【Docker 完整版教程笔记】
文章目录
- 前言
- Docker 概述
-
- Docker 架构图
- Docker安装
-
- 在线安装
- 离线安装
- Docker 常用命令
-
- 帮助命令(--help)
- 镜像命令(images)
-
- docker images 查看镜像列表
- docker search 搜索镜像
- docker rmi 删除镜像
- 容器命令(container)
-
- docker run 新建/启动容器
- docker ps 查看容器
- exit 退出容器
- docker start/stop/restart 启停容器
- docker rm 删除容器
- docker commit 生成新镜像
- docker export 导出容器为归档文件
- docker import 从归档文件生成镜像
- docker save 保存镜像为归档文件
- docker load 从归档文件加载镜像
- 常用其他命令
-
- docker run -d 后台启动容器
- docker logs 查看日志
- docker top 查看容器内进程信息
- docker inspect 查看镜像的元数据
- docker exec/attach 进入运行中容器
- docker cp 拷贝容器内的文件到主机上
- docker events 从服务器获取实时事件
- Docker命令总结
- Docker镜像分层原理
-
- 文件联合系统(UnionFS)
- Docker使用UnionFS
-
- 资源共享
- 写时拷贝(Copy-on-Write)
- 优点
- Docker 镜像原理
- Docker 数据卷
-
- 挂载数据卷
- 具名挂载和匿名挂载
-
- 具名挂载
- 匿名挂载
- 容器间的数据共享
- 初识Dockerfile
- DockerFile
-
- 简述
- DockerFile指令
-
- CMD 和 ENTRYPOINT的区别
- Dockerfile 流程小结图
- Docker 网络
-
- Docker0
- --link
- 自定义网络
- 容器跨网络联通
- Docker Compose
-
- OVERVIEW(概述)
- compose 安装
- compose 实例
-
- Step 1: Setup
- Step 2: Create a Dockerfile
- Step 3: Define services in a Compose file
- Step 4: Build and run your app with Compose
- Step 5: Edit the Compose file to add a bind mount
- Step 6: Re-build and run the app with Compose
- Step 7: Update the application
- Step 8: Experiment with some other commands
- yaml 文件
- 引用
前言
Docker官网网址:https://docs.docker.com/
(强烈建议初学者参考官方文档进行学习使用,里面有Docker的所有学习文档!)
此教程笔记参考 Docker官方文档 及 网络资源 结合记录学习
Docker 概述
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
- Docker是一个用于开发、发布和运行应用程序的开源平台
- Docker能将应用程序和基础架构分离,以便于快速交付软件
- 使用Docker,可以像管理应用程序一样管理你的基础设施(架构)
- 通过Docker快速交付、测试和部署代码的方法,可以显著减少编写代码和在生产环境中运行它的延迟
- 上面的概述来源于官方文档,此处仅作了解入门,详情请参考官方文档,建议阅读英文文档。
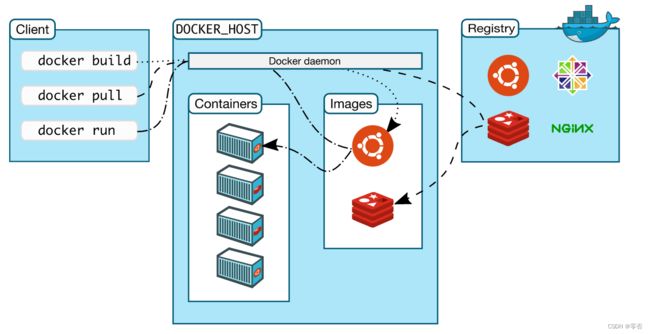
Docker 架构图
Docker客户端 管理引擎 仓库
- 镜像(image)
docker镜像好比是一个模板,可以通过这个模板来创建(一个或多个)容器服务,最终服务或项目的运行是在容器中的。
- 容器(container)
Docker利用容器技术,独立运行(一个或一组)应用,通过镜像来创建的。
基本命令:启动,停止,删除
可以理解为一个简易的linux系统
- 仓库(repository)
仓库就是存放镜像的地方,分为共有仓库和私有仓库
Docker Hub/阿里云镜像仓库(配置镜像加速)等
Docker安装
准备:
- 了解linux基础命令
- centos服务器 (vps或本地虚拟机VMware)
- 若使用vps,需要安装远程连接软件,如MobaXterm
官方文档——在CentOS上安装Docker引擎
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/centos/
在线安装
- (官方安装教程) 不推荐!
官方docker仓库下载安装极慢,不推荐此方法
(若设置为国内镜像源,如阿里云仓库,也可在线安装,安装教程详看阿里云官方教程)
# Uninstall old versions (卸载旧版本)
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
# Set up the repository (设置docker仓库)
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# 安装docker
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
# 启动docker
sudo systemctl start docker
# 验证docker
sudo docker run hello-world
# 查看可用版本(可跳过)
yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r
# 安装指定版本(可跳过)
sudo yum install docker-ce-<VERSION_STRING> docker-ce-cli-<VERSION_STRING> containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
- (国内仓库安装) 推荐!
注:docker官方仓库,下载速度极慢,可替换为国内仓库
https://get.daocloud.io/docker
curl -sSL https://get.daocloud.io/docker | sh
# 卸载docker
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-common \
container-selinux \
docker-selinux \
docker-engine \
# 删除相关文件夹
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
离线安装
推荐!
# 下载安装包,yum install docker安装包即可
sudo yum install /path/to/package.rpm
# 启动docker
sudo systemctl start docker
# 查看版本
docker --version
Docker 常用命令
Docker参考文档:https://docs.docker.com/reference/
例:
Docker CLI (docker run)参考文档:https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/run/
帮助命令(–help)
# docker 帮助命令
docker 命令 --help
# 显示docker版本信息
docker version
# 显示docker详细信息
docker info
镜像命令(images)
docker images 查看镜像列表
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
nextcloud-example_proxy latest 792f6d7fadda 4 weeks ago 42.1MB
REPOSITORY # 镜像的仓库源
TAG # 镜像的标签
IMAGE ID # 镜像的ID
CREATED # 镜像的创建时间
SIZE # 镜像的大小
# 可选项
-a --all # 列出所有镜像
-q --quiet # 只显示镜像的ID
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker images -aq
792f6d7fadda
61a190336ff6
cc44224bfe20
130b9666de2e
docker search 搜索镜像
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker search nginx
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
nginx Official build of Nginx. 16904 [OK]
linuxserver/nginx An Nginx container, brought to you by LinuxS… 168
bitnami/nginx Bitnami nginx Docker Image 131 [OK]
ubuntu/nginx Nginx, a high-performance reverse proxy & we… 50
bitnami/nginx-ingress-controller Bitnami Docker Image for NGINX Ingress Contr… 18 [OK]
rancher/nginx-ingress-controller 10
clearlinux/nginx Nginx reverse proxy server with the benefits… 4
# 可选项,通过搜索来过滤
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
# 筛选stars大于100的
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker search nginx -f=STARS=100
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
nginx Official build of Nginx. 16904 [OK]
linuxserver/nginx An Nginx container, brought to you by LinuxS… 168
bitnami/nginx Bitnami nginx Docker Image 131 [OK]
- docker pull 下载镜像
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker pull --help
Usage: docker pull [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG|@DIGEST]
Pull an image or a repository from a registry
Options:
-a, --all-tags Download all tagged images in the repository
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
-q, --quiet Suppress verbose output
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker pull python
Using default tag: latest # 镜像版本,如果不写tag,默认为latest
latest: Pulling from library/python
e756f3fdd6a3: Pull complete # 分层下载,docker images的核心,联合文件系统
bf168a674899: Pull complete
e604223835cc: Pull complete
6d5c91c4cd86: Pull complete
2cc8d8854262: Pull complete
2767dbfeeb87: Pull complete
e5f27d860d89: Pull complete
98a3e4f5f5ed: Pull complete
5f15c8bc4073: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:cddebe04ec7846e28870cf8624b46313a22e6407b51ced3776588784caa12d27
Status: Downloaded newer image for python:latest
docker.io/library/python:latest # 真实地址
# 查看刚才下载的镜像
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
python latest e4ccc57bca82 2 days ago 920MB
docker rmi 删除镜像
docker rmi -f 容器名/id # 删除单个容器
docker rmi -f 容器id 容器id # 删除多个容器
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) # 删除全部容器
容器命令(container)
docker run 新建/启动容器
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run --help
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Run a command in a new container
--name 容器名字,用来区分容器
-d Run container in background and print container ID
-it 使用交互方式运行,进入容器查看内容
-p 指定容器端口 -p 8080:8080
-p ip:主机端口:容器端口
-p 主机端口:容器端口(常用)
-p 容器端口
-P 随机指定端口
# 启动并进入容器
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -it python /bin/bash
root@6e47c6e12ff8:/# ls
bin boot dev etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
root@6e47c6e12ff8:/# exit
exit
docker run -dit python /bin/bash #启动后台交互式容器
docker ps 查看容器
docker ps # 列出当前正在运行的容器
-a # 列出当前+历史运行过的容器
-n=? #显示最近的容器(个数)
-q # 只显示容器编号
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
96016d8178a9 python "python3" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes xenodochial_driscoll
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
96016d8178a9 python "python3" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes xenodochial_driscoll
b0888c48befa python "/bin/bash" 4 minutes ago Exited (0) 3 minutes ago admiring_brown
exit 退出容器
#退出
exit
