有向图的表示、存储及DFS/BFS实现(C++)--丰富注释+功能完整版
1 基本概念
1.1 图的定义
图是由顶点的有穷非空集合和顶点之间边的集合组成,通常表示为:
G=(V,E)
其中:G表示一个图,V是图G中顶点的集合,E是图G中顶点之间边的集合。
注:
在线性表中,元素个数可以为零,称为空表;
在树中,结点个数可以为零,称为空树;
在图中,顶点个数不能为零,但可以没有边。
1.2 图的存储结构
考虑图的定义,图是由顶点和边组成的,分别考虑如何存储顶点、如何存储边。
1.2.1 邻接矩阵存储(数组表示法)
基本思想:用一个一维数组存储图中顶点的信息,用一个二维数组(称为邻接矩阵)存储图中各顶点之间的邻接关系。
假设图G=(V,E)有n个顶点,则邻接矩阵是一个n×n的方阵,定义为:
1.2.2 邻接表存储
邻接表存储的基本思想:对于图的每个顶点vi,将所有邻接于vi的顶点链成一个单链表,称为顶点vi的边表(对于有向图则称为出边表),所有边表的头指针和存储顶点信息的一维数组构成了顶点表。
邻接表有两种结点结构:顶点表结点和边表结点。
其中:
vertex:数据域,存放顶点信息。firstedge:指针域,指向边表中第一个结点。
adjvex:邻接点域,边的终点在顶点表中的下标。next:指针域,指向边表中的下一个结点。(本文在实现的时候将adjvex设置为了顶点元素)
2 代码实现
本文使用面向对象的思想实现,将图的两种存储方式及相应的成员变量,成员函数封装在了类Graph中。为方便实现,顶点数据类型设为char。关于边的添加删除,点的添加删除因为实现原理简单,但实现过程繁琐本文未给予实现。
2.1 使用邻接矩阵存储(adjacency matrix)
2.1.1 成员变量
使用邻接矩阵存储图时,不需要定义新的结构体。
int VexNum, ArcNum; //顶点数和边数
//邻接矩阵所需成员变量
int** AM_Edge; //邻接矩阵边集
char* AM_Node; //邻接矩阵顶点集
//深度和广度优先搜索中,用于标记结点是否被访问的数组,按序号对应每个顶点
bool *visited;
复制代码2.1.2 创建图
依次从控制台输入所有顶点,及所有的边创建完整的图,例如:
ABCDEFGH (enter)
AB AC BF CD FD CE FH DG (enter,再ctrl+z标示输入中止)
//创建邻接矩阵存储的图
void AM_GraphInitial() { //初始化邻接矩阵并构造该图
cout << "please input all the vextex: " << endl;
string s;
cin >> s;
VexNum = s.length(); //确定顶点总数
AM_Node = new char[VexNum]; //创建存储顶点的数组
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) //给顶点数组赋值
AM_Node[i] = s[i];
AM_Edge = new int*[VexNum]; //申请邻接矩阵存储空间
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) //对邻接矩阵初始化
{
AM_Edge[i] = new int[VexNum];
for (int j = 0; j < VexNum; j++)
AM_Edge[i][j] = 0;
}
//输入所有的边,形式为 AB CD ED
cout << "please input all the edge,format as:AB CD...,end with ctrl+'z'!"<> s) {//输入所有的边后回车,再输入ctrl+z用于中止输入
int i = AM_locate(s[0]);
int j= AM_locate(s[1]);
if (i != -1 && j != -1)
{
AM_Edge[i][j] = 1;
ArcNum++; //统计边数
}
}
}
int AM_locate(char vex) { //寻找顶点在顶点数组中的下标
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AM_Node[i] == vex)
return i;
cout << vex << " is not exit in this graph!" << endl;
return -1;
}
复制代码 2.1.3 以邻接矩阵的形式输出该图
void AM_GraphPrint() { //以邻接矩阵的形式输出该图
cout << "adjacency matrix of this graph:" << endl;
cout << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
cout << AM_Node[i]<<" ";
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
cout << AM_Node[i] << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < VexNum; j++)
cout << AM_Edge[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
复制代码2.1.4 求某个顶点的入度和出度及输出所有点的入度出度
某个顶点的入度,即顶点所在列非零项个数;出度,即顶点所在行非零项个数。
//输出所有点的入度出度;
cout << "vertex in-degree out-degree" << endl;
int d1, d2;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
AM_degree(AM_Node[i], d1, d2);
cout << setw(6) << AM_Node[i] << setw(10) << d1 << setw(11) << d2 << endl;
}
}
//求某个顶点的入度和出度
void AM_degree(char vex,int &d1,int &d2) {
d1 = d2 = 0;
int loc = AM_locate(vex);
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AM_Edge[i][loc] != 0) //入度,即顶点所在列非零项个数
d1++;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AM_Edge[loc][i] != 0) //出度,即顶点所在行非零项个数
d2++;
}
复制代码2.1.5 广度优先遍历(BFS)(针对一个连通分量)
基本思想:
⑴ 访问顶点v;
⑵ 依次访问v的各个未被访问的邻接点v1, v2, …, vk;
⑶ 分别从v1,v2,…,vk出发依次访问它们未被访问的邻接点,并使“先被访问顶点的邻接点”先于“后被访问顶点的邻接点”被访问。直至图中所有与顶点v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。
已访问过的结点后续不需要再次访问,因此需要使用一个数组visited[VeNum]标记每个顶点的访问状态,未访问过标记为false。实现方式类似于二叉树的层次遍历,每次将队列最前元素取出并将与其相连且未访问过的顶点加入队尾。
//使用队列实现,类似于二叉树的层次遍历
void AM_BFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AL_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The BFS of this graph(stored by adjacency matrix):" << endl;
