使用pgd和fgsm方法进行攻击并使用map方法评估
本次实验对100张飞机图片组成的数据集,分别使用pgd攻击和fgsm攻击,达到对每张图片飞机区域的攻击,并使用getmap程序对攻击的效果进行评估。
文章目录
- 1、运行1.py程序和auto.py程序对飞机数据集的所有图片进行获取掩码操作
-
- (1)1.py程序
- (2)auto.py程序
- (3)运行后得到自动生成的掩码图像
- 2、使用pgd对数据集生成对抗样本
- 3、使用fgsm方法生成对抗样本
- 4、使用map方法进行评估
-
- (1)使用get_mappgd对生成的对抗样本进行评估
- (2)使用get_mapfgsm对生成的对抗样本进行评估
1、运行1.py程序和auto.py程序对飞机数据集的所有图片进行获取掩码操作
(1)1.py程序
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from auto import YOLO
if __name__ == "__main__":
yolo = YOLO()
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# dir_origin_path指定了用于检测的图片的文件夹路径
# dir_save_path指定了检测完图片的保存路径
# dir_origin_path和dir_save_path仅在mode='dir_predict'时有效
dir_origin_path = "/home/yolo程序/yolov4/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages"
dir_save_path = "/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/mask"
img_names = os.listdir(dir_origin_path)
for img_name in tqdm(img_names):
if img_name.lower().endswith(('.bmp', '.dib', '.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.pbm', '.pgm', '.ppm', '.tif', '.tiff')):
image_path = os.path.join(dir_origin_path, img_name)
image = Image.open(image_path)
mask = yolo.auto_mask(image)
toPIL = transforms.ToPILImage() # 这个函数可以将张量转为PIL图片,由小数转为0-255之间的像素值
mask = toPIL(mask)
if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
mask.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, img_name))
(2)auto.py程序
import colorsys
import os
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
from PIL import ImageDraw, ImageFont
from nets.yolo import YoloBody
from utils.utils import (cvtColor, get_anchors, get_classes, preprocess_input,
resize_image)
from utils.utils_bbox import DecodeBox
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
'''
训练自己的数据集必看注释!
'''
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 使用自己训练好的模型进行预测一定要修改model_path和classes_path!
# model_path指向logs文件夹下的权值文件,classes_path指向model_data下的txt
#
# 训练好后logs文件夹下存在多个权值文件,选择验证集损失较低的即可。
# 验证集损失较低不代表mAP较高,仅代表该权值在验证集上泛化性能较好。
# 如果出现shape不匹配,同时要注意训练时的model_path和classes_path参数的修改
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------#
"model_path": '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/ep098-loss0.443-val_loss1.670.pth',
"classes_path": '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/dota.txt',
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# anchors_path代表先验框对应的txt文件,一般不修改。
# anchors_mask用于帮助代码找到对应的先验框,一般不修改。
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"anchors_path": '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"anchors_mask": [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 输入图片的大小,必须为32的倍数。
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"input_shape": [1024, 1024],
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 只有得分大于置信度的预测框会被保留下来
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"confidence": 0.3,
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 非极大抑制所用到的nms_iou大小
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"nms_iou": 0.3,
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 该变量用于控制是否使用letterbox_image对输入图像进行不失真的resize,
# 在多次测试后,发现关闭letterbox_image直接resize的效果更好
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------#
"letterbox_image": False,
# -------------------------------#
# 是否使用Cuda
# 没有GPU可以设置成False
# -------------------------------#
"cuda": True,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 初始化YOLO
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults)
for name, value in kwargs.items():
setattr(self, name, value)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得种类和先验框的数量
# ---------------------------------------------------#
self.class_names, self.num_classes = get_classes(self.classes_path)
self.anchors, self.num_anchors = get_anchors(self.anchors_path)
self.bbox_util = DecodeBox(self.anchors, self.num_classes, (self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1]),
self.anchors_mask)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 画框设置不同的颜色
# ---------------------------------------------------#
hsv_tuples = [(x / self.num_classes, 1., 1.) for x in range(self.num_classes)]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)), self.colors))
self.generate()
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成模型
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def generate(self):
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 建立yolo模型,载入yolo模型的权重
# ---------------------------------------------------#
self.net = YoloBody(self.anchors_mask, self.num_classes)
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# device = torch.device('cpu')
