机器学习---道路拥堵案例
一、道路拥堵情况预测
1、构建训练集:
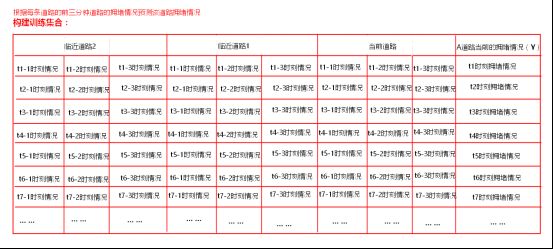
每条道路的拥堵情况不仅和当前道路前一个时间点拥堵情况有关系,还和与这条道路临近的其他道路的拥堵情况有关。甚至还和昨天当前时间点当前道路是否拥堵有关联。我们可以根据这个规律,构建训练集,预测一条道路拥堵情况。
假设现在要训练一个模型:使用某条道路最近三分钟拥堵的情况,预测该条道路下一分钟的拥堵情况。如何构建训练集?
构建的训练集有什么样的特点,依靠训练集训练的模型就具备什么样的功能。
2、步骤
1)、计算道路每分钟经过的车辆数和速度总和,可以得到道路实时拥堵情况
2)、预测道路的拥堵情况受当前道路附近道路拥堵的情况,受这几个道路过去几分钟道路拥堵的情况。预测道路拥堵情况可以根据附近每条道路和当前道路前3分钟道路拥堵的情况来预测。用附近每条道路和当前道路前3分钟道路的拥堵情况来当做维度。统计这些道路过去5个小时内每分钟的前3分钟拥堵情况构建数据集。
3)、训练逻辑回归模型
4)、保存模型
5)、使用模型预测道路的拥堵情况
3、道路拥堵预测注意问题:
注意:提高模型的分类数,会提高模型的抗干扰能力。比如道路拥堵情况就分为两类:“畅通”、“拥堵”,如果模型针对一条本来属于“畅通”分类的数据预测错了,那么预测结果只能就是“拥堵”,那么就发生了质的改变。
如果我们将道路拥堵情况分为四类:“畅通”,“比较畅通”,“比较拥堵”,“拥堵”。如果模型针对一条本来数据“畅通”分类的数据预测错了,那么预测结果错的情况下就不是只有“拥堵”这个情况,有可能是其他三类的一种,也有一定的概率预测分类为“比较畅通”,那么就相当于提高了模型的抗干扰能力。
二、道路拥堵情况代码
1、实时分析Kafka中数据,将结果存入Redis
1.val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("CarEventCountAnalytics")
2.conf.set("spark.streaming.kafka.consumer.cache.enabled","false")
3.conf.setMaster("local[*]")
4.val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(5))
5.val topics = Set("car_events")
6.val brokers = "mynode1:9092,mynode2:9092,mynode3:9092"
7.val kafkaParams = Map[String, Object](
8. "bootstrap.servers" -> brokers,
9. "key.deserializer" -> classOf[StringDeserializer],
10. "value.deserializer" -> classOf[StringDeserializer],
11. "group.id" -> "predictGroup",//
12. "auto.offset.reset" -> "earliest",
13. "enable.auto.commit" -> (false: java.lang.Boolean)//默认是true
14.)
15.val dbIndex = 1
16.// Create a direct stream
17.val kafkaStream: InputDStream[ConsumerRecord[String, String]] = KafkaUtils.createDirectStream[String, String](
18. ssc,
19. PreferConsistent,
20. Subscribe[String, String](topics, kafkaParams)
21.)
22.val events: DStream[JSONObject] = kafkaStream.map(line => {
23. //JSONObject.fromObject 将string 转换成jsonObject
24. val data: JSONObject = JSONObject.fromObject(line.value())
25. println(data)
26. data
27.})
28.
29.val carSpeed : DStream[(String, (Int, Int))]= events.map(jb => (jb.getString("camera_id"),jb.getInt("speed")))
30..mapValues((speed:Int)=>(speed,1))
31..reduceByKeyAndWindow((a:Tuple2[Int,Int], b:Tuple2[Int,Int]) => {(a._1 + b._1, a._2 + b._2)},Seconds(60),Seconds(60))
32.
