Java之IO流(其他流)
目录
一、缓冲流
(一)、概述
(二)、字节缓冲流
1、构造方法
2、read和write方法
(三)、字符缓冲流
1、构造方法
2、特有方法
二、转换流
(一)、InputStreamReader类
1、构造方法
(一)、OutputStreamWriter类
1、构造方法
三、序列化
(一)、概述
(二)、ObjectOutputStream类
1、构造方法
2、序列化操作
3、写出对象方法
(二)、ObjectInputStream类
1、构造方法
2、反序列化操作1
3、反序列化操作2
四、打印流
(一)、概述
(二)、PrintStream类
1、构造方法
2、特有方法
(三)、PrintWriter类
1、构造方法
2、特有方法
五、压缩流和解压缩流
(一)、压缩流:
(二)、解压缩流:
一、缓冲流
(一)、概述
缓冲流,也叫高效流,是对4个基本的
FileXxx流的增强,所以也是4个流,按照数据类型分类:
- 字节缓冲流:
BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream- 字符缓冲流:
BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
缓冲流的基本原理,是在创建流对象时,会创建一个内置的默认大小的缓冲区数组,通过缓冲区读写,减少系统IO次数,从而提高读写的效率。
(二)、字节缓冲流
底层自带了长度为8192的缓冲区提高性能
1、构造方法
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in):创建一个 新的缓冲输入流。public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建一个新的缓冲输出流。
// 创建字节缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("bis.txt"));
// 创建字节缓冲输出流
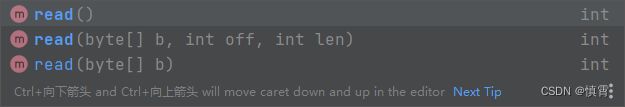
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("bos.txt"));2、read和write方法
(三)、字符缓冲流
1、构造方法
public BufferedReader(Reader in):创建一个 新的缓冲输入流。public BufferedWriter(Writer out): 创建一个新的缓冲输出流。
// 创建字符缓冲输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("br.txt"));
// 创建字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("bw.txt"));2、特有方法
- BufferedReader:
public String readLine(): 读一行文字。
- 一次读一行,遇到回车换行结束,但是不会把回车换行读到内存中
- BufferedWriter:
public void newLine(): 写一行行分隔符,由系统属性定义符号。
public class BufferedWriterDemo throws IOException {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("out.txt"));
// 写出数据
bw.write("a");
// 写出换行
bw.newLine();
bw.write("b");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("c");
bw.newLine();
// 释放资源
bw.close();
}
}
二、转换流
(一)、InputStreamReader类
转换流
java.io.InputStreamReader,是Reader的子类,是从字节流到字符流的桥梁。它读取字节,并使用指定的字符集将其解码为字符。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。
1、构造方法
InputStreamReader(InputStream in): 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName): 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt"));
InputStreamReader isr2 = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("in.txt") , "GBK");(一)、OutputStreamWriter类
转换流
java.io.OutputStreamWriter,是Writer的子类,是从字符流到字节流的桥梁。使用指定的字符集将字符编码为字节。它的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以接受平台的默认字符集。
1、构造方法
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in): 创建一个使用默认字符集的字符流。OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream in, String charsetName): 创建一个指定字符集的字符流。
OutputStreamWriter isr = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("out.txt"));
OutputStreamWriter isr2 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("out.txt") , "GBK");read方法和write方法都差不多就不写了
三、序列化
(一)、概述
Java 提供了一种对象序列化的机制。用一个字节序列可以表示一个对象,该字节序列包含该
对象的数据、对象的类型和对象中存储的属性等信息。字节序列写出到文件之后,相当于文件中持久保存了一个对象的信息。反之,该字节序列还可以从文件中读取回来,重构对象,对它进行反序列化。
对象的数据、对象的类型和对象中存储的数据信息,都可以用来在内存中创建对象。
(二)、ObjectOutputStream类
java.io.ObjectOutputStream类,将Java对象的原始数据类型写出到文件,实现对象的持久存储。
1、构造方法
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out): 创建一个指定OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream。
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("employee.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);2、序列化操作
一个对象要想序列化,必须满足两个条件:
该类必须实现
java.io.Serializable接口,Serializable是一个标记接口,不实现此接口的类将不会使任何状态序列化或反序列化,会抛出NotSerializableException。- 该类的所有属性必须是可序列化的。如果有一个属性不需要可序列化的,则该属性必须注明是瞬态的,使用
transient关键字修饰。
public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {
public String name;
public String address;