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_path, map_location=device))
self.net = self.net.eval()
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(self.model_path))
if self.cuda:
self.net = nn.DataParallel(self.net)
self.net = self.net.cuda()
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 制作mask
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def auto_mask(self,image):
# mask = np.ones((1024, 1024, 3), dtype=float)
# mask = mask.transpose(2, 0, 1)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 计算输入图片的高和宽
# ---------------------------------------------------#
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres=self.confidence,
nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
if results[0] is None:
mask = np.ones((3,1024, 1024))
mask = torch.from_numpy(mask) # ndarray转换为tensor
return mask
mask = np.zeros((1024, 1024, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
top_label = np.array(results[0][:, 6], dtype='int32')
top_conf = results[0][:, 4] * results[0][:, 5]
top_boxes = results[0][:, :4]
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 图像绘制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_label)):
box = top_boxes[i]
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right).astype('int32'))
polygon = np.array([[left, top], [right, top], [right, bottom], [left, bottom]], np.int32) # 坐标为顺时针方向
cv2.fillConvexPoly(mask, polygon, (255, 255, 255))
mask = torch.from_numpy(mask.transpose(2, 0, 1)) # ndarray转换为tensor
return mask
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 检测图片
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def detect_image(self, image):
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 计算输入图片的高和宽
# ---------------------------------------------------#
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres=self.confidence,
nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
if results[0] is None:
return image
top_label = np.array(results[0][:, 6], dtype='int32')
top_conf = results[0][:, 4] * results[0][:, 5]
top_boxes = results[0][:, :4]
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 设置字体与边框厚度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='model_data/simhei.ttf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = int(max((image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // np.mean(self.input_shape), 1))
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 图像绘制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_label)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
box = top_boxes[i]
score = top_conf[i]
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right).astype('int32'))
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
label = label.encode('utf-8')
print(label, top, left, bottom, right)
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i], outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle([tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)], fill=self.colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, str(label, 'UTF-8'), fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
return image
def get_FPS(self, image, test_interval):
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres=self.confidence,
nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
t1 = time.time()
for _ in range(test_interval):
with torch.no_grad():
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image,
conf_thres=self.confidence, nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
t2 = time.time()
tact_time = (t2 - t1) / test_interval
return tact_time
def get_map_txt(self, image_id, image, class_names, map_out_path):
f = open(os.path.join(map_out_path, "detection-results/" + image_id + ".txt"), "w")
image_shape = np.array(np.shape(image)[0:2])
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 在这里将图像转换成RGB图像,防止灰度图在预测时报错。
# 代码仅仅支持RGB图像的预测,所有其它类型的图像都会转化成RGB
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image = cvtColor(image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 给图像增加灰条,实现不失真的resize
# 也可以直接resize进行识别
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = resize_image(image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[0]), self.letterbox_image)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 添加上batch_size维度
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
image_data = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(preprocess_input(np.array(image_data, dtype='float32')), (2, 0, 1)), 0)
with torch.no_grad():
images = torch.from_numpy(image_data)
if self.cuda:
images = images.cuda()
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将图像输入网络当中进行预测!
