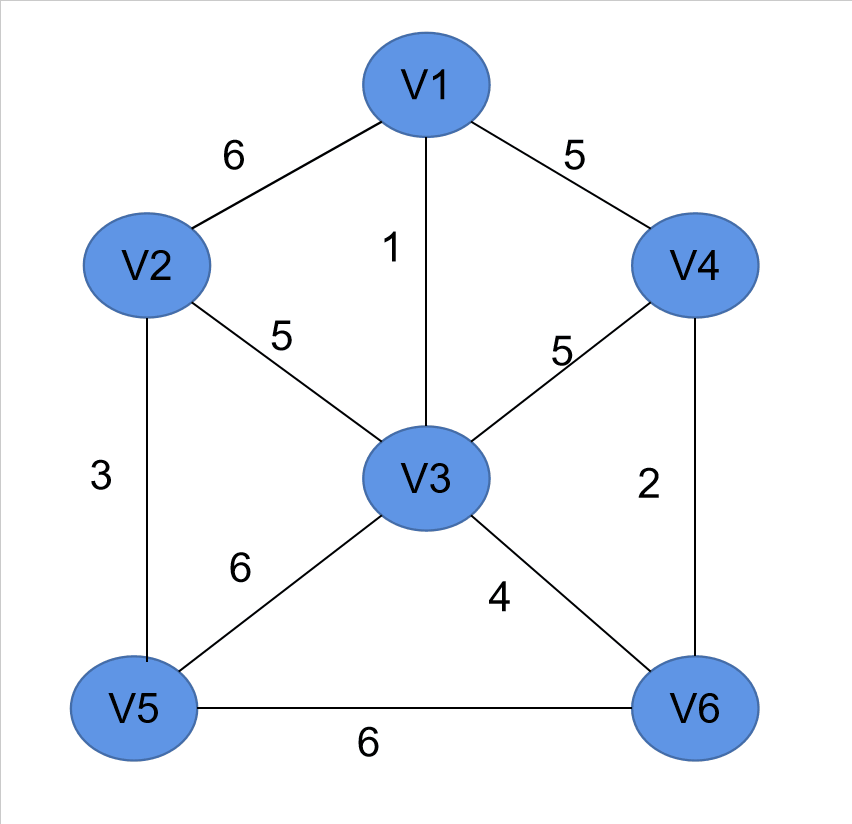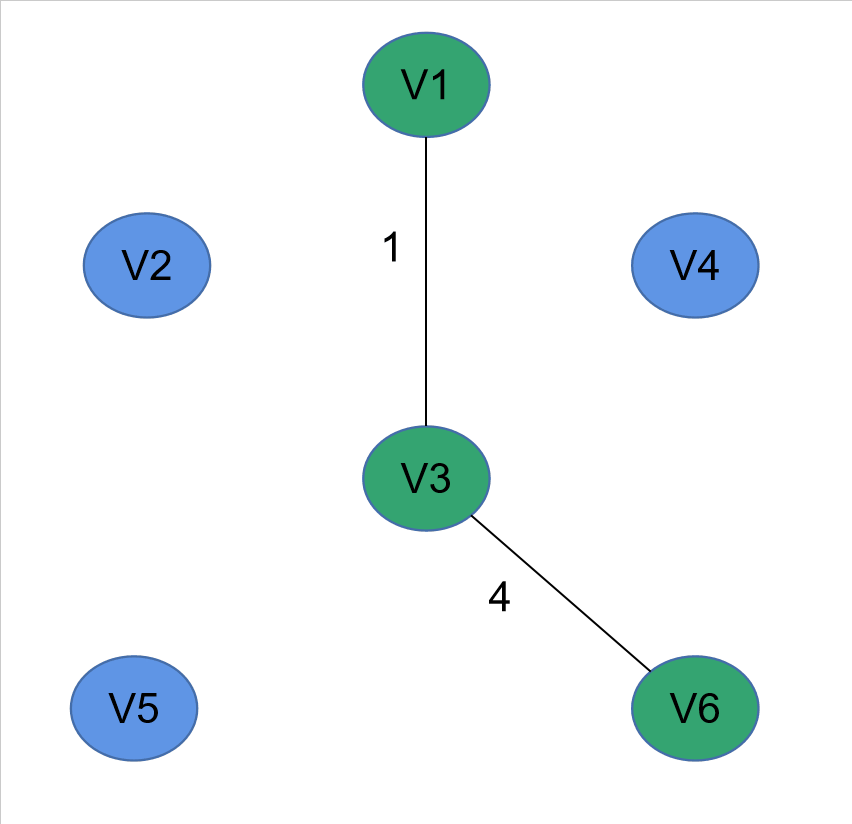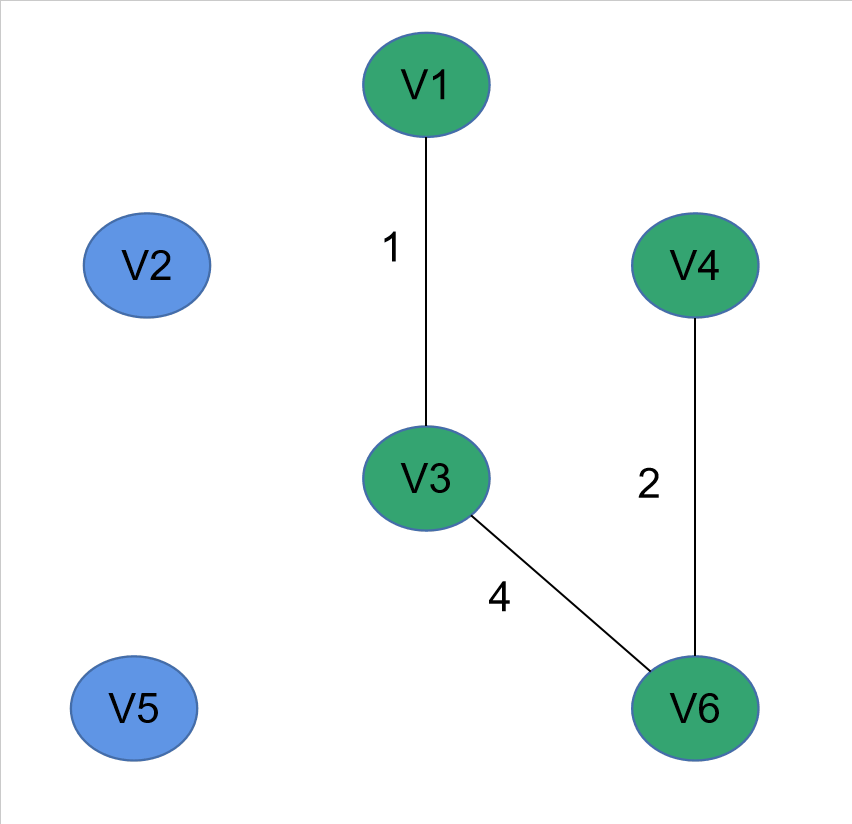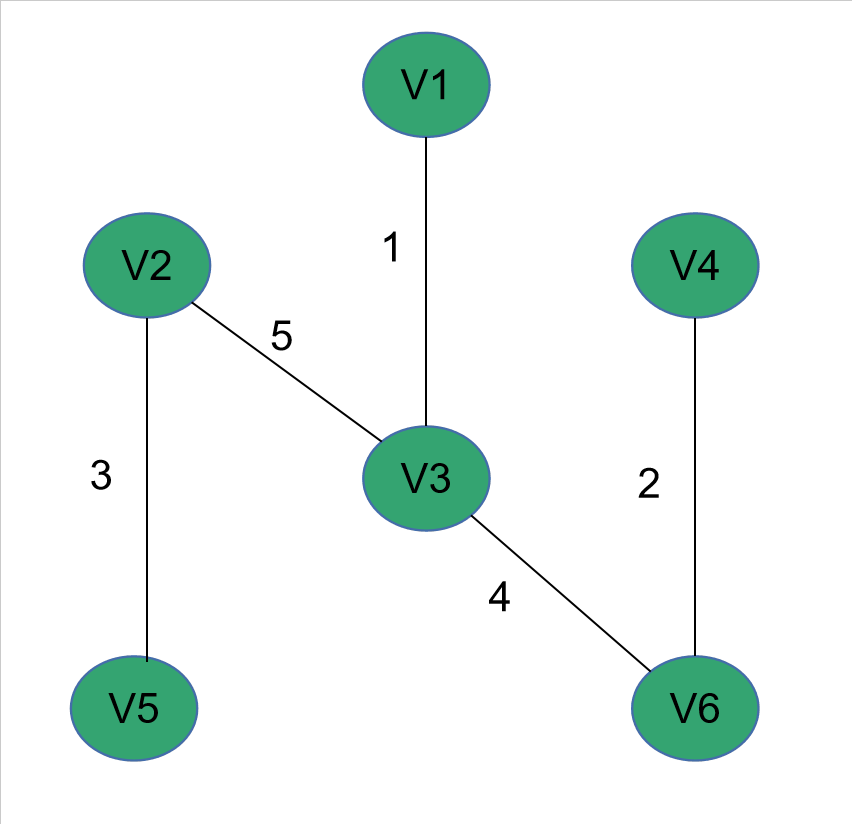
生成树(基础)
目录
一、生成树的相关概念
二、最小生成树的相关概念
(一)最小生成树的性质(MST性质)
(二)MST性质解释
三、Prim算法(普里姆算法)
(一)动态演示
(二)核心代码
(三)完整代码
(四)运行结果
四、Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法
(一)演示
(二)关键代码
(三)完整代码
(四)结果
一、生成树的相关概念
- 生成树:所有顶点均由边连接在一起,但不存在回路的图。
- 一个图可以有许多棵不同的生成树
- 所有生成树具有以下共同特点:
1.生成树的顶点个数和图的顶点个数相同
2.生成树是图的极小连通子图,去掉一条边则非连通
3.一个有n个顶点的连通图的生成树有n-1条边
4.在生成树中再加上一条边必然形成回路
5.生成树中任意两个顶点间的路径是唯一的 - 求无向图的生成树
1.对无向图进行遍历(深度或者广度优先)
2.所经过的边的集合 + 所有顶点 = 生成树 - 深度优先生成树:深度优先遍历得到的生成树
- 广度优先生成树:广度优先遍历得到的生成树
二、最小生成树的相关概念
- 最小生成树:给定一个无向网络,在该网的所有生成树中,使得各边权值最小的那棵生成树称为该网的最小生成树,也叫最小代价生成树。
(一)最小生成树的性质(MST性质)
- 1.设连通网 N = (V, { E })
2.U为V的非空子集
3.F = { (v1,v2) | (v1,v2)∈E,v1∈U,v2∈V - U }
4.设(u, v)是F中权值最小的边,则必存在一棵包含(u, v)的最小生成树
(二)MST性质解释
- 在生成树的构造过程中,图中n个顶点分属两个集合:
1.已经落在生成树的顶点集:U
2.尚未落在生成树上的顶点集:V-U
接下来则应在所有连通U中顶点和V-U中顶点的边中选取权值最小的边。
- 举例:
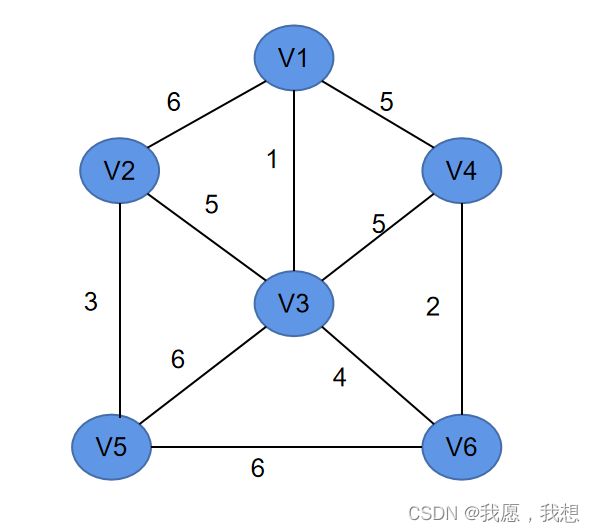
三、Prim算法(普里姆算法)
- 基本思想:从某一个顶点开始构建生成树;每次将代价最小的新顶点纳入生成树中,直到所有顶点都纳入为止
- 注:普利姆算法逐步增加U中的顶点, 可称为“加点法”。
- 时间复杂度:
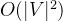
(一)演示
(二)核心代码
template
void Prim(MGraph G, T v)
//v是第一个进入集合U中的顶点的序号
{
closedge[v].lowcost = 0;//用于标记序号为v的顶点已经加入集合U中
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)//初始化closedge数组
{
if (j != v)
{
closedge[j].adjvex = v;
closedge[j].lowcost = G.edges[v][j];
}
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < G.n; i++)//找出剩下的n-1个顶点
{
int min = INF;//min用于记录暂时的生成树外的任意点到生成树内的任意点的最小权值
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)//在V-U中找出离U最近的顶点k
{
if (closedge[j].lowcost < min && closedge[j].lowcost != 0)