33.carSpeed.foreachRDD(rdd => {
34. rdd.foreachPartition(partitionOfRecords => {
35. val jedis = RedisClient.pool.getResource
36. partitionOfRecords.foreach(pair => {
37. val camera_id = pair._1
38. val speedTotal = pair._2._1
39. val CarCount = pair._2._2
40. val now = Calendar.getInstance().getTime()
41. // create the date/time formatters
42. val dayFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd")
43. val minuteFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HHmm")
44. val day = dayFormat.format(now)
45. val time = minuteFormat.format(now)
46. if(CarCount!=0&&speedTotal!=0){
47. jedis.select(dbIndex)
48. jedis.hset(day + "_" + camera_id, time , speedTotal + "_" + CarCount)
49. }
50. })
51. RedisClient.pool.returnResource(jedis)
52. })
53.})
54.
55./**
56.* 异步更新offset
57.*/
58.kafkaStream.foreachRDD { rdd =>
59. val offsetRanges: Array[OffsetRange] = rdd.asInstanceOf[HasOffsetRanges].offsetRanges
60. // some time later, after outputs have completed
61. kafkaStream.asInstanceOf[CanCommitOffsets].commitAsync(offsetRanges)
62.}
63.ssc.start()
64.ssc.awaitTermination()2、逻辑回归训练模型
1.val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("train traffic model").setMaster("local[*]")
2.val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
3.
4.// create the date/time formatters
5.val dayFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd")
6.val minuteFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HHmm")
7.
8.def main(args: Array[String]) {
9. // fetch data from redis
10. val jedis = RedisClient.pool.getResource
11. jedis.select(1)
12. // find relative road monitors for specified road
13. val camera_ids = List("310999003001","310999003102")
14. val camera_relations:Map[String,Array[String]] = Map[String,Array[String]](
15."310999003001" -> Array("310999003001","310999003102","310999000106","310999000205","310999007204"),
16."310999003102" -> Array("310999003001","310999003102","310999000106","310999000205","310999007204")
17. )
18. val temp = camera_ids.map({ camera_id =>
19. val hours = 5
20. val nowtimelong = System.currentTimeMillis()
21. val now = new Date(nowtimelong)
22. val day = dayFormat.format(now)//yyyyMMdd
23. val array = camera_relations.get(camera_id).get
24.
25. /**
26. * relations中存储了每一个卡扣在day这一天每一分钟的平均速度
27. */
28. val relations: Array[(String, util.Map[String, String])] = array.map({ camera_id =>
29. // fetch records of one camera for three hours ago
30. val minute_speed_car_map: util.Map[String, String] = jedis.hgetAll(day + "_'" + camera_id + "'")
31. (camera_id, minute_speed_car_map)
32. })
33.
34. // organize above records per minute to train data set format (MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile)
35. val dataSet = ArrayBuffer[LabeledPoint]()
36. // start begin at index 3
37. //Range 从300到1 递减 不包含0
38. for(i <- Range(60*hours,0,-1)){
39. val features = ArrayBuffer[Double]()
40. val labels = ArrayBuffer[Double]()
41. // get current minute and recent two minutes
42. for(index <- 0 to 2){
43. //当前时刻过去的时间那一分钟
44. val tempOne = nowtimelong - 60 * 1000 * (i-index)
45. val d = new Date(tempOne)
46. val tempMinute = minuteFormat.format(d)//HHmm
47. //下一分钟
48. val tempNext = tempOne - 60 * 1000 * (-1)
49. val dNext = new Date(tempNext)
50. val tempMinuteNext = minuteFormat.format(dNext)//HHmm
51.
52. for((k,v) <- relations){
53. val map = v //map -- k:HHmm v:Speed_count
54. if(index == 2 && k == camera_id){
55. if (map.containsKey(tempMinuteNext)) {
56. val info = map.get(tempMinuteNext).split("_")
57. val f = info(0).toFloat / info(1).toFloat
58. labels += f
59. }
60. }
61. if (map.containsKey(tempMinute)){
62. val info = map.get(tempMinute).split("_")
63. val f = info(0).toFloat / info(1).toFloat
64. features += f
65. } else{
66. features += -1.0
67. }
68. }
69. }
70.
71. if(labels.toArray.length == 1 ){
72. //array.head 返回数组第一个元素
73. val label = (labels.toArray).head
74. val record = LabeledPoint(if ((label.toInt/10)<10) (label.toInt/10) else 10.0, Vectors.dense(features.toArray))
75. dataSet += record
76. }
77. }
78.
