python实验报告6 组合数据类型的应用
1、实验题目:好友管理系统
请设计一个好友管理系统,每个功能都对应一个序号,用户可根据提示“请输入您的选项”选择序号执行相应的操作,包括:
(1)添加好友:用户根据提示“请输入要添加的好友:”。
(输入要添加好友的姓名,添加后会提示“好友添加成功”)
(2)删除好友:用户根据提示“请输入删除好友姓名:”
(输入要删除好友的姓名,删除后提示“删除成功”)
(3)备注好友:用户根据提示“请输入要修改的好友姓名:”和“请输入修改后的好友姓名:”。
(分别输入修改前和修改后的好友姓名,修改后会提示“备注成功”)
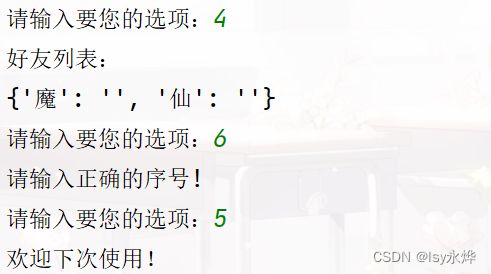
(4)展示好友:若用户还没有添加过好友,提示“好友列表为空”,否则返回每个好友的姓名。
(5)退出:关闭好友系统。
源代码:
class FriendManager():
def __init__(self):
self.friends = {} # 大括号表示集合,但是直接写的情况下,表示这是个空字典
def add_friend(self):
name = input("请输入要添加的好友:")
self.friends[name] = ""
print("好友添加成功!")
def delete_friend(self):
name = input("请输入删除好友姓名:")
if name in self.friends:
del self.friends[name]
print("删除成功!")
else:
print("没有该姓名!")
def remark_friend(self):
old_name = input("请输入要修改的好友姓名:")
new_name = input("请输入修改后的好友姓名:")
if old_name in self.friends:
self.friends[new_name] = self.friends.pop(old_name)
print("备注成功!")
else:
print("不存在该姓名!")
def show_friend(self):
if not self.friends:
print("好友列表为空")
else:
print("好友列表:")
print(self.friends)
def main():
friend_manager = FriendManager()
print("欢迎使用好友管理系统:")
print("1.添加好友 2.删除好友 3.备注好友 4.展示好友 5.退出")
while (1):
choice = input("请输入要您的选项:")
if choice == "1":
friend_manager.add_friend()
elif choice == "2":
friend_manager.delete_friend()
elif choice == "3":
friend_manager.remark_friend()
elif choice == "4":
friend_manager.show_friend()
elif choice == "5":
print("欢迎下次使用!")
exit()
else:
print("请输入正确的序号!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
2、实验题目:中文数字对照表
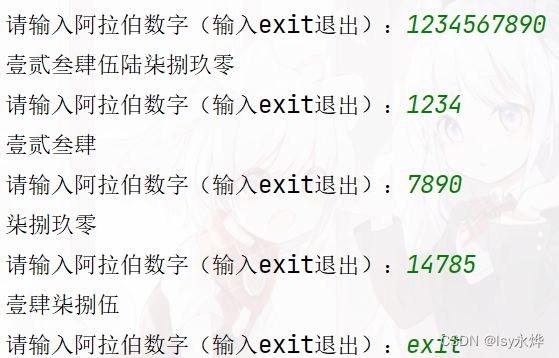
输入一个数字,转换成中文数字。比如:1234567890 -> 壹贰叁肆伍陆柒捌玖零。
源代码:
class ChineseNumberConverter:
def __init__(self):
self.digicts={'1':'壹','2':'贰','3':'叁',
'4':'肆','5':'伍','6':'陆',
'7':'柒','8':'捌','9':'玖',
'0':'零'}
def converter(self,number):
chinese_number=''
for digit in str(number):
chinese_number+=self.digicts[digit]
return chinese_number
def main():
converter1=ChineseNumberConverter()
while(1):
try:
number=input("请输入阿拉伯数字(输入exit退出):")
if number.lower()=='exit':
break
chinese_num=converter1.converter(number)
print(chinese_num)
except ValueError:
print("请输入正确的数字!")