ctrl + P + Q # 退出不停止
docker start/stop/restart 启停容器
docker start 容器id # 启动容器
docker restart 容器id # 重启容器
docker stop 容器id # 停止当前正在运行的容器
docker kill 容器id # 强制停止当前容器
docker rm 删除容器
docker rm 容器ID # 删除停止的容器,不能删除运行的容器,-f 可强制删除
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) # 删除所有容器
docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm # 删除所有容器
docker commit 生成新镜像
(from容器)
docker commit 提交容器成为一个新的副本
docker commit -m="提交的描述信息" -a="作者" 容器id 目标镜像名:[tag]
# docker commit 帮助命令
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker commit --help
Usage: docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Create a new image from a container's changes
Options:
-a, --author string Author (e.g., "John Hannibal Smith " )
-c, --change list Apply Dockerfile instruction to the created image
-m, --message string Commit message
-p, --pause Pause container during commit (default true)
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker commit -a="zzh" -m="volume1 2" 6cd225ef78d9 python_volume:2.0
sha256:d7efce3de1532b9934dd78512797833f766eb7c674302a3abf8c72825e3e77aa
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
python_volume 2.0 d7efce3de153 7 seconds ago 920MB
docker export 导出容器为归档文件
(tar)
# docker export -o 归档文件名 容器id
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker export --help
Usage: docker export [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
Options:
-o, --output string Write to a file, instead of STDOUT
# docker export
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker export -o python_export 6cd225ef78d9
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# ls -hl
total 890M
-rw------- 1 root root 890M Jul 3 20:29 python_export
docker import 从归档文件生成镜像
# docker import 归档文件 REPOSITORY[:TAG]
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker import --help
Usage: docker import [OPTIONS] file|URL|- [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
Options:
-c, --change list Apply Dockerfile instruction to the created image
-m, --message string Set commit message for imported image
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker import python_export python_export:1.0
sha256:ba99372f6da8c387d9d41e7cb006ba564ffbc980aa598120a88b7a91f1b961a7
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
python_export 1.0 ba99372f6da8 6 seconds ago 911MB
docker save 保存镜像为归档文件
(一个或多个)
# docker save -o 镜像名1 2 3 ...
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker save --help
Usage: docker save [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
Options:
-o, --output string Write to a file, instead of STDOUT
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker save -o python_save python_export python_volume
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# ll
total 2740716
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 2 13:37 docker_file
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7 Jul 2 13:04 docker_v
-rw------- 1 root root 932292608 Jul 3 20:29 python_export
-rw------- 1 root root 1874179584 Jul 3 20:44 python_save
docker load 从归档文件加载镜像
(一个或多个)
# docker load -i 归档文件名
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker load --help
Usage: docker load [OPTIONS]
Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
Options:
-i, --input string Read from tar archive file, instead of STDIN
-q, --quiet Suppress the load output
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker load -i python_save
Loaded image: python_volume:2.0
Loaded image: python_export:1.0
Loaded image: python_volume:1.0
常用其他命令
docker run -d 后台启动容器
docker run -d 镜像名 # 后台启动
# docker ps 发现没有正在运行的容器
# docker 容器使用后台运行,如果没有前台进程,会自动停止
# 即容器启动后,发现自己没有提供服务,会立刻停止
docker run -dit 镜像名 /bin/bash # 可以启动不会自动停止的后台容器
docker logs 查看日志
docker logs -f --tail 100 容器id/name
# 持续查看最新日志
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker logs --help
Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Fetch the logs of a container
Options:
--details Show extra details provided to logs
-f, --follow Follow log output
--since string Show logs since timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
-n, --tail string Number of lines to show from the end of the logs (default "all")
-t, --timestamps Show timestamps
--until string Show logs before a timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
docker top 查看容器内进程信息
# docker top 容器id
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker top d2df53bc7527
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 2848722 2848702 0 00:05 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
docker inspect 查看镜像的元数据
# docker inspect 容器id
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker inspect d2df53bc7527
[
{
"Id": "d2df53bc75271b7154ad9b32cc89304501ae0d5c92e21aa00eee616f1c338fb6",
"Created": "2022-06-29T16:05:43.20344352Z",
"Path": "bash",
"Args": [],
"State": {
"Status": "running",
"Running": true,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 2848722,
"ExitCode": 0,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2022-06-29T16:05:43.582446583Z",
"FinishedAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
},
"Image": "sha256:0f95b1e38607bbf15b19ad0d111f2316e92eb047a35370eac71973c636acb9d2",
"ResolvConfPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/d2df53bc75271b7154ad9b32cc89304501ae0d5c92e21aa00eee616f1c338fb6/resolv.conf",
"HostnamePath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/d2df53bc75271b7154ad9b32cc89304501ae0d5c92e21aa00eee616f1c338fb6/hostname",
"HostsPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/d2df53bc75271b7154ad9b32cc89304501ae0d5c92e21aa00eee616f1c338fb6/hosts",
"LogPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/d2df53bc75271b7154ad9b32cc89304501ae0d5c92e21aa00eee616f1c338fb6/d2df53bc75271b7154ad9b32cc89304501ae0d5c92e21aa00eee616f1c338fb6-json.log",
"Name": "/amazing_einstein",
"RestartCount": 0,
"Driver": "overlay2",
"Platform": "linux",
"MountLabel": "",
"ProcessLabel": "",
"AppArmorProfile": "",
"ExecIDs": null,
"HostConfig": {
"Binds": null,
"ContainerIDFile": "",
"LogConfig": {
"Type": "json-file",
"Config": {}
},
"NetworkMode": "default",
"PortBindings": {},
"RestartPolicy": {
"Name": "no",
"MaximumRetryCount": 0
},
"AutoRemove": false,
"VolumeDriver": "",
"VolumesFrom": null,
"CapAdd": null,
"CapDrop": null,
"CgroupnsMode": "host",
"Dns": [],
"DnsOptions": [],
"DnsSearch": [],
"ExtraHosts": null,
"GroupAdd": null,
"IpcMode": "private",
"Cgroup": "",
"Links": null,
"OomScoreAdj": 0,
"PidMode": "",
"Privileged": false,
"PublishAllPorts": false,
"ReadonlyRootfs": false,
"SecurityOpt": null,
"UTSMode": "",
"UsernsMode": "",
"ShmSize": 67108864,
"Runtime": "runc",
"ConsoleSize": [
0,
0
],
"Isolation": "",
"CpuShares": 0,
"Memory": 0,
"NanoCpus": 0,
"CgroupParent": "",
"BlkioWeight": 0,
"BlkioWeightDevice": [],
"BlkioDeviceReadBps": null,
"BlkioDeviceWriteBps": null,
"BlkioDeviceReadIOps": null,
"BlkioDeviceWriteIOps": null,
"CpuPeriod": 0,
"CpuQuota": 0,
"CpuRealtimePeriod": 0,
"CpuRealtimeRuntime": 0,
"CpusetCpus": "",
"CpusetMems": "",
"Devices": [],
"DeviceCgroupRules": null,
"DeviceRequests": null,
"KernelMemory": 0,
"KernelMemoryTCP": 0,
"MemoryReservation": 0,
"MemorySwap": 0,
"MemorySwappiness": null,
"OomKillDisable": false,
