A星(A*,A star)寻路算法c++
A星(A*,A star)寻路算法
1. 整体思想是
对每个节点来说,有父节点,fcost,hcost,gcost,其中
- gcost是从起点到当前点的实际代价
- hcost是从当前点到终点的估计代价
gcost好理解,就是从起点到当前点的代价;hcost叫估计代价是因为在到底终点之前不知道实际代价是多少,我们只能估计,例如,不考虑影响到终点的阻碍,它会是多少。而 f c o s t = g c o s t + h c o s t fcost = gcost+hcost fcost=gcost+hcost,整体寻路过程就是找到一条到终点的fcost最小的路径。
2. 整体流程是
-
建一个空的容器open_list,保存还没访问的点;一个空的容器close_list,
保存已经访问过的节点;起点进入open_list -
当open_list不为空,do
2.1 找出当前open_list中 f c o s t fcost fcost最小的节点(method)作为当前节点cur_grid
2.2 cur_grid从open_list中移除
2.3 cur_grid加入到close_list中
2.4 找到cur_grid的所有邻近点(method,需要检查节点有效性<越界、已经在open_list中,已经在close_list中>)
2.5 对cur_grid的所有邻近节点,更新他们的父节点、gcost、hcost、fcost(method),并放入到open_list中;如果发现其中一个邻近的节点已经是终点,返回这个是终点的邻近节点,算法结束。 -
否则open_list已经空,还没有找到终点,说明查找路径失败,算法结束
-
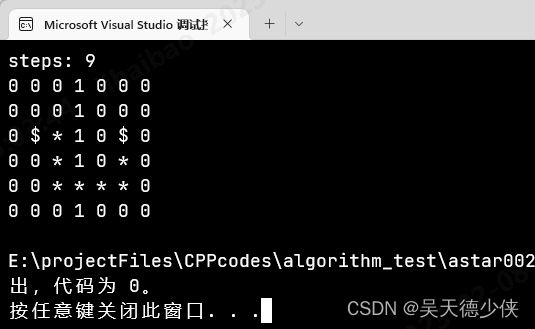
如果程序从2结束,则从终点回溯父节点,显示路径。
3. 代码实现上
我觉得需要考虑的问题大概有:
3.1 如何表示节点
这个最基础,这个实现的好,那么后面节点的父节点、fcost、gcost、hcost的更新就会简单
3.2 如何表示open_list,close_list
3.3 如何组织整个框架,把各个模块联系起来
4.代码
下面就看看代码吧
AStar.h
#pragma once
#includeAStar.cpp
#include "AStar.h"
#includemain.cpp
#include"AStar.h"
#include