public transient int age; // transient瞬态修饰成员,不会被序列化
public void addressCheck() {
System.out.println("Address check : " + name + " -- " + address);
}
}3、写出对象方法
public final void writeObject (Object obj): 将指定的对象写出。
public class SerializeDemo{
public static void main(String [] args) {
Employee e = new Employee(); e.name = "zhangsan";
e.address = "宛平南路600号";
e.age = 20;
try {
// 创建序列化流对象
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("employee.txt"));
// 写出对象
out.writeObject(e);
// 释放资源
out.close();
fileOut.close();
// 姓名,地址被序列化,年龄没有被序列化。
System.out.println("Serialized data is saved");
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 输出结果: Serialized data is saved(二)、ObjectInputStream类
ObjectInputStream反序列化流,将之前使用ObjectOutputStream序列化的原始数据恢复为对象。
1、构造方法
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in): 创建一个指定InputStream的ObjectInputStream。
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("oos.txt"));2、反序列化操作1
public final Object readObject (): 读取一个对象。
public class DeserializeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee e = null;
try {
// 创建反序列化流
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("employee.txt");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);
// 读取一个对象
e = (Employee) in.readObject();
// 释放资源
in.close();
fileIn.close();
} catch (IOException i) {
// 捕获其他异常
i.printStackTrace();
return;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException c) {
// 捕获类找不到异常
System.out.println("Employee class not found");
c.printStackTrace();
return;
}
// 无异常,直接打印输出
System.out.println("Name: " + e.name);
// zhangsan
System.out.println("Address: " + e.address);
// beiqinglu
System.out.println("age: " + e.age);
// 0
}
}
对于JVM可以反序列化对象,它必须是能够找到class文件的类。如果找不到该类的class文件,则抛出一个
ClassNotFoundException异常。
3、反序列化操作2
另外,当JVM反序列化对象时,能找到class文件,但是class文件在序列化对象之后发生了修改,那么反序列化操作也会失败,抛出一个
InvalidClassException异常。发生这个异常的原因如下:
- 该类的序列版本号与从流中读取的类描述符的版本号不匹配
- 该类包含未知数据类型
- 该类没有可访问的无参数构造方法
Serializable接口给需要序列化的类,提供了一个序列版本号。serialVersionUID该版本号的目的在于验证序列化的对象和对应类是否版本匹配。
public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {
// 加入序列版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public String name;
public String address;
// 添加新的属性 ,重新编译, 可以反序列化,该属性赋为默认值
public int eid;
public void addressCheck() {
System.out.println("Address check : " + name + " -- " + address);
}
}四、打印流
(一)、概述
平时我们在控制台打印输出,是调用
println方法完成的,这两个方法都来自于java.io.PrintStream类,该类能够方便地打印各种数据类型的值,是一种便捷的输出方式。打印流不能读,只能写
特点:
- 打印流只操作文件目的地,不操作数据源
- 特有的写出方法,可以实现数据原样写出
- 特有的写出方法,可以实现自动刷新,自动换行
(二)、PrintStream类
1、构造方法
- public PrintStream(OutputStream/File/String):关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径
- public PrintStream(String fileName,Charset charset):指定字符编码
- public PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush):自动刷新
- 字节流底层没有缓冲区,开不开自动刷新都一样
- public PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush,String encoding):指定字符编码且自动刷新
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("ps.txt");2、特有方法
- public void println(XXX xx) :打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行
- public void print(XXX xx):打印任意数据,不换行
- public void printf(String format , Object ... args):带有占位符的打印语句,不换行
(三)、PrintWriter类
1、构造方法
- public PrintWriter(Writer/File/String):关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径
- public PrintWriter(String fileName,Charset charset):指定字符编码
- public PrintWriter(Writer w,boolean autoFlush):自动刷新
- public PrintWriter(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush,String encoding):指定字符编码且自动刷新
