JavaSE 优先级队列(堆)
目录
- 1 二叉树的顺序存储
-
- 1.1 存储方式
- 1.2 下标关系
- 2 堆(heap)
-
- 2.1 概念
- 2.2 操作-向下调整
- 2.3 操作-建堆
- 3 堆的应用-优先级队列
-
- 3.1 概念
- 3.2 内部原理
- 3.3 操作-入队列(向上调整)
- 3.4 操作-出队列(优先级最高)
- 3.5 返回队首元素(优先级最高)
- 3.6 java 中的优先级队列
- 3.7 堆的常见用途
-
- 3.7.1 topK问题
- 3.7.2 堆排序
1 二叉树的顺序存储
1.1 存储方式
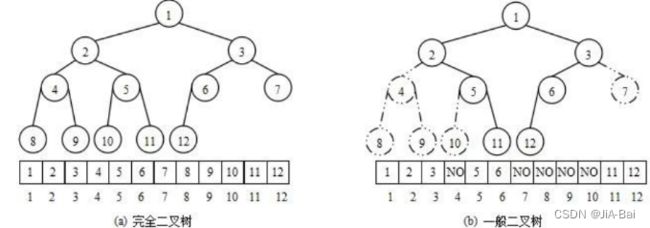
使用数组保存二叉树结构,方式即将二叉树用层序遍历方式放入数组中。
一般只适合表示完全二叉树,因为非完全二叉树会有空间的浪费。
这种方式的主要用法就是堆的表示。
1.2 下标关系
1. 已知双亲(parent)的下标,则:
左孩子(left)下标 = 2 * parent + 1;
右孩子(right)下标 = 2 * parent + 2。
2. 已知孩子(不区分左右)(child)下标,则:
双亲(parent)下标 = (child - 1) / 2
2 堆(heap)
2.1 概念
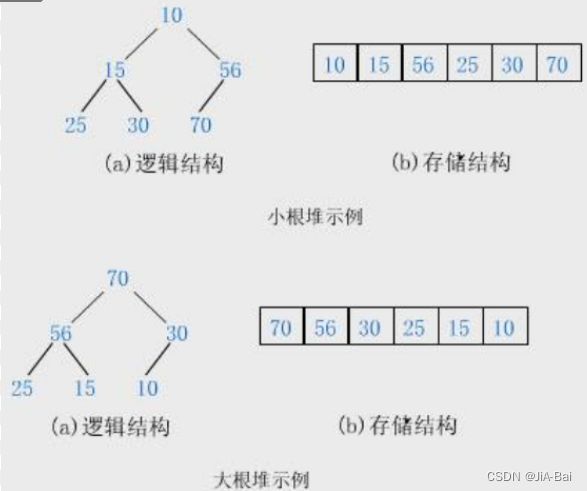
- 堆逻辑上是一棵完全二叉树;
- 堆物理上是保存在数组中;
- 满足任意结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆,或者大根堆,或者最大堆;
- 反之,则是小堆,或者小根堆,或者最小堆;
- 堆的基本作用是,快速找集合中的最值。
2.2 操作-向下调整
前提: 左右子树必须已经是一个堆,才能调整。
说明:
- array 代表存储堆的数组;
- size 代表数组中被视为堆数据的个数;
- index 代表要调整位置的下标;
- left 代表 index 左孩子下标;
- right 代表 index 右孩子下标;
- min 代表 index 的最小值孩子的下标;
过程(以小堆为例):
- index 如果已经是叶子结点,则整个调整过程结束。
(1)判断 index 位置有没有孩子;
(2)因为堆是完全二叉树,没有左孩子就一定没有右孩子,所以判断是否有左孩子;
(3)因为堆的存储结构是数组,所以判断是否有左孩子即判断左孩子下标是否越界,即 left >= size 越界。 - 确定 left 或 right,谁是 index 的最小孩子 min。
(1)如果右孩子不存在,则 min = left;
(2)否则,比较 array[left] 和 array[right] 值得大小,选择小的为 min。 - 比较 array[index] 的值 和 array[min] 的值,如果 array[index] <= array[min],则满足堆的性质,调整结束。
- 否则,交换 array[index] 和 array[min] 的值。
- 然后因为 min 位置的堆的性质可能被破坏,所以把 min 视作 index,向下重复以上过程。
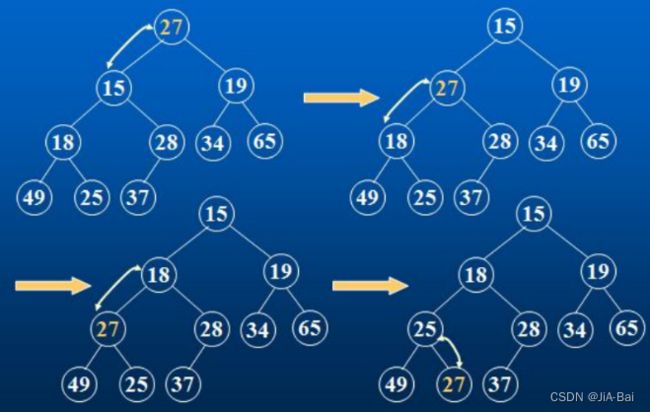
图示:
// 调整前
int[ ] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
// 调整后
int[ ] array = { 15,18,19,25,28,34,65,49,27,37 };
时间复杂度分析:
最坏的情况即图示的情况,从根一路比较到叶子,比较的次数为完全二叉树的高度,即时间复杂度为 O(log2(n))。
代码:
public static void shiftDown(int[] array, int size, int index) {
int left = 2 * index + 1;
while (left < size) {
int min = left;
int right = 2 * index + 2;
if (right < size) {
if (array[right] < array[left]) {
min = right;
}
}
if (array[index] <= array[min]) {
break;
}
int t = array[index];
array[index] = array[min];
array[min] = t;
index = min;
left = 2 * index + 1;
}
}
2.3 操作-建堆
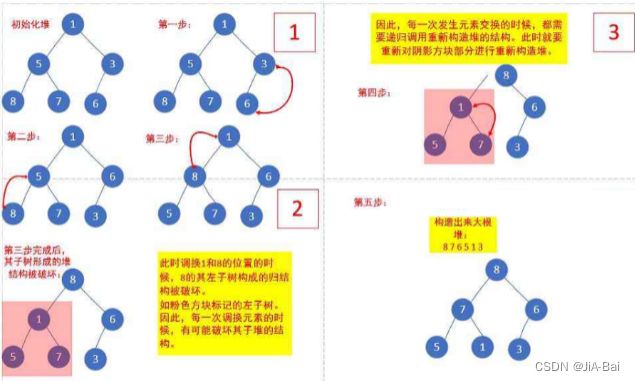
下面我们给出一个数组,这个数组逻辑上可以看做一颗完全二叉树,但是还不是一个堆,现在我们通过算法,把它构建成一个堆。
根节点左右子树不是堆,我们怎么调整呢?这里我们从倒数的第一个非叶子节点的子树开始调整,一直调整到根节点的树,就可以调整成堆。
图示(以大堆为例):
// 建堆前
int[ ] array = { 1,5,3,8,7,6 };
// 建堆后
int[ ] array = { 8,7,6,5,1,3 };
时间复杂度分析:
粗略估算,可以认为是在循环中执行向下调整,为 O(n * log2(n));了解后实际上是 O(n)。