{
min = closedge[j].lowcost;
k = j;//记录当前最近顶点的编号
}
}
cout << "边" << G.vexs[closedge[k].adjvex] << "--" << G.vexs[k] << "权值:" << closedge[k].lowcost << endl;
closedge[k].lowcost = 0;//将序号为k的顶点加入到集合U
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)//仅仅考虑V-U中的顶点,更新closedge数组的内容
{
if (G.edges[k][j] < closedge[j].lowcost && closedge[j].lowcost != 0)
//如果集合U中序号为k的顶点到V-U中的其它顶点的权值小于当前最小权值,则更新
{
closedge[j].adjvex = k;
closedge[j].lowcost = G.edges[k][j];
}
}
}
} (三)完整代码
//MGraph.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100//顶点数目的最大值
#define INF 10000//宏定义常量“无穷”
#define MAXV 100
typedef char VertexType;//顶点的数据类型
typedef int EdgeType;//带权图中边上权值的数据类型
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MaxVertexNum];//顶点表(存放顶点)
EdgeType edges[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];//邻接矩阵,边表(存放任意两个顶点之间的距离)
int n, e;//图的当前顶点数和边数/弧数
}MGraph;
struct
{
int adjvex;
int lowcost;
}closedge[MAXV];
void CreatMat(MGraph& G, int A[][MAXV], int n);//由数组A[n][n]生成邻接矩阵G
//生成图的邻接矩阵
void DisMGraph(MGraph& G);//打印
template
void Prim(MGraph G, T v);//普里姆算法
template
void Prim(MGraph G, T v)
//v是第一个进入集合U中的顶点的序号
{
closedge[v].lowcost = 0;//用于标记序号为v的顶点已经加入集合U中
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)//初始化closedge数组
{
if (j != v)
{
closedge[j].adjvex = v;
closedge[j].lowcost = G.edges[v][j];
}
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < G.n; i++)//找出剩下的n-1个顶点
{
int min = INF;//min用于记录暂时的生成树外的任意点到生成树内的任意点的最小权值
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)//在V-U中找出离U最近的顶点k
{
if (closedge[j].lowcost < min && closedge[j].lowcost != 0)
{
min = closedge[j].lowcost;
k = j;//记录当前最近顶点的编号
}
}
cout << "边" << G.vexs[closedge[k].adjvex] << "--" << G.vexs[k] << "权值:" << closedge[k].lowcost << endl;
closedge[k].lowcost = 0;//将序号为k的顶点加入到集合U
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)//仅仅考虑V-U中的顶点,更新closedge数组的内容
{
if (G.edges[k][j] < closedge[j].lowcost && closedge[j].lowcost != 0)
//如果集合U中序号为k的顶点到V-U中的其它顶点的权值小于当前最小权值,则更新
{
closedge[j].adjvex = k;
closedge[j].lowcost = G.edges[k][j];
}
}
}
}
//MGraph1.cpp
#include"MGraph.h"
void CreatMat(MGraph& G, int A[][MAXV], int n)//由数组A[n][n]生成邻接矩阵G
{
G.n = n;
G.e = 0;
cout << "请依次输入顶点信息:";
for (int i = 1; i <=G.n; i++)
{
cin >> G.vexs[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
G.edges[i+1][j+1] = A[i][j];//i+1,j+1是为了从为了从二维数组[1][1]开始存储
if (A[i][j] != 0 && A[i][j] != INF)
{
G.e++;//边数加1
}
}
}
}
void DisMGraph(MGraph& G)//遍历打印
{
for (int i = 1; i <= G.n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= G.n; j++)
{
cout << G.edges[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} //Text.cpp
#include"MGraph.h"
int main()
{
MGraph G;
int A[][MAXV] = { {0,6,1,5,INF,INF},{6,0,5,INF,3,INF},{1,5,0,5,6,4},{5,INF,5,0,INF,2},{INF,3,6,INF,0,6},{INF,INF,4,2,6,0}};
CreatMat(G, A, 6);
cout << "图的邻接矩阵:" << endl;
DisMGraph(G);
cout << endl;
cout << "由Prim(普里姆)算法得到最小生成树是:"<(四)运行结果
四、Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法
- 基本思想: 是将各边按权值大小从小到大排列,接着从权值最低的边开始建立最小成本生成树,如果加入的边会造成回路就舍弃不用,直到加入n-1个边为止。
- 时间复杂度:
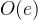
(一)演示
(二)核心代码
void Sort(struct Edge E[], int n)//对每条边进行从小到大排序
{
for (int i = n-1; i > 0; i--)//扫描次数
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (E[j].weight > E[j + 1].weight)
{
Swap(E[j], E[j + 1]);
//Swap(E[j].vex2, E[j + 1].vex2);
//Swap(E[j].weight, E[j + 1].weight);
}
}
}
}