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
outputs = self.net(images)
outputs = self.bbox_util.decode_box(outputs)
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测框进行堆叠,然后进行非极大抑制
# ---------------------------------------------------------#
results = self.bbox_util.non_max_suppression(torch.cat(outputs, 1), self.num_classes, self.input_shape,
image_shape, self.letterbox_image, conf_thres=self.confidence,
nms_thres=self.nms_iou)
if results[0] is None:
return
top_label = np.array(results[0][:, 6], dtype='int32')
top_conf = results[0][:, 4] * results[0][:, 5]
top_boxes = results[0][:, :4]
for i, c in list(enumerate(top_label)):
predicted_class = self.class_names[int(c)]
box = top_boxes[i]
score = str(top_conf[i])
top, left, bottom, right = box
if predicted_class not in class_names:
continue
f.write("%s %s %s %s %s %s\n" % (
predicted_class, score[:6], str(int(left)), str(int(top)), str(int(right)), str(int(bottom))))
f.close()
return
(3)运行后得到自动生成的掩码图像
2、使用pgd对数据集生成对抗样本
运行train_PGD.py
#-------------------------------------#
# 对数据集进行训练
#-------------------------------------#
import numpy as np
from rsa import sign
from sqlalchemy import false, true
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from nets.yolo import YoloBody
from nets.yolo_training1 import YOLOLoss, weights_init
from utils.callbacks import LossHistory
from utils.dataloader import YoloDataset, yolo_dataset_collate
from utils.utils import get_anchors, get_classes
from utils.utils_fit import fit_one_epoch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from torch import autograd
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
import os
def getimg(img_path,height,width):
#读取图片和mask,
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = img.resize((height,width),Image.ANTIALIAS)
if isinstance(img, Image.Image):
width_ = img.width
height_ = img.height
img = torch.ByteTensor(torch.ByteStorage.from_buffer(img.tobytes()))
img = img.view(height_, width_, 3).transpose(0, 1).transpose(0, 2).contiguous()
img = img.view(1, 3, height_, width_)
img = img.float().div(255.0)
elif type(img) == np.ndarray and len(img.shape) == 3: # cv2 image
img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose(2, 0, 1)).float().div(255.0).unsqueeze(0)
elif type(img) == np.ndarray and len(img.shape) == 4:
img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)).float().div(255.0)
elif type(img) == torch.Tensor and len(img.shape) == 4:
img = img
else:
print("unknow image type")
exit(-1)
if cuda :
img = img.cuda()
return img
def yolo_single_loss(output, conf_thresh, num_classes, num_anchors, only_objectness=1):
# output 是不同大小的feature map(每次输入一层feature map)
if len(output.shape) == 3:
output = np.expand_dims(output, axis=0)
batch = output.shape[0] # patch数量,默认为1
print(output.shape[1])
print((5 + num_classes) * num_anchors)
assert (output.shape[1] == (5 + num_classes) * num_anchors)
h = output.shape[2] # feature map 的宽
w = output.shape[3] # feature map 的高 (1, 0, 2)
output = output.reshape(batch * num_anchors, 5 + num_classes, h * w).transpose(1, 0).reshape(5 + num_classes,batch * num_anchors * h * w) # 将 feature map 转换为(80+5,*)
det_confs = torch.sigmoid(output[4]) # 当前feature map该点处存在目标的概率 sigmoid(output[4])
loss = 0.0
idx = np.where((det_confs[:]).cpu().data > conf_thresh)
loss += torch.sum(det_confs[idx])
return loss
def getmask2():
img = np.ones((1024,1024,3),dtype=float)
img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose(2, 0, 1)).float().div(255.0).unsqueeze(0)
pmask = np.ones((1024,1024,3),dtype=float)
pmask = torch.from_numpy(pmask.transpose(2, 0, 1)).float().div(255.0).unsqueeze(0)
for i in range(input_shape[0]):
for j in range(input_shape[1]):
for k in range(3):
if (i>512) & (j>512):
pmask[0][k][i][j]=1
else:pmask[0][k][i][j]=0
print(img.shape)
return img,pmask
if __name__ == "__main__":
epsilon=6
eps=0.3
alpha=2/255
cuda = True
conf_thresh=0.5
norm_ord = 'L2'
classes_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/dota.txt'
anchors_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
anchors_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
model_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/ep098-loss0.443-val_loss1.670.pth'
input_shape = [1024, 1024]
Cosine_lr = False
n_epochs = 10
batch_size = 1
lr = 1e-3
num_workers = 4
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 获取classes和anchor
#----------------------------------------------------#
class_names, num_classes = get_classes(classes_path)
anchors, num_anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
val_annotation_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/2007_test.txt'
val_txt_name = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt'
path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/mask/'
with open(val_annotation_path) as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
line=f.readlines
with open(val_txt_name) as f:
