LangChain 16 通过Memory记住历史对话的内容
LangChain系列文章
- LangChain 实现给动物取名字,
- LangChain 2模块化prompt template并用streamlit生成网站 实现给动物取名字
- LangChain 3使用Agent访问Wikipedia和llm-math计算狗的平均年龄
- LangChain 4用向量数据库Faiss存储,读取YouTube的视频文本搜索Indexes for information retrieve
- LangChain 5易速鲜花内部问答系统
- LangChain 6根据图片生成推广文案HuggingFace中的image-caption模型
- LangChain 7 文本模型TextLangChain和聊天模型ChatLangChain
- LangChain 8 模型Model I/O:输入提示、调用模型、解析输出
- LangChain 9 模型Model I/O 聊天提示词ChatPromptTemplate, 少量样本提示词FewShotPrompt
- LangChain 10思维链Chain of Thought一步一步的思考 think step by step
- LangChain 11实现思维树Implementing the Tree of Thoughts in LangChain’s Chain
- LangChain 12调用模型HuggingFace中的Llama2和Google Flan t5
- LangChain 13输出解析Output Parsers 自动修复解析器
- LangChain 14 SequencialChain链接不同的组件
- LangChain 15根据问题自动路由Router Chain确定用户的意图

1. Memory 记忆
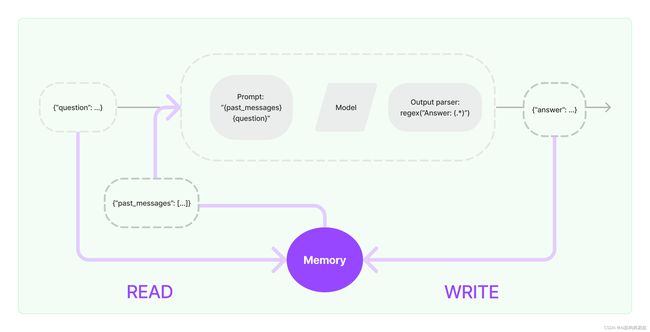
大多数LLM应用程序都有对话界面。对话的一个重要组成部分是能够引用先前在对话中介绍的信息。最基本的是,对话系统应该能够直接访问某些过去的信息窗口。更复杂的系统将需要具有一个世界模型,它不断更新,这使它能够维护有关实体及其关系的信息。
我们称这种存储关于过去交互的信息的能力为“记忆”。LangChain为系统添加记忆提供了许多实用工具。这些实用工具可以单独使用,也可以无缝地整合到链中。
记忆系统需要支持两个基本操作:读取和写入。请记住,每个链定义了一些核心执行逻辑,期望某些输入。其中一些输入直接来自用户,但一些输入可以来自记忆。链将在给定运行中两次与其记忆系统交互。
- 在接收到初始用户输入但在执行核心逻辑之前,链将从其记忆系统中读取并增强用户输入。
- 在执行核心逻辑但在返回答案之前,链将把当前运行的输入和输出写入记忆中,以便在将来的运行中可以引用它们。
2. 将内存构建到系统中
在任何内存系统中的两个核心设计决策是:
- 状态如何存储
- 状态如何查询
2.1 存储:聊天消息列表
任何记忆的基础都是所有聊天互动的历史。即使这些并非全部直接使用,也需要以某种形式存储。LangChain记忆模块的关键部分之一是一系列用于存储这些聊天消息的集成,从内存列表到持久性数据库。
- 聊天消息存储:如何处理聊天消息以及提供的各种集成。
2.2 查询:在聊天消息之上的数据结构和算法
保留聊天消息列表相当简单。不太简单的是建立在聊天消息之上的数据结构和算法,以便提供最有用的消息视图。
一个非常简单的记忆系统可能只返回每次运行最近的消息。一个稍微复杂一点的记忆系统可能会返回过去K条消息的简明总结。一个更复杂的系统可能会从存储的消息中提取实体,并且只返回当前运行中涉及的实体信息。
每个应用程序对于如何查询记忆都可能有不同的要求。记忆模块应该让简单的记忆系统易于入门,并且如果需要,也能够编写自定义系统。
- 记忆类型:LangChain支持的各种数据结构和算法所构成的记忆类型
3. 代码实现
让我们来看看LangChain中Memory实际上是什么样子。在这里,我们将介绍与任意记忆类互动的基础知识。
让我们来看看如何在链中使用ConversationBufferMemory。ConversationBufferMemory是记忆的一种极其简单的形式,它只是在缓冲区中保留聊天消息的列表,并将其传递到提示模板中。
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
memory.chat_memory.add_user_message("hi!")
memory.chat_memory.add_ai_message("what's up?")