"PidsLimit": null,
"Ulimits": null,
"CpuCount": 0,
"CpuPercent": 0,
"IOMaximumIOps": 0,
"IOMaximumBandwidth": 0,
"MaskedPaths": [
"/proc/asound",
"/proc/acpi",
"/proc/kcore",
"/proc/keys",
"/proc/latency_stats",
"/proc/timer_list",
"/proc/timer_stats",
"/proc/sched_debug",
"/proc/scsi",
"/sys/firmware"
],
"ReadonlyPaths": [
"/proc/bus",
"/proc/fs",
"/proc/irq",
"/proc/sys",
"/proc/sysrq-trigger"
]
},
"GraphDriver": {
"Data": {
"LowerDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/d1f97469bf8dc721d3544ee0603843c45766d38fe08a5a41448a09fb2b0523c0-init/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a34dc8c6fd5f524c445da51fff81a50b3e15cf53c1db69aadca32c732b88209b/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/f4cd5061845ac5514f5aaa387dd58b63ea37c14d4383e6f01360c5ab1a6357b5/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a2eeebe65fe6050b40368dfaaf6115998e46544636faf3c820c686d7fb1bde16/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/4866d5cf1beb0816ba148e1700d92ea0c42cf1f7ba1ffd80e53113f95dcc2c8e/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/bc1115c2e1d53bfd674718bdd08ef6a2c82c73667067fed2e05c18f2131e1c3d/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/616914d1a8c57dd7386b550dbcd1ba501d11c09380afffa39fd227dcf3e4123d/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/34ed671ac7b1d2cf8e30cf0f3cf85da97c34b643e217325c8110dea59c36c730/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/b4e5edd486054fdcfbc558c6c2b64ccdd27e62776e6330828beab3674acfdcd6/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a09d8bfe4e8ff39f2b4b6589d36dc5bb97d3440aa2afc8d86e671a584f460eaa/diff",
"MergedDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/d1f97469bf8dc721d3544ee0603843c45766d38fe08a5a41448a09fb2b0523c0/merged",
"UpperDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/d1f97469bf8dc721d3544ee0603843c45766d38fe08a5a41448a09fb2b0523c0/diff",
"WorkDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/d1f97469bf8dc721d3544ee0603843c45766d38fe08a5a41448a09fb2b0523c0/work"
},
"Name": "overlay2"
},
"Mounts": [],
"Config": {
"Hostname": "d2df53bc7527",
"Domainname": "",
"User": "",
"AttachStdin": true,
"AttachStdout": true,
"AttachStderr": true,
"Tty": true,
"OpenStdin": true,
"StdinOnce": true,
"Env": [
"PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin",
"LANG=C.UTF-8",
"GPG_KEY=A035C8C19219BA821ECEA86B64E628F8D684696D",
"PYTHON_VERSION=3.10.5",
"PYTHON_PIP_VERSION=22.0.4",
"PYTHON_SETUPTOOLS_VERSION=58.1.0",
"PYTHON_GET_PIP_URL=https://github.com/pypa/get-pip/raw/6ce3639da143c5d79b44f94b04080abf2531fd6e/public/get-pip.py",
"PYTHON_GET_PIP_SHA256=ba3ab8267d91fd41c58dbce08f76db99f747f716d85ce1865813842bb035524d"
],
"Cmd": [
"bash"
],
"Image": "python",
"Volumes": null,
"WorkingDir": "",
"Entrypoint": null,
"OnBuild": null,
"Labels": {}
},
"NetworkSettings": {
"Bridge": "",
"SandboxID": "71af81ca4e9382a5c7cc63a1266c4b60aa27306fbe7c35ea57ff784977dd905f",
"HairpinMode": false,
"LinkLocalIPv6Address": "",
"LinkLocalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"Ports": {},
"SandboxKey": "/var/run/docker/netns/71af81ca4e93",
"SecondaryIPAddresses": null,
"SecondaryIPv6Addresses": null,
"EndpointID": "10cd7e0d3967516c2a6e93d2e7406a3e64d8132cf456544e3d7679193b639d4c",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.3",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:03",
"Networks": {
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "b7c80489a8d359c23120b77e174cb055562d692c0f23aa6336a3725ecbecb1c1",
"EndpointID": "10cd7e0d3967516c2a6e93d2e7406a3e64d8132cf456544e3d7679193b639d4c",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.3",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:03",
"DriverOpts": null
}
}
}
}
]
docker exec/attach 进入运行中容器
docker exec -it 容器id bashshell
# 进入容器后,打开新的终端交互窗口
docker attach 容器id
# 进入容器正在执行的终端
docker cp 拷贝容器内的文件到主机上
docker cp 容器id:文件路径 主机路径
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it fea3408bae4f /bin/bash
root@fea3408bae4f:/# cd home/
root@fea3408bae4f:/home# ls
root@fea3408bae4f:/home# touch cp_test
root@fea3408bae4f:/home#
exit
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker cp fea3408bae4f:/home/cp_test ./
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# ls
cp_test hostname script_tmp software stu_dir
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]#
# docker cp 拷贝是手动过程,-v 可进行卷挂载,自动拷贝
docker events 从服务器获取实时事件
# 此处仅作了解
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker events -f images="python" --since="2022-07-03"
2022-07-03T20:09:07.197434122+08:00 container exec_create: bash 6cd225ef78d97870620a978a0f02ef74023e4171473a1334c001f82be2d55bcd (execID=41898ca3cf2d3fafcf8205468c12fe45fc78177a8734c5f758f6163410392237, image=python_volume:1.0, name=trusting_archimedes)
2022-07-03T20:09:07.198131143+08:00 container exec_start: bash 6cd225ef78d97870620a978a0f02ef74023e4171473a1334c001f82be2d55bcd (execID=41898ca3cf2d3fafcf8205468c12fe45fc78177a8734c5f758f6163410392237, image=python_volume:1.0, name=trusting_archimedes)
2022-07-03T20:09:20.417084440+08:00 container exec_die 6cd225ef78d97870620a978a0f02ef74023e4171473a1334c001f82be2d55bcd (execID=41898ca3cf2d3fafcf8205468c12fe45fc78177a8734c5f758f6163410392237, exitCode=0, image=python_volume:1.0, name=trusting_archimedes)
2022-07-03T20:11:07.130722375+08:00 container pause 6cd225ef78d97870620a978a0f02ef74023e4171473a1334c001f82be2d55bcd (image=python_volume:1.0, name=trusting_archimedes)
Docker命令总结
# 本地镜像管理命令
docker images # 列出本地镜像。
docker rmi # 删除本地一个或多个镜像。
docker tag # 标记本地镜像,将其归入某一仓库。
docker build # 使用 Dockerfile 创建镜像。
docker history # 查看指定镜像的创建历史。
docker save # 将指定镜像保存成 tar 归档文件。
docker load # 导入使用 docker save 命令导出的镜像。
docker import # 从归档文件中创建镜像。
# 容器操作命令
docker ps # 列出本地容器.
docker inspect # 获取容器/镜像的元数据。
docker top # 查看容器中运行的进程信息,支持 ps 命令参数。
docker attach # 连接到正在运行中的容器,类比exec。
docker events # 从服务器获取实时事件。
docker logs # 获取容器的日志。
docker wait # 阻塞运行直到容器停止,然后打印出它的退出代码。
dokcer export # 将文件系统作为一个tar归档文件导出到STDOUT。
docker port # 列出指定的容器的端口映射,或者查找将PRIVATE_PORT NAT到面向公众的端口。
# 容器生命周期管理命令
docker run # 创建一个新的容器并运行一个命令
docker start/stop/restart # 启动/停止/重启 一个或多个容器
docker kill # 杀掉一个运行中的容器。
docker rm # 删除一个或多个容器。
docker pause/unpause # 暂停/恢复 容器中所有的进程。
docker create # 创建一个新的容器但不启动它。
docker exec # 在运行的容器中执行命令(新的终端窗口),类比attach。
# 容器rootfs命令
docker commit # 从容器创建一个新的镜像。
docker cp # 用于容器与主机之间的数据拷贝。
docker diff # 检查容器里文件结构的更改。
# 镜像仓库管理命令
docker login # 登陆到一个Docker镜像仓库,如果未指定镜像仓库地址,默认为官方仓库 Docker Hub
docker logout # 登出一个Docker镜像仓库,如果未指定镜像仓库地址,默认为官方仓库 Docker Hub
docker pull # 从镜像仓库中拉取或者更新指定镜像
docker push # 将本地的镜像上传到镜像仓库,要先登陆到镜像仓库
docker search # 从Docker Hub查找镜像
# docker 信息
docker info # 显示 Docker 系统信息,包括镜像和容器数。
docker version # 显示 Docker 版本信息。
Docker镜像分层原理
文件联合系统(UnionFS)
UnionFS (Union File System)
2004年由纽约州立大学开发,它可以把多个目录内容联合挂载到同一个目录下,而目录的物理位置是分开的。UnionFs可以把只读和可读写文件系统合并在一起,具有写时复制功能,允许只读文件系统的修改可以保存到可写文件系统当中。
- UnionFs: UnionFS 时一种分层、轻量级并且高性能的文件系统,它支持对文件系统的修改作为一次提交来一层层的叠加,同时可以将不同目录挂载到同一个虚拟文件系统下。
- 特性: 一次同时加载多个文件系统,但从外面看起来,只能看到一个文件系统,联合加载会把各层文件系统叠加起来,这样最终的文件系统会包含所有底层的文件和目录。
Docker使用UnionFS
资源共享
当我们浏览Docker hub时,能发现大多数镜像为什么都不是从头开始制作,而是从一些base镜像基础上创建(比如centos基础镜像)
- 想象这样一个场景,一台宿主机上运行了100个基于centos base镜像的容器,难道每个容器里都有一份重复的centos拷贝呢?