以大堆为例的代码如下所示:
HeapDemo.java
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/*
* 在这里 为什么可以传len
* 是因为每棵树的结束位置 实际上都是一样的
*
* 假设长度为10,len就是10
* */
public void adjustDown(int parent,int len){
int child = 2*parent+1;
//child < len 说明有左孩子
while(child < len){
//child+1 < len 判断当前是否有右孩子
if(child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]){
child++;
}
//child下标一定是左右孩子的最大值下标
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else{
//因为是从最后一棵树开始调整的,只要我们找到了这个
//this.elem[child] <= this.elem[parent]
//说明后续就不需要循环了,后面的都是大根堆了
break;
}
}
}
public void creatBigHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
//elem当中已经存放了元素
for(int i = (this.usedSize-1-1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){
adjustDown(i,this.usedSize);
}
}
public void show(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
TestDemo.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapDemo heapDemo = new HeapDemo();
int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
heapDemo.creatBigHeap(array);
heapDemo.show();
}}
3 堆的应用-优先级队列
3.1 概念
在很多应用中,我们通常需要按照优先级情况对待处理对象进行处理,比如首先处理优先级最高的对象,然后处理次高的对象。最简单的一个例子就是,在手机上玩游戏的时候,如果有来电,那么系统应该优先处理打进来的电话。
在这种情况下,我们的数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这种数据结构就是优先级队列(Priority Queue)。
3.2 内部原理
优先级队列的实现方式有很多,但最常见的是使用堆来构建。
3.3 操作-入队列(向上调整)
过程(以大堆为例):
- 首先按尾插方式放入数组;
- 比较其和其双亲的值的大小,如果双亲的值大,则满足堆的性质,插入结束;
- 否则,交换其和双亲位置的值,重新进行 2、3 步骤;
- 直到根结点。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public void creatBigHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
//elem当中已经存放了元素
for(int i = (this.usedSize-1-1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){
adjustDown(i,this.usedSize);
}
}
public void push(int val){
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize] = val;
this.usedSize++;
adjustUp(this.usedSize-1);
}
public void adjustUp(int child){
int parent = (child-1)/2;
while(child > 0){
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child-1)/2;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
public void show(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
TestDemo.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapDemo heapDemo = new HeapDemo();
int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
heapDemo.creatBigHeap(array);
heapDemo.show();
