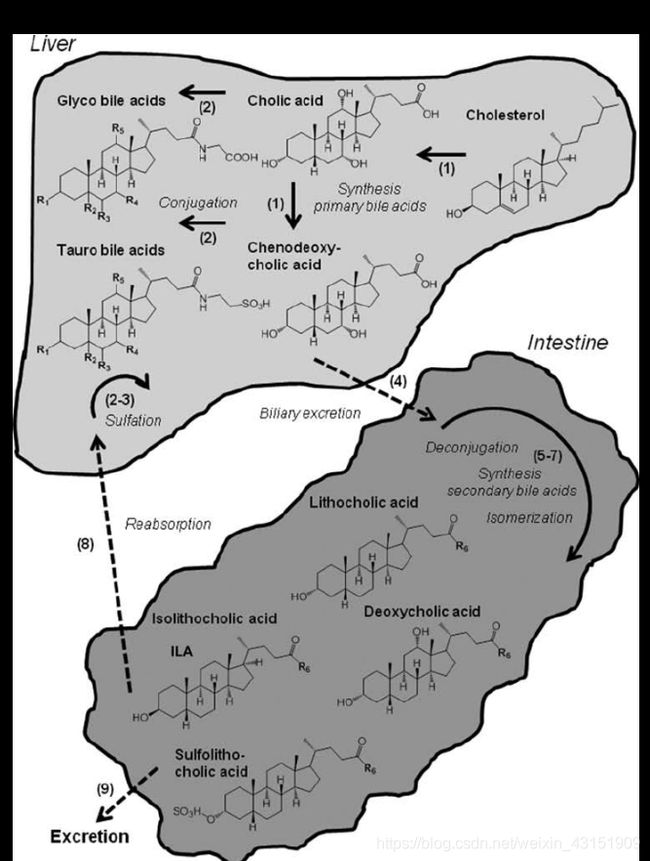
初级胆汁酸和次级胆汁酸
人体内的微生物通过作用到代谢物上面影响宿主的稳态. 所以在微生物研究中, 代谢研究非常的重要. 在target metabolomics里通常会测SCFA和Bile acids.
因为对bile acid的各种初级以及次级有诸多疑惑, 所以这里查阅资料的总结.
最开始还是从wiki入手, 然后再有初步了解之后再去看paper里面说的.
0. 什么是bile salts
大量的胆汁酸在肝脏合成, 胆汁酸和牛磺酸, 甘氨酸通常共轭结合, 他们叫做bile salts.
1.什么是primary bile acids?(初级胆汁酸)
胆汁酸的合成发生在肝脏细胞, 合成了初级胆汁酸(cholic acid 和 chenodeoxycholic acid).
2.什么是secondary bile acid?
一旦被分泌进小肠, 这些胆汁酸盐就会被细菌所修饰, 他们会暂时脱羟基, 他们的甘氨酸和牛磺酸基团也被移调. Cholic acid 转换成 deoxycholic acid; chenodeoxycholic acid 转换成 lithocholic ac
下面摘抄2段特别有用的描述胆汁酸代谢的, 可以结合下图来看:
总的来说Cholic acid(CA)和chenodeoxycholic(CDA)是初级胆汁酸. (它倾向于和氨基酸或者牛磺酸结合), 然后被转移到肠中, 被细菌deconjucation和isomeriation, 转换成次级胆汁酸. (LCA和DCA)
在文章中, 常常出现这些缩写, 记住大概的次级和初级胆汁酸还是非常有用的.
详细解释: 胆汁酸是哺乳动物胆固醇代谢的主要排泄终产物。胆汁酸的形成及其结合是一个复杂的生化过程,导致多种化合物和同种型(图1)。胆汁酸(胆酸和鹅去氧胆酸)是由胆固醇在肝细胞中产生的,并以牛磺酸和甘氨酸结合物的形式排泄到胆汁中。胆汁酸及其结合物然后通过胆囊排至肠。然后由小肠中的细菌从初级胆汁酸形成次级胆汁酸,包括石胆酸和脱氧胆酸及其相应的同工型,例如异石胆酸(5β-羟基-3β-胆酸,ILA)。它还负责初级胆汁酸缀合物的解偶联和异构化,然后将其重新吸收到肝细胞中并转化为甘氨酸或牛磺酸缀合物。胆酸在C3位被另外硫酸化。结合后,胆汁酸再次排入胆管,完成了肠肝循环。结肠中未吸收的胆汁酸几乎全部出现在健康人的粪便中。硫酸化的胆汁酸吸收差,排泄速度更快。[Bile acids are major excretory end-products of the cholesterol metabolism in mammals. The formation of bile acids and their conjugatesis a complex biochemical process resulting in multiple compounds and iso-forms (Figure 1). The primary bile acids—cholic acid and chenodeoxycholicacid—are produced in hepatocytes from cholesterol and excreted to the bileduct, mainly as taurine and glycine conjugates. The bile acids and their conjugates are then exported via the gall bladder to the intestine. Secondary bile acids, including lithocholic acid and deoxycholic acid, and their respective isoforms, e.g., isolithocholic acid (5β-hydroxy-3β-cholanic acid, ILA), are then formed from the primary bile acids by bacteria in the small intestine. Gut flora is also responsible for deconjugation and isomerization of the primary bile acid conjugates, which are then reabsorbed to the hepatocytes and converted into glycine or taurine conjugates. Lithocholic acid is additionally sulfated at the C3 position. After conjugation, bile acids are again excreted into the bile duct, completing the enterohepatic circulation.]
另外的综述, 引用在下面, 总结了胆汁酸代谢过程,
大概描述过程和前面一样:
这里就和前面说的一样. classical 方式是被CPYP7A1催化的, alternative pathway是被CYP27A1修饰的. 经典的pathway生成CDCA和CA. alternative pathwya生成CDCA. 捏齿动物还包括额外的初级胆汁酸, UDCA和MCA.
肝脏中的胆汁酸会共轭结合牛磺酸和甘氨酸.The bile acids in the liver are then conjugated (amidated) with glycine (G) or taurine (T).
这些初级胆汁酸会被肠道微生物首先去共轭,去羧基,脱氢,差向异构,形成次级胆汁酸(包括DCA,HCA,HDCA,LCA,MCA MDCA).
第三篇综述,最推荐的综述, 第一部分还是很详细了解了胆汁酸代谢过程.包括催化的酶, 在人和鼠种的不同
classical (or neutral) pathway:at least 75% of bile acid production under normal conditions and is initiated by 7a-hydroxylation of cholesterol catalyzed by cholesterol 7a-hydroxylase (CYP7A1). generates CDCA and CA.
The alternative (or acidic) pathway is initiated by sterol-27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1). further hydroxylated by oxysterol 7a-hydroxylase (CYP7B1). produce CA.
The ratio between these two primary bile acids is determined by the CYP8B1.(required for CA synthesis, not under microbial regulation.)
gut microbiota regulates expression of several of these enzymes, including CYP7A1, CYP7B1, and CYP27A1.
In addition to CA and CDCA, mice also produce MCAs and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) as primary bile acids (Sayin et al.,2013). In humans, UDCA is a secondary bile acid, and MCAs are generally not detected.
UDCA在人类里面是次级代谢产物,在小鼠是初级代谢产物.
Ref:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bile_acid
https://www.cell.com/trends/endocrinology-metabolism/fulltext/S1043-2760(17)30151-0
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262534251_Polyclonal_Murine_and_Rabbit_Antibodies_for_the_Bile_Acid_Isolithocholic_Acid
Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism