操作系统详解(2)——异常处理(Exception)
系列文章:
操作系统详解(1)——操作系统的作用
文章目录
- System Calls
- Event & Exception
-
- Exception Table
- Exception Handler
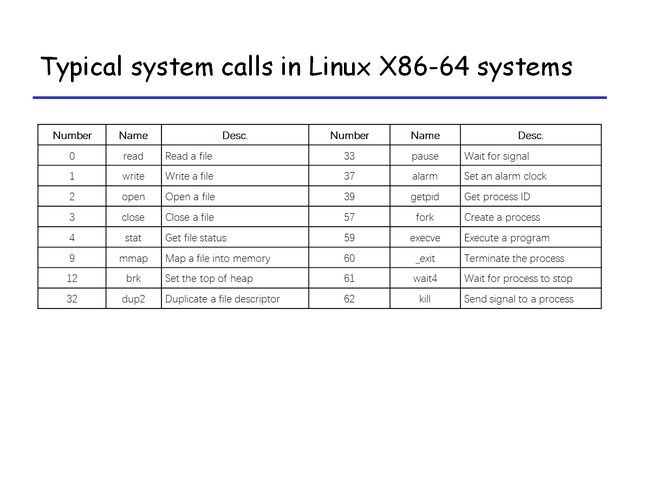
- Exceptions的种类
-
- Synchronous exceptions (同步调用)
- Asynchronous exception(interrupts)
- 总结
System Calls
引发异常的过程一定涉及到控制流的改变(用户态 ↔ \leftrightarrow ↔内核态)
前面提到的jump指令和call/return指令都能改变控制流,但都只能在同一个mode中
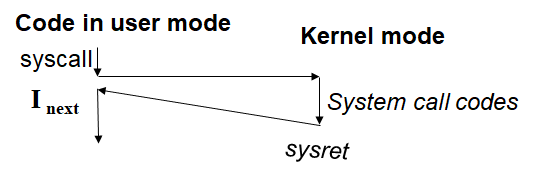
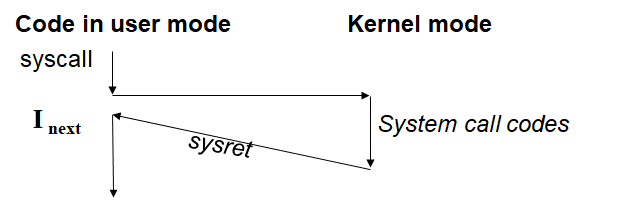
新指令: syscall & sysret
调用syscall后控制流的变化:
举个栗子:
# hello world
int mian()
{
write(1, "hello, world\n", 13);
// 1:文件描述符, 1这里指标准输出stdout->屏幕
// 13:写入的字节数
_exit(0);
}
.section .data
2 string:
3 .ascii "hello, world\n"
4 string_end:
5 .equ len, string_end - string
6 .section .text
7 .globl main
main:
# First, call write(1, "hello, world\n", 13)
9 movq $1, %rax # write is system call 1
10 movq $1, %rdi # Arg1:stdout has descriptor 1
11 movq $string, %rsi # Arg2:Hello world string
12 movq $len, %rdx # Arg3:string length
13 syscall # Make the system call
# Next, call exit(0)
14 movq $60, %rax # _exit is system call 60
15 movq $0, %rdi # Arg1:exit status is 0
16 syscall # Make the system call
系统调用的参数: 最多6个参数在两个modes间传递:
%rdi, %rsi, %rdx, %r10, %r8, %r9
caller-saved registers必须在user mode中保存好
%rcx和%r11 被销毁了