InitialVisited(); //初始化标记数组
queue bfs;
bfs.push(startLoc);
visited[startLoc] = true; //将起始结点加入队列并标记为已访问
while (!bfs.empty()) { //每次取出队列最前的顶点,并将其相连且未标记过的顶点加入队列尾部
int j = bfs.front();
cout << AM_Node[j]<<" ";
// visited[j] = true;
bfs.pop();
//寻找该结点为起始结点,为结点未访问过的边;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
if (AM_Edge[j][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true) //存在指向顶点i的边且该点未被访问则加入队列
{
bfs.push(i);
visited[i] = true; //应该在进入队列的时候标记为已经访问,而不能是输出时,否则可能会多次入队
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
复制代码 2.1.6 深度优先遍历(DFS)(针对一个连通分量)
基本思想 :
⑴ 访问顶点v;
⑵ 从v的未被访问的邻接点中选取一个顶点w,从w出发进行深度优先遍历;
⑶ 重复上述两步,直至图中所有和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。
这里使用了两种实现方式,递归实现和借助栈实现,递归实现较为简单,使用栈实现时,注意设置压栈和出栈的条件和时间即可,详细步骤见代码注释。
//深度优先遍历(DFS),输入为起始点在数组中的下标(针对一个连通分量)
void AM_DFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AM_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The DFS of this graph(stored by adjacency matrix):" << endl;
cout << "use recursion: ";
InitialVisited(); //切记要先初始化标记数组
AM_RecursiveDFS(startLoc); //使用递归;
cout << endl;
cout << "use stack: ";
InitialVisited();
AM_StackDFS(startLoc); //使用栈
cout << endl;
}
//使用递归实现DFS(针对一个连通分量)
void AM_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc) {
cout << AM_Node[startLoc]<<" ";
visited[startLoc] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
//如果发现存在相连且未标记的顶点,则递归为对该顶点的访问
if (AM_Edge[startLoc][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true)
AM_RecursiveDFS(i);
}
}
//使用栈实现DFS(针对一个连通分量)
void AM_StackDFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AM_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
InitialVisited();
stack dfsStack;
dfsStack.push(startLoc);//将起始点压栈并输出,标记该点已访问
cout << AM_Node[startLoc] << " ";
visited[startLoc] = true;
int* visitedPos; //visitedPos用来记录栈中每个顶点在矩阵对应行中已经访问到的位置,
// 避免回溯时while中的for循环每次都从0开始从而提高效率
visitedPos = new int[VexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
visitedPos[i] = 0; //初始化为0
}
while (!dfsStack.empty()) { //每次取栈顶元素,寻找与其相连且未标记过的顶点
int j = dfsStack.top();
for (int i = visitedPos[j]; i < VexNum; i++) //每次从visitedPos[j]开始,提高效率
{
if (AM_Edge[j][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true) //寻找到未访问过的结点则加入栈中并输出
{
dfsStack.push(i);
cout << AM_Node[i] << " ";
visitedPos[j] = i; //更新该顶点在矩阵对应行中已查询到的位置
visited[i] = true; //将顶点i标记为已访问
break; //找到符合要求的点则退出for循环(进入while下一轮,进行更深的搜索)
}
if (i == VexNum-1) //能执行到此说明与该点相关的点全部被访问,将该结点其退栈
dfsStack.pop();
}
}
//注意销毁其空间
delete visitedPos;
visitedPos = NULL;
}
复制代码 2.1.7 寻找两个顶点之间的简单路径
这里借助DFS的思路,使用栈并通过递归实现。当查询到目标顶点时,栈中元素即是从i到j的路径;实现过程需注意压栈和出栈的时间和条件,当栈顶顶点不存在和它相连且未标记过的结点时,将其出栈。
//借助栈,使用DFS实现寻找i到j的简单路径(此为逆序输出)
void AM_FindPath(int i,int j) {
cout << "path between " << AM_Node[i] << " and " << AM_Node[j]<< " : ";
stack pathStack;
InitialVisited();
if (AM_RecursiveDFS(i, j, pathStack)) //存在路径,则输出栈中保存路径的所有顶点
while (!pathStack.empty()) {
cout << AM_Node[pathStack.top()] << " ";
pathStack.pop();
}
else {
cout << "not existed!";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool AM_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc,int endLoc,stack &p) {
p.push(startLoc);
visited[startLoc] = true;
if (startLoc == endLoc) //栈顶顶点为要寻找的目标顶点则中止,直接返回
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
//如果发现存在相连且未标记的顶点,则递归为对该顶点的访问
if (AM_Edge[startLoc][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true)
return AM_RecursiveDFS(i, endLoc, p); //返回与startLoc相连的顶点i
//是否存在到endLoc路径的搜索结果
}
p.pop();//执行到此说明startLoc无法到达endLoc,将其退栈
return false;
}
复制代码 2.2 使用邻接表存储(adjacency list)
使用邻接表时,顶点和边结点存储的内容可能不一致(比如边结点可增加weight属性表示该边权值),因此需在类外定义两个结构体分别表示顶点和边结点。
//邻接表顶点和边结点的结构体
struct EdgeNode { //边结点结构
char adjVex; //该边结点指向的顶点
EdgeNode* next; //指向的下一边结点
// int weight;//该边的权值
EdgeNode(char data) {
adjVex = data;
next = NULL;
//weight = -1;
}
};
struct VertexNode { //顶点结构
char data; //顶点元素
EdgeNode* first; //指向第一条依附该顶点的边的指针
VertexNode() {
first = NULL;
}
};
复制代码2.2.1 成员变量
int VexNum, ArcNum; //顶点数和边数
/邻接表所需成员变量
VertexNode* AL_Node; //存储邻接表顶点的数组
//深度和广度优先搜索中,用于标记结点是否被访问的数组,按序号对应每个顶点
bool *visited;
复制代码2.2.2 初始化并创建图
依次从控制台输入所有顶点,及所有的边创建完整的图,例如:
ABCDEFGH (enter)
AB AC BF CD FD CE FH DG (enter,再ctrl+z标示输入中止)
//初始化并创建该图
void AL_GraphInitial() {
cout << "please input all the vextex: " << endl;
string s;
cin >> s;
VexNum = s.length(); //确定顶点数
AL_Node = new VertexNode[VexNum]; //创建顶点数组
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) //给顶点赋值
AL_Node[i].data = s[i];
cout << "please input all the edge,format as:AB CD...,end with ctrl+'z'!" << endl;
while (cin >> s) {
int i = AL_Locate(s[0]);
if (i == -1)
continue;
if (AL_Node[i].first == NULL)
AL_Node[i].first = new EdgeNode(s[1]);
else { //找到最后一个边结点
EdgeNode *tmp = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmp->next) {
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp->next = new EdgeNode(s[1]);
}
ArcNum++; //统计边数
}
}
int AL_Locate(char vex) { //寻找vex位于顶点集的位置
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AL_Node[i].data == vex)
return i;
cout << vex << " is not exit in this graph!" << endl;
return -1;
}
复制代码2.2.3 以邻接表的形式输出该图
void AL_GraphPrint() { //以邻接表形式输出该图
cout << "adjacency list of this graph:" << endl;
EdgeNode *tmp = NULL;
for (int i= 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
cout << AL_Node[i].data;
tmp = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmp) {
cout << " -> " << tmp->adjVex;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
//输出所有顶点的入度和出度
cout << "vertex in-degree out-degree" << endl;
int d1, d2;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
AL_degree(AL_Node[i].data, d1, d2);
cout << setw(6) << AL_Node[i].data << setw(10) << d1 << setw(11) << d2 << endl;
}
}
复制代码2.2.4 求某个顶点的入度和出度
//求某个顶点的入度和出度
void AL_degree(char vex,int &s1,int &s2) {
s1 = s2 = 0;
EdgeNode* tmp = NULL;
int loc = AL_Locate(vex);
//入度 ,即寻找vex出现在边结点中的次数
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
if (i == loc) //vex对应顶点的边结点无需查找
continue;
tmp = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmp) {
if (tmp->adjVex == vex)
{
s1++;
break; //只存在一次,找到即可退出,进入for的下一轮循环
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
//出度
tmp = AL_Node[loc].first; //即vex对应顶点的边结点个数
while (tmp) {
s2++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
复制代码2.2.5 广度优先遍历(BFS)(针对一个连通分量)
基本思想:
⑴ 访问顶点v;
⑵ 依次访问v的各个未被访问的邻接点v1, v2, …, vk;
⑶ 分别从v1,v2,…,vk出发依次访问它们未被访问的邻接点,并使“先被访问顶点的邻接点”先于“后被访问顶点的邻接点”被访问。直至图中所有与顶点v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。
已访问过的结点后续不需要再次访问,因此需要使用一个数组visited[VeNum]标记每个顶点的访问状态,未访问过标记为false。实现方式类似于二叉树的层次遍历,每次将队列最前元素取出并将与其相连且未访问过的顶点加入队尾。
//使用队列实现广度优先遍历(针对一个连通分量)
void AL_BFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AL_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The BFS of this graph(stored by adjacency list):" << endl;