data = f.read().splitlines()
num_val = len(val_lines)
imgList=os.listdir(path)
listLen = len(imgList) # 该文件夹图片个数
listNum = 0
with open(val_annotation_path) as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
num_val = len(val_lines)
with open(val_txt_name) as f:
data = f.read().splitlines()
val_dataset = YoloDataset(val_lines, input_shape, num_classes, mosaic=False, train = False)
gen_val = DataLoader(val_dataset , shuffle =False, batch_size = batch_size, num_workers = num_workers, pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=yolo_dataset_collate)
p_img_batch,pmask= getmask2()
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 创建yolo模型
#------------------------------------------------------#
model = YoloBody(anchors_mask, num_classes)
weights_init(model)
if model_path != '':
#------------------------------------------------------#
# 权值文件请看README,百度网盘下载
#------------------------------------------------------#
print('Load weights {}.'.format(model_path))
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location = device)
pretrained_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrained_dict.items() if np.shape(model_dict[k]) == np.shape(v)}
model_dict.update(pretrained_dict)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
yolo_loss = YOLOLoss(anchors, num_classes, input_shape, cuda, anchors_mask)
if cuda:
model_train = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
cudnn.benchmark = True
model_train = model_train.cuda()
p_img_batch = p_img_batch.cuda()
pmask= pmask.cuda()
p_img_batch.requires_grad_(True)
optimizer = optim.Adam([p_img_batch], lr, weight_decay = 5e-4)
if Cosine_lr:
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=5, eta_min=1e-5)
else:
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=0.94)
model_train = model.eval()
#tensor设置可求导迭代多少轮
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
loss = 0
val_loss = 0
print("epochs:"+str(epoch) )
for iteration, batch in enumerate(gen_val):
pm = getimg(path+data[iteration]+'.jpg',input_shape[0], input_shape[1])
images, targets = batch[0], batch[1]
#pm = getimg(path+data[iteration]+'.jpg',input_shape[0], input_shape[1])
if cuda:
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor).cuda()
targets = [torch.from_numpy(ann).type(torch.FloatTensor).cuda() for ann in targets]
else:
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor)
targets = [torch.from_numpy(ann).type(torch.FloatTensor) for ann in targets]
images.requires_grad_(True)
temp=p_img_batch*pmask
adv_images=p_img_batch*pm + images
#adv_images = p_img_batch*pmask+images
#adv_images = p_img_batch+images
outputs= model_train(adv_images)
img1 = F.interpolate(adv_images, (input_shape[0], input_shape[1]))
img1 = img1[0, :, :,]
imm1 = transforms.ToPILImage('RGB')(img1)
imm1.save("/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/PGD/img/"+ data[iteration] +".jpg")
img1 = F.interpolate(p_img_batch, (input_shape[0], input_shape[1]))
img1 = img1[0, :, :,]
imm1 = transforms.ToPILImage('RGB')(img1)
imm1.save("/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/PGD/adv/p_img_batch.jpg")
# img3 = F.interpolate(temp, (input_shape[0], input_shape[1]))
# img3 = img3[0, :, :,]
# imm3 = transforms.ToPILImage('RGB')(img3)
# imm3.save("D:/Anaconda3.8/python/yolov4/patch/PGDare/adv/pmask3"+ data[iteration] +".jpg")
loss_value_all = 0
num_pos_all = 0
#----------------------#
# 计算损失
#----------------------#
for l in range(len(outputs)):
loss, loss_loc ,loss_conf ,loss_cls,num_pos = yolo_loss(l,outputs[l],targets)
loss_item=loss_conf
loss_value_all += loss_item
num_pos_all += num_pos
loss_value = loss_value_all / num_pos_all
grad= torch.autograd.grad(loss_item,adv_images,retain_graph=False,create_graph=False)[0]
adv_images = adv_images.detach()+alpha*grad.sign()
delta = torch.clamp(adv_images-images, min=-eps, max=eps)
adv_images = torch.clamp(images + delta, min=0, max=1).detach()
p_img_batch=adv_images-images
#p_img_batch.clip_(0,1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss += loss_value.item()
print(loss)
得到的对抗样本只有少部分被系统识别飞机并生成对抗
左图没有生成明显对抗,右图生成了明显对抗
3、使用fgsm方法生成对抗样本
将train_PGD.py修改为使用fgsm方法,形成train_fgsm.py文件
import numpy as np
from rsa import sign
from sqlalchemy import false, true
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from nets.yolo import YoloBody
from nets.yolo_training1 import YOLOLoss, weights_init
from utils.callbacks import LossHistory
from utils.dataloader import YoloDataset, yolo_dataset_collate
from utils.utils import get_anchors, get_classes
from utils.utils_fit import fit_one_epoch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from torch import autograd
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
import os
def getimg(img_path,height,width):
#读取图片和mask,
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = img.resize((height,width),Image.ANTIALIAS)
if isinstance(img, Image.Image):