这显然不合理!借助Linux的UnionFS,宿主机只需要在磁盘上保存一份base镜像,内存中也只需要加载一份,就能被基于这个镜像的所有容器共享。
写时拷贝(Copy-on-Write)
- 当某个容器修改了基础镜像的内容,比如 /bin文件夹下的文件,这时其他容器的/bin文件夹是否会发生变化呢?
根据容器镜像的 写时拷贝(Copy-on-Write) 技术,某个容器对基础镜像的修改会被限制在单个容器内。
容器镜像由多个镜像层组成,所有镜像层会联合在一起组成一个统一的文件系统。如果不同层中有一个相同路径的文件,比如 /text,上层的 /text 会覆盖下层的 /text,也就是说用户只能访问到上层中的文件 /text,这就是COW技术。
优点
Union文件系统是Docker镜像的基础。镜像可以通过分层来进行继承,基于基础镜像。可以制作各种具体的应用镜像。
分层的优点:
- 分层最大的一个优点是共享资源;
- 多个镜像都从相同的base镜像构建而来,那么宿主机只需在磁盘上保存一份base镜像即可;
- 同时内存中也只需要加载一份base镜像,就可以为所有容器服务,而且镜像的每一层都可以被共享。
Docker 镜像原理
![]()
-
docker的镜像实际上由一层一层的文件系统组成,这种层级的文件系统也即前文所说的UnionFS。
-
bootfs(boot file system) 主要包含bootloader 和 kernel,bootloader主要引导加载kernel,linux刚启动时会加载bootfs文件系统,在Docker镜像的最底层是bootfs。这一层与我们典型的Linux/Unix系统是一样的,包含boot加载器和内核。当boot加载完成之后整个内核就都在内存中了,此时内存的使用权已由bootfs转交给内核,此使系统也会卸载bootfs。
-
rootfs(root file system) ,在bootfs之上。包含的就是典型Linux系统中的/dev、/proc、/bin、/etc等标准目录和文件。rootfs就是各种不同的操作系统发行版,比如Ubuntu,CentOS等等
-
中间只读的 rootfs 的集合就可以称为 Docker 镜像,Docker 镜像构建时,会一层层构建,前一层是后一层的基础。每一层构建完就不会再发生改变,后一层上的任何改变只发生在自己这一层。

![]()
当用docker run启动容器时,实际上在镜像的顶部添加了一个新的可写层,这个可写层也叫容器层。
![]()
- 容器启动后,其内的应用所有对容器的改动,文件的增删改操作都只会发生在容器层中,对容器层下面的所有只读镜像层没有影响。
Docker 镜像都是只读的,当容器启动时,一个新的写层加载到镜像的顶部,这一层就是我们通常说的容器层,容器之下的都叫镜像层!
UnionFS 使得镜像的复用、定制变得更为容易。甚至可以用之前构建好的镜像作为基础层,然后进一步添加新的层,以定制自己所需的内容,构建新的镜像。
- layer
# docker image inspect 镜像名
# 查看镜像分层方式
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker image inspect python
[
{
"Id": "sha256:0f95b1e38607bbf15b19ad0d111f2316e92eb047a35370eac71973c636acb9d2",
"RepoTags": [
"python:latest"
],
"RepoDigests": [
"python@sha256:eeed7cac682f9274d183f8a7533ee1360a26acb3616aa712b2be7896f80d8c5f"
],
"Parent": "",
"Comment": "",
"Created": "2022-06-23T10:44:58.474893642Z",
"Container": "fceecb8656d753a144b3968d1c6c9b8f5453ff307d0688242f642743d9680beb",
"ContainerConfig": {
"Hostname": "fceecb8656d7",
"Domainname": "",
"User": "",
"AttachStdin": false,
"AttachStdout": false,
"AttachStderr": false,
"Tty": false,
"OpenStdin": false,
"StdinOnce": false,
"Env": [
"PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin",
"LANG=C.UTF-8",
"GPG_KEY=A035C8C19219BA821ECEA86B64E628F8D684696D",
"PYTHON_VERSION=3.10.5",
"PYTHON_PIP_VERSION=22.0.4",
"PYTHON_SETUPTOOLS_VERSION=58.1.0",
"PYTHON_GET_PIP_URL=https://github.com/pypa/get-pip/raw/6ce3639da143c5d79b44f94b04080abf2531fd6e/public/get-pip.py",
"PYTHON_GET_PIP_SHA256=ba3ab8267d91fd41c58dbce08f76db99f747f716d85ce1865813842bb035524d"
],
"Cmd": [
"/bin/sh",
"-c",
"#(nop) ",
"CMD [\"python3\"]"
],
"Image": "sha256:f968cc011b4d45dae5d5973d55488b86535bf317efb8f81481889503b79d1f8a",
"Volumes": null,
"WorkingDir": "",
"Entrypoint": null,
"OnBuild": null,
"Labels": {}
},
"DockerVersion": "20.10.12",
"Author": "",
"Config": {
"Hostname": "",
"Domainname": "",
"User": "",
"AttachStdin": false,
"AttachStdout": false,
"AttachStderr": false,
"Tty": false,
"OpenStdin": false,
"StdinOnce": false,
"Env": [
"PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin",
"LANG=C.UTF-8",
"GPG_KEY=A035C8C19219BA821ECEA86B64E628F8D684696D",
"PYTHON_VERSION=3.10.5",
"PYTHON_PIP_VERSION=22.0.4",
"PYTHON_SETUPTOOLS_VERSION=58.1.0",
"PYTHON_GET_PIP_URL=https://github.com/pypa/get-pip/raw/6ce3639da143c5d79b44f94b04080abf2531fd6e/public/get-pip.py",
"PYTHON_GET_PIP_SHA256=ba3ab8267d91fd41c58dbce08f76db99f747f716d85ce1865813842bb035524d"
],
"Cmd": [
"python3"
],
"Image": "sha256:f968cc011b4d45dae5d5973d55488b86535bf317efb8f81481889503b79d1f8a",
"Volumes": null,
"WorkingDir": "",
"Entrypoint": null,
"OnBuild": null,
"Labels": null
},
"Architecture": "amd64",
"Os": "linux",
"Size": 919687727,
"VirtualSize": 919687727,
"GraphDriver": {
"Data": {
"LowerDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/f4cd5061845ac5514f5aaa387dd58b63ea37c14d4383e6f01360c5ab1a6357b5/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a2eeebe65fe6050b40368dfaaf6115998e46544636faf3c820c686d7fb1bde16/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/4866d5cf1beb0816ba148e1700d92ea0c42cf1f7ba1ffd80e53113f95dcc2c8e/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/bc1115c2e1d53bfd674718bdd08ef6a2c82c73667067fed2e05c18f2131e1c3d/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/616914d1a8c57dd7386b550dbcd1ba501d11c09380afffa39fd227dcf3e4123d/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/34ed671ac7b1d2cf8e30cf0f3cf85da97c34b643e217325c8110dea59c36c730/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/b4e5edd486054fdcfbc558c6c2b64ccdd27e62776e6330828beab3674acfdcd6/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a09d8bfe4e8ff39f2b4b6589d36dc5bb97d3440aa2afc8d86e671a584f460eaa/diff",
"MergedDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a34dc8c6fd5f524c445da51fff81a50b3e15cf53c1db69aadca32c732b88209b/merged",
"UpperDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a34dc8c6fd5f524c445da51fff81a50b3e15cf53c1db69aadca32c732b88209b/diff",
"WorkDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/a34dc8c6fd5f524c445da51fff81a50b3e15cf53c1db69aadca32c732b88209b/work"
},
"Name": "overlay2"
},
"RootFS": {
"Type": "layers",
"Layers": [
"sha256:97d5fec864d84417c057008f153140193d2cc924b545b0c6fec10ae891fb26f9",
"sha256:6840c8ff46bd2c0ab4086d311c3e4903639b586c84d4f4ad28d156a2cc749e5f",
"sha256:66183893ba248fa10375cfec3e598d7df626b44c7740156e935ce2fcd5589aa7",
"sha256:5afd661c6106dfe99ed40c2dd18b8f6ffc5d978fa3302037b513c7a6e366609f",
"sha256:33a247b4fc529be9d43b5e70cc7d1beadf12e58c6e74967a4ade33e5e58f936d",
"sha256:ca5c6d5c3d01e1e0463415cd97adc7da3d3d5bb09f9ed01ec9d27cf6eeacb928",
"sha256:a8db90eb5ce025d596d828c84dec139ef539fb2bfb67c47e046fff306cb8b79b",
"sha256:9d17ba627a77ee6184993444d132f0dc9b7527db91af69f5fd9493dc29006957",
"sha256:a84ac09f498fca42148b003e0a51971916a5ef676e676c9522910f1e406e12bb"
]
},
"Metadata": {
"LastTagTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
}
}
]
- 平时我们安装进虚拟机的CentOS都是好几个G,而docker为什么只需要200多M?