在使用链式内存时,有一些关键概念需要理解。请注意,这里我们涵盖了对大多数类型的内存都有用的一般概念。每种个别的内存类型可能都有自己必须理解的参数和概念。
3.1 从内存中返回哪些变量
在进入链之前,会从内存中读取各种变量。这些变量有特定的名称,需要与链期望的变量相匹配。您可以通过调用memory.load_memory_variables({})来查看这些变量是什么。请注意,我们传入的空字典只是真实变量的占位符。如果您使用的内存类型依赖于输入变量,您可能需要传入一些变量。
print(memory.load_memory_variables({}))
输出结果
{'history': "Human: hi!\nAI: what's up?"}
在这种情况下,您可以看到load_memory_variables返回一个名为history的key。这意味着您的链条(很可能是您的提示)应该期望一个名为history的输入。通常您可以通过内存类的参数来控制这个变量。例如,如果您希望将内存变量返回到键chat_history中,您可以这样做:
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history")
memory.chat_memory.add_user_message("hi!")
memory.chat_memory.add_ai_message("what's up?")
print(memory.load_memory_variables({}))
输出结果
{'chat_history': "Human: hi!\nAI: what's up?"}
这些键的控制参数名称可能因内存类型而异,但重要的是要明白:(1)这是可控的,(2)如何控制它。
3.2 Memory是string字符串还是chat list消息列表
最常见的记忆类型之一涉及返回聊天消息列表。这些可以作为单个字符串返回,全部连接在一起(当它们将被传递到LLMs时很有用),或者作为ChatMessages列表返回(当它们被传递到ChatModels时很有用)。
默认情况下,它们作为单个字符串返回。为了返回消息列表,您可以设置return_messages=True
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
memory.chat_memory.add_user_message("hi!")
memory.chat_memory.add_ai_message("what's up?")
print(memory.load_memory_variables({}))
输出结果
{'chat_history': [HumanMessage(content='hi!', additional_kwargs={}, example=False),
AIMessage(content='what's up?', additional_kwargs={}, example=False)]}
3.3 什么Keys保存在内存中
通常情况下,链条会接收或返回多个输入/输出键。在这种情况下,我们如何知道要保存哪些键到聊天消息历史记录中?这通常可以通过内存类型的input_key和output_key参数来控制。这些参数默认为None-如果只有一个输入/输出键,则可以直接使用它。但是,如果有多个输入/输出键,则必须指定要使用哪一个的名称。
最后,让我们来看看如何在一个链中使用这个。我们将使用LLMChain,并展示如何同时使用LLM和ChatModel。
# 导入 Langchain 库的 ChatOpenAI 类,用于与 OpenAI 聊天模型进行交互。
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
# 导入 Langchain 库的不同提示模板类,用于构建会话提示。
from langchain.prompts import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
MessagesPlaceholder,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
# 导入 Langchain 的 LLMChain 类,用于创建语言模型链。
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
# 导入 Langchain 的 ConversationBufferMemory 类,用于存储和管理会话记忆。
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
# 导入 dotenv 库,用于从 .env 文件加载环境变量,管理敏感数据,如 API 密钥。
from dotenv import load_dotenv
# 调用 load_dotenv 函数来加载 .env 文件中的环境变量。
load_dotenv()
# 创建 ChatOpenAI 的实例。
llm = ChatOpenAI()
# 创建聊天提示模板,包含一个系统消息、一个聊天历史占位符和一个人类消息模板。
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate(
messages=[
SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(
"You are a nice chatbot having a conversation with a human."
),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{question}")
]
)
# 创建一个会话记忆,用于存储和返回会话中的消息。
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
# 创建一个 LLMChain 实例,包括语言模型、提示、详细模式和会话记忆。
conversation = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt,
verbose=True,
memory=memory
)
# 使用会话链处理第一个问题,并打印回应。
response = conversation({"question": "hi"})
print(response)
# 使用相同的会话链处理第二个问题,并打印回应。
response = conversation({"question": "how are you?"})
print(response)
输出
zgpeace at zgpeaces-MBP in ~/Workspace/LLM/langchain-llm-app (develop●) (.venv)
$ python Memory/memory_theory.py
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
System: You are a nice chatbot having a conversation with a human.
Human: hi
> Finished chain.
{'question': 'hi', 'chat_history': [HumanMessage(content='hi'), AIMessage(content='Hello! How can I assist you today?')], 'text': 'Hello! How can I assist you today?'}
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
System: You are a nice chatbot having a conversation with a human.
Human: hi
AI: Hello! How can I assist you today?
Human: how are you?
> Finished chain.
{'question': 'how are you?', 'chat_history': [HumanMessage(content='hi'), AIMessage(content='Hello! How can I assist you today?'), HumanMessage(content='how are you?'), AIMessage(content="Thank you for asking! As an AI, I don't have feelings, but I'm here to help you. How can I assist you today?")], 'text': "Thank you for asking! As an AI, I don't have feelings, but I'm here to help you. How can I assist you today?"}
代码
https://github.com/zgpeace/pets-name-langchain/tree/develop
参考
https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/memory/