width_ = img.width
height_ = img.height
img = torch.ByteTensor(torch.ByteStorage.from_buffer(img.tobytes()))
img = img.view(height_, width_, 3).transpose(0, 1).transpose(0, 2).contiguous()
img = img.view(1, 3, height_, width_)
img = img.float().div(255.0)
elif type(img) == np.ndarray and len(img.shape) == 3: # cv2 image
img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose(2, 0, 1)).float().div(255.0).unsqueeze(0)
elif type(img) == np.ndarray and len(img.shape) == 4:
img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)).float().div(255.0)
elif type(img) == torch.Tensor and len(img.shape) == 4:
img = img
else:
print("unknow image type")
exit(-1)
if cuda :
img = img.cuda()
return img
def fgsm_attack(image, epsilon, data_grad):
# 使用sign(符号)函数,将对x求了偏导的梯度进行符号化(正数为1,零为0,负数为-1)
sign_data_grad = data_grad.sign()
# 通过epsilon生成对抗样本
perturbed_image = image + epsilon * sign_data_grad
# 噪声越来越大,机器越来越难以识别,但人眼可以看出差别
# 做一个剪裁的工作,将torch.clamp内部大于1的数值变为1,小于0的数值等于0,防止image越界
perturbed_image = torch.clamp(perturbed_image, 0, 1)
# 返回对抗样本
return perturbed_image
def getmask2():
img = np.ones((1024,1024,3),dtype=float)
img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose(2, 0, 1)).float().div(255.0).unsqueeze(0)
pmask = np.ones((1024,1024,3),dtype=float)
pmask = torch.from_numpy(pmask.transpose(2, 0, 1)).float().div(255.0).unsqueeze(0)
for i in range(input_shape[0]):
for j in range(input_shape[1]):
for k in range(3):
if (i>512) & (j>512):
pmask[0][k][i][j]=1
else:pmask[0][k][i][j]=0
print(img.shape)
return img,pmask
if __name__ == "__main__":
epsilon=6
eps=0.3
alpha=2/255
cuda = True
conf_thresh=0.5
norm_ord = 'L2'
classes_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/dota.txt'
anchors_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
anchors_mask = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
model_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/ep098-loss0.443-val_loss1.670.pth'
input_shape = [1024, 1024]
Cosine_lr = False
n_epochs = 10
batch_size = 1
lr = 1e-3
num_workers = 4
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 获取classes和anchor
# ----------------------------------------------------#
class_names, num_classes = get_classes(classes_path)
anchors, num_anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
val_annotation_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/2007_test.txt'
val_txt_name = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt'
path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/mask/'
with open(val_annotation_path) as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
line = f.readlines
with open(val_txt_name) as f:
data = f.read().splitlines()
num_val = len(val_lines)
imgList = os.listdir(path)
listLen = len(imgList) # 该文件夹图片个数
listNum = 0
with open(val_annotation_path) as f:
val_lines = f.readlines()
num_val = len(val_lines)
with open(val_txt_name) as f:
data = f.read().splitlines()
val_dataset = YoloDataset(val_lines, input_shape, num_classes, mosaic=False, train=False)
gen_val = DataLoader(val_dataset, shuffle=False, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True, collate_fn=yolo_dataset_collate)
p_img_batch, pmask = getmask2()
# ------------------------------------------------------#
# 创建yolo模型
# ------------------------------------------------------#
model = YoloBody(anchors_mask, num_classes)
weights_init(model)
if model_path != '':
# ------------------------------------------------------#
# 权值文件请看README,百度网盘下载
# ------------------------------------------------------#
print('Load weights {}.'.format(model_path))
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
pretrained_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrained_dict.items() if np.shape(model_dict[k]) == np.shape(v)}
model_dict.update(pretrained_dict)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
yolo_loss = YOLOLoss(anchors, num_classes, input_shape, cuda, anchors_mask)
if cuda:
model_train = torch.nn.DataParallel(model)
cudnn.benchmark = True
model_train = model_train.cuda()
p_img_batch = p_img_batch.cuda()
pmask = pmask.cuda()
p_img_batch.requires_grad_(True)
# optimizer = optim.Adam([p_img_batch], lr, weight_decay=5e-4)
# if Cosine_lr:
# lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=5, eta_min=1e-5)
# else:
# lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=0.94)
#
# model_train = model.eval()
# ============================ step 3/5 损失函数 ============================
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 选择损失函数
# ============================ step 4/5 优化器 ============================
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=0.9) # 选择优化器
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.1) # 设置学习率下降策略
# ============================ step 5/5 训练 ============================
train_curve = list()
valid_curve = list()
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
loss_mean = 0.