- 这是因为对于精简的 OS,rootfs 可以很小,只需要包合最基本的命令,工具和程序库就可以了,因为底层直接用宿主机的kernel,自己只需要提供 rootfs 就可以了。
- 由此可见对于不同的Linux发行版, bootfs 基本是一致的,rootfs会有差別,因此不同的发行版可以公用 bootfs。
Docker 数据卷
- 容器的持久化和同步操作!
- 容器间也是可以数据共享的!
挂载数据卷
# -v 挂载容器文件到本地指定路径
docker run -it -v 主机路径:容器路径 镜像名 bash
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# docker run -it -v /root/docker:/home python bash
root@5713f008c70b:/# pwd
/
root@5713f008c70b:/# cd /home
root@5713f008c70b:/home# ls
docker_v
root@5713f008c70b:/home# cat docker_v
root@5713f008c70b:/home# echo 挂载 > docker_v
root@5713f008c70b:/home# cat docker_v
挂载
root@5713f008c70b:/home#
exit
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]# cat docker_v
挂载
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker]#
-
修改文件只需要在本地修改即可,容器内会自动同步!
-
删除容器后,挂载在本地的数据卷依旧没有消失,即容器的持久化!
具名挂载和匿名挂载
具名挂载
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume --help
Usage: docker volume COMMAND
Manage volumes
Commands:
create Create a volume
inspect Display detailed information on one or more volumes
ls List volumes
prune Remove all unused local volumes
rm Remove one or more volumes
Run 'docker volume COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
# 查看volumes列表
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume ls
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local f2ca5c3e4d50011c23484c04dbe1389b84e4b5cd4ccdc3c5fe0727a7cb506d4f
local nextcloud-example_acme
local nextcloud-example_certs
local nextcloud-example_db
local nextcloud-example_html
local nextcloud-example_nextcloud
local nextcloud-example_vhost.d
#具名挂载
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -it -v volumes_name:/home python bash
root@17a1cd2bf41f:/#
exit
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume ls
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local f2ca5c3e4d50011c23484c04dbe1389b84e4b5cd4ccdc3c5fe0727a7cb506d4f
local nextcloud-example_acme
local nextcloud-example_certs
local nextcloud-example_db
local nextcloud-example_html
local nextcloud-example_nextcloud
local nextcloud-example_vhost.d
local volumes_name
# -v 卷名:容器内路径
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume inspect volumes_name
[
{
"CreatedAt": "2022-07-02T13:14:23+08:00",
"Driver": "local",
"Labels": null,
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/volumes_name/_data",
"Name": "volumes_name",
"Options": null,
"Scope": "local"
}
]
# 挂载卷本地路径
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/volumes_name/_data"
匿名挂载
# 查看当前已挂载卷信息
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume ls
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local 4b141a71816e9afde2b99000408c463fa2d083185f636338fd3730fb96b76524
local 18b88b7ec6b3493bdb64e3d44b3502cf2a8dfcd3db0bb6007ff4c351a5c97210
local 7084c84ab678249b5d94aac5dd75f4ee4593190817826e3a500f028b0a6d853c
local ababaeecc1ec0a57c05093c00b6572570bfb132603389cbaa19a49fe47bc4863
local f2ca5c3e4d50011c23484c04dbe1389b84e4b5cd4ccdc3c5fe0727a7cb506d4f
# 匿名挂载
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt -v /home python bash
16d35a25083ead16a9458b7722df79427de5f5c19e861bfc442ca56a99aa08dd
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume ls
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local 4b141a71816e9afde2b99000408c463fa2d083185f636338fd3730fb96b76524
local 18b88b7ec6b3493bdb64e3d44b3502cf2a8dfcd3db0bb6007ff4c351a5c97210
local 085c3ac7e4c1dec6a32fe3a3305b10a72d94af1e569c1e212988ac0054695df4
local 7084c84ab678249b5d94aac5dd75f4ee4593190817826e3a500f028b0a6d853c
local ababaeecc1ec0a57c05093c00b6572570bfb132603389cbaa19a49fe47bc4863
local f2ca5c3e4d50011c23484c04dbe1389b84e4b5cd4ccdc3c5fe0727a7cb506d4f
# local 7084c84ab678249b5d94aac5dd75f4ee4593190817826e3a500f028b0a6d853c
# 查看新增卷信息
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker volume inspect 085c3ac7e4c1dec6a32fe3a3305b10a72d94af1e569c1e212988ac0054695df4
[
{
"CreatedAt": "2022-07-17T00:11:31+08:00",
"Driver": "local",
"Labels": null,
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/085c3ac7e4c1dec6a32fe3a3305b10a72d94af1e569c1e212988ac0054695df4/_data",
"Name": "085c3ac7e4c1dec6a32fe3a3305b10a72d94af1e569c1e212988ac0054695df4",
"Options": null,
"Scope": "local"
}
]
# 挂载卷本地路径
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/085c3ac7e4c1dec6a32fe3a3305b10a72d94af1e569c1e212988ac0054695df4/_data"
/var/lib/docker/volumes/卷名/_data
# 如何判断具名挂载和匿名挂载
-v 容器内路径 # 匿名挂载
-v 卷名:容器内路径 #具名挂载
-v /宿主机路径:容器内路径 # 指定路径挂载
- 拓展
# 通过-v 容器内路径:ro rw 改变读写权限
ro readonly # 只读
rw readwrite # 读写
# 一旦设置了容器读写权限,容器对我们挂载出的内容就有了限制!
# ro 该路径只能通过宿主机操作,容器内无法操作!
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -it -v volumes_name:/home python:ro bash
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -it -v volumes_name:/home python:rw bash
容器间的数据共享
#--volumes-from 共享的容器名
docker run -d -v /home/docker --name python01 python_volume
docker run -d -v /home/docker --name python02 --volumes-from python01 python_volume
# 实现两个容器的数据同步!
# 若多个容器进行数据同步,删除其中一个,数据不会丢失!拷贝概念!
- 结论
容器之间配置信息的传递,数据卷容器的生命周期一直持续到容器消失!
一旦持久化到本地,容器停止,本地数据不会被删除!
初识Dockerfile
dockefile 是用来构建docker镜像的构建文件,命令脚本!
通过这个脚本可以生成镜像,镜像是一层一层生成的,脚本是一个一个的命令,每个命令都是一层!
