初学者:java练习题———含答案------对象序列化(7)
import java.io.*;
class Student implements Serializable {
String id; //学号
String name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
//float average; //平均成绩
transient float average; //平均成绩,测试一下,有transient和没有transient结果有何不同。
//构造方法
Student(String s_id, String s_name, int s_age, float s_average) {
id = s_id;
name = s_name;
age = s_age;
average = s_average;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public float getAverage() {
return average;
}
public void setAverage(float average) {
this.average = average;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student: 学号=" + id + "\t姓名=" + name + "\t年龄=" + age + "\t平均成绩=" + average;
}
}
public class SerializableDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student zhang = new Student("0712345601","张小三",19,87.6f);
Student li = new Student("0712345602","李阿四",21,91.3f);
Student wang = new Student("0712345603","王连五",20,77.2f);
try {
FileOutputStream file_out = new FileOutputStream("Student.dat");
ObjectOutputStream object_out = new ObjectOutputStream(file_out);
object_out.writeObject(zhang);
object_out.writeObject(li);
object_out.writeObject(wang);
object_out.close();
}
catch(IOException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
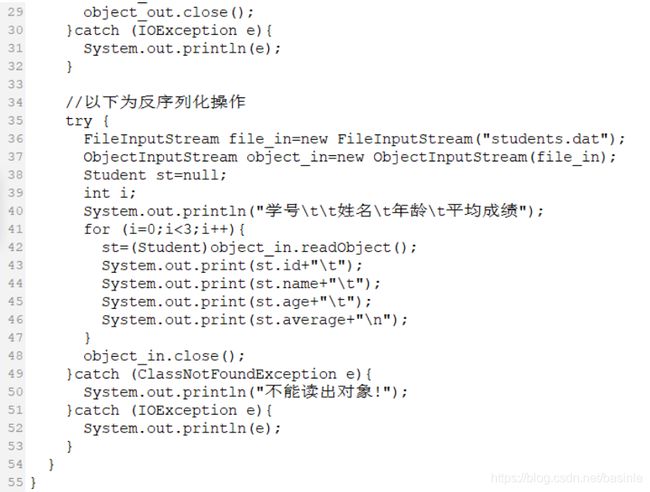
try {
FileInputStream file_in = new FileInputStream("Student.dat");
ObjectInputStream object_in = new ObjectInputStream(file_in);
Student st = null;
int i;
System.out.println("学号\t\t姓名\t年龄\t平均成绩");
for(i=0;i<3;i++) {
st = (Student)object_in.readObject();
System.out.print(st.id + "\t");
System.out.print(st.name + "\t");
System.out.print(st.age + "\t");
System.out.println(st.average + "\n");
}
object_in.close();
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("不能读出对象!");
}catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
答案:略
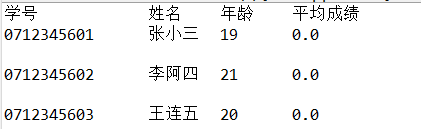
运行结果为
2. 自定义序列化 ,编辑编译运行以下程序 ,并说明为什新建学生对象的总评成绩 total 与读入对象 student 的总评成绩为什么不一致?
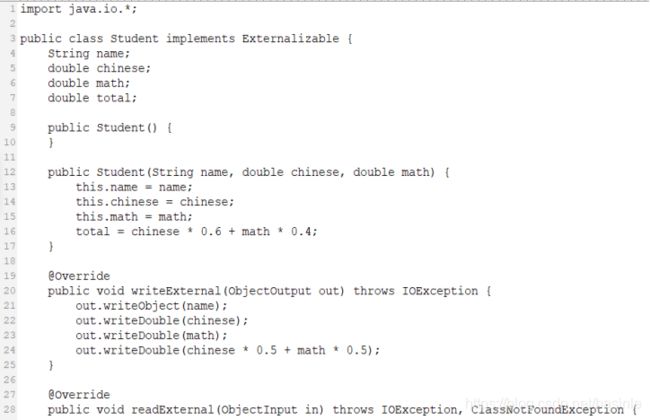
import java.io.*;
public class StudentEx implements Externalizable {
private String id; //学号
private String name; //姓名
private double chinese; //语文成绩
private double math; //数学成绩
//private double average; //平均成绩
transient private double average; //平均成绩,排除在序列化之外,思考一下,此处的transient是否有用呢?
public StudentEx() { //默认构造方法
}
//参数化构造方法
public StudentEx(String id, String name, double chinese, double math) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
this.average = chinese * 0.6 + math * 0.4;
}
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput oo) throws IOException {
oo.writeObject(id);
oo.writeObject(name);
oo.writeDouble(chinese);
oo.writeDouble(math);
//oo.writeDouble(chinese * 0.5 + math * 0.5);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput oi) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
id = (String)oi.readObject();
name = (String)oi.readObject();
chinese = oi.readDouble();
math = oi.readDouble();
//average = oi.readDouble();
average = chinese * 0.5 + math * 0.5;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getChinese() {
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(double chinese) {
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public double getMath() {
return math;
}
public void setMath(double math) {
this.math = math;
}
public double getAverage() {
return average;
}
public void setAverage(double average) {
this.average = average;
}
public void setAverage(double chinese, double math) {
this.average = chinese * 0.6 + math * 0.4;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String str = "StudentEx: 学号=" + id + " 姓名=" + name + " 语文=" + chinese + " 数学=" + math + " 平均=" + average;
return str;
}
}
StudentExText
import java.io.*;
public class StudentExTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StudentEx stu1 = new StudentEx("0712345602", "王五", 88, 92);
System.out.println("新建对象:" + stu1);
StudentEx stu2 = new StudentEx("0712345609", "李四", 95, 91);
System.out.println("新建对象:" + stu2);
StudentEx stu[];
try {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("StudentEx.dat"));
stu1.writeExternal(oos);
System.out.println("对象王五写入到文件中。");
stu2.writeExternal(oos);
System.out.println("对象李四写入到文件中。");
oos.close();
System.out.println("完成对象写入到文件。");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("StudentEx.dat"));
stu = new StudentEx[2];
stu[0] = new StudentEx();
stu[0].readExternal(ois);
System.out.println("从文件StudentEx.dat中读取第一个对象。\n" + stu[0]);
stu[1] = new StudentEx();
stu[1].readExternal(ois);
System.out.println("从文件StudentEx.dat中读取第二个对象。\n" + stu[1]);
System.out.println("从文件读取对象已完成!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
SerialInheritTest
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class SerialInheritTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Master ma = new Master("0712345601", "张三", new Date(0), "广州", "软件工程");
try {
System.out.println("开始写研究生记录");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("Master.dat");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(ma);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
System.out.println("研究生记录写文件完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//读取记录
Master m2;
try {
System.out.println("从文件读取研究生记录");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("Master.dat");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
m2 = (Master)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println("读取完成,读入的研究生记录:" + m2);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//非序列化的父类?
class StudentBas {
String id;
String name;
Date birthday;
public StudentBas(String id, String name, Date birthday) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
//测试一下没有默认构造方法的情况,程序可正确执行吗?
public StudentBas() {
super();
id = "0700000000";
name = "无名氏";
birthday = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "学号=" + id + "\t姓名=" + name + "\t生日=" + birthday;
}
}
//序列化的子类定义
class Master extends StudentBas implements Serializable {
static final long serialVersionUID = 0121231212;
String address;
String major;
public Master(String id, String name, Date birthday, String address, String major) {
super(id, name, birthday);
this.address = address;
this.major = major;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "\t地址=" + address + "\t专业=" + major;
}
}