被除数dividend和除数divisor。将两数相除,要求不使用乘法、除法和取余运算。整数除法应该向零截断,也就是截去(truncate)其小数部分。例如,8.345将被截断为8,-2.7335将被截断至-2。返回被除数dividend除以除数divisor得到的商。注意:假设我们的环境只能存储32位有符号整数,其数值范围是[−231,231−1]。
- 算法及数据结构系列 - 动态规划
诺亚凹凸曼
算法及数据结构算法数据结构动态规划
系列文章目录算法及数据结构系列-二分查找算法及数据结构系列-BFS算法文章目录框架思路子序列问题解题模板一维dp数组二维dp数组经典题型322.零钱兑换暴力递归带备忘录的暴力递归动态规划300.最长上升子序列1143.最长公共子序列72.编辑距离框架思路动态规划问题的一般形式就是求最值。动态规划其实是运筹学的一种最优化方法,只不过在计算机问题上应用比较多,比如说求最长递增子序列,最小编辑距离等等。
- python函数闭包和递归_闭包和递归_个人文章 - SegmentFault 思否
weixin_39830313
python函数闭包和递归
js变量的作用域:全局作用域(全局变量):在函数外面声明的变量**生命周期(变量从声明到销毁):页面从打开到关闭.局部作用域(局部变量):在函数里面声明的变量**生命周:开始调用函数到函数执行完毕1.闭包使用介绍1.闭包介绍(closure)1.1闭包:是一个可以在函数外部访问函数内部变量的函数->闭包是函数1.2闭包作用:可以在函数外部访问函数内部变量->延长局部变量的生命周期1.3闭包语法:-
- python函数闭包和递归_python函数基础3--闭包 + 递归 + 函数回调
weixin_39532019
python函数闭包和递归
一、闭包1.函数嵌套defouter():print("外层函数")definner():print("内层函数")returninner()outer()函数嵌套流程图2.闭包闭包的表现形式:函数里面嵌套函数,外层函数返回内层函数的函数名,这种情况就称之为闭包defouter():print("外层函数")definner():print("内层函数")returninnerret=outer(
- python中的递归、回调函数以及闭包总结
敲代码敲到头发茂密
Python成长之路python开发语言
这里写目录标题一、递归例1:利用递归函数计算1到10的和例2:利用递归函数计算10的阶乘二、回调函数特别注意:在函数中的调用函数分为以下情况:1、同步回调2、异步回调三、闭包一、递归作用:在函数内部调用自己若干次例1:利用递归函数计算1到10的和defsum_num(num):ifnum>=1:sum=num+sum_num(num-1)else:sum=0returnsumprint(sum_n
- B2143 进制转换
1101.01
算法c++
题目描述用递归算法将一个十进制整数X(1≤X≤109)转换成任意进制数M(2≤M≤16,M为整数)。输入格式一行两个数,第一个十进制整数X,第二个为进制M。输出格式输出结果。输入输出样例输入#1复制3116输出#1复制1F说明/提示样例解释。将十进制31转化为十六进制数。#includeusingnamespacestd;chars[16]={'0','1','2','3','4','5','6'
- 栈 力扣hot100热门面试算法题 面试基础 核心思路 背题 滑动窗口最大值 字符串解码 每日温度 柱状图中最大矩形 有效的括号 最小栈
尘土哥
算法leetcode面试
栈栈的核心思路:每个数都要进栈or队列,但是要及时维护栈or队列,当某元素没有存在的意义时就删掉,关键是思考栈尾什么时候有用与没用。滑动窗口最大值https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/题解链接https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/solutions/3067170/d
- leetcode日记(108)验证回文串
梭七y
leetcode算法职场和发展
看上去很简单,其实很麻烦。一开始写的递归,但是内存超限……搜了下发现原因是每次递归调用都会创建一个新的字符串副本,这在处理长字符串时会占用大量内存。classSolution{public:boolisPalindrome(strings){if(s.size()==0||s.size()==1)return1;elseif(s[s.size()-1]==s[0]||(s[s.size()-1]-
- 个人学习编程(3-21) leetcode刷题
Rsecret2
编程笔记学习leetcode算法
