Java进击框架:Spring-数据存取(七)
Java进击框架:Spring-数据存取(七)
- 前言
-
- 事务管理
-
- 声明式事务管理
- DAO支持
- JDBC的数据访问
-
- 使用JdbcTemplate
- 控制数据库连接
- JDBC批处理操作
- 封装 SQL 语句中的参数
- 使用R2DBC进行数据访问
- 对象关系映射(ORM)数据访问
-
- Hibernate
- JPA
- XML模式
前言
参考文档的这一部分涉及数据访问以及数据访问层和业务或服务层之间的交互。
Spring全面的事务管理支持被详细讨论,然后是Spring框架集成的各种数据访问框架和技术。
事务管理
全面的事务支持是使用Spring框架的最有说服力的理由之一。Spring框架为事务管理提供了一致的抽象,提供了以下好处:
- 跨不同事务API的一致编程模型,如Java事务API (JTA)、JDBC、Hibernate和Java持久性API (JPA)。
- 支持声明式事务管理。
- 更简单的API节目的事务管理比复杂的事务API,如JTA。
- 与Spring的数据访问抽象完美集成。
Spring框架的事务管理支持改变了企业Java应用程序何时需要应用服务器的传统规则。
- 全局事务
全局事务允许您使用多个事务资源,通常是关系数据库和消息队列。
应用服务器通过JTA(Java 平台上的一种事务管理标准) 管理全局事务,这是一个麻烦的 API(部分是由于它的异常模型),用于实现分布式事务的管理。在分布式环境中,多个应用程序或服务可能需要协调执行一个复杂的事务,全局事务的使用限制了应用程序代码的任何潜在重用,因为JTA通常只在应用服务器环境中可用。
以前,使用全局事务的首选方法是通过EJB CMT(一种在企业 Java Bean(EJB) 中使用的事务管理模型)。它是由 EJB 容器负责管理事务的一种方式,开发人员无需显式地编写事务管理代码。显著的缺点是CMT依赖于JTA和应用服务器环境。此外,只有当选择在EJB中实现业务逻辑时(或者至少在事务性EJB外观后面),它才是可用的。
- 本地事务
本地事务是特定于资源的,例如与JDBC连接关联的事务。本地事务可能更容易使用,但有一个明显的缺点:它们不能跨多个事务资源工作。由于应用服务器不参与事务管理,因此它无法帮助确保跨多个资源的正确性。(值得注意的是,大多数应用程序使用单个事务资源。)另一个缺点是本地事务对编程模型是侵入性的。
- Spring解决了全局和局部事务的缺点。它允许应用程序开发人员在任何环境中使用一致的编程模型。您只需编写一次代码,就可以在不同的环境中受益于不同的事务管理策略。Spring框架提供了声明式和编程式的事务管理。大多数用户更喜欢声明式事务管理
- Spring框架允许您选择何时将应用程序扩展到完全加载的应用程序服务器。使用EJB CMT或JTA的唯一替代方案是使用本地事务(例如JDBC连接上的事务)编写代码,并且如果需要在全局容器管理的事务中运行该代码,则面临大量重做的日子已经一去不复返了。使用Spring Framework,只需要更改配置文件中的一些bean定义(而不需要更改代码)。
Spring事务抽象的关键是事务策略的概念。事务策略由TransactionManager,特别是PlatformTransactionManager命令式事务管理接口和ReactiveTransactionManager反应式事务管理界面。如图显示了PlatformTransactionManager类的API

PlatformTransactionManager在Spring Framework IoC容器中,实现的定义类似于任何其他对象(或bean)。仅仅这个好处就使得Spring框架事务成为一个有价值的抽象,甚至当你和JTA一起工作的时候。与直接使用JTA相比,您可以更容易地测试事务性代码。
同样,为了与Spring的理念保持一致,可以由PlatformTransactionManager接口的任何方法抛出的TransactionException是未检查的(也就是说,它扩展了java.lang.RuntimeException类)。
getTransaction(..)方法根据TransactionDefinition参数返回一个TransactionStatus对象。如果当前调用堆栈中存在匹配的事务,则返回的TransactionStatus可以表示新事务,也可以表示现有事务。后一种情况的含义是,与Jakarta EE事务上下文一样,TransactionStatus与执行线程相关联。
TransactionDefinition接口指定:
- 传播:通常,事务范围内的所有代码都在该事务中运行。但是,如果在已经存在事务上下文的情况下运行事务方法,则可以指定该行为。例如,代码可以继续在现有事务中运行(常见情况),或者可以挂起现有事务并创建新事务。Spring提供了EJB CMT中熟悉的所有事务传播选项。
- 隔离:此事务与其他事务的工作隔离的程度。例如,这个事务是否可以看到来自其他事务的未提交写。
- 超时:此事务在超时和被底层事务基础结构自动回滚之前运行的时间。
- 只读状态:当代码读取但不修改数据时,可以使用只读事务。在某些情况下,只读事务可能是一种有用的优化,比如在使用Hibernate时。
这些设置反映了标准的事务概念。如有必要,请参考讨论事务隔离级别和其他核心事务概念的资源。理解这些概念是使用Spring框架或任何事务管理解决方案的基础。
不管您在Spring中选择声明式还是编程式事务管理,定义正确的TransactionManager执行是绝对必要的。您通常通过依赖注入来定义这种实现。
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
bean>
声明式事务管理
大多数Spring Framework用户选择声明式事务管理。这个选项对应用程序代码的影响最小,因此最符合非侵入式轻量级容器的理念。
关于Spring框架的声明性事务支持,需要掌握的最重要的概念是这种支持是启用的通过AOP代理并且事务性通知是由元数据驱动的(目前是基于XML或注释的)。AOP与事务性元数据的结合产生了一个AOP代理,它使用TransactionInterceptor结合适当的TransactionManager实现来驱动围绕方法调用的事务。
在 Spring AOP 中,可以使用
transaction-manager属性:指定要使用的事务管理器的名称。
(1)
(2)
name属性:用于指定方法名称的模式,支持通配符 “*” 和 “?”。
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*"/>
tx:attributes>
propagation属性:该属性用于指定事务的传播行为,即事务如何在方法调用之间传播。
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW" />
tx:attributes>
isolation属性:指定事务的隔离级别,即事务如何隔离并发操作。
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get*" isolation="READ_COMMITTED" />
tx:attributes>
timeout属性:用于指定事务的超时时间,即事务最多能够运行多长时间。
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="delete*" timeout="30" />
tx:attributes>
read-only属性:用于指定事务是否只读,即事务是否仅用于读取数据而不进行修改操作。
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" />
tx:attributes>
rollback-for属性:用于指定触发事务回滚的异常类。
<tx:advice id="transactionAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="delete*" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" />