heapDemo.push(100);
heapDemo.show();
}}
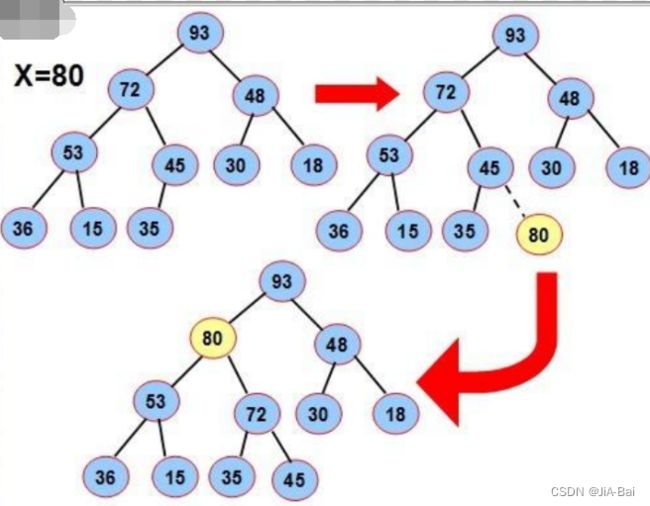
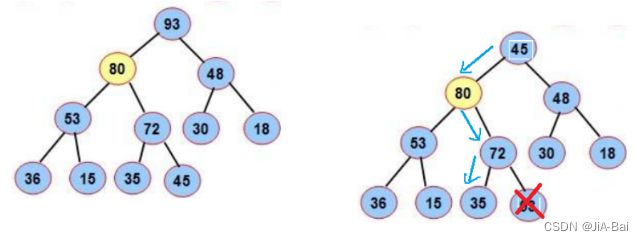
3.4 操作-出队列(优先级最高)
为了防止破坏堆的结构,删除时并不是直接将堆顶元素删除,而是用数组的最后一个元素替换堆顶元素,然后通过向下调整方式重新调整成堆。
图示:
代码:
HeapDemo.java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public void creatBigHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
//elem当中已经存放了元素
for(int i = (this.usedSize-1-1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){
adjustDown(i,this.usedSize);
}
}
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
int ret = this.elem[0];
//删除
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
this.elem[this.usedSize-1] = tmp;
this.usedSize--;
adjustDown(0,this.usedSize);
return ret;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
public void show(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
TestDemo.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapDemo heapDemo = new HeapDemo();
int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
heapDemo.creatBigHeap(array);
heapDemo.show();
System.out.println(heapDemo.poll());
heapDemo.show();
}}
3.5 返回队首元素(优先级最高)
返回堆顶元素即可。
代码:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public void creatBigHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
//elem当中已经存放了元素
for(int i = (this.usedSize-1-1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){
adjustDown(i,this.usedSize);
}
}
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
return this.elem[0];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
public void show(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
3.6 java 中的优先级队列
PriorityQueue implements Queue
PriorityQueue的使用方法:
| 操作 | 错误处理-抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 |
|---|---|---|
| 入队列 | add(e) | offer(e) |
| 出队列 | remove() | poll() |
| 队首元素 | element() | peek() |
使用PriorityQueue的代码示例如下所示:
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* PriorityQueue 优先级队列 底层是由堆来实现的
* PriorityQueue 底层默认是一个小根堆
* 每次存元素的时候 一定要保证 数据进入堆中后 依然可以维持为一个小堆/大堆
* 每次取出一个元素的时候 一定要保证 剩下的元素 也要调整为一个小堆/大堆
* */
PriorityQueue<Integer> qu = new PriorityQueue<>();
qu.offer(3);
qu.offer(1);
qu.offer(4);
qu.offer(2);
qu.offer(5);
System.out.println(qu.poll());//1
System.out.println(qu.poll());//2
System.out.println(qu.poll());//3
//默认是小堆,我就要一个大堆呢?
