D15+D16|递归好难!!!
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
其处理方法分为:1)按普通树来处理
2)按完全二叉树来处理
1)按完全二叉树来处理,我们可以按照其特性,寻找其中的满二叉树,然后满二叉树的计算规则2^n-1,再加上根节点的。
2)如何判断是否为满二叉树:
判断其向左递归的深度和向右递归的深度是否相等。
class Solution {
/**
* 针对完全二叉树的解法
*
* 满二叉树的结点数为:2^depth - 1
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
int leftDepth = 0, rightDepth = 0; // 这里初始为0是有目的的,为了下面求指数方便
while (left != null) { // 求左子树深度
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
while (right != null) { // 求右子树深度
right = right.right;
rightDepth++;
}
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (2 << leftDepth) - 1; // 注意(2<<1) 相当于2^2,所以leftDepth初始为0
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
1)使用位运算计算2的n次方,从而depth是从0开始的
2)递归三部曲:
a.输入输出:输入根节点,返回根节点下所有节点的数目
b.终止条件:判断其子树是不是满二叉树,如果是则利用公式计算这个子树(满二叉树)的节点数量,如果不是则继续递归,那么 在递归三部曲中,第二部:终止条件的写法应该是这样的:
c.单层逻辑:
int leftTreeNum = countNodes(root->left); // 左
int rightTreeNum = countNodes(root->right); // 右
int result = leftTreeNum + rightTreeNum + 1; // 中
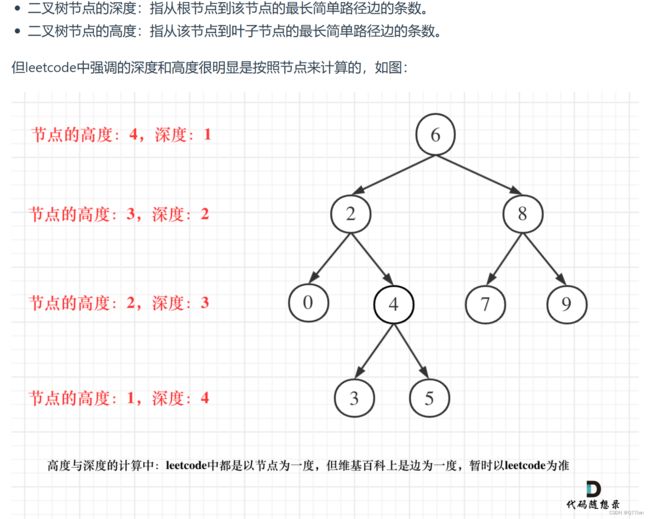
return result;110.平衡二叉树
高度和深度
初始思路:
很混乱。
题解复盘:
递归三部曲:
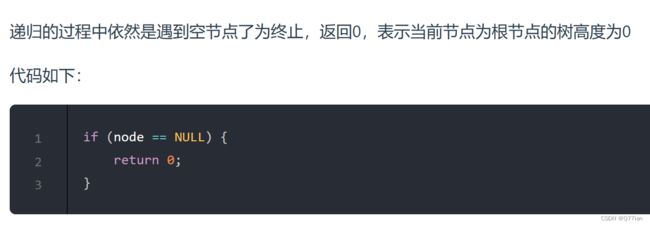
1)输入输出:输入一个节点(TreeNode),输出(int)(如果两边平衡的话输出高度,如果两边不平衡的话,返回-1)
2)终止条件:因为是计算高度,如果是空节点就返回高度是0
3)单层循环逻辑:
计算左侧高度,计算右侧高度,最终高度为左右高度中的最大值+1
257. 二叉树的所有路径
题解复盘:
递归加回溯是吧,那我就先看题解了。
递归三部曲:
1)输入输出:输入:根节点,记录本次路径的path,记录所有路径的result。
输出:void无需返回值
2)终止条件:如果当前节点是叶子节点,就将本次路径转换为String然后添加进result。
3)单层循环逻辑:前序
首先将当前节点加入path
如果左侧节点不为0就继续寻找路径,进行一次回溯
如果右侧节点不为0就继续寻找路径,进行一次回溯
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();// 存最终的结果
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
List paths = new ArrayList<>();// 作为结果中的路径
traversal(root, paths, res);
return res;
}
private void traversal(TreeNode root, List paths, List res) {
paths.add(root.val);// 前序遍历,中
// 遇到叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 输出
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();// StringBuilder用来拼接字符串,速度更快
for (int i = 0; i < paths.size() - 1; i++) {
sb.append(paths.get(i)).append("->");
}
sb.append(paths.get(paths.size() - 1));// 记录最后一个节点
res.add(sb.toString());// 收集一个路径
return;
}
// 递归和回溯是同时进行,所以要放在同一个花括号里
if (root.left != null) { // 左
traversal(root.left, paths, res);
paths.remove(paths.size() - 1);// 回溯
}
if (root.right != null) { // 右
traversal(root.right, paths, res);
paths.remove(paths.size() - 1);// 回溯
}
}
} 回溯,回溯了什么?