InitialVisited(); //初始化访问标记数组
queue bfs;
bfs.push(startLoc); //标记初始结点已访问并入队
visited[startLoc] = true;
EdgeNode *tmp=NULL;
while (!bfs.empty()) {
int j = bfs.front();
bfs.pop(); //队列最前元素出队并输出
cout << AL_Node[j].data<<" ";
tmp = AL_Node[j].first;
while (tmp) { //寻找与队列最前顶点相连,且未被标记的所有边结点,将其入队并标记
int i = AL_Locate(tmp->adjVex); //边结点在顶点数组中的位置
if (visited[i] != true) { //第i个结点未被标记,将其入队并标记
bfs.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
复制代码 2.2.6 深度优先遍历(DFS)(针对一个连通分量)
基本思想 :
⑴ 访问顶点v;
⑵ 从v的未被访问的邻接点中选取一个顶点w,从w出发进行深度优先遍历;
⑶ 重复上述两步,直至图中所有和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问到。
这里使用了两种实现方式,递归实现和借助栈实现,递归实现较为简单,使用栈实现时,注意设置压栈和出栈的条件和时间即可,详细步骤见代码注释。
//使用递归实现深度优先遍历(DFS)(针对一个连通分量)
void AL_DFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AL_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The DFS of this graph(stored by adjacency list):" << endl;
InitialVisited();
cout << "use Recursion: ";
AL_RecursiveDFS(startLoc); //递归DFS
cout << endl;
InitialVisited();
cout<<"use Stack: ";
AL_StackDFS(startLoc); //栈DFS
cout << endl;
}
void AL_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc) {
cout << AL_Node[startLoc].data<<" ";
visited[startLoc] = true; //输出当前点并标记
EdgeNode* tmp;
tmp = AL_Node[startLoc].first;
while (tmp) {
int i = AL_Locate(tmp->adjVex); //找到第一个邻接点在顶点数组中的位置
if (visited[i] != true)
AL_RecursiveDFS(i);//邻接点i未被标记,开始递归访问该结点
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
//使用栈实现深度优先遍历(DFS)(针对一个连通分量)
void AL_StackDFS(int startLoc) {
stack dfsStack;
dfsStack.push(startLoc); //将起始顶点压栈,并输出其值
visited[startLoc] = true; //标记该节点
cout << AL_Node[startLoc].data << " ";
EdgeNode** visitedPos; //用来记录每个顶点下一个将查询的边结点的位置,
//避免while内层循环while(1)中每个顶点每次都从头开始查询未标记的边结点,从而提高效率
visitedPos = new EdgeNode*[VexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) { //每个顶点对应的访问位置都初始化第一个边结点;
visitedPos[i] = AL_Node[i].first;
}
while (!dfsStack.empty()) {
int j = dfsStack.top();
while (1) { //不断查询第j个顶点下一个将查询的边结点
if (visitedPos[j] != NULL) { //若存在未查询过的边结点
int i = AL_Locate(visitedPos[j]->adjVex); //获取该边结点对应的顶点在顶点数组中的序号
if (visited[i] != true) { //如果该边结点未被标记,则将其压栈输出然后退出内层循环
dfsStack.push(i);
cout << AL_Node[i].data << " ";
visited[i] = true;
visitedPos[j] = visitedPos[j]->next; //更新结点j的下一个将查询的边结点指针
break; //退出内层while循环,进入外层while下一轮循环从而进行更深的访问
}
else //仍存在未查询过的边结点,visitedPos[j]指向下一边结点
{
visitedPos[j] = visitedPos[j]->next;
}
} //如果该顶点的可查询的边结点为空,则将该顶点退出
else {
dfsStack.pop();
break;
}
}
}
delete[] visitedPos; //把指针数组销毁即可,不要把每个数组元素指向的空间销毁
visitedPos = NULL;
}
复制代码 2.2.7 寻找两个顶点之间的简单路径
这里借助DFS的思路,使用栈并通过递归实现。当查询到目标顶点时,栈中元素即是从i到j的路径;实现过程需注意压栈和出栈的时间和条件,当栈顶顶点不存在未标记过的边结点时,将其出栈。
//借助栈,使用深度遍历(DFS),寻找i到j的简单路径(此为逆序输出)
void AL_FindPath(int i, int j) {
cout << "path between " << AL_Node[i].data << " and " << AL_Node[j].data << " : ";
stack pathStack;
InitialVisited();
if (AL_RecursiveDFS(i, j, pathStack)) //存在路径,则输出栈中保存路径的所有顶点
while (!pathStack.empty()) {
cout << AL_Node[pathStack.top()].data<<" ";
pathStack.pop();
}
else {
cout << "not existed!";
}
cout<< endl;
}
bool AL_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc,int endLoc, stack &p) {
p.push(startLoc);
visited[startLoc] = true; //输出当前点并标记
if (startLoc == endLoc) //栈顶顶点等于要寻找的顶点j时,说明存在路径i-j,沿途顶点都存在栈中,此时直接返回
return true;
EdgeNode* tmp;
tmp = AL_Node[startLoc].first;
while (tmp) {
int i = AL_Locate(tmp->adjVex); //找到第一个邻接点在顶点数组中的位置
if (visited[i] != true) {
