力扣题(6) —— z字形变换
z字形变换
题目描述
将一个给定字符串 s 根据给定的行数 numRows ,以从上往下、从左到右进行 Z 字形排列。
比如输入字符串为 “PAYPALISHIRING” 行数为 3 时,排列如下:
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
之后,你的输出需要从左往右逐行读取,产生出一个新的字符串,比如:“PAHNAPLSIIGYIR”。
请你实现这个将字符串进行指定行数变换的函数:
string convert(string s, int numRows);
示例 1:
输入:s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3
输出:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
示例 2:
输入:s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4
输出:"PINALSIGYAHRPI"
解释:
P I N
A L S I G
Y A H R
P I
示例 3:
输入:s = "A", numRows = 1
输出:"A"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000
s 由英文字母(小写和大写)、',' 和 '.' 组成
1 <= numRows <= 1000
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zigzag-conversion
做法一
一开始真的不知道怎么做,那就只好把问题写下来找规律了,为了规律可见,我们将字符串的索引进行排序。如图:
我的建议是找到规律后自己实现一下代码,说实话我自己的代码也写得很乱(毕竟是小白)
s = input()
numRows = int(input())
def convert(s, numRows):
T = (numRows-1) * 2 # 周期
if T == 0: # 此时 numRows == 1,其实就不用变化
return s
else:
res = ''
count = 0 # 表示是第几行
while count < numRows:
index = count # index 表示索引
flag = True
while flag:
if count == 0 or count == numRows-1: # 第 0 行和最后一行不用考虑 V 字的右边
if index < len(s): # 判断是否越界
res += s[index]
index += T
else:
break
# 剩下的条件语句,都是考虑可能出现的情况
elif (index - count*2) > 0 and index < len(s) :
res += s[index-count*2] + s[index]
index += T
elif 0 < (index - count*2) < len(s) and index >= len(s):
res += s[index-count*2]
index += T
elif (index - count) == 0 and count < len(s): # 避免越界,比如 s = 'A', numRows = 3
res += s[count]
index += T
else:
flag = False
count += 1
return res
print(convert(s, numRows))
做法二
字符串是怎么变化的我们就怎么解决
还是以索引为例(其实直接用字符串也可以,因为不用刻意找规律)
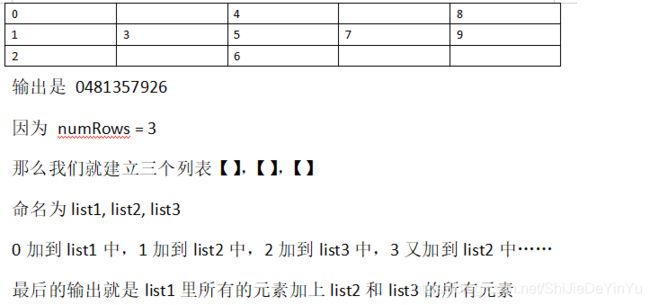
不过要把这样的思路转换成代码还是比前一个解法要困难一点的。
s = input()
numRows = int(input())
def convert(s, numRows):
if numRows == 1:
return s
# 建立一个二维数组
res_list = []
for i in range(numRows):
res_list.append([])
# 先把第一个字符加入到list1
res_list[0].append(s[0])
res = ""
index = 1
flag = 1 # 因为有list1 到 list2 到 list3,到 list2 这样的规律,我们就立一个 flag 来判断是正序还是逆序。我用 flag = 1 表示正序。
count = 1 # 表示 list几
while index < len(s):
if flag == 1:
res_list[count].append(s[index])
if index % (numRows - 1) == 0:
index += 1
flag = -flag
count -= 1
'''
何时从正序到逆序(或是从逆序到正序)我们又是找规律,发现当 index 是 (numrows-1) 的倍数时转换。这也是把index = 0 特别讨论的原因,0 % 任何数 == 0,但实际上index == 0 顺序并不改变
'''
else:
index += 1
count += 1
else:
res_list[count].append(s[index])
if index % (numRows - 1) == 0:
index += 1
flag = -flag
count += 1
else:
index += 1
count -= 1
for i in res_list:
for j in i:
res += j
return res
print(convert(s, numRows))