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
3、实验题目:学生成绩管理
将学生对象存入列表中,并按成绩对学生进行排序;
并获取成绩最高和成绩最低的学生信息;
并将最高分和最低分的学生从列表删除;
最后再对列表进行拷贝;
对拷贝的列表进行翻转输出。
源代码:
class Student:
def __init__(self,name,score):
self.name=name
self.score=score
def main():
students=[
Student('郑梓妍',90),
Student('肖鹿',80),
Student('浩浩妈',70),
Student('沈慧星',60)
]
#初始排序
print('初始排序:')
for s in students:
print(f'{s.name},{s.score}')
#从小到大排序之后
students.sort(key=lambda x:x.score)
print('\n排序之后:')
for s in students:
print(f'{s.name},{s.score}')
#删除最大值和最小值
max_student=students[-1]
min_student=students[0]
students.remove(max_student)
students.remove(min_student)
print('\n删除最大值和最小值后:')
for s in students:
print(f'{s.name},{s.score}')
#拷贝之后翻转输出
copy_student=students.copy()
copy_student.reverse()
print('\n翻转之后输出:')
for s in students:
print(f'{s.name},{s.score}')
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
4、实验题目:商品筛选
有如下商品价格:568,239,368,425,121,219,834,1263,26;
请输入随意一个价格区间进行商品的筛选;
并能够对筛选出的商品进行从大到小和从小到大进行排序;
并求出这个区间的商品的平均价格。
源代码:
goods = [568, 239, 368, 425, 121, 219, 834, 1263, 26]
max_price = int(input('请输入您能接受的最大价格:'))
min_price = int(input('请输入您能接受的最小价格:'))
filter_price = [x for x in goods if min_price <= x <= max_price]
g1 = sorted(filter_price)
g2 = sorted(filter_price, reverse=True)
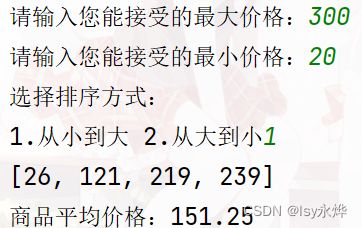
print('选择排序方式:')
choice = input('1.从小到大 2.从大到小')
if choice == '1':
print(g1)
else:
print(g2)
average_price = sum(filter_price) / len(filter_price)
print(f'商品平均价格:{average_price}')
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
5、实验题目:生成验证码
验证码一般是包括一些随机产生的数字或符号,请实现随机生成一组6位验证码的功能。
每个字符可以是大写字母、小写字母或数字,有且只能是这三种类型中的一种。
源代码:
import random
import string
def RandomCode():
AllSet = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
randomCode = ''.join(random.choice(AllSet) for _ in range(6))
return randomCode
code = RandomCode()
print(f'验证码:{code}')
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
6、实验题目:奇不变偶变
编写程序,使用列表生成表达式生成一个包含20个随机整数的列表,然后对其中偶数下标的元素进行降序排列,奇数下标的元素不变。(提示,使用切片)
源代码(这里是按第一个是奇数下标1,第二个是偶数下标2来算的):
import random
old_list = [random.randint(0, 100) for _ in range(20)]
new_list = old_list[::2]+[ ' '] + sorted(old_list[1::2], reverse=True)
print(f'初始:{old_list}')
print(f'改后:{new_list}')
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
7、实验题目:列表生成表达式
编写程序,使用列表生成表达式生成一个包含50个随机整数的列表,然后删除其中所有奇数(提示:从后向前删。)
源代码:
import random
old_list = [random.randint(1, 100) for _ in range(50)]
# [::-1]:最后的切片操作再次将得到的列表逆序,以恢复到与原始列表相同的顺序。
new_list=[x for x in old_list[::-1] if x%2==0][::-1]
print(f'原来:{old_list}')
print(f'改完:{new_list}')
列出测试数据和实验结果截图(太多了无法展示完):
![]()
8、实验题目:统计词频 (选做)
给一段文本,例如:“who have an apple apple is free free is money you know”,请统计单词出现的次数。(提示:需要用正则表达式去掉标点符号和空格)
源代码:
import re
text = "who have an apple apple is free free is money you know"
# 使用正则表达式去掉标点符号和空格,并将文本转换为小写
cleaned_text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', text).lower()
# 将文本拆分成单词列表
words = cleaned_text.split()
# 使用字典统计单词出现的次数
word_count = {}
for word in words:
if word in word_count:
word_count[word] += 1
else:
word_count[word] = 1
# 输出结果
print("单词频次统计:")
for word, count in word_count.items():
print(f"{word}: {count}次")
列出测试数据和实验结果截图:
实验总结:
1.在字典中key值也可看成索引值(index),因此可以通过名字[key]找到对应的value值,也就是直接用这个value值。
2.str(number) 将输入的数字 number 转换为字符串,字符串是可迭代的,可以逐个访问其中的字符,整数并不是可迭代的对象,因此需要将其转换为字符串以便按位访问数字。
3.排序默认是顺序排序。
4.目前看只有列表可以进行排序sort()。
5.for _ in range(6) 是一个循环语句,用于迭代执行某个代码块6次。在这里,使用下划线 _ 作为迭代变量名,这是一种Python中的惯例,表示我们在循环体内并不使用这个变量。