算法设计与分析复习--分支界限法
文章目录
- 上一篇
- 分支界限法性质
- 装载问题
- 0-1背包问题
- 单源最短路问题
- 最大团问题
- 下一篇
上一篇
算法设计与分析复习–回溯法(二)
分支界限法性质
分支界限法是按广度优先策略或最小耗费优先遍历问题的解空间树。
搜索解空间:
- 子集树
- 排列树
搜索方式:广度优先遍历(队列)或最小耗费优先(堆)
方法:确定解空间,设计合适的限界函数(在拓展时删除不必要的孩子结点),组织活结点表
但是由于每一层对应的cw, rw是不同的,所以需要用一个node的数据结构存储每一个节点的
装载问题
问题描述:n个集装箱要装到2艘重量分别 c 1 c_1 c1, c 2 c_2 c2的货轮,其中集装箱 i i i的重量为 w i w_i wi器满足集装箱重量之和小于两轮船载重。
最优装载方案:将第一艘船尽可能装满,将剩余的货箱装到第二搜轮船上。
约束函数:所装货物重量小于第一艘船载重
上界函数是:已装重量+剩余重量上界
使用队列的方式
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int a[N], n, c1, sum = 0, bw = 0;
struct node
{
int idx; // 层数
int cw; // 当前层的重量
int rw; // 剩余的重量
};
void bfs()
{
queue q;
q.push({0, 0, sum});
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
bw = max(bw, t.cw); // 更新最大重量
// 左扩展
if (t.idx < n && t.cw + a[t.idx] <= c1)
{
q.push({t.idx + 1, t.cw + a[t.idx], t.rw - a[t.idx]});
}
// 右扩展
if (t.idx < n && t.cw + t.rw > bw)
{
q.push({t.idx + 1, t.cw, t.rw - a[t.idx]});
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &c1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sum += a[i];
}
bfs();
printf("%d\n", bw);
return 0;
}
利用优先级进行查找时
我们将利用当前结点的价值上界
c w + r w cw + rw cw+rw
进行堆的构造
重构堆需要
priority_queue, cmp> heap;
cmp为比较函数,不过要比较符相反

例如greater是返回更大的
而构造小根堆就用greater
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int a[N], n, c1, sum = 0, bw = 0;
struct node
{
int idx; // 层数
int cw; // 当前层的重量
int rw; // 剩余的重量
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator ()(const node &x, const node &y) const
{
return (x.cw + x.cw) < (y.cw + y.rw); // 优先队列的优先级按当前上界要用更大排,这里就要是小于
}
};
void bfs()
{
priority_queue, cmp > heap;
heap.push({0, 0, sum});
while (!heap.empty())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
bw = max(bw, t.cw); // 更新最大重量
// 左扩展
if (t.idx < n && t.cw + a[t.idx] <= c1)
{
heap.push({t.idx + 1, t.cw + a[t.idx], t.rw - a[t.idx]});
}
// 右扩展
if (t.idx < n && t.cw + t.rw > bw)
{
heap.push({t.idx + 1, t.cw, t.rw - a[t.idx]});
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &c1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
sum += a[i];
}
bfs();
printf("%d\n", bw);
return 0;
}
由于优先队列的方式更难一些所以后面实现都是优先队列的方式
0-1背包问题
求法与装载问题一样,不如说装载问题特化成了0-1背包问题
但是在右剪枝的求法上和回溯法一样
但是bound函数用法不同了,bound就是求上界的函数,并且求得是当前结点的上界
左剪枝:不超过背包容量
右剪枝:cv + rv >= bv
rv是利用贪心背包的方式求得的
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef pair PDD;
const int N = 110;
int n, c;
vector ob;
double bv = 0, sv = 0; // 将bv, sv初始化为0
struct node
{
int idx;
double cw;
double cv;
double ub;
bool operator< (const node &x) const
{
return ub < x.ub;//利用ub堆排序
}
};
bool cmp(PDD x, PDD y)
{
return (x.second / x.first) > (y.second / y.first);//贪心排序
}
double bound(node x)
{
double rcv = x.cv, rw = c - x.cw;
int i = x.idx;//不同于回溯法,在输入时改变i的值,因为要计算当前结点的上界
while (i < n && ob[i].first <= rw)
{
rw -= ob[i].first;
rcv += ob[i].second;
i++;
}
if (i < n)
rcv += rw * (ob[i].second / ob[i].first);
return rcv;
}
void bfs()
{
priority_queue heap;
heap.push({0, 0, 0, bound({0, 0, 0, 0})}); // 初始节点的上界需要计算
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
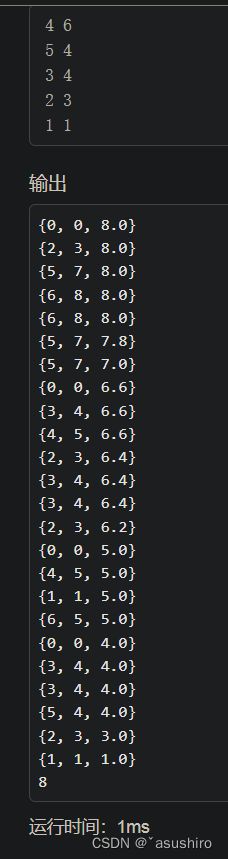