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
no-rollback-for属性:用于指定不触发事务回滚的异常类。
<tx:advice id="transactionAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="find*" no-rollback-for="java.lang.RuntimeException" />
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
示例代码如下:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="oneService" class="com.example.OneServiceImpl">bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*">tx:method>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="oneServiceTransaction" expression="execution(* com.example.OneService.*(..))">aop:pointcut>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="oneServiceTransaction">aop:advisor>
aop:config>
beans>
public interface OneService {
void getMethod();
void insertMethod();
void updateMethod();
void removeMethod();
}
public class OneServiceImpl implements OneService {
@Override
public void getMethod() { }
@Override
public void insertMethod() { }
@Override
public void updateMethod() { }
@Override
public void removeMethod() { }
}
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
OneService bean = applicationContext.getBean(OneService.class);
bean.getMethod();
}
}
首先,定义一个切入点,该切入点OneService 定义的任何操作的执行相匹配。然后通过使用advisor将切入点与txAdvice关联起来。结果表明,在执行OneService 时,将运行由txAdvice定义的通知。
命令式和响应式事务管理在事务边界和事务属性定义方面共享相同的语义。命令式事务和响应式事务的主要区别在于后者的延迟性质。响应式事务管理的另一个方面与数据转义有关,这是编程模型的自然结果。
-
命令式事务的方法返回值在成功终止方法时从事务性方法返回,这样部分计算的结果就不会逃过方法闭包。
-
响应式事务方法返回一个响应式包装器类型,它表示一个计算序列以及开始和完成计算的承诺。
发布者可以在事务正在进行但不一定完成时发出数据。因此,依赖于整个事务成功完成的方法需要确保在调用代码中完成并缓冲结果。Mono 是 Reactor 框架中的一个类,用于表示包含零个或一个元素的异步序列。它是 Reactor 中的一种响应式流类型,用于处理异步和非阻塞的操作(不做过多讲解)。
public interface OneService {
Flux getMethod();
Mono<Void> insertMethod();
Mono<Void> updateMethod();
Mono<Void> removeMethod();
}
除了基于XML的事务配置声明方法之外,还可以使用基于注释的方法。可以使用@Transactional注解对接口定义、接口方法。
@Transactional
public class OneServiceImpl implements OneService {
@Override
public void getMethod() throws SQLException { }
@Override
public void insertMethod() throws SQLException { }
@Override
public void updateMethod() { }
@Override
public void removeMethod() { }
}
您可以通过@Configuration类中的@EnableTransactionManagement注释使bean实例事务性。
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
// todo 配置数据源
return new MyDataSource();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
// 配置事务管理器
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
在XML配置中,可以使用
<beans>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
<bean id="oneService" class="com.example.OneServiceImpl">
<property name="dataSource2" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
@Transactional 注解里的属性和XML中的属性并无太大区别,没有指定 transactionManager 属性,默认情况下尝试从容器中获取一个类型为 PlatformTransactionManager 的 Bean。
除此之外Spring框架提供了两种编程事务管理的方法:TransactionTemplate或者TransactionalOperator。
示例代码如下:
public class OneServiceImpl implements OneService {
DataSource dataSource2;
TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate2;
public void setDataSource2(DataSource dataSource2) {
this.dataSource2 = dataSource2;
}
public void setTransactionTemplate2(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate2) {
this.transactionTemplate2 = transactionTemplate2;
//设置事务属性
transactionTemplate2.setReadOnly(false);
transactionTemplate2.setTimeout(10);
}
@Override
public void insertMethod() {
transactionTemplate2.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult(){
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus transactionStatus) {