if (true == AL_RecursiveDFS(i, endLoc, p))//如果顶点i存在到endLoc的路径,则返回true
return true;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
p.pop(); //执行到此说明startLoc无法到达endLoc,将其退栈
return false;
}
复制代码 2.3 构造函数,析构函数及标记数组初始化
对二维数组析构时,注意先析构每个一级指针指向的空间,再析构二级指针指向的空间。
//构造和析构函数
Graph() {
VexNum = ArcNum = 0;
AM_Node = NULL;
AM_Edge = NULL;
AL_Node = NULL;
visited = NULL;
}
~Graph() {
//邻接矩阵析构
delete[] AM_Node;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
delete[] AM_Edge[i];
delete[] AM_Edge;
//邻接表析构
//1.先析构边结点
EdgeNode* tmpCurr, *tmpNext;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
tmpCurr = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmpCurr) {
tmpNext = tmpCurr->next;
delete tmpCurr;
tmpCurr = tmpNext;
}
}
//2.再析构顶点
delete[] AL_Node;
}
//初始化标记数组,全部设为未被访问(false)
void InitialVisited() {
if (visited == NULL)
visited = new bool[VexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
visited[i] = false;
}
复制代码3 完整代码(Graph.hpp)
/*图的存储和相关算法*/
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/*使用邻接矩阵时无需声明结构体,使用邻接表时需要声明顶点和边结点的结构体*/
//邻接表顶点和边结点的结构体
struct EdgeNode { //边结点结构
char adjVex; //该边结点指向的顶点
EdgeNode* next; //指向的下一边结点
// int weight;//该边的权值
EdgeNode(char data) {
adjVex = data;
next = NULL;
//weight = -1;
}
};
struct VertexNode { //顶点结构
char data; //顶点信息
EdgeNode* first; //指向第一条依附该顶点的边的指针
VertexNode() {
first = NULL;
}
};
class Graph
{
int VexNum, ArcNum; //顶点数和边数
//邻接矩阵所需成员变量
int** AM_Edge; //邻接矩阵边集
char* AM_Node; //邻接矩阵顶点集
//邻接表所需成员变量
VertexNode* AL_Node; //邻接表顶点集
//深度和广度优先搜索中,用于标记结点是否被访问的数组,按序号对应每个顶点
bool *visited;
public:
//构造和析构函数
Graph() {
VexNum = ArcNum = 0;
AM_Node = NULL;
AM_Edge = NULL;
AL_Node = NULL;
visited = NULL;
}
~Graph() {
//邻接矩阵析构
delete[] AM_Node;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
delete[] AM_Edge[i];
delete[] AM_Edge;
//邻接表析构
//1.先析构边结点
EdgeNode* tmpCurr, *tmpNext;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
tmpCurr = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmpCurr) {
tmpNext = tmpCurr->next;
delete tmpCurr;
tmpCurr = tmpNext;
}
}
//2.再析构顶点
delete[] AL_Node;
}
///1 使用邻接矩阵法储存图 相关成员函数
//创建邻接矩阵存储的图
void AM_GraphInitial() { //初始化邻接矩阵并构造该图
cout << "please input all the vextex: " << endl;
string s;
cin >> s;
VexNum = s.length(); //确定顶点总数
AM_Node = new char[VexNum]; //创建存储顶点的数组
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) //给顶点数组赋值
AM_Node[i] = s[i];
AM_Edge = new int*[VexNum]; //申请邻接矩阵存储空间
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) //对邻接矩阵初始化
{
AM_Edge[i] = new int[VexNum];
for (int j = 0; j < VexNum; j++)
AM_Edge[i][j] = 0;
}
//输入所有的边,形式为 AB CD ED
cout << "please input all the edge,format as:AB CD...,end with ctrl+'z'!"<> s) {//输入所有的边后回车,再输入ctrl+z用于中止输入
int i = AM_locate(s[0]);
int j= AM_locate(s[1]);
if (i != -1 && j != -1)
{
AM_Edge[i][j] = 1;
ArcNum++; //统计边数
}
}
}
int AM_locate(char vex) { //寻找顶点在顶点数组中的下标
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AM_Node[i] == vex)
return i;
cout << vex << " is not exit in this graph!" << endl;
return -1;
}
void AM_GraphPrint() { //以邻接矩阵的形式输出该图
cout << "adjacency matrix of this graph:" << endl;
cout << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
cout << AM_Node[i]<<" ";
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
cout << AM_Node[i] << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < VexNum; j++)
cout << AM_Edge[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
//输出所有点的入度出度;
cout << "vertex in-degree out-degree" << endl;