链接列表的中间值:测试用例1:创建链表[1,2,3,4,5],调用middleNode,预期返回值是3。测试用例2:创建链表[1,2,3,4,5,6],调用middleNode,预期返回值是3。判断长度,然后length/2structListNode*middleNode(structListNode*head){intlength=0;for(structListNode*curr=head;
- 算法刷题记录——LeetCode篇(1) [第1~100题](持续更新)
Allen Wurlitzer
实战-算法解题算法leetcode职场和发展
更新时间:2025-03-21LeetCode刷题目录:算法刷题记录——专题目录汇总技术博客总目录:计算机技术系列博客——目录页优先整理热门100及面试150,不定期持续更新,欢迎关注!1.两数之和给定一个整数数组nums和一个整数目标值target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值target的那两个整数,并返回它们的数组下标。你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案,并且你不能使用两次相同的元素。你可以
- 【贪心算法】1、分发饼干
念奕玥
【Java】数据结构与算法javaleetcode贪心算法
贪心算法或贪心思想采用贪心的策略,保证每次操作都是局部最优的,从而使最后得到的结果是全局最优的。可用于解决分配问题e.g.leetcode455分发饼干解题思路:目标:尽可能满足越多数量的孩子。根据目标,可以容易想到,先去满足胃口值小的孩子。为了尽量使饼干可以满足更多的孩子,所以要把饼干尺寸大于等于孩子胃口值的饼干中挑尺寸最小的饼干给孩子。满足了这个孩子之后,再采取同样的策略去考虑剩下的孩子,直到
- 笔记-LeetCode 787: K 站中转内最便宜的航班
我只是什么都不会而已
算法
题目描述有n个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组flights,其中flights[i]=[fromi,toi,pricei],表示该航班都从城市fromi开始,以价格pricei抵达toi。现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市src和目的地dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过k站中转的路线,使得从src到dst的价格最便宜,并返回该价格。如果不存在这样的路线,则输出-1。代码模板(BFS+最短
- 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II
请向我看齐
LeetCode算法
题目分析LeetCode第122题是“买卖股票的最佳时机II”。题目描述为:给定一个数组prices,其中prices[i]是一支给定股票第i天的价格。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票)。模式识别本题属于动态规划或者贪心算法的范畴。由于可以进行多次交易,且没有交易次数限制,所以可以通过比较相邻两天的价格,只要后一天价格比前一天高,就进行一次交易
- C语言复习笔记6---while循环for循环
.又是新的一天.
C语言复习笔记c语言算法c++
感谢张学长为大家整理的笔记~考点整合A+B问题分离一个整数每一位从后往前从前往后→字符数组(字符串)/看成一堆字符栈(先入后出)→递归while→循环版的if(while循环的直接应用→模拟)gcd和lcm打擂法求max,min判断素数O(n)O(sqrt(n))→分离因子的快捷的求法打印素数表数列求和、斐波那契数列(递推)递推和递归递推往往用迭代(循环)来实现讲从前往后分离整数的递归写法实现方式
- Python函数完全解读:从零基础到高阶实战
藍海琴泉
python开发语言
目标读者:编程新手|转行者|需系统掌握函数用法的开发者目录一、函数是什么?为什么需要函数?二、函数基础语法详解1.定义与调用2.返回值:函数的输出结果3.参数传递机制4.案例:计算BMI指数三、变量作用域:理解局部与全局1.局部变量2.全局变量四、函数进阶:lambda与高阶函数1.lambda匿名函数2.高阶函数五、函数高级特性1.装饰器:增强函数功能2.递归函数六、实战案例:文件处理工具一、函
- 【JavaScript】11-JS高阶技巧
beibeibeiooo
JavaScript【已完结】javascript前端ecmascriptes6
本文介绍JS中的一些高阶技巧。目录1.深浅拷贝1.1浅拷贝1.2深拷贝1.2.1通过递归实现1.2.2lodash/cloneDeep1.2.3JSON.stringify()2.异常处理2.1throw抛异常2.2try/catch捕获异常2.3debugger3.处理this3.1this指向3.1.1普通函数this3.1.2箭头函数的this3.2改变this3.2.1call方法改变3.
