基于 OpenVINO Python API 部署 RT-DETR 模型
作者:颜国进 英特尔边缘计算创新大使
RT-DETR是在DETR模型基础上进行改进的,一种基于 DETR 架构的实时端到端检测器,它通过使用一系列新的技术和算法,实现了更高效的训练和推理,我们将将在Python、C++、C# 三个平台实现OpenVINO 部署RT-DETR模型实现深度学习推理加速, 在本文中,我们将首先介绍基于 OpenVINO Python API 部署 RT-DETR 模型。
该项目所使用的全部代码已经在GitHub上开源,并且收藏在OpenVINO-CSharp-API项目里,项目所在目录链接为:
https://github.com/guojin-yan/OpenVINO-CSharp-API/tree/csharp3.0/tutorial_examples也可以直接访问该项目,项目链接为:https://github.com/guojin-yan/RT-DETR-OpenVINO.git
1. RT-DETR
飞桨在去年 3 月份推出了高精度通用目标检测模型 PP-YOLOE ,同年在 PP-YOLOE 的基础上提出了 PP-YOLOE+。而继 PP-YOLOE 提出后,MT-YOLOv6、YOLOv7、DAMO-YOLO、RTMDet 等模型先后被提出,一直迭代到今年开年的 YOLOv8。
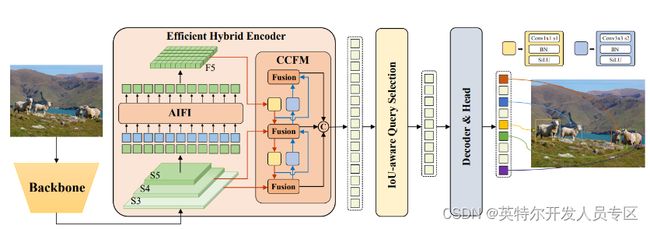
YOLO 检测器有个较大的待改进点是需要 NMS 后处理,其通常难以优化且不够鲁棒,因此检测器的速度存在延迟。DETR是一种不需要 NMS 后处理、基于 Transformer 的端到端目标检测器。百度飞桨正式推出了——RT-DETR (Real-Time DEtection TRansformer) ,一种基于 DETR 架构的实时端到端检测器,其在速度和精度上取得了 SOTA 性能。
RT-DETR是在DETR模型基础上进行改进的,它通过使用一系列新的技术和算法,实现了更高效的训练和推理。具体来说,RT-DETR具有以下优势:
1、实时性能更佳:RT-DETR采用了一种新的注意力机制,能够更好地捕获物体之间的关系,并减少计算量。此外,RT-DETR还引入了一种基于时间的注意力机制,能够更好地处理视频数据。
2、精度更高:RT-DETR在保证实时性能的同时,还能够保持较高的检测精度。这主要得益于RT-DETR引入的一种新的多任务学习机制,能够更好地利用训练数据。
3、更易于训练和调参:RT-DETR采用了一种新的损失函数,能够更好地进行训练和调参。此外,RT-DETR还引入了一种新的数据增强技术,能够更好地利用训练数据。
2. OpenVINO
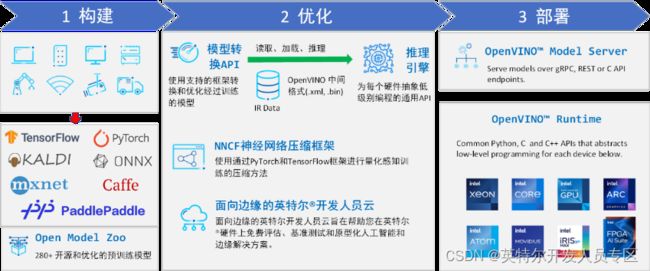
英特尔发行版 OpenVINO™工具套件基于oneAPI 而开发,可以加快高性能计算机视觉和深度学习视觉应用开发速度工具套件,适用于从边缘到云的各种英特尔平台上,帮助用户更快地将更准确的真实世界结果部署到生产系统中。通过简化的开发工作流程, OpenVINO™可赋能开发者在现实世界中部署高性能应用程序和算法。
OpenVINO™ 2023.1于2023年9月18日发布,该工具包带来了挖掘生成人工智能全部潜力的新功能。生成人工智能的覆盖范围得到了扩展,通过PyTorch*等框架增强了体验,您可以在其中自动导入和转换模型。大型语言模型(LLM)在运行时性能和内存优化方面得到了提升。聊天机器人、代码生成等的模型已启用。OpenVINO更便携,性能更高,可以在任何需要的地方运行:在边缘、云中或本地。
3. 环境配置
在该项目中主要包括两个环境的配置,一个是模型的下载,另一个是模型转换与部署,为了更好的大家复现该项目,所以提供主要的环境配置:
3.1 模型下载环境
paddlepaddle:2.5.1
imageio:2.31.5
imgaug:0.4.0
onnx=1.13.0
opencv-python=4.5.5.64
paddle2onnx:0.5
paddledet3.2 模型部署环境
Numpy:1.26.0
opencv-python:4.8.1.78
openvino:2023.1.0
openvino-telemetry:2023.2.0
pillow:10.0.1
python:3.10.134 模型下载与转换
PaddleDetection https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection提供了预训练模型以及模型训练教程,大家可以基于该教程训练自己的模型。在该项目中我们基于预训练模型展开部署案例测试,下面我们根据官方教程导出推理模型。
4.1 PaddlePaddle模型下载
首先参考[PaddleDetection安装文档]安装PaddlePaddle和PaddleDetection,其中PaddlePaddle要安装最新版本才可以导出RT-DETR模型。安装完成后,通过命令行下载该模型:
cd PaddleDetection
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/rtdetr/rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.yml -o weights=https://bj.bcebos.com/v1/paddledet/models/rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.pdparams trt=True --output_dir=output_inference下表为导出模型输入输出节点信息:
| Inout |
