【数据结构】二叉树
1.二叉树的遍历
前序,中序,后序遍历
学习二叉树结构,最简单的方式就是遍历。所谓二叉树遍历(Traversal)是按照某种特定的规则,依次对二叉树中的节点进行相应的操作,并且每个节点只操作一次。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题。 遍历是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,也是二叉树上进行其它运算的基础。
- 前序遍历——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
- 中序遍历——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。
- 后序遍历——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
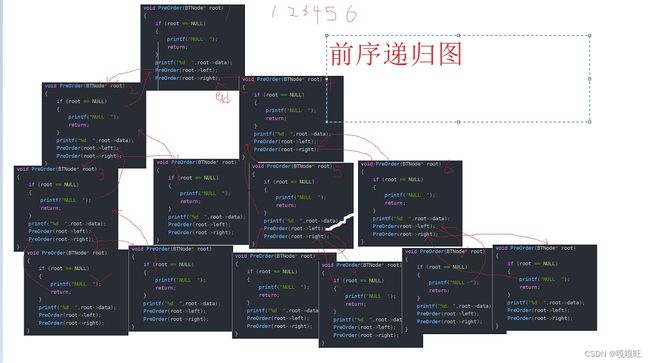
1.前序遍历:根,左子树,右子树
2.中序遍历:左子树,根,右子树
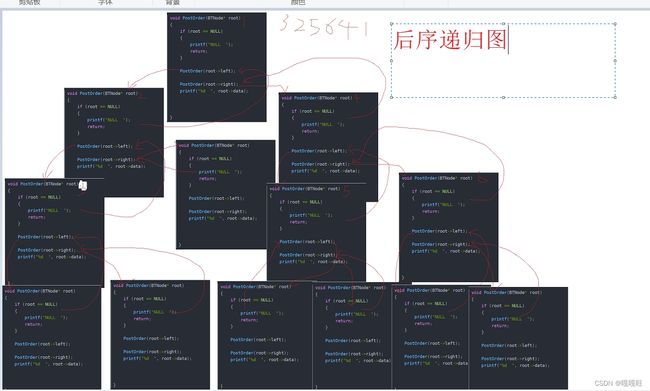
3.后序遍历:左子树,右子树,根.
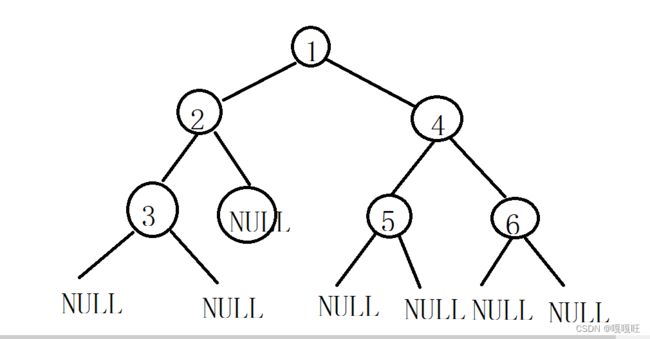
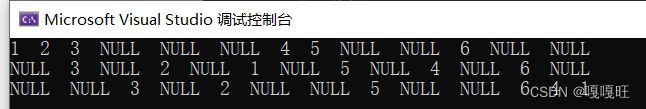
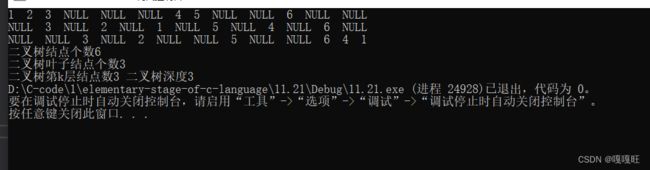
前序遍历访问数据为1,2, 3,NULL(3的左子树),NULL(3的右子树),NULL(2的右子树),4,5,NULL(5的左数),NULL(5的右树),6,NULL(6的左树),NULL(6的右树).