- 代码随想录算法训练营第八天| 344 反转字符串、541 反转字符串II
Anjoubecoding
算法数据结构c++c语言leetcode
这两天开的是字符串专题,我准备在做题的时候用C++做一遍,再用C做一遍,因为一直刷leetcode用的都是C++,导致C的基础太薄弱了,之后工作中有可能用到C,相当于再复习复习一、Leetcode344反转字符串题目链接:Leetcode344反转字符串这道题很简单,这才是真正的简单题voidreverseString(char*s,intsSize){intleft=0,right=sSize-
- 【leetcode hot 100 39】组合总和
longii11
leetcodewindows算法
错误解法一:每一次回溯都遍历提供的数组classSolution{publicList>combinationSum(int[]candidates,inttarget){List>result=newArrayList>();Listtemp=newArrayList();intsum=0;backtrack(candidates,target,result,temp,sum);returnre
- 深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索详细解析和区别
潇杨爱吃粉
深度优先宽度优先算法数据结构
一、深度优先搜索(DFS)1.核心思想像探险家走迷宫,遇到岔路就选一条路走到头,无路可走时返回上一个岔路口换另一条路。2.实现方式数据结构:栈(Stack,先进后出)或递归(隐式栈)遍历顺序:纵向深入,优先访问最深层的节点3.图解示例假设有以下树结构:A/\BC/\/DEFDFS遍历顺序(从根节点A出发):A→B→D→E→C→F4.代码实现(Python)defdfs(graph,start):s
- 自用leetcode IDEA插件配置
QHG7C0
数据结构与算法(二刷)leetcode
文件名:P$!{question.frontendQuestionId}$!velocityTool.camelCaseName(${question.titleSlug})代码模版:${question.content}packageleetcode.editor.cn;//${question.title}publicclassP${question.frontendQuestionId}_$
- Swift高效解法!一文搞懂 LeetCode 236「二叉树的最近公共祖先」,助你快速拿下面试!
网罗开发
Swiftswiftleetcode面试
摘要最近公共祖先(LCA,LowestCommonAncestor)在二叉树、二叉搜索树(BST)等数据结构中有广泛应用,比如权限管理、网络路由、基因分析等。今天我们用Swift来解LeetCode236:「二叉树的最近公共祖先」,不仅会给出代码,还会分析它的时间复杂度、空间复杂度,并结合实际场景聊聊它的应用。问题描述给定一个二叉树,找到两个节点的最近公共祖先(LCA)。LCA的定义:“对于两个节
- (LeetCode 热题 100) 74. 搜索二维矩阵(二分查找)
岁忧
java版刷题LeetCode热题100LeetCodeleetcode矩阵算法c++java
题目:74.搜索二维矩阵方法一:数组按行拼接为一个不下降的一维数组。采用二分查找,时间复杂度0(lognm)。C++版本:classSolution{public:boolsearchMatrix(vector>&matrix,inttarget){intn=matrix.size(),m=matrix[0].size();intl=0,r=n*m-1;while(ltarget){r=mid-1
- Leetcode 剑指 Offer II 032. 有效的变位词
我不是程序员~~~~
C&C++leetcode算法职场和发展
给定两个字符串s和t,编写一个函数来判断它们是不是一组变位词(字母异位词)。注意:若s和t中每个字符出现的次数都相同且字符顺序不完全相同,则称s和t互为变位词(字母异位词)。示例1:输入:s="anagram",t="nagaram"输出:true示例2:输入:
- LeetCode146.LRU 缓存(哈希表+双向链表)
techpupil
缓存散列表链表
请你设计并实现一个满足LRU(最近最少使用)缓存约束的数据结构。实现LRUCache类:LRUCache(intcapacity)以正整数作为容量capacity初始化LRU缓存intget(intkey)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。voidput(intkey,intvalue)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组k
- (LeetCode 每日一题) 2680. 最大或值(前缀和、位运算)
岁忧
LeetCodejava版刷题leetcode算法职场和发展javac++
题目:2680.最大或值思路:在多个数上乘2,不如都在一个数上乘。这样只需要枚举每一个数乘k次2,也就是位运算移位k次。通过前缀和可以预处理出左右俩边的或值,实际上只需要预处理出一边的,另外一边在遍历时可得出。时间复杂度0(n)classSolution{public:longlongmaximumOr(vector&nums,intk){intn=nums.size();vectorv(n);f
- 图论:以二维数组表示的连通图/树应如何表示?leetcode1042.不邻接种花
坠金
技术面算法图论算法leetcode
1042.不邻接植花-力扣(LeetCode)容器在这道题中输入类似[[1,2],[3,4]],这意味着花园1连通了花园2,花园3连通了花园4。那么该怎么根据这个输入,获取一个方便后面算法的表示呢?我们通常管这种存放邻居的数据格式叫做:邻接表通常我的思路是使用下列容器作为邻接表:哈希表,key就是花园i,value是与花园i接壤的其他所有花园。二维数组,第i个数组中的元素是与花园i接壤的其他所有花
- LeetCode 热题 100_跳跃游戏 II(79_45_中等_C++)(贪心算法)
Dream it possible!