分别保存%rsp以及%rflags
%rflags除了conditional code, 还包括:
IF(是否会被中断)
TF(Trap Flag)(用于单步执行)
Event & Exception
(事件以及异常)
处理器状态:
处理器中的一系列bits和signals,例如kernel bit
当processor’s state发生变化时:
- 调用syscall/sysret
- 从磁盘/网络适配器接收数据
- 引发错误的指令,比如除0
异常: 对事件产生反应,以改变控制流的硬件机制
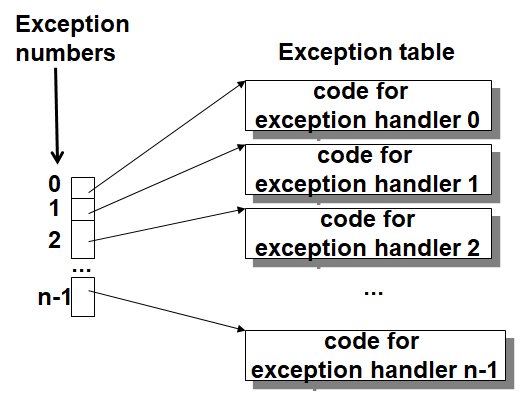
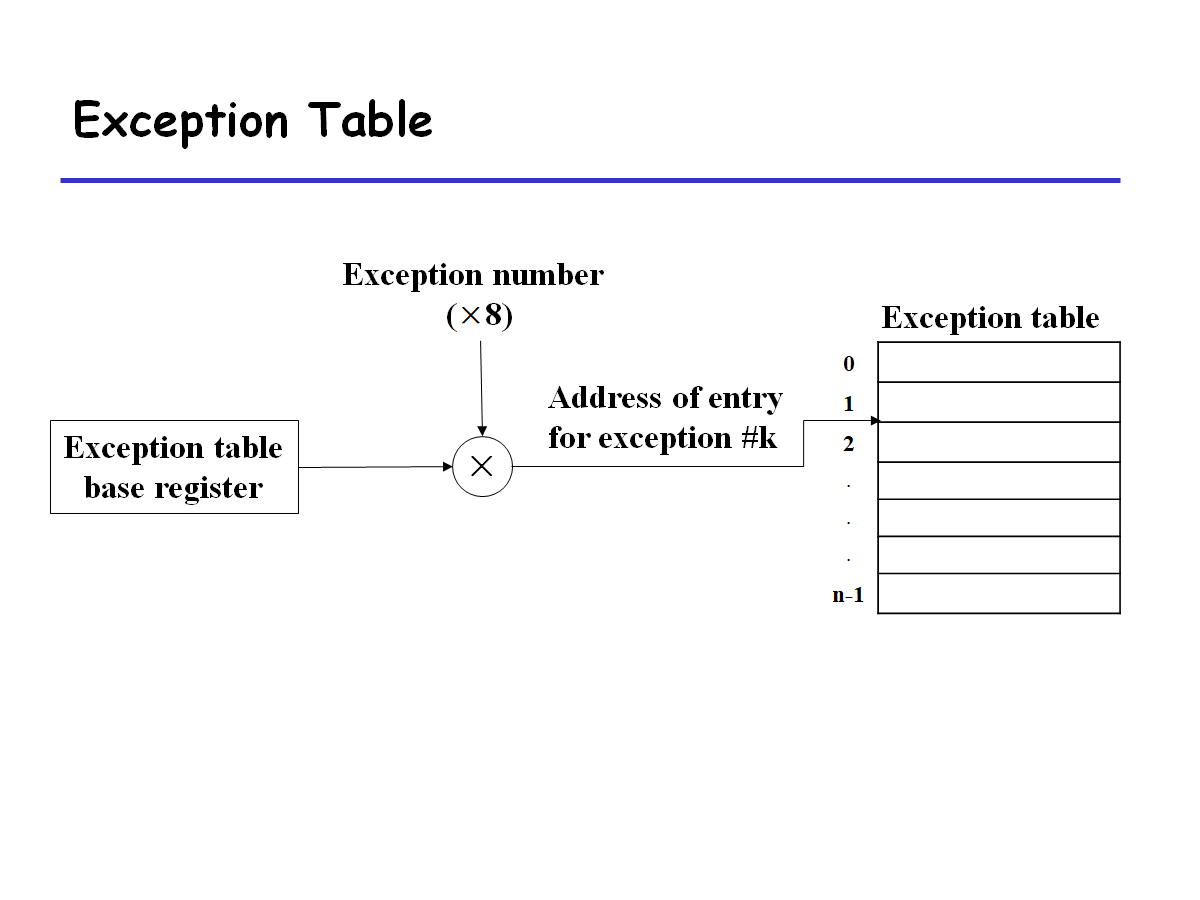
Exception Table
- Each type of event has a unique exception number k
- Exception table entry k points to a function (exception handler)
- Handler k is called each time exception k occurs.
Exception Handler
内核mode中的代码
将需要恢复被中断进程的必要信息储存在kernel栈上
- Return address ( I c u r r / I n e x t I_{curr}/I_{next} Icurr/Inext)
- RFLAGS, RSP
exception handler处理结束后:
- returns control to the current instruction Icurr
- returns control to the next instruction Inext
- aborts the interrupted program
Exceptions的种类
Synchronous exceptions (同步调用)
执行一个指令的结果
-
Traps
Intentional
return to I n e x t I_{next} Inext
e.g. syscall, breakpoint traps -
Faults
Unintentioanl
可能可以恢复
重新执行Icurr或者中断
e.g. page faults(recoverable), protection faults(unrecoverable) -
Aborts
Unintentional
Unrecoverable
中断当前程序
e.g. parity error(奇偶校验), machine check
Tips:
Fault: software error
Abort: hardware error (fatal)
Fault Example #1
访问内存时,有可能该部分的内存还没有准备好.