correct = 0.
total = 0.
model.train()
print("epochs:" + str(epoch))
for iteration, batch in enumerate(gen_val):
pm = getimg(path+data[iteration]+'.jpg',input_shape[0], input_shape[1])
images, targets = batch[0], batch[1]
#pm = getimg(path+data[iteration]+'.jpg',input_shape[0], input_shape[1])
if cuda:
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor).cuda()
targets = [torch.from_numpy(ann).type(torch.FloatTensor).cuda() for ann in targets]
else:
images = torch.from_numpy(images).type(torch.FloatTensor)
targets = [torch.from_numpy(ann).type(torch.FloatTensor) for ann in targets]
images.requires_grad_(True)
temp=p_img_batch*pmask
adv_images=p_img_batch*pm + images
outputs = model_train(adv_images)
img1 = F.interpolate(adv_images, (input_shape[0], input_shape[1]))
img1 = img1[0, :, :, ]
imm1 = transforms.ToPILImage('RGB')(img1)
imm1.save("/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/fgsm/img/" + data[iteration] + ".jpg")
img1 = F.interpolate(p_img_batch, (input_shape[0], input_shape[1]))
img1 = img1[0, :, :, ]
imm1 = transforms.ToPILImage('RGB')(img1)
imm1.save("/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/fgsm/adv/p_img_batch.jpg")
loss_value_all = 0
num_pos_all = 0
# ----------------------#
# 计算损失
# ----------------------#
for l in range(len(outputs)):
loss, loss_loc, loss_conf, loss_cls, num_pos = yolo_loss(l, outputs[l], targets)
loss_item = loss_conf
loss_value_all += loss_item
num_pos_all += num_pos
loss_value = loss_value_all / num_pos_all
# loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
# loss.backward()
# 收集datagrad
# data_grad = adv_images.grad.data
grad = torch.autograd.grad(loss, adv_images, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0]
# 调用FGSM攻击
perturbed_data = fgsm_attack(adv_images, eps, grad)
adv_images = adv_images.detach() + alpha * grad.sign()
delta = torch.clamp(adv_images - images, min=-eps, max=eps)
adv_images = torch.clamp(images + delta, min=0, max=1).detach()
p_img_batch = adv_images - images
# p_img_batch.clip_(0,1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss += loss.item()
# loss.backward()
print(loss)
生成的对抗样本对大部分图片有明显攻击
4、使用map方法进行评估
(1)使用get_mappgd对生成的对抗样本进行评估
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from utils.utils import get_classes
from utils.utils_map import get_coco_map, get_map
from yolo import YOLO
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK'] = 'TRUE'
if __name__ == "__main__":
'''
Recall和Precision不像AP是一个面积的概念,在门限值不同时,网络的Recall和Precision值是不同的。
map计算结果中的Recall和Precision代表的是当预测时,门限置信度为0.5时,所对应的Recall和Precision值。
此处获得的./map_out/detection-results/里面的txt的框的数量会比直接predict多一些,这是因为这里的门限低,
目的是为了计算不同门限条件下的Recall和Precision值,从而实现map的计算。
'''
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# map_mode用于指定该文件运行时计算的内容
# map_mode为0代表整个map计算流程,包括获得预测结果、获得真实框、计算VOC_map。
# map_mode为1代表仅仅获得预测结果。
# map_mode为2代表仅仅获得真实框。
# map_mode为3代表仅仅计算VOC_map。
# map_mode为4代表利用COCO工具箱计算当前数据集的0.50:0.95map。需要获得预测结果、获得真实框后并安装pycocotools才行
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
map_mode = 0
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 此处的classes_path用于指定需要测量VOC_map的类别
# 一般情况下与训练和预测所用的classes_path一致即可
#-------------------------------------------------------#
classes_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/dota.txt'
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# MINOVERLAP用于指定想要获得的mAP0.x
# 比如计算mAP0.75,可以设定MINOVERLAP = 0.75。
#-------------------------------------------------------#
MINOVERLAP = 0.5
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# map_vis用于指定是否开启VOC_map计算的可视化
#-------------------------------------------------------#
map_vis = False
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 指向VOC数据集所在的文件夹
# 默认指向根目录下的VOC数据集
#-------------------------------------------------------#
VOCdevkit_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/VOCdevkit'
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 结果输出的文件夹,默认为map_out
#-------------------------------------------------------#
map_out_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/PGD/map_oup-mom'
image_ids = open(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt")).read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists(map_out_path):