void Kruskal(MGraph G)
{
struct Edge E[MAXV];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)//取邻接矩阵的下三角部分边
{
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
if (G.edges[i][j] != 0 && G.edges[i][j] != INF)
{
E[k].vex1 = i;
E[k].vex2 = j;
E[k].weight = G.edges[i][j];
k++;
}
}
}
Sort(E, k);
int vset[MAXV];//用于记录顶点是否属于同一集合的辅助数组
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)//初始化辅助数组
{
vset[i] = i;
}
k = 1;//k表示当前构造最小生成树的第几条边,初值为1
int j = 0;
while (k <= G.n - 1)
{
int m1 = E[j].vex1;
int m2 = E[j].vex2;
if (vset[m1] != vset[m2])
{
cout << "边" << E[j].vex1 << "--" << E[j].vex2 << " 权值为:" << E[j].weight << endl;
}
k++;//生成边数加1
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)//两个集合统一编号
{
if (vset[i] == vset[m2])
{
vset[i] = vset[m1];
}
}
j++;//扫描下一条边
}
}(三)完整代码
//MGraph.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MaxVertexNum 100//顶点数目的最大值
#define INF 10000//宏定义常量“无穷”
#define MAXV 100
typedef char VertexType;//顶点的数据类型
typedef int EdgeType;//带权图中边上权值的数据类型
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MaxVertexNum];//顶点表(存放顶点)
EdgeType edges[MaxVertexNum][MaxVertexNum];//邻接矩阵,边表(存放任意两个顶点之间的距离)
int n, e;//图的当前顶点数和边数/弧数
}MGraph;
struct Edge
{
int vex1;//边的起始顶点
int vex2;//边的终止顶点
int weight;//边的权值
};
void CreatMat(MGraph& G, int A[][MAXV], int n);//由数组A[n][n]生成邻接矩阵G
//生成图的邻接矩阵
void DisMGraph(MGraph& G);//打印
template
void Sort(struct Edge E[], int n);//对每条边进行从小到大排序
void Kruskal(MGraph G);//Kruskal算法
template
void Swap(T& a, T& b)
{
T tmp;
tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
//MGraph1.cpp
#include"MGraph.h"
void CreatMat(MGraph& G, int A[][MAXV], int n)//由数组A[n][n]生成邻接矩阵G
{
G.n = n;
G.e = 0;
cout << "请依次输入顶点信息:";