Output |
||||
| Node Name |
im_shape |
image |
scale_factor |
reshape2_95.tmp_0 |
tile_3.tmp_0 |
| Data Type |
flaot32 |
flaot32 |
flaot32 |
flaot32 |
int32 |
| Data Shape |
[?, 2] |
[?, 3, 640, 640] |
[?, 2] |
[?, 6] |
[?] |
通过该表,我们可以看出,该模型存在三个输入与两个输出,其中输入“im_shape”与“scale_factor”节点信息主要是该模型集成了部分后处理内容,如果大家对这种多输入的模型使用不太习惯,在下次文章中,我们将讲解如何个导出并部署不含后处理的模型部署流程。
因此该模型中比较关键的节点为“image”图片数据输入以及“reshape2_95.tmp_0”输出节点,其中模型输出的格式为: [clasid, scores, x, y, w, h]。
4.2 IR模型转换
接下来我们将模型转换为IR格式,首先将模型转ONNX格式:
paddle2onnx --model_dir=./output_inference/rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco/ --model_filename model.pdmodel --params_filename model.pdiparams --opset_version 16 --save_file rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.onnx由于导出来的模型是动态形状,未固定bath_size信息,所以我们可以通过OpenVINO模型优化工具对模型的输入形状进行设置,命令如下:
ovc rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.onnx –input “ image[1,3,640,640], im_shape[1,2], scale_factor[1,2]”最后我们可以获取到转憨厚的模型“ rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.xml”以及“rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.bin”文件。
5. Python代码实现
5.1 模型推理流程实现
在Python代码中我们定义了一个RT-DETR模型推理方法:
def rtdert_infer(model_path, image_path, device_name, lable_path, postprocess=True):该方法主要实现了RT-DETR模型推理全流程,包括模型读取与加载、文件的读取与预处理、模型推理、结果处理以及结果展示。方法输入为:
model_path:推理模型路径
image_path:预测图片路径
device_name:加速推理设备名称
lable_path,:识别类别文件
postprocess:模型是否包含后处理,在本文中我们只讲解包含后处理的模型,因此默认为True。
1. 加载推理模型
这一步主要实现初始化Core、读取本地模型以及将模型编译到本地,代实现代码如下述代码所示:
ie_core = Core()
model = ie_core.read_model(model=model_path)
compiled_model = ie_core.compile_model(model=model, device_name=device_name)2. 预处理图片数据
这一步主要对读取的本地图片数据进行处理,在此处我们定义了一个RtdetrProcess Class专门用于处理RT-DETR模型的输入输出数据,代码实现如下所示:
image = cv.imread(image_path)
rtdetr_process = RtdetrProcess([640,640],lable_path)
im, im_info= rtdetr_process.preprocess(image)3. 加载推理数据和模型推理
这一步主要实现模型推理数据的加载以及进行模型推理,由于我们预测的模型是自带后处理的模型,因此模型输入有三个,分别是“im_shape”、“scale_factor”和“ image“。
im_shape:表示模型的输入形状,此处输入为[640, 640];
scale_factor:表示图片的缩放比,为模型输入/图像形状;
image:表示图像归一化后的数据矩阵,形状为[1, 3, 640, 640];、
最后将模型输入字典带入到编译好的模型中进行模型推理,获取推理结果。
inputs = dict()
inputs["image"] = np.array(im).astype('float32')
inputs["scale_factor"] = np.array(im_info['scale_factor']).reshape(1,2).astype('float32')
inputs["im_shape"] = np.array([640.0,640.0]).reshape(1,2).astype('float32')
results = compiled_model(inputs=inputs)4. 处理推理结果
上一步中已经获取到的模型推理结果,最后将模型推理结果带入到我们定义中的后处理方法中,左后获取模型预测结果。
re = rtdetr_process.postprocess(results[compiled_model.output(0)])