# dockerfile 文件名任意,建议使用dockerfile
# 命令都为大写
FROM python
VOLUME ["vloume1","volume2"] # 匿名挂载
CMD echo "===end==="
CMD /bin/bash
- dockerfile 构建镜像
# docker build
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker build -f dockerfile -t python_volume:1.0 .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.048kB
Step 1/4 : FROM python
---> 0f95b1e38607
Step 2/4 : VOLUME ["vloume1","volume2"] # 匿名挂载
---> Running in d09b4475696c
Removing intermediate container d09b4475696c
---> 0ea5b96f7203
Step 3/4 : CMD echo "===end==="
---> Running in 53b31c4cfc01
Removing intermediate container 53b31c4cfc01
---> b4f80a55bbf3
Step 4/4 : CMD /bin/bash
---> Running in fcc5d246157f
Removing intermediate container fcc5d246157f
---> fe5ede65e101
Successfully built fe5ede65e101
Successfully tagged python_volume:1.0
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
python_volume 1.0 fe5ede65e101 13 seconds ago 920MB
# docker run
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker run -it python_volume:1.0 bash
root@6cd225ef78d9:/# ls
bin boot dev etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var vloume1 volume2
- docker volume
# 查看容器信息
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker inspect 6cd225ef78d9
"Mounts": [
{
"Type": "volume",
"Name": "ababaeecc1ec0a57c05093c00b6572570bfb132603389cbaa19a49fe47bc4863",
"Source": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/ababaeecc1ec0a57c05093c00b6572570bfb132603389cbaa19a49fe47bc4863/_data",
"Destination": "vloume1",
"Driver": "local",
"Mode": "",
"RW": true,
"Propagation": ""
},
{
"Type": "volume",
"Name": "4b141a71816e9afde2b99000408c463fa2d083185f636338fd3730fb96b76524",
"Source": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/4b141a71816e9afde2b99000408c463fa2d083185f636338fd3730fb96b76524/_data",
"Destination": "volume2",
"Driver": "local",
"Mode": "",
"RW": true,
"Propagation": ""
}
],
# 可以看到本地挂在卷路径
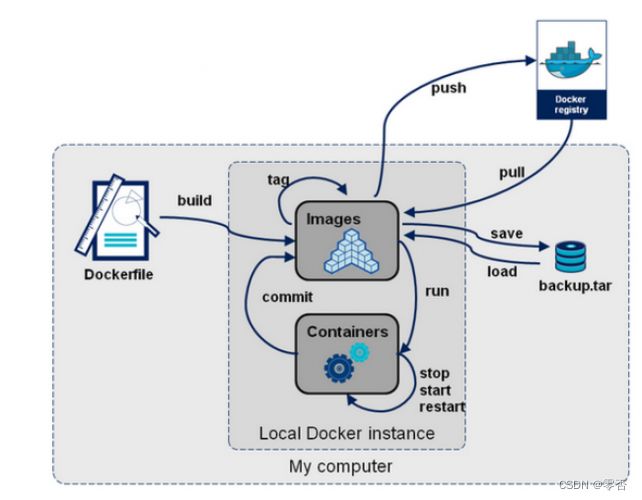
DockerFile
简述
dockerfile 是用来构建docker镜像的文件(命令脚本)!
- 步骤
- 编写dockerfile文件
- docker build 构建镜像
- docker run 运行镜像
- docker commit 从容器创建新镜像
- docker push 发布镜像
可参考官方镜像dockerfile文件
- 构建过程
- 每个保留关键字(指令)必须是大写字母
- 执行顺序从上到下
#表示注释- 每个指令都会创建提交一个新的镜像层(只读),并提交!
- 名词解释
- DockerFile:构建文件,定义一切步骤,源代码;
- DockerImages:通过dockerfile构建生成的镜像,最终发布运行的产品;;
- Docker容器:镜像运行起来的服务器!
dockerfile是面向开发的,发布项目,编写dockerfile文件即可;
dockerfile逐渐成为企业交付标准;
DockerFile指令
FROM # 基础镜像,一切从这里开始构建
MAINTAINER # 镜像的作者,姓名+邮箱
RUN # 镜像构建时要执行的命令
ADD # 拷贝文件到镜像中,如果是压缩包,会自动解压
COPY # 类似ADD,拷贝文件到镜像,不会解压
CMD # 指定容器启动时需要执行的命令,只有最后一个会生效,可被替换
ENTRYPOINT # ···同上,可以追加命令
ONBUILD # 当构建一个被继承DockerFile 时会触发ONBUILD的指令
ENV # 设置环境变量
WORKDIR # 镜像的工作目录
VOLUME # 挂载的目录
EXPOSE # 暴露的端口配置
USER # 指定容器启动时的用户,默认root
ARG # 外部变量
CMD 和 ENTRYPOINT的区别
CMD # 指定容器启动时运行的命令,只有最后一个会生效
ENTRYPOINT # 指定容器启动时运行的命令,追加命令
- CMD
# dockerfile
FROM centos
CMD ["ls","-a"]
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker build -f dockerfile -t cmdtest .
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker run cmdtest
.
..
bin
......
# 若追加一个 -l 命令,即 ls -al
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker run cmdtest -l
···
ERROR exec: \"-l\": executable file not found in "$PATH"...
# 使用CMD,-l替换了CMD ["ls","-a"]的整个命令,即CMD ["-l"],因此会报错
- ENTRYPOINT
# dockerfile
FROM centos
ENTRYPOINT ["ls","-a"]
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker build -f dockerfile -t entrytest .
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker run entrytest
# 若追加一个 -l 命令,即 ls -al
[root@VM-16-4-centos docker_file]# docker run entrytest -l
.
..
bin
......
# 使用ENTRYPOINT,-l会追加到ENTRYPOINT ["ls","-a"]命令之后,即ENTRYPOINT ["ls","-a","-l"]
Dockerfile 流程小结图
Docker 网络
Docker0
- Docker启动(未指定网络模式)时会在主机上自动创建一个docker0网桥,即一个Linux网桥。
- 容器借助网桥和主机或者其他容器进行通讯。
- 后文会介绍构建自定义网络
- docker 如何处理网络访问的?
每启动一个docker容器,docker就会给docker容器分配一个IP,只要安装docker,就会有个docker0网卡。
# 启动第一个容器,查看ip,本地ping 容器ip
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name centos_net centos
42e14108985540727960841df596336a887b2737ecffa34dba20435d8293544c
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_net ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
263: eth0@if264: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:03 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.3/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# ping 172.17.0.3
PING 172.17.0.3 (172.17.0.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.17.0.3: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.102 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.3: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.047 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.3: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.052 ms
^C
--- 172.17.0.3 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2066ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.047/0.067/0.102/0.024 ms
- 本地可以ping通容器ip
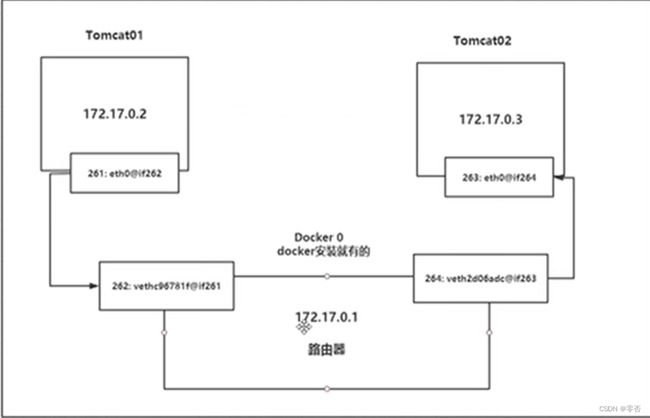
- 容器生成的网卡是一对一对的
- evth-pair 是一对虚拟设备的接口,成对出现,一端连着协议,一端彼此相连
- evth-pair 充当一个桥梁,连接各种网络设备
# 启动第二个容器,查看ip,容器2 ping 容器1 ip
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name centos_net1 centos
621864016bdf085502878052b35efbebaf67ea5ffb73950fdbc116c05cdc14ee
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_net1 ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
261: eth0@if262: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.2/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
# ping 容器ip
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_net1 ping 172.17.0.3
PING 172.17.0.3 (172.17.0.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.17.0.3: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.110 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.3: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.061 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.3: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.061 ms
^C
--- 172.17.0.3 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2080ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.061/0.077/0.110/0.024 ms
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]#
- 同一台主机上的容器之间可以ping通!
所有容器在不指定网络的情况下,都是docker0路由,docker会给容器分配默认ip
删除容器后,对应的网桥就消失了!
–link
# 使用容器名ping容器
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name docker0_1 centos
004443532a735140d758a3c694ed3341aca3421d060f326e453f295e4cba2d54
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name docker0_2 centos
2edd5a7b1460a8df615968f77745b86d8f828459651bdde9653b66cf2e6c7355
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it docker0_2 ping docker0_1
ping: docker0_1: Name or service not known
# --link
# docker0_3
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name docker0_3 --link docker0_1 centos
da81ccb5d949178226426aeacc882fb5f792a8a75439032fe2012b6b89cbd0b2
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it docker0_3 ping docker0_1
PING docker0_1 (172.17.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from docker0_1 (172.17.0.2): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.110 ms
64 bytes from docker0_1 (172.17.0.2): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.067 ms
^C
--- docker0_1 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1017ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.067/0.088/0.110/0.023 ms
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it docker0_3 cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
172.17.0.2 docker0_1 004443532a73
172.17.0.6 da81ccb5d949
# docker0_1
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it docker0_1 ping docker0_3
ping: docker0_3: Name or service not known
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it docker0_1 cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
172.17.0.2 004443532a73
docker0_3 --link docker0_1
docker0_3 可以使用容器名ping通docker0_1
反向不可以!