LeetCode热题100leetcodec++贪心算法算法
LeetCode热题100_跳跃游戏II(79_45)题目描述:输入输出样例:题解:解题思路:思路一(贪心选择):代码实现代码实现(思路一(贪心算法)):以思路一为例进行调试题目描述:给定一个长度为n的0索引整数数组nums。初始位置为nums[0]。每个元素nums[i]表示从索引i向后跳转的最大长度。换句话说,如果你在nums[i]处,你可以跳转到任意nums[i+j]处:0&nums){in
- 写leetcode常用的库函数和常量
xsh219
golang小知识点算法数据结构golang
在Go中刷LeetCode,以下是一些常用的标准库函数和数据类型的最大值、最小值:✅常用标准库函数数学与排序math包math.Max(x,y):返回两个float64类型数中的较大值。math.Min(x,y):返回两个float64类型数中的较小值。math.Abs(x):取绝对值。math.Pow(x,y):计算x^y。math.Sqrt(x):计算平方根。sort包sort.Ints(sl
- rust学习笔记16-206.反转链表(递归)
水蜜桃one
学习笔记链表
rust函数递归在14中已经提到,接下来我们把206.反转链表,用递归法实现递归函数通常包含两个主要部分:基准条件(BaseCase):递归终止的条件,避免无限递归。递归步骤(RecursiveStep):将问题分解为更小的子问题,并调用自身来解决这些子问题。//Definitionforsingly-linkedlist.#[derive(PartialEq,Eq,Clone,Debug)]pu
- windows下源码安装golang
616050468
golang安装golang环境windows
系统: 64位win7, 开发环境:sublime text 2, go版本: 1.4.1
1. 安装前准备(gcc, gdb, git)
golang在64位系
- redis批量删除带空格的key
bylijinnan
redis
redis批量删除的通常做法:
redis-cli keys "blacklist*" | xargs redis-cli del
上面的命令在key的前后没有空格时是可以的,但有空格就不行了:
$redis-cli keys "blacklist*"
1) "blacklist:12:
[email protected]
- oracle正则表达式的用法
0624chenhong
oracle正则表达式
方括号表达示
方括号表达式
描述
[[:alnum:]]
字母和数字混合的字符
[[:alpha:]]
字母字符
[[:cntrl:]]
控制字符
[[:digit:]]
数字字符
[[:graph:]]
图像字符
[[:lower:]]
小写字母字符
[[:print:]]
打印字符
[[:punct:]]
标点符号字符
[[:space:]]
- 2048源码(核心算法有,缺少几个anctionbar,以后补上)
不懂事的小屁孩
2048
2048游戏基本上有四部分组成,
1:主activity,包含游戏块的16个方格,上面统计分数的模块
2:底下的gridview,监听上下左右的滑动,进行事件处理,
3:每一个卡片,里面的内容很简单,只有一个text,记录显示的数字
4:Actionbar,是游戏用重新开始,设置等功能(这个在底下可以下载的代码里面还没有实现)
写代码的流程
1:设计游戏的布局,基本是两块,上面是分
- jquery内部链式调用机理
换个号韩国红果果
JavaScriptjquery
只需要在调用该对象合适(比如下列的setStyles)的方法后让该方法返回该对象(通过this 因为一旦一个函数称为一个对象方法的话那么在这个方法内部this(结合下面的setStyles)指向这个对象)
function create(type){
var element=document.createElement(type);
//this=element;
- 你订酒店时的每一次点击 背后都是NoSQL和云计算
蓝儿唯美
NoSQL
全球最大的在线旅游公司Expedia旗下的酒店预订公司,它运营着89个网站,跨越68个国家,三年前开始实验公有云,以求让客户在预订网站上查询假期酒店时得到更快的信息获取体验。
云端本身是用于驱动网站的部分小功能的,如搜索框的自动推荐功能,还能保证处理Hotels.com服务的季节性需求高峰整体储能。
Hotels.com的首席技术官Thierry Bedos上个月在伦敦参加“2015 Clou
- java笔记1
a-john
java
1,面向对象程序设计(Object-oriented Propramming,OOP):java就是一种面向对象程序设计。
2,对象:我们将问题空间中的元素及其在解空间中的表示称为“对象”。简单来说,对象是某个类型的实例。比如狗是一个类型,哈士奇可以是狗的一个实例,也就是对象。
3,面向对象程序设计方式的特性:
3.1 万物皆为对象。
- C语言 sizeof和strlen之间的那些事 C/C++软件开发求职面试题 必备考点(一)
aijuans
C/C++求职面试必备考点
找工作在即,以后决定每天至少写一个知识点,主要是记录,逼迫自己动手、总结加深印象。当然如果能有一言半语让他人收益,后学幸运之至也。如有错误,还希望大家帮忙指出来。感激不尽。
后学保证每个写出来的结果都是自己在电脑上亲自跑过的,咱人笨,以前学的也半吊子。很多时候只能靠运行出来的结果再反过来
- 程序员写代码时就不要管需求了吗?