就比如
我第一次进入去寻找root.left的路径,我path里面其实变成12了,但是我去findright的时候我里面一开始只有1,所以在findleft之后,要删一下left,这就是回溯了一下。
404.左叶子之和
节点A的左孩子不为空,且左孩子的左右孩子都为空(说明是叶子节点),那么A节点的左孩子为左叶子节点
// 层序遍历迭代法
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
int sum = 0;
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size -- > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) { // 左节点不为空
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null){ // 左叶子节点
sum += node.left.val;
}
}
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return sum;
}
} 513.找树左下角的值
初始思路:
层序遍历,只需要记录最后一行第一个节点的数值就可以了。
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) { Queue que = new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null){que.offer(root);}
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
while(que.size()!=0){
int size = que.size();
List res = new ArrayList<>();
while(size>0){
TreeNode node = que.poll();
res.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null){que.offer(node.left);}
if(node.right!=null){
que.offer(node.right);
}
size--;
}
result.add(res);
}
return result.get(result.size()-1).get(0);
}
} 题解复盘:
保证优先左边搜索,然后记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值。
递归相较于层序遍历更难一点。
1)输入输出:
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为void。
本题还需要类里的两个全局变量,maxLen用来记录最大深度,result记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
代码如下:
int maxDepth = INT_MIN; // 全局变量 记录最大深度
int result; // 全局变量 最大深度最左节点的数值
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth)注意此处为全局变量
2)终止条件:
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
代码如下:
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth; // 更新最大深度
result = root->val; // 最大深度最左面的数值
}
return;
}两个更新并且return
3)单层循环逻辑:
// 中
if (root->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度加一
traversal(root->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度减一
}
if (root->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度加一
traversal(root->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度减一
}
return;112. 路径总和
初始思路:
在找二叉树的所有路径中我们已经可以得到所有路径了,那么得到所有路径的和也不是一件难事,最后再在结果中find是否有target就可以了。
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List path = new ArrayList<>();
List result = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){return false;}
pathSum(root,path,result);
for(int i:result){
if(i==targetSum){return true;}
}
return false;
}
public void pathSum(TreeNode root,List path,List result){
if(root!=null){path.add(root.val);}
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
int sum = 0;
for(int i :path){
sum = sum+i;
}
result.add(sum);
}
if(root.left!=null){
pathSum(root.left,path,result);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
if(root.right!=null){
pathSum(root.right,path,result);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
} 题解复盘:
class solution {
public boolean haspathsum(treenode root, int targetsum) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
targetsum -= root.val;
// 叶子结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return targetsum == 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
boolean left = haspathsum(root.left, targetsum);
if (left) { // 已经找到
return true;
}
}
if (root.right != null) {
boolean right = haspathsum(root.right, targetsum);
if (right) { // 已经找到
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}- 确定递归函数的参数和返回类型
参数:需要二叉树的根节点,还需要一个计数器,这个计数器用来计算二叉树的一条边之和是否正好是目标和,计数器为int型。
如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)(有就行不用遍历全部?)遍历的路线,并不要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,可以用bool类型表示。
2.确定终止条件(用递减,谁一开始能想到啊!)
首先计数器如何统计这一条路径的和呢?
不要去累加然后判断是否等于目标和,那么代码比较麻烦,可以用递减,让计数器count初始为目标和,然后每次减去遍历路径节点上的数值。
如果最后count == 0,同时到了叶子节点的话,说明找到了目标和。
如果遍历到了叶子节点,count不为0,就是没找到。
3.确定单层循环条件
前序,如果当前节点为叶子节点且count=0,就return true
不然再继续其左,其右。
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
题解复盘:
来看一下一共分几步:
-
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
-
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
-
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
-
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
-
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
-
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(postorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0)
return null;
TreeNode root = Treebuild(inorder,0,inorder.length,postorder,0,postorder.length);
return root;
}
public TreeNode Treebuild(int[] inorder,int inorderbegin,int inorderend,int[] postorder,int postorderbegin, int postorderend){
if(postorderbegin == postorderend)
return null;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(postorder[postorderend-1]);
if(postorderend==0){return node;}
int rootindex = 0;;
for(int i = inorderbegin;i前序:
root.left = Treebuild(preorder,preorderbegin+1,preorderbegin+(rootindex-inorderbegin)+1,inorder,inorderbegin,rootindex);
root.right = Treebuild(preorder,preorderbegin+(rootindex-inorderbegin)+1,preorderend,inorder,rootindex+1,inorderend);注意因为是左闭右开区间:
所以后序时postorderbegin+(rootindex - inorderbegin))
前序时preorderbegin+(rootindex-inorderbegin)+1
主要原因在于每次preorderbegin都要+1,很重要!!!我的报错原因