int d1, d2;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
AM_degree(AM_Node[i], d1, d2);
cout << setw(6) << AM_Node[i] << setw(10) << d1 << setw(11) << d2 << endl;
}
}
//求某个顶点的入度和出度
void AM_degree(char vex,int &d1,int &d2) {
d1 = d2 = 0;
int loc = AM_locate(vex);
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AM_Edge[i][loc] != 0) //入度,即顶点所在列非零项个数
d1++;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AM_Edge[loc][i] != 0) //出度,即顶点所在行非零项个数
d2++;
}
//广度优先搜索,输入为起始顶点在数组中的位置(针对一个连通分量)
//使用队列实现,类似于二叉树的层次遍历
void AM_BFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AL_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The BFS of this graph(stored by adjacency matrix):" << endl;
InitialVisited(); //初始化标记数组
queue bfs;
bfs.push(startLoc);
visited[startLoc] = true; //将起始结点加入队列并标记为已访问
while (!bfs.empty()) { //每次取出队列最前的顶点,并将其相连且未标记过的顶点加入队列尾部
int j = bfs.front();
cout << AM_Node[j]<<" ";
// visited[j] = true;
bfs.pop();
//寻找该结点为起始结点,为结点未访问过的边;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
if (AM_Edge[j][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true) //存在指向顶点i的边且该点未被访问则加入队列
{
bfs.push(i);
visited[i] = true; //应该在进入队列的时候标记为已经访问,而不能是输出时,否则可能会多次入队
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//深度优先遍历(DFS),输入为起始点在数组中的下标(针对一个连通分量)
void AM_DFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AM_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The DFS of this graph(stored by adjacency matrix):" << endl;
cout << "use recursion: ";
InitialVisited(); //切记要先初始化标记数组
AM_RecursiveDFS(startLoc); //使用递归;
cout << endl;
cout << "use stack: ";
InitialVisited();
AM_StackDFS(startLoc); //使用栈
cout << endl;
}
//使用递归实现DFS(针对一个连通分量)
void AM_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc) {
cout << AM_Node[startLoc]<<" ";
visited[startLoc] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
//如果发现存在相连且未标记的顶点,则递归为对该顶点的访问
if (AM_Edge[startLoc][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true)
AM_RecursiveDFS(i);
}
}
//使用栈实现DFS(针对一个连通分量)
void AM_StackDFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AM_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
InitialVisited();
stack dfsStack;
dfsStack.push(startLoc);//将起始点压栈并输出,标记该点已访问
cout << AM_Node[startLoc] << " ";
visited[startLoc] = true;
int* visitedPos; //visitedPos用来记录栈中每个顶点在矩阵对应行中已经访问到的位置,
// 避免回溯时while中的for循环每次都从0开始从而提高效率
visitedPos = new int[VexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
visitedPos[i] = 0; //初始化为0
}
while (!dfsStack.empty()) { //每次取栈顶元素,寻找与其相连且未标记过的顶点
int j = dfsStack.top();
for (int i = visitedPos[j]; i < VexNum; i++) //每次从visitedPos[j]开始,提高效率
{
if (AM_Edge[j][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true) //寻找到未访问过的结点则加入栈中并输出
{
dfsStack.push(i);
cout << AM_Node[i] << " ";
visitedPos[j] = i; //更新该顶点在矩阵对应行中已查询到的位置
visited[i] = true; //将顶点i标记为已访问
break; //找到符合要求的点则退出for循环(进入while下一轮,进行更深的搜索)
}
if (i == VexNum-1) //能执行到此说明与该点相关的点全部被访问,将该结点其退栈
dfsStack.pop();
}
}
//注意销毁其空间
delete visitedPos;
visitedPos = NULL;
}
//借助栈,使用DFS实现寻找i到j的简单路径(此为逆序输出)
void AM_FindPath(int i,int j) {
cout << "path between " << AM_Node[i] << " and " << AM_Node[j]<< " : ";
stack pathStack;
InitialVisited();
if (AM_RecursiveDFS(i, j, pathStack)) //存在路径,则输出栈中保存路径的所有顶点
while (!pathStack.empty()) {
cout << AM_Node[pathStack.top()] << " ";
pathStack.pop();
}
else {