new_image=rtdetr_process.draw_box(image,re)
cv.imshow("result",new_image)
cv.waitKey(0)5.2 模型数据处理方法实现
1. 定义RtdetrProcess
class RtdetrProcess(object):
def __init__(self, target_size, label_path=None, threshold=0.5, interp=cv.INTER_LINEAR):
self.im_info = dict()
self.target_size =target_size
self.interp = interp
self.threshold = threshold
if label_path is None:
self.labels = []
self.flabel = False
else:
self.labels = self.read_lable(label_path=label_path)
self.flabel = True2. 输入数据处理方法
def preprocess(self,im):
assert len(self.target_size) == 2
assert self.target_size[0] > 0 and self.target_size[1] > 0
origin_shape = im.shape[:2]
resize_h, resize_w = self.target_size
im_scale_y = resize_h / float(origin_shape[0])
im_scale_x = resize_w / float(origin_shape[1])
out_im = cv.cvtColor(im,cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
out_im = cv.resize(
out_im.astype('float32'),
None,
None,
fx=im_scale_x,
fy=im_scale_y,
interpolation=self.interp)
self.im_info['im_shape'] = np.array(im.shape[:2]).astype('float32')
self.im_info['scale_factor'] = np.array([im_scale_y, im_scale_x]).astype('float32')
scale = 1.0 / 255.0
out_im *= scale
out_im = out_im.transpose((2, 0, 1)).copy()
return np.expand_dims(out_im.astype('float32'),0), self.im_info3. 预测结果数据处理方法
def postprocess(self,scores,bboxs=None):
results = []
if bboxs is None:
scores = np.array(scores).astype('float32')
for l in scores:
if(l[1]>=self.threshold):
re = dict()
re["clsid"]=int(l[0])
if(self.flabel):
re["label"]=self.labels[int(l[0])]
else:
re["label"]=int(l[0])
re["score"]=l[1]
bbox=[l[2],l[3],l[4],l[5]]
re["bbox"]=bbox
results.append(re)
else:
scores = np.array(scores).astype('float32')
bboxs = np.array(bboxs).astype('float32')
for s,b in zip(scores,bboxs):
s = self.sigmoid(s)
if(np.max(np.array(s)>=self.threshold)):
ids = np.argmax(np.array(s))
re = dict()
re["clsid"]=int(ids)
if(self.flabel):
re["label"]=self.labels[int(ids)]
else:
re["label"]=int(ids)
re["score"]=s[ids]
cx=(b[0]*640.0)/self.im_info["scale_factor"][1]
cy=(b[1]*640.0)/self.im_info["scale_factor"][0]
w=(b[2]*640.0)/self.im_info["scale_factor"][1]
h=(b[3]*640.0)/self.im_info["scale_factor"][0]
bbox=[cx-w/2.0,
cy-h/2.0,
cx+w/2.0,
cy+h/2.0]
re["bbox"]=bbox
results.append(re)
return results6. 预测结果展示
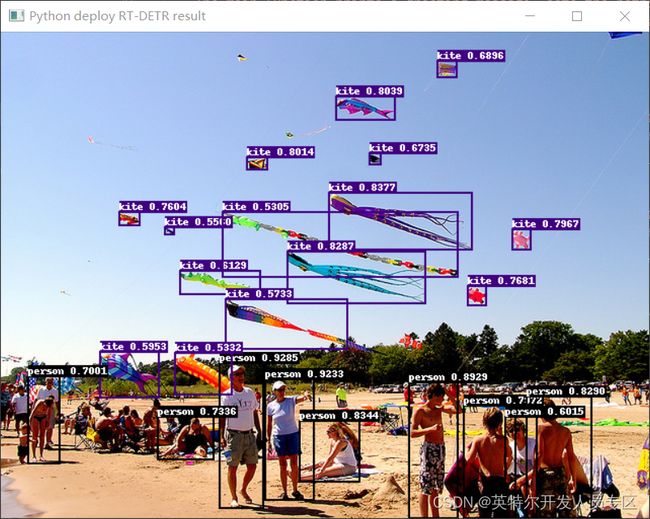
最后通过上述代码,我们最终可以直接实现RT-DETR模型的推理部署,RT-DETR与训练模型采用的是COCO数据集,最终我们可以获取预测后的图像结果,如图所示:
上图中展示了RT-DETR模型预测结果,同时,我们对模型图里过程中的关键信息以及推理结果进行了打印:
[INFO] This is an RT-DETR model deployment case using Python!