asia007
程序员不能一味跟需求走
编程也有2年了,刚开始不懂的什么都跟需求走,需求是怎样就用代码实现就行,也不管这个需求是否合理,是否为较好的用户体验。当然刚开始编程都会这样,但是如果有了2年以上的工作经验的程序员只知道一味写代码,而不在写的过程中思考一下这个需求是否合理,那么,我想这个程序员就只能一辈写敲敲代码了。
我的技术不是很好,但是就不代
- Activity的四种启动模式
百合不是茶
android栈模式启动Activity的标准模式启动栈顶模式启动单例模式启动
android界面的操作就是很多个activity之间的切换,启动模式决定启动的activity的生命周期 ;
启动模式xml中配置
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:launchMode="standard&quo
- Spring中@Autowired标签与@Resource标签的区别
bijian1013
javaspring@Resource@Autowired@Qualifier
Spring不但支持自己定义的@Autowired注解,还支持由JSR-250规范定义的几个注解,如:@Resource、 @PostConstruct及@PreDestroy。
1. @Autowired @Autowired是Spring 提供的,需导入 Package:org.springframewo
- Changes Between SOAP 1.1 and SOAP 1.2
sunjing
ChangesEnableSOAP 1.1SOAP 1.2
JAX-WS
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 0: Primer (Second Edition)
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 1: Messaging Framework (Second Edition)
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 2: Adjuncts (Second Edition)
Which style of WSDL
- 【Hadoop二】Hadoop常用命令
bit1129
hadoop
以Hadoop运行Hadoop自带的wordcount为例,
hadoop脚本位于/home/hadoop/hadoop-2.5.2/bin/hadoop,需要说明的是,这些命令的使用必须在Hadoop已经运行的情况下才能执行
Hadoop HDFS相关命令
hadoop fs -ls
列出HDFS文件系统的第一级文件和第一级
- java异常处理(初级)
白糖_
javaDAOspring虚拟机Ajax
从学习到现在从事java开发一年多了,个人觉得对java只了解皮毛,很多东西都是用到再去慢慢学习,编程真的是一项艺术,要完成一段好的代码,需要懂得很多。
最近项目经理让我负责一个组件开发,框架都由自己搭建,最让我头疼的是异常处理,我看了一些网上的源码,发现他们对异常的处理不是很重视,研究了很久都没有找到很好的解决方案。后来有幸看到一个200W美元的项目部分源码,通过他们对异常处理的解决方案,我终
- 记录整理-工作问题
braveCS
工作
1)那位同学还是CSV文件默认Excel打开看不到全部结果。以为是没写进去。同学甲说文件应该不分大小。后来log一下原来是有写进去。只是Excel有行数限制。那位同学进步好快啊。
2)今天同学说写文件的时候提示jvm的内存溢出。我马上反应说那就改一下jvm的内存大小。同学说改用分批处理了。果然想问题还是有局限性。改jvm内存大小只能暂时地解决问题,以后要是写更大的文件还是得改内存。想问题要长远啊
- org.apache.tools.zip实现文件的压缩和解压,支持中文
bylijinnan
apache
刚开始用java.util.Zip,发现不支持中文(网上有修改的方法,但比较麻烦)
后改用org.apache.tools.zip
org.apache.tools.zip的使用网上有更简单的例子
下面的程序根据实际需求,实现了压缩指定目录下指定文件的方法
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWrit
- 读书笔记-4
chengxuyuancsdn
读书笔记
1、JSTL 核心标签库标签
2、避免SQL注入
3、字符串逆转方法
4、字符串比较compareTo
5、字符串替换replace
6、分拆字符串
1、JSTL 核心标签库标签共有13个,
学习资料:http://www.cnblogs.com/lihuiyy/archive/2012/02/24/2366806.html
功能上分为4类:
(1)表达式控制标签:out
- [物理与电子]半导体教材的一个小问题
comsci
问题
各种模拟电子和数字电子教材中都有这个词汇-空穴
书中对这个词汇的解释是; 当电子脱离共价键的束缚成为自由电子之后,共价键中就留下一个空位,这个空位叫做空穴
我现在回过头翻大学时候的教材,觉得这个
- Flashback Database --闪回数据库
daizj
oracle闪回数据库