Connection connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource2);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = null;
try {
preparedStatement1 = connection.prepareStatement("insert into user values(?,?,?)");
preparedStatement1.setInt(1,4);
preparedStatement1.setString(2,"qe");
preparedStatement1.setString(3,"12");
preparedStatement1.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new NullPointerException();
}
});
}
}
创建一个transactionTemplate的bean然后注入到oneService中
<beans>
<bean id="oneService" class="com.example.OneServiceImpl">
<property name="dataSource2" ref="dataSource">property>
<property name="transactionTemplate2" ref="transactionTemplate">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="txManager"/>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
除了在代码中设置事务属性,也可在xml中设置,示例代码如下:
<bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="isolationLevelName" value="ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED"/>
<property name="timeout" value="30"/>
bean>
使用 TransactionTemplate 可以更加灵活地控制事务的边界和行为,但也增加了代码的复杂性。
- 事务绑定事件
从Spring 4.2开始,事件的监听器可以绑定到事务的一个阶段。典型的示例是在事务成功完成时处理事件。这样做可以在当前事务的结果对侦听器有实际影响时更灵活地使用事件。您可以通过使用@EventListener注释。如果需要将其绑定到事务,请使用@TransactionalEventListener。
示例代码如下:
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.example");
MyEventPublisher bean = applicationContext.getBean(MyEventPublisher.class);
bean.publishEvent("hello message");
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class Config {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
MysqlDataSource mysqlDataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
mysqlDataSource.setURL("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data");
mysqlDataSource.setUser("root");
mysqlDataSource.setPassword("123456");
return mysqlDataSource;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
// 配置事务管理器
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
@Component
public class MyEventPublisher {
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
public void publishEvent(String message) {
MyEvent event = new MyEvent(message);
eventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
@Component
public class MyEventListener {
@TransactionalEventListener
public void handleEvent(MyEvent event) {
System.out.println("Received event: " + event.getMessage());
}
}
@TransactionalEventListener 注解只有在事务成功提交后才会触发事件处理。所以上面的示例在报异常后不会触发事件。
DAO支持
Spring中的数据访问对象(DAO)支持旨在以一致的方式简化数据访问技术(如JDBC、Hibernate或JPA)的工作。这让您可以相当容易地在上述持久性技术之间切换,并且还让您无需担心捕捉特定于每种技术的异常就可以进行编码。
Spring提供了从特定于技术的异常(如SQLException)到自己的异常类层次结构的方便转换,其中将DataAccessException作为根异常。这些异常包装了原始异常,这样就不会有丢失任何有关可能出错的信息的风险。下图显示了Spring提供的异常层次结构。
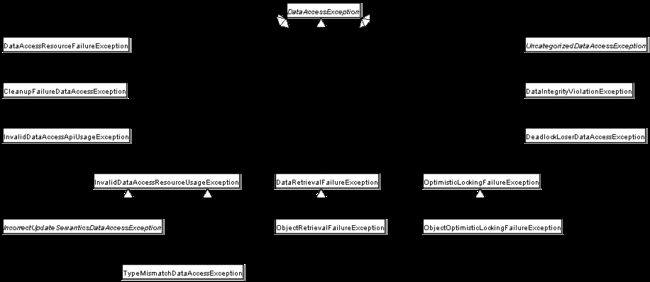
保证数据访问对象(dao)或存储库提供异常转换的最佳方法是使用@Repository注释。该注释还允许组件扫描支持查找和配置dao和存储库,而不必为它们提供XML配置项。
@Repository
public class UserDao {
}
任何DAO或存储库实现都需要访问持久性资源,具体取决于所使用的持久性技术。例如,基于JDBC的存储库需要访问JDBC数据源,而基于jpa的存储库需要访问EntityManager。
public class MyService {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void saveEntity(MyEntity entity) {
//创建
entityManager.persist(entity);
}
public void updateEntity(MyEntity entity) {
//更新
entityManager.merge(entity);
}
public void deleteEntity(MyEntity entity) {
//删除
entityManager.remove(entity);
}
}
如果您使用传统的Hibernate APIs,您可以注入SessionFactory,如下例所示:
public class MyService {
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public static void initSessionFactory() {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
}
public void doDatabaseOperation() {
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
// 执行数据库操作
session.close();
}
}
