2661. 找出叠涂元素 : 常规哈希表运用题
题目描述
这是 LeetCode 上的 「2661. 找出叠涂元素」 ,难度为 「中等」。
Tag : 「模拟」、「哈希表」、「计数」
给你一个下标从 开始的整数数组 arr 和一个 的整数矩阵 mat。
arr 和 mat 都包含范围 , 内的所有整数。
从下标 开始遍历 arr 中的每个下标 i ,并将包含整数 arr[i] 的 mat 单元格涂色。
请你找出 arr 中在 mat 的某一行或某一列上都被涂色且下标最小的元素,并返回其下标 。
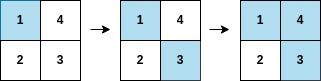
输入:arr = [1,3,4,2], mat = [[1,4],[2,3]]
输出:2
解释:遍历如上图所示,arr[2] 在矩阵中的第一行或第二列上都被涂色。
image explanation for example 2
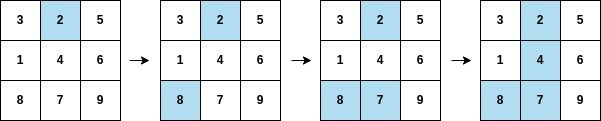
输入:arr = [2,8,7,4,1,3,5,6,9], mat = [[3,2,5],[1,4,6],[8,7,9]]
输出:3
解释:遍历如上图所示,arr[3] 在矩阵中的第二列上都被涂色。
提示:
-
arr中的所有整数互不相同 -
mat中的所有整数互不相同
哈希表
利用 mat 的数值各不相同,先使用「哈希表」对 mat 进行转存,以 为键, 为值,方便后续快速查询某个值所在位置。
创建数组 c1 和 c2,分别记录某行某列有多少单元格被涂色,如 c1[x] = a 代表第 行被涂色单元格数量为 个,c2[y] = b 代表第 列被涂色单元格数量为 个。
遍历所有的 ,查询到 的所在位置 后,更新 c1 和 c2,若某行或某列被完全涂色,返回当前下标。
Java 代码:
class Solution {
public int firstCompleteIndex(int[] arr, int[][] mat) {
int n = mat.length, m = mat[0].length;
Mapint[]> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
map.put(mat[i][j], new int[]{i, j});
}
}
int[] c1 = new int[n], c2 = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < n * m; i++) {
int[] info = map.get(arr[i]);
int x = info[0], y = info[1];
if (++c1[x] == m || ++c2[y] == n) return i;
}
return -1; // never
}
}
C++ 代码:
class Solution {
public:
int firstCompleteIndex(vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int n = mat.size(), m = mat[0].size();
unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> map;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
map[mat[i][j]] = make_pair(i, j);
}
}
vector<int> c1(n), c2(m);
for (int i = 0; i < n * m; i++) {
pair<int, int> info = map[arr[i]];
int x = info.first, y = info.second;
if (++c1[x] == m || ++c2[y] == n) return i;
}
return -1; // never
}
};
Python 代码:
class Solution:
def firstCompleteIndex(self, arr: List[int], mat: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n, m = len(mat), len(mat[0])
mapping = {mat[i][j]: (i, j) for i in range(n) for j in range(m)}
c1, c2 = [0] * n, [0] * m
for i in range(n * m):
x, y = mapping[arr[i]]
c1[x], c2[y] = c1[x] + 1, c2[y] + 1
if c1[x] == m or c2[y] == n: return i
return -1 # never
TypeScript 代码:
function firstCompleteIndex(arr: number[], mat: number[][]): number {
const n = mat.length, m = mat[0].length;
const map: { [key: number]: [number, number] } = {};
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {
map[mat[i][j]] = [i, j];
}
}
const c1 = new Array(n).fill(0), c2 = new Array(m).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < n * m; i++) {
const [x, y] = map[arr[i]];
if (++c1[x] == m || ++c2[y] === n) return i;
}
return -1; // never
};
- 时间复杂度:
- 空间复杂度:
最后
这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 No.2661 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。
在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。
为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。
在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。
更多更全更热门的「笔试/面试」相关资料可访问排版精美的 合集新基地