查看/etc/hosts,发现配置了域名
现在已不推荐使用,建议使用
自定义网络
自定义网络
# 帮助文档
# docker network --help
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network --help
Usage: docker network COMMAND
Manage networks
Commands:
connect Connect a container to a network
create Create a network
disconnect Disconnect a container from a network
inspect Display detailed information on one or more networks
ls List networks
prune Remove all unused networks
rm Remove one or more networks
Run 'docker network COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
- 查看所有docker网络
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
289ad861ab5c bridge bridge local
bb07841ecfc4 host host local
18661cf55012 nextcloud-example_default bridge local
6dd93f153306 nextcloud-example_proxy-tier bridge local
9247c7d8bcb1 none null local
- 网络模式
bridge:桥接 (docker默认)
none:不配置网络
host:和宿主机共享网络
container:容器网络连接(用的很少,局限大)
#docker0 是默认网络,特点是不能使用域名直接访问,需要--link打通连接!
# 自定义网络
# --driver bridge
# --subnet 192.168.0.0/16
# --gateway 192.168.0.1
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network create --driver bridge --subnet 192.168.0.0/16 --gateway 192.168.0.1 mynet
77d74473449ab956dd98e3f9d9776f0bd45fcfedbc71e42131d512ef4c3d8bba
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
289ad861ab5c bridge bridge local
bb07841ecfc4 host host local
77d74473449a mynet bridge local
18661cf55012 nextcloud-example_default bridge local
6dd93f153306 nextcloud-example_proxy-tier bridge local
9247c7d8bcb1 none null local
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network inspect mynet
[
{
"Name": "mynet",
"Id": "77d74473449ab956dd98e3f9d9776f0bd45fcfedbc71e42131d512ef4c3d8bba",
"Created": "2022-07-17T20:39:53.735686053+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "192.168.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "192.168.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
- 测试-创建容器(mynet)
# 在自定义网络下创建两个容器
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name centos_1 --net mynet centos
52d4109263713a8c57b2ead0c727ba727847ecdb53a0910b9a10ee2f0972f662
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name centos_2 --net mynet centos
cc6d28e74626de4d537551a375292ad3e6a604a0b27fa53dd4ed14ca39b1d1dc
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network inspect mynet
[
{
"Name": "mynet",
"Id": "77d74473449ab956dd98e3f9d9776f0bd45fcfedbc71e42131d512ef4c3d8bba",
"Created": "2022-07-17T20:39:53.735686053+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "192.168.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "192.168.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {
"52d4109263713a8c57b2ead0c727ba727847ecdb53a0910b9a10ee2f0972f662": {
"Name": "centos_1",
"EndpointID": "5cc6b2e603e319c21e844b1a3c4ec8c5ecfa0817fd098466b48efe8a85b11b0a",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:02",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.2/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
},
"cc6d28e74626de4d537551a375292ad3e6a604a0b27fa53dd4ed14ca39b1d1dc": {
"Name": "centos_2",
"EndpointID": "891bb08057cfe4623eb8f24952f4384215c496cb7273a8e7ea060a0ca6c80f02",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:03",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.3/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
}
},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
- 测试-连通性(ping)
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_1 ping centos_2
PING centos_2 (192.168.0.3) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from centos_2.mynet (192.168.0.3): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.099 ms
64 bytes from centos_2.mynet (192.168.0.3): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.076 ms
^C
--- centos_2 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.076/0.087/0.099/0.014 ms
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_2 ping centos_1
PING centos_1 (192.168.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from centos_1.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.100 ms
64 bytes from centos_1.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.064 ms
64 bytes from centos_1.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.067 ms
^C
--- centos_1 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2084ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.064/0.077/0.100/0.016 ms
# 不适用--link 也可以通过容器名字(id)ping通
自定义docker
弥补了docker0网络不能直接通过容器名字访问的弊端!不同的集群使用不同的网络,保证集群是安全和健康的!
容器跨网络联通
- 帮助命令
# docker network connect
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network connect --help
Usage: docker network connect [OPTIONS] NETWORK CONTAINER
Connect a container to a network
Options:
--alias strings Add network-scoped alias for the container
--driver-opt strings driver options for the network
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
--ip6 string IPv6 address (e.g., 2001:db8::33)
--link list Add link to another container
--link-local-ip strings Add a link-local address for the container
- 容器连通另一个网络
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker run -idt --name centos_docker0 centos
b0d8964907c7da3574d59e51ba06691b2f9c2475643519dd1753c9a4b6325e58
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_docker0 ping centos_1
ping: centos_1: Name or service not known
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network connect mynet centos_docker0
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker network inspect mynet
[
{
"Name": "mynet",
"Id": "77d74473449ab956dd98e3f9d9776f0bd45fcfedbc71e42131d512ef4c3d8bba",
"Created": "2022-07-17T20:39:53.735686053+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "192.168.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "192.168.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {
"52d4109263713a8c57b2ead0c727ba727847ecdb53a0910b9a10ee2f0972f662": {
"Name": "centos_1",
"EndpointID": "5cc6b2e603e319c21e844b1a3c4ec8c5ecfa0817fd098466b48efe8a85b11b0a",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:02",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.2/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
},
"b0d8964907c7da3574d59e51ba06691b2f9c2475643519dd1753c9a4b6325e58": {
"Name": "centos_docker0",
"EndpointID": "11fc2e66fd2af9ecd6c20b887fdcb2735fb787495d7714ac9f8d3661d9ef7f58",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:04",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.4/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
},
"cc6d28e74626de4d537551a375292ad3e6a604a0b27fa53dd4ed14ca39b1d1dc": {
"Name": "centos_2",
"EndpointID": "891bb08057cfe4623eb8f24952f4384215c496cb7273a8e7ea060a0ca6c80f02",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:03",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.3/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
}
},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
一个容器两个IP地址(类似于公网ip/私网ip)
打通之后就是将容器centos_docker0添加到了mynet网络下
- 测试连通性
# 已连通mynet的容器
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_docker0 ping centos_1
PING centos_1 (192.168.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from centos_1.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.119 ms
64 bytes from centos_1.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.072 ms
^C
--- centos_1 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1057ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.072/0.095/0.119/0.025 ms
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_1 ping centos_docker0
PING centos_docker0 (192.168.0.4) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from centos_docker0.mynet (192.168.0.4): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.104 ms
64 bytes from centos_docker0.mynet (192.168.0.4): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.084 ms
64 bytes from centos_docker0.mynet (192.168.0.4): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.083 ms
^C
--- centos_docker0 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2078ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.083/0.090/0.104/0.012 ms
# 未连通mynet的容器
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker exec -it centos_net ping centos_1
ping: centos_1: Name or service not known
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]#
结论:跨网络操作别人的容器,可以使用docker worknet connect 连接网络
Docker Compose
此处使用官网教程
OVERVIEW(概述)
Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With Compose, you use a YAML file to configure your application’s services. Then, with a single command, you create and start all the services from your configuration. To learn more about all the features of Compose, see the list of features.
Compose works in all environments: production, staging, development, testing, as well as CI workflows. You can learn more about each case in Common Use Cases.
Using Compose is basically a three-step process:
- Define your app’s environment with a
Dockerfileso it can be reproduced anywhere. - Define the services that make up your app in
docker-compose.ymlso they can be run together in an isolated environment. - Run
docker compose upand the Docker compose command starts and runs your entire app. You can alternatively rundocker-compose upusing the docker-compose binary.
dockerfile让程序在任何地方都可以运行,构建镜像
docker compose进行多容器编排
compose 安装
- Docker Compose requires Docker Engine.
- Docker Compose plugin requires Docker CLI.
# github下载
DOCKER_CONFIG=${DOCKER_CONFIG:-$HOME/.docker}
mkdir -p $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins
curl -SL https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.6.1/docker-compose-linux-x86_64 -o $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins/docker-compose
# github下载较慢
国内下载网站
https://get.daocloud.io/
# daocloud下载
curl -L https://get.daocloud.io/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.6.1/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` > /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
# 添加执行权限
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
# 查看版本
[root@VM-16-4-centos ~]# docker-compose --version
Docker Compose version v2.6.1
compose 实例
官方教程
https://docs.docker.com/compose/gettingstarted/
Step 1: Setup
Define the application dependencies.