cout << "not existed!";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool AM_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc,int endLoc,stack &p) {
p.push(startLoc);
visited[startLoc] = true;
if (startLoc == endLoc) //栈顶顶点为要寻找的目标顶点则中止,直接返回
return true;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
//如果发现存在相连且未标记的顶点,则递归为对该顶点的访问
if (AM_Edge[startLoc][i] != 0 && visited[i] != true)
return AM_RecursiveDFS(i, endLoc, p); //返回与startLoc相连的顶点i
//是否存在到endLoc路径的搜索结果
}
p.pop();//执行到此说明startLoc无法到达endLoc,将其退栈
return false;
}
///使用邻接表法储存图--相关成员函数
//初始化并创建该图
void AL_GraphInitial() {
cout << "please input all the vextex: " << endl;
string s;
cin >> s;
VexNum = s.length(); //确定顶点数
AL_Node = new VertexNode[VexNum]; //创建顶点数组
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) //给顶点赋值
AL_Node[i].data = s[i];
cout << "please input all the edge,format as:AB CD...,end with ctrl+'z'!" << endl;
while (cin >> s) {
int i = AL_Locate(s[0]);
if (i == -1)
continue;
if (AL_Node[i].first == NULL)
AL_Node[i].first = new EdgeNode(s[1]);
else { //找到最后一个边结点
EdgeNode *tmp = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmp->next) {
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp->next = new EdgeNode(s[1]);
}
ArcNum++; //统计边数
}
}
int AL_Locate(char vex) { //寻找vex位于顶点集的位置
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
if (AL_Node[i].data == vex)
return i;
cout << vex << " is not exit in this graph!" << endl;
return -1;
}
void AL_GraphPrint() { //以邻接表形式输出该图
cout << "adjacency list of this graph:" << endl;
EdgeNode *tmp = NULL;
for (int i= 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
cout << AL_Node[i].data;
tmp = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmp) {
cout << " -> " << tmp->adjVex;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
//输出所有顶点的入度和出度
cout << "vertex in-degree out-degree" << endl;
int d1, d2;
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) {
AL_degree(AL_Node[i].data, d1, d2);
cout << setw(6) << AL_Node[i].data << setw(10) << d1 << setw(11) << d2 << endl;
}
}
//求某个顶点的入度和出度
void AL_degree(char vex,int &s1,int &s2) {
s1 = s2 = 0;
EdgeNode* tmp = NULL;
int loc = AL_Locate(vex);
//入度 ,即寻找vex出现在边结点中的次数
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
{
if (i == loc) //vex对应顶点的边结点无需查找
continue;
tmp = AL_Node[i].first;
while (tmp) {
if (tmp->adjVex == vex)
{
s1++;
break; //只存在一次,找到即可退出,进入for的下一轮循环
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
//出度
tmp = AL_Node[loc].first; //即vex对应顶点的边结点个数
while (tmp) {
s2++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
//使用队列实现广度优先遍历(针对一个连通分量)
void AL_BFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AL_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The BFS of this graph(stored by adjacency list):" << endl;
InitialVisited(); //初始化访问标记数组
queue bfs;
bfs.push(startLoc); //标记初始结点已访问并入队
visited[startLoc] = true;
EdgeNode *tmp=NULL;
while (!bfs.empty()) {
int j = bfs.front();
bfs.pop(); //队列最前元素出队并输出
cout << AL_Node[j].data<<" ";
tmp = AL_Node[j].first;
while (tmp) { //寻找与队列最前顶点相连,且未被标记的所有边结点,将其入队并标记
int i = AL_Locate(tmp->adjVex); //边结点在顶点数组中的位置
if (visited[i] != true) { //第i个结点未被标记,将其入队并标记
bfs.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//使用递归实现深度优先遍历(DFS)(针对一个连通分量)
void AL_DFS(int startLoc) {
if (startLoc > VexNum - 1)
{
cout << "AL_BFS start location is error!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "The DFS of this graph(stored by adjacency list):" << endl;
InitialVisited();