我们在这里展示的最后一个示例是典型的JDBC支持。您可以将DataSource注入到初始化方法或构造函数中,通过使用此DataSource创建JdbcTemplate和其他数据访问支持类(如simplejdbcall等)。
<beans>
<bean id="oneService" class="com.example.OneServiceImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate2" ref="jdbcTemplate">property>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
bean>
beans>
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
OneService bean = applicationContext.getBean(OneService.class);
bean.getMethod();
}
}
public class OneServiceImpl implements OneService {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate2;
public void setJdbcTemplate2(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate2) {
this.jdbcTemplate2 = jdbcTemplate2;
}
@Override
public void getMethod() throws SQLException {
String a = "select * from user ";
List<Map<String, Object>> list = jdbcTemplate2.queryForList(a);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
JDBC的数据访问
表格显示了Spring负责哪些操作,哪些操作是您的责任。
| 行为 | Spring | 你负责 |
|---|---|---|
| 定义连接参数。 | X | |
| 打开连接。 | X | |
| 指定SQL语句。 | X | |
| 声明参数并提供参数值 | X | |
| 准备并运行语句。 | X | |
| 设置循环以遍历结果(如果有)。 | X | |
| 为每个迭代做工作。 | X | |
| 处理任何异常。 | X | |
| 处理交易。 | X | |
| 关闭连接、语句和结果集。 | X |
您可以从几种方法中进行选择,以形成JDBC数据库访问的基础。除了JdbcTemplate之外,新的SimpleJdbcInsert和SimpleJdbcCall方法优化了数据库元数据,RDBMS对象风格采用了类似于JDO查询设计的更加面向对象的方法。一旦您开始使用其中一种方法,您仍然可以混合搭配以包含来自不同方法的特性。
- JdbcTemplate是最经典和最流行的Spring JDBC方法。这种“最低级别”的方法和所有其他方法都在幕后使用JdbcTemplate(示例参考前面的案例)。
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate 是 JdbcTemplate 的一个扩展,它提供了一种更方便的方式来执行带有命名参数的 SQL 查询和更新操作。相比于传统的使用问号占位符的方式,NamedParameterJdbcTemplate 允许我们使用命名参数来代替占位符,使得 SQL 语句更易读、易维护。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="oneService" class="com.example.OneServiceImpl">
<property name="namedParameterJdbcTemplate2" ref="namedParameterJdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
</bean>
</beans>
public class OneServiceImpl implements OneService {
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate2;
public void setNamedParameterJdbcTemplate2(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate) {
this.namedParameterJdbcTemplate2 = namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public void getMethod() throws SQLException {
//:id 是一个命名参数,它使用冒号开头。与传统的占位符不同,命名参数更直观地表示了参数的含义。
String a = "select * from user where id=:id";
//设置参数
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id",1);
List<Map<String, Object>> list = namedParameterJdbcTemplate2.queryForList(a,map);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
- SimpleJdbcInsert这种方法简化了编码,因此您只需要提供表或过程的名称,并提供与列名匹配的参数映射,而无需手动编写 SQL 语句。
<beans>
<bean id="oneService" class="com.example.OneServiceImpl">
<property name="simpleJdbcInsert2" ref="simpleJdbcInsert">property>
bean>
<bean id="simpleJdbcInsert" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.simple.SimpleJdbcInsert">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource" />
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
bean>
beans>
public class OneServiceImpl implements OneService {
SimpleJdbcInsert simpleJdbcInsert2;
public void setSimpleJdbcInsert2(SimpleJdbcInsert simpleJdbcInsert) {
this.simpleJdbcInsert2 = simpleJdbcInsert;
}
@Override
public void insertMethod() {
simpleJdbcInsert2.withTableName("user");
MapSqlParameterSource mapSqlParameterSource = new MapSqlParameterSource();
mapSqlParameterSource.addValue("id",4);
mapSqlParameterSource.addValue("name","gl");
mapSqlParameterSource.addValue("age","19");
Number number = simpleJdbcInsert2.execute(mapSqlParameterSource);
System.out.println(number.intValue());
}
}