printf("{%d, %d, %.1lf}\n", (int)t.cw, (int)t.cv, t.ub);//搜索顺序可视化
if (t.idx == n)//到达叶子结点
{
if (t.cv > bv)
{
bv = t.cv;
}
continue;
}
if (t.cw + ob[t.idx].first <= c) // 向左走
heap.push({t.idx + 1, t.cw + ob[t.idx].first, t.cv + ob[t.idx].second, t.ub});
node tmp = {t.idx + 1, t.cw, t.cv, bound({t.idx + 1, t.cw, t.cv, 0})};//需要填两次,定义临时变量
if (bound(tmp) > bv)
heap.push(tmp); // 向右走
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &c);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double w, v;
scanf("%lf%lf", &w, &v);
sv += v;
ob.push_back({w, v});
}
sort(ob.begin(), ob.end(), cmp);
bfs();
printf("%d\n", (int)bv);
return 0;
}
单源最短路问题
问题描述:给定一个带权有向图G = (V, E), 每条边的权值是一个正整数, 给定V中的一个顶点S,称作源点。要求:计算从源点到其他所有顶点的最短路径长度。
AcWing 850. Dijkstra求最短路 II
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef pair PII;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int h[N], e[N], w[N], ne[N], idx = 0;
int dist[N], pre[N];
vector ans;
bool st[N];
int n, m;
void add (int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
void traceback(int k)
{
if (k == 0) return;
ans.push_back(k);
traceback(pre[k]);
}
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue, greater> heap;
heap.push({0, 1});// first表示距离, second表示节点编号,这是因为在优先队列中是优先按元祖第一个元素进行排序
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second, distance = t.first;// ver表示节点编号
if (st[ver])continue;
st[ver] = true;
for (int i = h[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > distance + w[i])// 因为要遍历Ver相连的所有边i所以提前将源点到ver的最短距离记作distance, 而w[i]记录的是第i个节点到j的距离(权重)i是与ver相连的边
// 将与ver相连的边更新为最短路径值,j是i的下一条边是一个指针关系
{
dist[j] = distance + w[i];
pre[j] = ver;
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
else {
traceback(n);
reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
puts("最短路径为:");
for (auto i : ans)
printf("%d ", i);
puts("");
return dist[n];
}
}
int main ()
{
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add (a, b, c);
}
printf("路径长度为:%d", dijkstra());
return 0;
}
最大团问题
问题描述:给定无向图G = (V, E)。如果 U ⊆ V U\subseteq V U⊆V, 求对任意 u , v ∈ U u, v \in U u,v∈U有 ( u , v ) ∈ E (u, v) \in E (u,v)∈E, 则称U是G的完全子图。
最大团就是一个图含顶点数最大的完全图,且要是这个图的子集。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int g[N][N], n, m, bn;
vector ans;
struct node
{
int idx;
int cn;
vector x;
int un;
bool operator< (const node &p) const{
return un < p.un;
}
};
bool constrain(node c)
{
for (int i = 0; i < c.idx - 1; i ++)//这里i不能到c.idx不然就会有它自身到自身为0会返回false,
{
if (c.x[i] == 1 && g[c.idx][i + 1] == 0)//x的下标是从0开始,而g[i][j]的下标是从1开始,所以要进行调整
return false;
}
return true;
}
void bfs()
{
priority_queue heap;
heap.push({0, 0, {}, n});
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
if (t.idx == n){
if (t.cn > bn){
ans = t.x;
bn = t.cn;
}
continue;
}
node tmp = {t.idx + 1, t.cn + 1, t.x, t.un};
tmp.x.push_back(1);//要提前加入,否则判断是少条件
if (constrain(tmp))
heap.push(tmp);
tmp = {t.idx + 1, t.cn, t.x, t.un - 1};
tmp.x.push_back(0);
if (tmp.un >= bn)
heap.push(tmp);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = 1;
}
bfs();
printf("%d\n", bn);
for (auto val : ans) {
printf("%d ", val);
}
return 0;
}
下一篇
未完待续