[INFO] Model path: E:\Model\rtdetr_r50vd_6x_coco.onnx
[INFO] Device name: CPU
[INFO] The input path: E:\GitSpace\RT-DETR-OpenVINO\image\000000570688.jpg
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.9284, left_top:[215.03,327.88],right_bottom:[259.24,469.64]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.9232, left_top:[260.34,343.99],right_bottom:[309.42,461.80]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.8929, left_top:[402.26,346.80],right_bottom:[451.54,479.55]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.8382, left_top:[323.52,159.82],right_bottom:[465.93,214.78]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.8342, left_top:[294.05,384.59],right_bottom:[354.15,443.96]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.8284, left_top:[518.88,360.37],right_bottom:[583.88,480.00]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.8281, left_top:[282.11,217.29],right_bottom:[419.96,267.66]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.8043, left_top:[330.01,64.70],right_bottom:[389.58,86.40]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.8016, left_top:[242.46,124.74],right_bottom:[263.87,135.74]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.7972, left_top:[456.74,369.06],right_bottom:[508.27,479.42]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.7970, left_top:[504.63,195.20],right_bottom:[523.44,214.82]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.7681, left_top:[460.08,251.92],right_bottom:[479.02,269.19]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.7601, left_top:[116.23,178.53],right_bottom:[137.02,190.61]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.7330, left_top:[154.12,380.38],right_bottom:[210.76,421.32]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.6998, left_top:[26.77,340.99],right_bottom:[58.48,425.10]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.6895, left_top:[430.29,29.91],right_bottom:[450.06,44.32]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.6739, left_top:[363.20,120.95],right_bottom:[375.84,130.11]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.6130, left_top:[176.50,236.77],right_bottom:[256.62,258.32]
[INFO] class_id:0, label:person, confidence:0.6001, left_top:[497.35,380.34],right_bottom:[529.73,479.49]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.5956, left_top:[97.84,316.90],right_bottom:[156.75,360.25]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.5730, left_top:[221.56,264.66],right_bottom:[342.60,312.92]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.5555, left_top:[161.12,193.06],right_bottom:[171.45,199.78]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.5332, left_top:[171.17,317.08],right_bottom:[228.08,357.65]
[INFO] class_id:33, label:kite, confidence:0.5322, left_top:[218.97,178.13],right_bottom:[451.95,241.61]7. 总结
在本项目中,我们介绍了OpenVINO Python API 部署自带后处理的RT-DETR模型的案例,并结合该模型的处理方式封装完整的代码案例,实现了在 Intel 平台使用OpenVINO 加速深度学习模型,有助于大家以后落地RT-DETR模型在工业上的应用。为了更好地大家落地RT-DETR模型,我们不仅开发了在Python、C++、C# 三个平台上的案例代码,还结合大家的模型部署习惯对该模型进行了裁剪,实现了去除掉后处理的单输入模型的部署案例。
在本文中。由于篇幅有限,对于其他编程平台的实现以及不包含后处理的模型的部署案例,将在后续的文章中推出,请大家关注本平台后续发布的文章:《基于 OpenVINO C++ API 部署 RT-DETR 模型》以及《基于 OpenVINO Python C# 部署 RT-DETR 模型》。如果大家有兴趣,可以先关注本项目代码仓库,获取项目实现源码。