SimpleJdbcCall 是 Spring JDBC 框架提供的一个类,用于调用存储过程和函数。它提供了一种更加简单和方便的方法来执行数据库操作,而无需编写复杂的 JDBC 代码。
- RDBMS对象——包括MappingSqlQuery(用于执行 SQL 查询并将结果映射到 Java 对象)、SqlUpdate(用于执行 SQL 更新操作(如插入、更新、删除))和StoredProcedure(用于执行存储过程)——要求您在数据访问层初始化期间创建可重用的线程安全对象。
MappingSqlQuery示例代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="userMappingSqlQuery" class="com.example.UserMappingSqlQuery">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
</bean>
</beans>
public class UserMappingSqlQuery extends MappingSqlQuery<User> {
public UserMappingSqlQuery(DataSource dataSource){
super(dataSource, "SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ?");
//声明参数的输入输出类型
declareParameter(new SqlParameter(Types.INTEGER));
compile();
}
@Override
protected User mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
user.setAge(resultSet.getString("age"));
return user;
}
}
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserMappingSqlQuery bean = applicationContext.getBean(UserMappingSqlQuery.class);
User object = bean.findObject(1);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(object));
}
}
SqlUpdate示例代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="userSqlUpdate" class="com.example.UserSqlUpdate">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
</bean>
</beans>
public class UserSqlUpdate extends SqlUpdate {
public UserSqlUpdate(DataSource dataSource){
//预先定义insert、update、delete语句
super(dataSource, "INSERT INTO user (id, name, age) VALUES (?, ?, ?)");
declareParameter(new SqlParameter(Types.INTEGER));
declareParameter(new SqlParameter(Types.VARCHAR));
declareParameter(new SqlParameter(Types.VARCHAR));
compile();
}
public void insertUser(User user) {
//统一调用方法
update(user.getId(), user.getName(), user.getAge());
}
}
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserSqlUpdate bean = applicationContext.getBean(UserSqlUpdate.class);
User user = new User();
user.setId(5);
user.setName("llz");
user.setAge("34");
bean.insertUser(user);
}
}
使用JdbcTemplate
在前面的示例中,简单的介绍过使用JdbcTemplate进行查询的操作,JdbcTemplate是JDBC核心课程的核心课程。它处理资源的创建和释放,这有助于避免常见的错误,比如忘记关闭连接。它执行核心JDBC工作流的基本任务(如语句创建和执行),留下应用程序代码来提供SQL和提取结果。
- 查询(SELECT)
public void getMethod() throws SQLException {
//查询总数,指定返回类型
Integer count = jdbcTemplate2.queryForObject("select count(*) from user", Integer.class);
//查询指定条件,指定返回类型(不能直接返回对象接收)
String name= jdbcTemplate2.queryForObject("select name from user where id=?", String.class, 1);
//可以使用这种方式返回对象(不建议使用)
User name = jdbcTemplate2.queryForObject("select * from user where id=?", new Object[]{1}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));
//通过lambda表达式,填充单个域对象
User user = jdbcTemplate2.queryForObject("select * from user where id=?", (resultSet, rowNum) -> {
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user2.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
user2.setAge(resultSet.getString("age"));
return user2;
}, 1);
//通过lambda表达式,填充域对象列表
List<User> list = jdbcTemplate2.query("select * from user",(resultSet, rowNum) -> {
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user2.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
user2.setAge(resultSet.getString("age"));
return user2;
});
}
建议每个实体类实现RowMapper接口,重载mapRow()方法,进行赋值。
public class User implements RowMapper<User> {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String age;
//getter() and setter()
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
user.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
user.setAge(resultSet.getString("age"));
return user;
}
}
- 更新(INSERT, UPDATE,以及DELETE)与JdbcTemplate