cout << "use Recursion: ";
AL_RecursiveDFS(startLoc); //递归DFS
cout << endl;
InitialVisited();
cout<<"use Stack: ";
AL_StackDFS(startLoc); //栈DFS
cout << endl;
}
void AL_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc) {
cout << AL_Node[startLoc].data<<" ";
visited[startLoc] = true; //输出当前点并标记
EdgeNode* tmp;
tmp = AL_Node[startLoc].first;
while (tmp) {
int i = AL_Locate(tmp->adjVex); //找到第一个邻接点在顶点数组中的位置
if (visited[i] != true)
AL_RecursiveDFS(i);//邻接点i未被标记,开始递归访问该结点
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
//使用栈实现深度优先遍历(DFS)(针对一个连通分量)
void AL_StackDFS(int startLoc) {
stack dfsStack;
dfsStack.push(startLoc); //将起始顶点压栈,并输出其值
visited[startLoc] = true; //标记该节点
cout << AL_Node[startLoc].data << " ";
EdgeNode** visitedPos; //用来记录每个顶点下一个将查询的边结点的位置,
//避免while内层循环while(1)中每个顶点每次都从头开始查询未标记的边结点,从而提高效率
visitedPos = new EdgeNode*[VexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++) { //每个顶点对应的访问位置都初始化第一个边结点;
visitedPos[i] = AL_Node[i].first;
}
while (!dfsStack.empty()) {
int j = dfsStack.top();
while (1) { //不断查询第j个顶点下一个将查询的边结点
if (visitedPos[j] != NULL) { //若存在未查询过的边结点
int i = AL_Locate(visitedPos[j]->adjVex); //获取该边结点对应的顶点在顶点数组中的序号
if (visited[i] != true) { //如果该边结点未被标记,则将其压栈输出然后退出内层循环
dfsStack.push(i);
cout << AL_Node[i].data << " ";
visited[i] = true;
visitedPos[j] = visitedPos[j]->next; //更新结点j的下一个将查询的边结点指针
break; //退出内层while循环,进入外层while下一轮循环从而进行更深的访问
}
else //仍存在未查询过的边结点,visitedPos[j]指向下一边结点
{
visitedPos[j] = visitedPos[j]->next;
}
} //如果该顶点的可查询的边结点为空,则将该顶点退出
else {
dfsStack.pop();
break;
}
}
}
delete[] visitedPos; //把指针数组销毁即可,不要把每个数组元素指向的空间销毁
visitedPos = NULL;
}
//借助栈,使用深度遍历(DFS),寻找i到j的简单路径(此为逆序输出)
void AL_FindPath(int i, int j) {
cout << "path between " << AL_Node[i].data << " and " << AL_Node[j].data << " : ";
stack pathStack;
InitialVisited();
if (AL_RecursiveDFS(i, j, pathStack)) //存在路径,则输出栈中保存路径的所有顶点
while (!pathStack.empty()) {
cout << AL_Node[pathStack.top()].data<<" ";
pathStack.pop();
}
else {
cout << "not existed!";
}
cout<< endl;
}
bool AL_RecursiveDFS(int startLoc,int endLoc, stack &p) {
p.push(startLoc);
visited[startLoc] = true; //输出当前点并标记
if (startLoc == endLoc) //栈顶顶点等于要寻找的顶点j时,说明存在路径i-j,沿途顶点都存在栈中,此时直接返回
return true;
EdgeNode* tmp;
tmp = AL_Node[startLoc].first;
while (tmp) {
int i = AL_Locate(tmp->adjVex); //找到第一个邻接点在顶点数组中的位置
if (visited[i] != true) {
if (true == AL_RecursiveDFS(i, endLoc, p))//如果顶点i存在到endLoc的路径,则返回true
return true;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
p.pop(); //执行到此说明startLoc无法到达endLoc,将其退栈
return false;
}
//初始化标记数组,全部设为未被访问(false)
void InitialVisited() {
if (visited == NULL)
visited = new bool[VexNum];
for (int i = 0; i < VexNum; i++)
visited[i] = false;
}
};
复制代码 4 测试代码(main.cpp)
///图的表示和存储
// ABCDEFGH AB AC BF CD FD CE FH DG
Graph graph;
///邻接矩阵存储 测试代码
graph.AM_GraphInitial();
graph.AM_GraphPrint();
graph.AM_BFS(0);
graph.AM_DFS(0);
graph.AM_FindPath(2, 7);
graph.AM_FindPath(0, 6);
///邻接表存储 测试代码
//graph.AL_GraphInitial();
//graph.AL_GraphPrint();
//graph.AL_BFS(0);
//graph.AL_DFS(0);
//graph.AL_FindPath(2, 7);
//graph.AL_FindPath(0, 6);
复制代码测试图:
输入:(依次输入点集和边集)
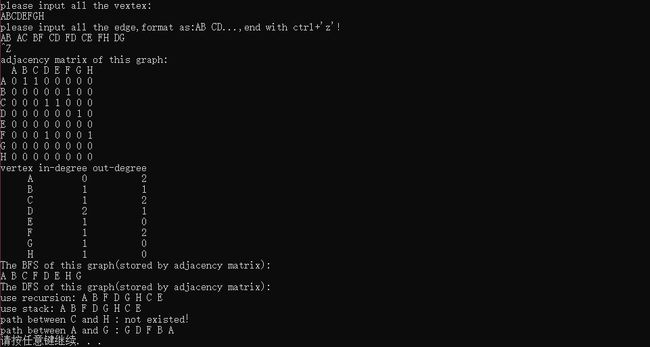
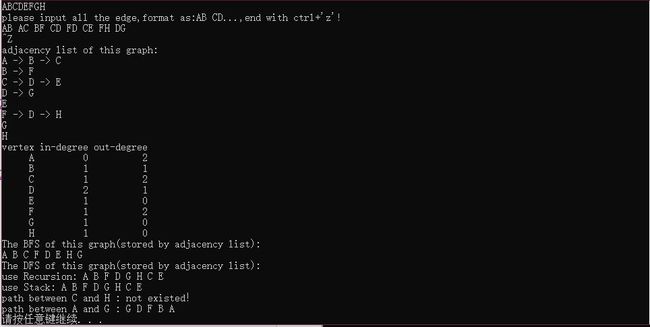
ABCDEFGH (enter)
AB AC BF CD FD CE FH DG (enter,再ctrl+z)
输出:
1.邻接矩阵实现
2.邻接表实现
5 参考资料
1.图的存储结构的实现(C/C++实现):www.cnblogs.com/ECJTUACM-87…
2.图的存储结构(邻接矩阵与邻接表)及其C++实现:www.cnblogs.com/smile233/p/…
3.图的表示方法 c++ 实现:blog.csdn.net/nichengwuxi…