79. val data: RDD[LabeledPoint] = sc.parallelize(dataSet)
80.
81. // Split data into training (80%) and test (20%).
82. //将data这个RDD随机分成 8:2两个RDD
83. val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.8, 0.2))
84. //构建训练集
85. val training = splits(0)
86. /**
87. * 测试集的重要性:
88. * 测试模型的准确度,防止模型出现过拟合的问题
89. */
90. val test = splits(1)
91.
92. if(!data.isEmpty()){
93. // 训练逻辑回归模型
94. val model = new LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS()
95. .setNumClasses(11)
96. .setIntercept(true)
97. .run(training)
98. // 测试集测试模型
99. val predictionAndLabels = test.map { case LabeledPoint(label, features) =>
100. val prediction = model.predict(features)
101. (prediction, label)
102. }
103.
104. predictionAndLabels.foreach(x=> println("预测类别:"+x._1+",真实类别:"+x._2))
105.
106. // Get evaluation metrics. 得到评价指标
107. val metrics: MulticlassMetrics = new MulticlassMetrics(predictionAndLabels)
108. val precision = metrics.accuracy// 准确率
109. println("Precision = " + precision)
110.
111. if(precision > 0.8){
112. val path = "hdfs://mycluster/model/model_"+camera_id+"_"+nowtimelong
113. model.save(sc, path)
114. println("saved model to "+ path)
115. jedis.hset("model", camera_id , path)
116.
117. }
118. }
119. })
120. RedisClient.pool.returnResource(jedis)
1.}3、加载模型进行道路预测
1.val sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("predict traffic").setMaster("local[4]")
2.val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
3.sc.setLogLevel("Error")
4.// create the date/time formatters
5.val dayFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd")
6.val minuteFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HHmm")
7.val sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd_HH:mm:ss")
8.
9.def main(args: Array[String]) {
10.
11. val input = "xxxx-xx-xx_17:15:00"
12. val date = sdf.parse(input)//yyyy-MM-dd_HH:mm:ss
13. val inputTimeLong = date.getTime()
14. val day = dayFormat.format(date)//yyyyMMdd
15.
16. // fetch data from redis
17. val jedis = RedisClient.pool.getResource
18. jedis.select(1)
19.
20. // find relative road monitors for specified road
21. val camera_ids = List("310999003001", "310999003102")
22. val camera_relations: Map[String, Array[String]] = Map[String, Array[String]](
23. "310999003001" -> Array("310999003001", "310999003102", "310999000106", "310999000205", "310999007204"),
24. "310999003102" -> Array("310999003001", "310999003102", "310999000106", "310999000205", "310999007204"))
25.
26. val temp = camera_ids.foreach({ camera_id =>
27. val array = camera_relations.get(camera_id).get
28.
29. val relations: Array[(String, util.Map[String, String])] = array.map({ camera_id =>
30. // fetch records of one camera for three hours ago
31. (camera_id, jedis.hgetAll(day + "_'" + camera_id + "'"))
32. })
33.
34. // organize above records per minute to train data set format (MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile)
35. val featers = ArrayBuffer[Double]()
36. // get current minute and recent two minutes
37. for (index <- 3 to (1,-1)) {
38. //拿到过去 一分钟,两分钟,过去三分钟的时间戳
39. val tempOne = inputTimeLong - 60 * 1000 * index
40. val currentOneTime = new Date(tempOne)
41. //获取输入时间的 "HHmm"
42. val tempMinute = minuteFormat.format(currentOneTime)//"HHmm"
43. println("inputtime ====="+currentOneTime)
44. for ((k, v) <- relations) {
45. val map = v //map : (HHmm,totalSpeed_total_carCount)
46. if (map.containsKey(tempMinute)) {
47. val info = map.get(tempMinute).split("_")
48. val f = info(0).toFloat / info(1).toFloat
49. featers += f
50. } else {
51. featers += -1.0
52. }
53. }
54. }
55.
56. // Run training algorithm to build the model
57. val path = jedis.hget("model", camera_id)
58. if(path!=null){
59. val model: LogisticRegressionModel = LogisticRegressionModel.load(sc, path)
60. // Compute raw scores on the test set.
61. val prediction = model.predict(Vectors.dense(featers.toArray))
62. println(input + "\t" + camera_id + "\t" + prediction + "\t")
63. }
64.
65. })
66.
67. RedisClient.pool.returnResource(jedis)
68.}