os.makedirs(map_out_path)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional'))
class_names, _ = get_classes(classes_path)
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 1:
print("Load model.")
yolo = YOLO(confidence = 0.001, nms_iou = 0.5)
print("Load model done.")
print("Get predict result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
image_path = os.path.join("/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/PGD/img/"+image_id+".jpg")
image = Image.open(image_path)
if map_vis:
image.save(os.path.join(map_out_path, "images-optional/" + image_id + ".jpg"))
yolo.get_map_txt(image_id, image, class_names, map_out_path)
print("Get predict result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 2:
print("Get ground truth result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
with open(os.path.join(map_out_path, "ground-truth/"+image_id+".txt"), "w") as new_f:
root = ET.parse(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/Annotations/"+image_id+".xml")).getroot()
for obj in root.findall('object'):
difficult_flag = False
if obj.find('difficult')!=None:
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
if int(difficult)==1:
difficult_flag = True
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
if obj_name not in class_names:
continue
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
left = bndbox.find('xmin').text
top = bndbox.find('ymin').text
right = bndbox.find('xmax').text
bottom = bndbox.find('ymax').text
if difficult_flag:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s difficult\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
else:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
print("Get ground truth result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 3:
print("Get map.")
get_map(MINOVERLAP, True, path = map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
if map_mode == 4:
print("Get map.")
get_coco_map(class_names = class_names, path = map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
#***********************************************************************************
map_out_path = 'D:/yolov4/patch/PGD/map_oup-imgforloc1'
image_ids = open(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt")).read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists(map_out_path):
os.makedirs(map_out_path)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional'))
class_names, _ = get_classes(classes_path)
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 1:
print("Load model.")
yolo = YOLO(confidence = 0.001, nms_iou = 0.5)
print("Load model done.")
print("Get predict result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
image_path = os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "../yolov4/patch/PGD/imgforloc1/"+image_id+".jpg")
image = Image.open(image_path)
if map_vis:
image.save(os.path.join(map_out_path, "images-optional/" + image_id + ".jpg"))
yolo.get_map_txt(image_id, image, class_names, map_out_path)
print("Get predict result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 2:
print("Get ground truth result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
with open(os.path.join(map_out_path, "ground-truth/"+image_id+".txt"), "w") as new_f:
root = ET.parse(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/Annotations/"+image_id+".xml")).getroot()
for obj in root.findall('object'):
difficult_flag = False
if obj.find('difficult')!=None:
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
if int(difficult)==1:
difficult_flag = True
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
if obj_name not in class_names:
continue
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
left = bndbox.find('xmin').text
top = bndbox.find('ymin').text
right = bndbox.find('xmax').text
bottom = bndbox.find('ymax').text
if difficult_flag:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s difficult\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
else:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
print("Get ground truth result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 3:
print("Get map.")
get_map(MINOVERLAP, True, path = map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
if map_mode == 4:
print("Get map.")