中序遍历访问数据为NULL(3的左子树),3,NULL(3的右子树),2,NULL(2的右子树),1,NULL(5的左子树),5,NULL(5的右子树),4,NULL(6的左子树),6,NULL(6的右子树).
后序遍历访问数据为NULL(3的左子树),NULL(3的右子树),3,NULL(2的右子树),2,NULL(5的左子树),NULL(5的右子树),5,NULL(6的左子树),NULL(6的右子树),6,4,1 .
前序遍历的实现
// 二叉树前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ",root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
前序递归打印数据
二叉树中序遍历
// 二叉树中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PreOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
二叉树后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
代码实现
include<stdio.h>
#include 二叉树结点的个数
int size = 0;//要统计每次递归的次数也就是二叉树结点的个数,定义 全局变量
// 二叉树节点个数
void BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
++size;
BinaryTreeSize(root->left);
BinaryTreeSize(root->right);
}
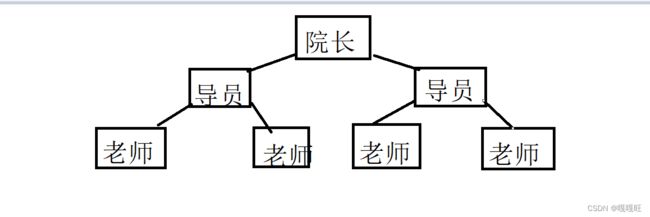
统计学校的人数,院长问导员,导员问老师,老师问班长,班长统计各班的人数。如果遇到空,返回0,其他情况都返回左子树的人数加右子树的人数加上自己,比如老师说要向导员报告人数,老师必须向导员汇报老师左子树的学生,以及右子树的学生加上自己。
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
代码简化
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == 0 ? NULL : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
二叉树叶结点的个数
叶结点的判断,如果该结点的左节点和右节点都为空的话,这个结点就是叶子结点,并且将该值返回
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
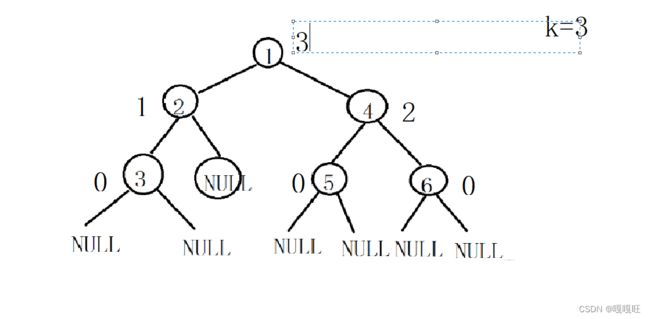
二叉树第k层结点个数
二叉树第k层结点个数
子问题:转换成左子树的第k-1层和右子树的第k-1层
结束条件:k==1且结点不为空
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left,k-1)+ BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right,k -1);
}
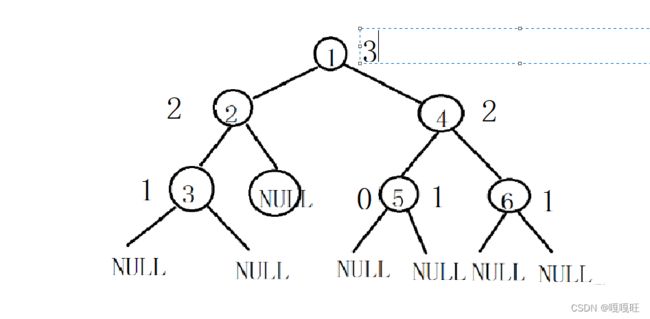
二叉树的深度
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return BTreeHeight(root->left) > BTreeHeight(root->right) ? BTreeHeight(root->left) + 1 : BTreeHeight(root->right) + 1;
}
方法2:
int BTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int left = BTreeHeight(root->left);
int right = BTreeHeight(root->right);
return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}
比较方法1和方法2,方法一效率要慢一些,因为方法一比较完左右子树返回的值后(这里算递归了一次)还必须再次递归左子树或者右子树,递归左右子树中大的那一个,时间上会翻倍。
整体代码实现
#include