/*
* 我们之前学过自定义比较器
* */
PriorityQueue<Integer> qu1 = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
//o2 > o1 o1小于o2
return o2-o1;
}
});
qu1.offer(3);
qu1.offer(1);
qu1.offer(4);
qu1.offer(2);
qu1.offer(5);
System.out.println(qu1.poll());//5
System.out.println(qu1.poll());//4
System.out.println(qu1.poll());//3
}
}
PriorityQueue的扩容方式:
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?(oldCapacity + 2) :oldCapacity >> 1));
3.7 堆的常见用途
堆有两个常见的用途:
- topK(求前K个最大/最小的元素)。
- 堆排序。
3.7.1 topK问题
关键记得:
- 找前 K 个最大的元素,要建 K 个大小的小堆;
- 找前 K 个最小的元素,要建 K 个大小的大堆;
- 找第K小的元素,要建立大小为K的大堆,等数组遍历完成后,堆顶元素就是第K小的元素。
时间复杂度为:O(nlog2(K))
找前K个最大的元素代码如下所示:
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
/*
* 找前K个最大的元素
* */
public static void topK(int[] array,int k){
//1、大小为K的小堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1-o2;
}
});
//2、遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (minHeap.size() < k){
minHeap.offer(array[i]);
}else{
int top = minHeap.peek();
if(array[i] > top){
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k ; i++) {
System.out.println(minHeap.poll());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
topK(array,3);
}}
3.7.2 堆排序
关键记得: 从小到大排序,应该建一个大堆。
从小到大排序的代码如下所示:
HeapDemo.java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapDemo {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public HeapDemo(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
/*
* 在这里 为什么可以传len
* 是因为每棵树的结束位置 实际上都是一样的
*
* 假设长度为10,len就是10
* */
public void adjustDown(int parent,int len){
int child = 2*parent+1;
//child < len 说明有左孩子
while(child < len){
//child+1 < len 判断当前是否有右孩子
if(child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]){
child++;
}
//child下标一定是左右孩子的最大值下标
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else{
//因为是从最后一棵树开始调整的,只要我们找到了这个
//this.elem[child] <= this.elem[parent]
//说明后续就不需要循环了,后面的都是大根堆了
break;
}
}
}
public void creatBigHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
//elem当中已经存放了元素
for(int i = (this.usedSize-1-1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){
adjustDown(i,this.usedSize);
}
}
public void show(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//排序
public void heapSort(){
int end = this.usedSize-1;
while(end > 0){
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[end];
this.elem[end] = tmp;
adjustDown(0,end);
end--;
}
}
}
TestDemo.java
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapDemo heapDemo = new HeapDemo();
int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
heapDemo.creatBigHeap(array);
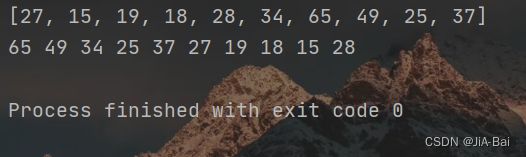
heapDemo.show();
heapDemo.heapSort();
heapDemo.show();
}}
将上面代码改装成数组也是一样的,具体代码如下所示:
import java.util.*;
public class TestDemo {
//改装成数组也是一样的
public static void adjustDown2(int[] array,int parent,int len){
int child = 2*parent+1;
while(child < len){
if(child+1 < len && array[child] < array[child+1]){
child++;
}
if(array[child] > array[parent]){
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
public static void creatBigHeap2(int[] array){
for(int i = (array.length-1-1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){
adjustDown2(array,i,array.length);
}
}
/*
* 时间复杂度:不管是最好,或是最坏,均为O(nlog2(n))
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* */
public static void heapSort2(int[] array){
creatBigHeap2(array);
int end = array.length-1;
while(end > 0){
int tmp = array[0];
array[0] = array[end];
array[end] = tmp;
adjustDown2(array,0,end);
end--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = { 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 };
heapSort2(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}}
所以,对于堆排序来说:
时间复杂度: 不管是最好,或是最坏,均为O(nlog2(n))。
空间复杂度: O(1)。