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("a.txt");2、特有方法
- public void println(XXX xx) :打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行
- public void print(XXX xx):打印任意数据,不换行
- public void printf(String format , Object ... args):带有占位符的打印语句,不换行
五、压缩流和解压缩流
注意:Java中只能识别zip的压缩包
(一)、压缩流:
负责压缩文件或者文件夹
压缩包里的每一个文件,在Java中是一个ZipEntry对象
压缩本质:把每一个文件或者文件夹看成ZipEntry对象放到压缩包中
// 压缩一个文件
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/* 压缩流
* 需求:
* 把D:\a.txt打包成一个压缩包
* */
//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件
File src = new File("D:\\a.txt");
//2.创建File对象表示压缩包的位置
File dest = new File("D:\\");
//3.调用方法用来压缩
toZip(src, dest);
}
/*
* 作用:压缩
* 参数一:表示要压缩的文件
* 参数二:表示压缩包的位置
* */
public static void toZip(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
//1.创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, "a.zip")));
//2.创建ZipEntry对象,表示压缩包里面的每一个文件和文件夹
//参数:压缩包里面的路径
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("a.txt");
//3.把ZipEntry对象放到压缩包当中
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//4.把src文件中的数据写到压缩包当中
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
zos.write(b);
}
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
}
// 压缩一个文件夹
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/* 压缩流
* 需求:
* 把D:\aaa文件夹压缩成一个压缩包
* */
//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件夹
File src = new File("D:\\aaa");
//2.创建File对象表示压缩包放在哪里(压缩包的父级路径)
File destParent = src.getParentFile();//D:\
// 3.创建File对象表示压缩包的路径
File dest = new File(destParent, src.getName() + ".zip");
//4.创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//5.获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
toZip(src, zos, src.getName());//aaa
// 6.释放资源
zos.close();
}
/*
* 作用:获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
* 参数一:数据源
* 参数二:压缩流
* 参数三:压缩包内部的路径
* */
public static void toZip(File src, ZipOutputStream zos, String name) throws IOException {
//1.进入src文件夹
File[] files = src.listFiles();
//2.遍历数组
if (files != null) {
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()) {
//3.判断-文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(name + "\\" + file.getName());//aaa\\no1\\a.txt
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//读取文件中的数据,写到压缩包
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
zos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
} else {
//4.判断-文件夹,递归
toZip(file, zos, name + "\\" + file.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
(二)、解压缩流:
负责把压缩包中的文件和文件夹解压出来
压缩包里的每一个文件,在Java中是一个ZipEntry对象
解压本质:把每一个ZipEntry按照层级拷贝到本地另一个文件夹中
public class ZipStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建一个File表示要解压的压缩包
File src = new File("D:\\aaa.zip");
//2.创建一个File表示解压的目的地
File dest = new File("D:\\");
//调用方法
unzip(src,dest);
}
//定义一个方法用来解压
public static void unzip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {
//解压的本质:把压缩包里面的每一个文件或者文件夹读取出来,按照层级拷贝到目的地当中
//创建一个解压缩流用来读取压缩包中的数据
ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
//要先获取到压缩包里面的每一个zipentry对象
//表示当前在压缩包中获取到的文件或者文件夹
ZipEntry entry;
while((entry = zip.getNextEntry()) != null){
System.out.println(entry);
if(entry.isDirectory()){
//文件夹:需要在目的地dest处创建一个同样的文件夹
File file = new File(dest,entry.toString());
file.mkdirs();
}else{
//文件:需要读取到压缩包中的文件,并把他存放到目的地dest文件夹中(按照层级目录进行存放)
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,entry.toString()));
int b;
while((b = zip.read()) != -1){
//写到目的地
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
//表示在压缩包中的一个文件处理完毕了。
zip.closeEntry();
}
}
zip.close();
}
}