统一调用update()方法进行处理。
public void updateMethod() {
//新增
jdbcTemplate2.update("insert into user(id,name,age) values(?,?,?)",6,"qq",32);
//修改
jdbcTemplate2.update("update user set name=?,age=? where id=?","zc",10,1);
//删除
jdbcTemplate2.update("delete from user where id=?",6);
}
控制数据库连接
Spring通过DataSource获得与数据库的连接。数据源是JDBC规范的一部分,是一个通用的连接工厂。它允许容器或框架对应用程序代码隐藏连接池和事务管理问题。作为一名开发人员,您不需要知道如何连接到数据库的细节。这是设置数据源的管理员的责任。在开发和测试代码时,您很可能同时担任这两个角色,但是您不必知道如何配置生产数据源。
您应该使用DriverManagerDataSource和SimpleDriverDataSource类(包含在Spring发行版中),仅用于测试目的!这些变体不提供池,并且在对一个连接发出多个请求时性能很差。
Java中配置DriverManagerDataSource:
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
以下示例显示了相应的XML配置:
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
bean>
国内用的比较多的是阿里巴巴开源的Druid 数据库连接池作为 Spring 的数据源。
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</bean>
JDBC批处理操作
如果对同一条预处理语句进行批量调用,大多数JDBC驱动程序都会提供改进的性能。通过将更新分组成批,可以限制到数据库的往返次数。
通过实现一个特殊接口BatchPreparedStatementSetter的两个方法,并将该实现作为batchUpdate()方法调用中的第二个参数传递进来,可以完成JdbcTemplate批处理。您可以使用getBatchSize()方法来提供当前批处理的大小。您可以使用setValues()方法为准备好的语句的参数设置值。此方法将按照您在getBatchSize()调用中指定的次数调用,调用完毕后返回int数组,对应批次执行 SQL 语句后影响的行数。
public void updateMethod(List<User> list) {
//也可以使用insert语句
int[] result= jdbcTemplate2.batchUpdate("update user set name=?,age=? where id=?", new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
User user = list.get(i);
//传参
preparedStatement.setString(1, user.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2, user.getAge());
preparedStatement.setInt(3, user.getId());
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return list.size();
}
});
}
你也可以使用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate命名参数进行批量修改:
public void updateMethod(List<User> list) {
//也可以使用insert语句
int[] ints = namedParameterJdbcTemplate2.batchUpdate("update user set name=:name,age=:age where id=:id"
, SqlParameterSourceUtils.createBatch(list));
}
封装 SQL 语句中的参数
SqlParameterSource 接口定义了一些方法,用于访问和获取参数的值。具体的实现类包括:
- MapSqlParameterSource:使用
java.util.Map实现的 SqlParameterSource。
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
//忽略参数
SqlParameterSource sqlParams = new MapSqlParameterSource(params);
String sql = "INSERT INTO user (id, name, age) VALUES (:id, :name, :age)";
int rowsAffected = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, sqlParams);
- BeanPropertySqlParameterSource:使用 JavaBean 的属性来作为参数的值。
User user = new User();
//忽略参数
SqlParameterSource sqlParams = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(user);
String sql = "INSERT INTO user (id, name, age) VALUES (:id, :name, :age)";
int rowsAffected = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, sqlParams);
- SqlParameterSourceUtils:提供了一些实用方法,用于将对象转换为 SqlParameterSource。
List<User> list = new ArrayList();
//忽略参数
SqlParameterSource[] sps = SqlParameterSourceUtils.createBatch(list);
String sql = "INSERT INTO user (id, name, age) VALUES (:id, :name, :age)";
int rowsAffected = namedParameterJdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, sps);
使用R2DBC进行数据访问
R2DBC是Reactive Relational Database Connectivity的缩写,它是一种针对关系型数据库的响应式编程接口标准。
所需依赖如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.datagroupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-r2dbcartifactId>
<version>1.0.0.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.mikugroupId>
<artifactId>r2dbc-mysqlartifactId>
<version>0.8.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
R2DBC解决了传统JDBC面临的一些挑战。JDBC中,所有的数据库操作都是同步的,每个操作都需要等待结果返回后才能继续执行下一个操作,这种方式在高并发场景下会导致性能瓶颈和资源浪费。而R2DBC则采用了异步和响应式的方式来处理数据库操作,使得我们可以更好地处理高并发和复杂的业务场景。目前支持的数据库包括PostgreSQL、MySQL、Microsoft SQL Server、Oracle和H2等。