-
Create a directory for the project:
mkdir composetest cd composetest -
Create a file called
app.pyin your project directory and paste this in:import time import redis from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) cache = redis.Redis(host='redis', port=6379) def get_hit_count(): retries = 5 while True: try: return cache.incr('hits') except redis.exceptions.ConnectionError as exc: if retries == 0: raise exc retries -= 1 time.sleep(0.5) @app.route('/') def hello(): count = get_hit_count() return 'Hello World! I have been seen {} times.\n'.format(count)In this example,
redisis the hostname of the redis container on the application’s network. We use the default port for Redis,6379. -
Create another file called
requirements.txtin your project directory and paste this in:flask redis
Step 2: Create a Dockerfile
In this step, you write a Dockerfile that builds a Docker image. The image contains all the dependencies the Python application requires, including Python itself.
In your project directory, create a file named Dockerfile and paste the following:
# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1
FROM python:3.7-alpine
WORKDIR /code
ENV FLASK_APP=app.py
ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST=0.0.0.0
RUN apk add --no-cache gcc musl-dev linux-headers
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
EXPOSE 5000
COPY . .
CMD ["flask", "run"]
This tells Docker to:
- Build an image starting with the Python 3.7 image.
- Set the working directory to
/code. - Set environment variables used by the
flaskcommand. - Install gcc and other dependencies
- Copy
requirements.txtand install the Python dependencies. - Add metadata to the image to describe that the container is listening on port 5000
- Copy the current directory
.in the project to the workdir.in the image. - Set the default command for the container to
flask run.
Step 3: Define services in a Compose file
Create a file called docker-compose.yml in your project directory and paste the following:
version: "3.9"
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "8000:5000"
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"
This Compose file defines two services: web and redis.
Step 4: Build and run your app with Compose
-
From your project directory, start up your application by running
docker compose up.$ docker compose up Creating network "composetest_default" with the default driver Creating composetest_web_1 ... Creating composetest_redis_1 ... Creating composetest_web_1 Creating composetest_redis_1 ... done Attaching to composetest_web_1, composetest_redis_1 web_1 | * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit) redis_1 | 1:C 17 Aug 22:11:10.480 # oO0OoO0OoO0Oo Redis is starting oO0OoO0OoO0Oo redis_1 | 1:C 17 Aug 22:11:10.480 # Redis version=4.0.1, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=1, just started redis_1 | 1:C 17 Aug 22:11:10.480 # Warning: no config file specified, using the default config. In order to specify a config file use redis-server /path/to/redis.conf web_1 | * Restarting with stat redis_1 | 1:M 17 Aug 22:11:10.483 * Running mode=standalone, port=6379. redis_1 | 1:M 17 Aug 22:11:10.483 # WARNING: The TCP backlog setting of 511 cannot be enforced because /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn is set to the lower value of 128. web_1 | * Debugger is active! redis_1 | 1:M 17 Aug 22:11:10.483 # Server initialized redis_1 | 1:M 17 Aug 22:11:10.483 # WARNING you have Transparent Huge Pages (THP) support enabled in your kernel. This will create latency and memory usage issues with Redis. To fix this issue run the command 'echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled' as root, and add it to your /etc/rc.local in order to retain the setting after a reboot. Redis must be restarted after THP is disabled. web_1 | * Debugger PIN: 330-787-903 redis_1 | 1:M 17 Aug 22:11:10.483 * Ready to accept connectionsCompose pulls a Redis image, builds an image for your code, and starts the services you defined. In this case, the code is statically copied into the image at build time.
-
Enter http://localhost:8000/ in a browser to see the application running.
If you’re using Docker natively on Linux, Docker Desktop for Mac, or Docker Desktop for Windows, then the web app should now be listening on port 8000 on your Docker daemon host. Point your web browser to http://localhost:8000 to find the
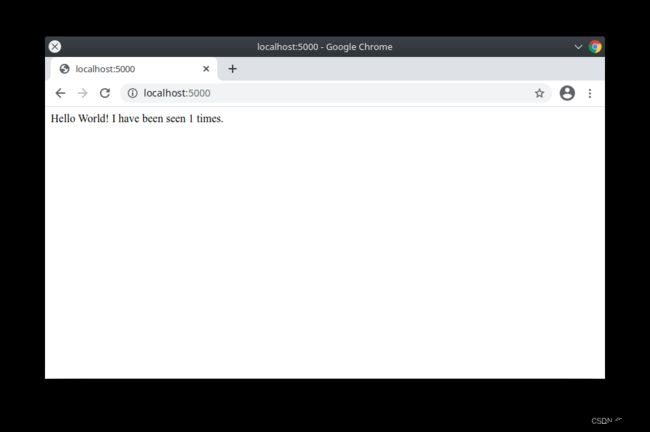
Hello Worldmessage. If this doesn’t resolve, you can also try http://127.0.0.1:8000.You should see a message in your browser saying:
Hello World! I have been seen 1 times.
-
Refresh the page.
The number should increment.
Hello World! I have been seen 2 times.
-
Switch to another terminal window, and type
docker image lsto list local images.Listing images at this point should return
redisandweb.$ docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE composetest_web latest e2c21aa48cc1 4 minutes ago 93.8MB python 3.4-alpine 84e6077c7ab6 7 days ago 82.5MB redis alpine 9d8fa9aa0e5b 3 weeks ago 27.5MBYou can inspect images with
docker inspect. -
Stop the application, either by running
docker compose downfrom within your project directory in the second terminal, or by hitting CTRL+C in the original terminal where you started the app.
Step 5: Edit the Compose file to add a bind mount
Edit docker-compose.yml in your project directory to add a bind mount for the web service:
version: "3.9"
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "8000:5000"
volumes:
- .:/code
environment:
FLASK_ENV: development
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"
The new volumes key mounts the project directory (current directory) on the host to /code inside the container, allowing you to modify the code on the fly, without having to rebuild the image. The environment key sets the FLASK_ENV environment variable, which tells flask run to run in development mode and reload the code on change. This mode should only be used in development.
Step 6: Re-build and run the app with Compose
From your project directory, type docker compose up to build the app with the updated Compose file, and run it.
$ docker compose up
Creating network "composetest_default" with the default driver
Creating composetest_web_1 ...
Creating composetest_redis_1 ...
Creating composetest_web_1
Creating composetest_redis_1 ... done
Attaching to composetest_web_1, composetest_redis_1
web_1 | * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
...
Check the Hello World message in a web browser again, and refresh to see the count increment.
Step 7: Update the application
Because the application code is now mounted into the container using a volume, you can make changes to its code and see the changes instantly, without having to rebuild the image.
Change the greeting in app.py and save it. For example, change the Hello World! message to Hello from Docker!:
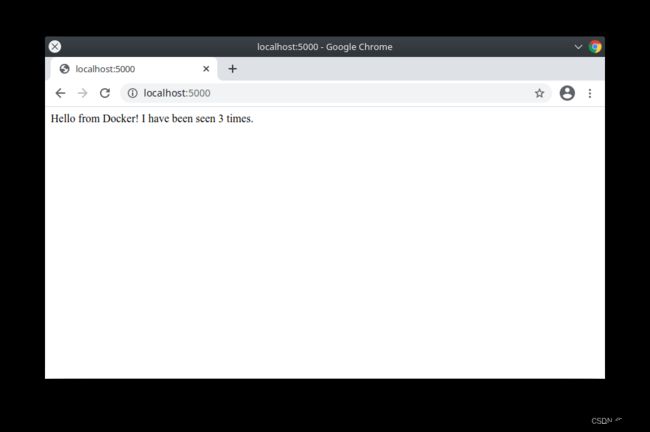
return 'Hello from Docker! I have been seen {} times.\n'.format(count)
Refresh the app in your browser. The greeting should be updated, and the counter should still be incrementing.
Step 8: Experiment with some other commands
If you want to run your services in the background, you can pass the -d flag (for “detached” mode) to docker compose up and use docker compose ps to see what is currently running:
$ docker compose up -d
Starting composetest_redis_1...
Starting composetest_web_1...
$ docker compose ps
Name Command State Ports
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
composetest_redis_1 docker-entrypoint.sh redis ... Up 6379/tcp
composetest_web_1 flask run Up 0.0.0.0:8000->5000/tcp
The docker compose run command allows you to run one-off commands for your services. For example, to see what environment variables are available to the web service:
$ docker compose run web env
See docker compose --help to see other available commands.
If you started Compose with docker compose up -d, stop your services once you’ve finished with them:
$ docker compose stop
You can bring everything down, removing the containers entirely, with the down command. Pass --volumes to also remove the data volume used by the Redis container:
$ docker compose down --volumes
At this point, you have seen the basics of how Compose works.
yaml 文件
# 3层
version: '' # 版本
services: # 服务
app1: web
images
build
vloumes
....
app2: sql
images
# 其他配置
volumes: # 网络
network: # 数据卷
config: # 全局规则
docker compose 手册
https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/
引用
docker 官网:https://docs.docker.com