get_coco_map(class_names = class_names, path = map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
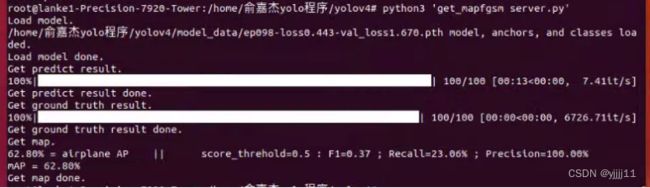
(2)使用get_mapfgsm对生成的对抗样本进行评估
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
from utils.utils import get_classes
from utils.utils_map import get_coco_map, get_map
from yolo import YOLO
os.environ['KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK'] = 'TRUE'
if __name__ == "__main__":
'''
Recall和Precision不像AP是一个面积的概念,在门限值不同时,网络的Recall和Precision值是不同的。
map计算结果中的Recall和Precision代表的是当预测时,门限置信度为0.5时,所对应的Recall和Precision值。
此处获得的./map_out/detection-results/里面的txt的框的数量会比直接predict多一些,这是因为这里的门限低,
目的是为了计算不同门限条件下的Recall和Precision值,从而实现map的计算。
'''
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# map_mode用于指定该文件运行时计算的内容
# map_mode为0代表整个map计算流程,包括获得预测结果、获得真实框、计算VOC_map。
# map_mode为1代表仅仅获得预测结果。
# map_mode为2代表仅仅获得真实框。
# map_mode为3代表仅仅计算VOC_map。
# map_mode为4代表利用COCO工具箱计算当前数据集的0.50:0.95map。需要获得预测结果、获得真实框后并安装pycocotools才行
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
map_mode = 0
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 此处的classes_path用于指定需要测量VOC_map的类别
# 一般情况下与训练和预测所用的classes_path一致即可
#-------------------------------------------------------#
classes_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/model_data/dota.txt'
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# MINOVERLAP用于指定想要获得的mAP0.x
# 比如计算mAP0.75,可以设定MINOVERLAP = 0.75。
#-------------------------------------------------------#
MINOVERLAP = 0.5
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# map_vis用于指定是否开启VOC_map计算的可视化
#-------------------------------------------------------#
map_vis = False
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 指向VOC数据集所在的文件夹
# 默认指向根目录下的VOC数据集
#-------------------------------------------------------#
VOCdevkit_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/VOCdevkit'
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 结果输出的文件夹,默认为map_out
#-------------------------------------------------------#
map_out_path = '/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/fgsm/map_oup-fgsm'
image_ids = open(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt")).read().strip().split()
if not os.path.exists(map_out_path):
os.makedirs(map_out_path)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'ground-truth'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'detection-results'))
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional')):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(map_out_path, 'images-optional'))
class_names, _ = get_classes(classes_path)
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 1:
print("Load model.")
yolo = YOLO(confidence=0.001, nms_iou=0.5)
print("Load model done.")
print("Get predict result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
image_path = os.path.join("/home/yolo程序/yolov4/patch/fgsm/img/" + image_id + ".jpg")
image = Image.open(image_path)
if map_vis:
image.save(os.path.join(map_out_path, "images-optional/" + image_id + ".jpg"))
yolo.get_map_txt(image_id, image, class_names, map_out_path)
print("Get predict result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 2:
print("Get ground truth result.")
for image_id in tqdm(image_ids):
with open(os.path.join(map_out_path, "ground-truth/" + image_id + ".txt"), "w") as new_f:
root = ET.parse(os.path.join(VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/Annotations/" + image_id + ".xml")).getroot()
for obj in root.findall('object'):
difficult_flag = False
if obj.find('difficult') != None:
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
if int(difficult) == 1:
difficult_flag = True
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
if obj_name not in class_names:
continue
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
left = bndbox.find('xmin').text
top = bndbox.find('ymin').text
right = bndbox.find('xmax').text
bottom = bndbox.find('ymax').text
if difficult_flag:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s difficult\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
else:
new_f.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (obj_name, left, top, right, bottom))
print("Get ground truth result done.")
if map_mode == 0 or map_mode == 3:
print("Get map.")
get_map(MINOVERLAP, True, path=map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")
if map_mode == 4:
print("Get map.")
get_coco_map(class_names=class_names, path=map_out_path)
print("Get map done.")