- 连接数据库
使用 ConnectionFactoryOptions 构建器来创建一个包含连接选项的对象。在这个示例中,我们使用了 host、port、database、user、password 和 connectTimeout 选项。您可以根据需要添加或修改其他连接选项。
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
ConnectionFactoryOptions options = ConnectionFactoryOptions.builder()
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.DRIVER, "mysql")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.HOST, "localhost")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.PORT, 3306)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.USER, "root")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.PASSWORD, "123456")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.DATABASE, "spring_data")
.build();
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = ConnectionFactories.get(options);
}
ConnectionFactory应该总是被配置为Spring IoC容器中的bean。
ConnectionFactoryUtils类是一个方便而强大的帮助器类,它提供了static从获取连接的方法ConnectionFactory并关闭连接(如有必要)。
- 使用DatabaseClient
DatabaseClient是R2DBC核心包中的中心类。它处理资源的创建和释放,这有助于避免常见的错误,例如忘记关闭连接。它执行核心R2DBC工作流的基本任务(比如语句创建和执行),留下应用程序代码来提供SQL和提取结果。
DatabaseClient client = DatabaseClient.create(connectionFactory);
- 执行语句
DatabaseClient提供运行语句的基本功能。以下示例显示了创建新表所需的最少但功能齐全的代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConnectionFactoryOptions options = ConnectionFactoryOptions.builder()
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.DRIVER, "mysql")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.HOST, "localhost")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.PORT, 3306)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.USER, "root")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.PASSWORD, "123456")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.DATABASE, "spring_data")
.build();
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = ConnectionFactories.get(options);
DatabaseClient databaseClient = DatabaseClient.create(connectionFactory);
String createTableSql = "CREATE TABLE student("
+ "id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY)";
databaseClient.execute(createTableSql)//执行SQL命令
.fetch()//获取执行结果
.rowsUpdated()//返回受影响的行数(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE计数)
.doOnSuccess(rowsUpdated -> System.out.println("Table created successfully"))//打印消息以指示表已成功创建
.block();//阻塞等待一个元素操作完成
}
- 查询(SELECT)
Map<String, Object> first = databaseClient.execute("select id,name,age from user")
.fetch()//获取执行结果
.all()//返回所有数据
.blockLast();//阻塞等待最后一个元素操作完成
Map<String, Object> first2 = databaseClient.execute("select id,name,age from user where id=:id")
.bind("id",2)//将一个值和一个函数绑定在一起
.fetch()
.first()//返回整个结果的第一行
.block();
除此之外还有很多其它的方法,有空单独再写一篇,比如,map()、filter()方法和我们常用的流式编程一样,除了使用block()方法,
关系数据库结果可以包含空值。响应式流规范禁止释放空值。该需求要求在提取器函数中进行适当的null处理。虽然可以从行中获取空值,您必须将任何空值包装在对象中(例如,对于单数值,可选),以确保提取器函数永远不会直接返回空值。
- 更新(INSERT, UPDATE,以及DELETE)
Mono<Integer> rowsUpdated = databaseClient.execute("update user set name=:name where id=:id")
.bind("id",1)//绑定数据
.bind("name","test")
.fetch()//获取执行结果
.rowsUpdated();//返回受影响的行数(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE计数)
- 将值绑定到查询
R2DBC使用依赖于实际数据库供应商的数据库本地绑定标记。例如,Postgres使用索引标记,如$1,$2,$n。另一个例子是SQL Server,它使用以@为前缀的命名绑定标记。
这与JDBC不同,JDBC需要?作为绑定标记。在JDBC中,实际的驱动程序转换为?将标记绑定到数据库本地标记,作为其语句执行的一部分。
Spring框架的R2DBC支持允许您使用本机绑定标记或带有:name语法的命名绑定标记。
命名参数支持利用BindMarkersFactory实例在查询执行时将命名参数扩展为本机绑定标记,这为您提供了跨各种数据库供应商的一定程度的查询可移植性。
对象关系映射(ORM)数据访问
Spring框架支持与Java Persistence API (JPA)的集成,并支持用于资源管理、数据访问对象(DAO)实现和事务策略的本机Hibernate。它们可以参与Spring的资源和事务管理,并且遵守Spring的通用事务和DAO异常层次结构。推荐的集成风格是针对普通Hibernate或JPA api编写dao。