for (int i = 0; i > G.vexs[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
G.edges[i][j] = A[i][j];
if (A[i][j] != 0 && A[i][j] != INF)
{
G.e++;//边数加1
}
}
}
}
void DisMGraph(MGraph& G)//遍历打印
{
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < G.n; j++)
{
cout << G.edges[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void Sort(struct Edge E[], int n)//对每条边进行从小到大排序
{
for (int i = n-1; i > 0; i--)//扫描次数
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (E[j].weight > E[j + 1].weight)
{
Swap(E[j], E[j + 1]);
//Swap(E[j].vex2, E[j + 1].vex2);
//Swap(E[j].weight, E[j + 1].weight);
}
}
}
}
void Kruskal(MGraph G)
{
struct Edge E[MAXV];
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)//取邻接矩阵的下三角部分边
{
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
if (G.edges[i][j] != 0 && G.edges[i][j] != INF)
{
E[k].vex1 = i;
E[k].vex2 = j;
E[k].weight = G.edges[i][j];
k++;
}
}
}
Sort(E, k);
int vset[MAXV];//用于记录顶点是否属于同一集合的辅助数组
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)//初始化辅助数组
{
vset[i] = i;
}
k = 1;//k表示当前构造最小生成树的第几条边,初值为1
int j = 0;
while (k <= G.n - 1)
{
int m1 = E[j].vex1;
int m2 = E[j].vex2;
if (vset[m1] != vset[m2])
{
cout << "边" << E[j].vex1 << "--" << E[j].vex2 << " 权值为:" << E[j].weight << endl;
}
k++;//生成边数加1
for (int i = 0; i < G.n; i++)//两个集合统一编号
{
if (vset[i] == vset[m2])
{
vset[i] = vset[m1];
}
}
j++;//扫描下一条边
}
} //Text.cpp
#include"MGraph.h"
int main()
{
MGraph G;
int A[][MAXV] = { {0,6,1,5,INF,INF},{6,0,5,INF,3,INF},{1,5,0,5,6,4},{5,INF,5,0,INF,2},{INF,3,6,INF,0,6},{INF,INF,4,2,6,0}};
CreatMat(G, A, 6);
cout << "图的邻接矩阵:" << endl;
DisMGraph(G);
cout << endl;
cout << "由Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法得到最小生成树是:"<