long a[1000];
main()
{
a[500] = 13;
}
报缺页错误(page fault), 切换到OS, 处理完错误(Create page and load into memory), 返回Icurr再执行一次
Fault Example #2
访问非法内存
int a[1000];
main()
{
a[5000] = 13;
}
报缺页错误(page fault), 切换到OS,操作系统发现了访问非法地址, 向user process发送SIGSEG信号,
user process exits with “segmentation fault”
| Exception Number | Description | Exception class |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Divide error | Fault |
| 13 | General protection fault | Fault |
| 14 | Page fault | Fault |
| 18 | Machine check | Abort |
| 32-255 | OS defined exception | Interrupt or trap |
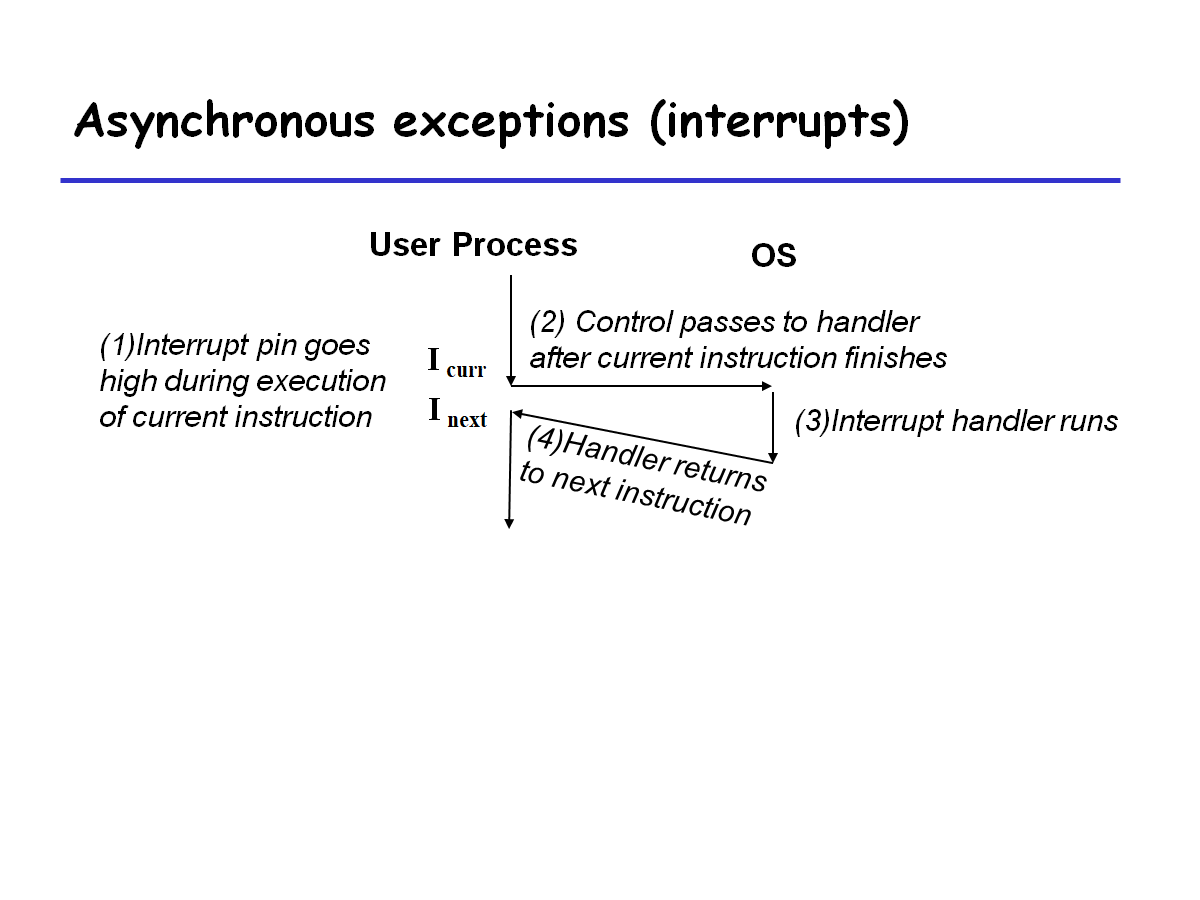
Asynchronous exception(interrupts)
由外部事件导致的.
- 设置处理器的中断引脚(interrupt pin)
- Handler返回"next" instruction
Examples:
- I/O interrupts
- hitting ctl-c at the keyboard
- 接受网络包
- 磁盘读写
- Hard reset interrupt
hitting the reset button - Soft reset interrupt
hitting ctl-alt-delete on a PC
以I/O interrupt为例, I/O devices 向system bus上放置一个数字用来识别造成interrupt的设备
导致CPU停止执行当前程序,并跳转到OS中的interrupt handler
I/O 与 processor 之间的关系:

异步中断的流程图:
举日常编程中出现异常的例子:
| Scenario | Exception Type | Synchronous/Asynchronous | Exception Handler Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Access content at address 0x0 | Fault | Synchronous | Never return |
| B. Memory corruption | Aborts | Synchronous | Never return |
| C. “kill -9 |
Traps | Synchronous | Return to next instruction |
| D. Click your mouse | Interrupt | Asynchronous | Return to next instruction |
总结
介绍了操作系统的异常处理机制,并区分了异常的种类以及它们相应不同的处理方式。
下一章将讲解进程的具体内容,包括并发的概念。