Flashback 技术是以Undo segment中的内容为基础的, 因此受限于UNDO_RETENTON参数。要使用flashback 的特性,必须启用自动撤销管理表空间。
在Oracle 10g中, Flash back家族分为以下成员: Flashback Database, Flashback Drop,Flashback Query(分Flashback Query,Flashbac
- 简单排序:插入排序
dieslrae
插入排序
public void insertSort(int[] array){
int temp;
for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
temp = array[i];
for(int k=i-1;k>=0;k--)
- C语言学习六指针小示例、一维数组名含义,定义一个函数输出数组的内容
dcj3sjt126com
c
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int * p; //等价于 int *p 也等价于 int* p;
int i = 5;
char ch = 'A';
//p = 5; //error
//p = &ch; //error
//p = ch; //error
p = &i; //
- centos下php redis扩展的安装配置3种方法
dcj3sjt126com
redis
方法一
1.下载php redis扩展包 代码如下 复制代码
#wget http://redis.googlecode.com/files/redis-2.4.4.tar.gz
2 tar -zxvf 解压压缩包,cd /扩展包 (进入扩展包然后 运行phpize 一下是我环境中phpize的目录,/usr/local/php/bin/phpize (一定要
- 线程池(Executors)
shuizhaosi888
线程池
在java类库中,任务执行的主要抽象不是Thread,而是Executor,将任务的提交过程和执行过程解耦
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
public class RunMain implements Executor{
@Override
pub
- openstack 快速安装笔记
haoningabc
openstack
前提是要配置好yum源
版本icehouse,操作系统redhat6.5
最简化安装,不要cinder和swift
三个节点
172 control节点keystone glance horizon
173 compute节点nova
173 network节点neutron
control
/etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward =
- 从c面向对象的实现理解c++的对象(二)
jimmee
C++面向对象虚函数
1. 类就可以看作一个struct,类的方法,可以理解为通过函数指针的方式实现的,类对象分配内存时,只分配成员变量的,函数指针并不需要分配额外的内存保存地址。
2. c++中类的构造函数,就是进行内存分配(malloc),调用构造函数
3. c++中类的析构函数,就时回收内存(free)
4. c++是基于栈和全局数据分配内存的,如果是一个方法内创建的对象,就直接在栈上分配内存了。
专门在
- 如何让那个一个div可以拖动
lingfeng520240
html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml
- 第10章 高级事件(中)
onestopweb
事件
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- 计算两个经纬度之间的距离
roadrunners
计算纬度LBS经度距离
要解决这个问题的时候,到网上查了很多方案,最后计算出来的都与百度计算出来的有出入。下面这个公式计算出来的距离和百度计算出来的距离是一致的。
/**
*
* @param longitudeA
* 经度A点
* @param latitudeA
* 纬度A点
* @param longitudeB
*
- 最具争议的10个Java话题
tomcat_oracle
java
1、Java8已经到来。什么!? Java8 支持lambda。哇哦,RIP Scala! 随着Java8 的发布,出现很多关于新发布的Java8是否有潜力干掉Scala的争论,最终的结论是远远没有那么简单。Java8可能已经在Scala的lambda的包围中突围,但Java并非是函数式编程王位的真正觊觎者。
2、Java 9 即将到来
Oracle早在8月份就发布
- zoj 3826 Hierarchical Notation(模拟)
阿尔萨斯
rar
题目链接:zoj 3826 Hierarchical Notation
题目大意:给定一些结构体,结构体有value值和key值,Q次询问,输出每个key值对应的value值。
解题思路:思路很简单,写个类词法的递归函数,每次将key值映射成一个hash值,用map映射每个key的value起始终止位置,预处理完了查询就很简单了。 这题是最后10分钟出的,因为没有考虑value为{}的情
![]()