使用Spring框架创建ORM dao的好处包括:
- 更容易测试
Spring的IoC方法可以很容易地交换Hibernate SessionFactory实例、JDBC DataSource实例、事务管理器和映射对象实现(如果需要)的实现和配置位置。这反过来又使得单独测试与持久性相关的每段代码变得容易得多。
- 常见的数据访问异常
Spring可以包装来自ORM工具的异常,将它们从专有(可能已检查)异常转换为公共运行时DataAccessException层次结构。
- 一般资源管理
Spring应用程序上下文可以处理Hibernate SessionFactory实例、JPA EntityManagerFactory实例、JDBC DataSource实例和其他相关资源的位置和配置。这使得这些值易于管理和更改。Spring提供了高效、简单和安全的持久性资源处理。
- 集成事务管理
您可以通过@Transactional注释或通过在XML配置文件中显式配置事务AOP通知,将ORM代码与声明式的、面向方面编程(AOP)风格的方法拦截器包装起来。
Hibernate
我们从介绍Spring环境中的Hibernate 5开始,用它来演示Spring集成OR映射器的方法。
依赖文件:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernategroupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-coreartifactId>
<version>5.6.6.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-ormartifactId>
<version>5.3.10version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.logginggroupId>
<artifactId>jboss-loggingartifactId>
<version>3.3.0.Finalversion>
dependency>
hibernate配置文件:
DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverproperty>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_dataproperty>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">rootproperty>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">123456property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialectproperty>
<mapping class="com.example.User"/>
session-factory>
hibernate-configuration>
java代码:
@Entity
@Table(name = "test")
public class User {
@Id
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "age")
private String age;
//getter()和setter()方法
}
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 Hibernate 配置对象
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
// 创建 SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
// 开始一个新的 session
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
// 开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
// 创建一个新的 User 对象
User user = new User();
user.setId(6);
user.setName("Doe");
user.setAge("26");
// 将新 User 对象保存到数据库
session.save(user);//除此之外:session.createQuery()查询方法、session.update()修改方法
// 提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
// 关闭 session 和 sessionFactory
session.close();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
JPA
Spring JPA,可在org.springframework.orm.jpa软件包,为提供全面的支持Java持久性API以类似于与Hibernate集成的方式,同时了解底层实现,以便提供额外的特性。
配置文件:
<persistence version="2.2"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_2.xsd">
<persistence-unit name="MyPersistenceUnit" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL">
<provider>org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProviderprovider>
<class>com.example.Userclass>
<properties>
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_data" />
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.user" value="root" />
<property name="javax.persistence.jdbc.password" value="123456" />
properties>
persistence-unit>
persistence>
java代码:
@Entity
@Table(name = "test")
public class User {
@Id
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String age;
//getter()和setter()方法
}
public class SpringData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("MyPersistenceUnit");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
// 插入数据
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
User user = new User();
user.setId(7);
user.setName("line");
user.setAge("16");
entityManager.persist(user);
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
// 查询数据
user = entityManager.find(User.class, 1);
System.out.println(user.getName());
//调用entityManager.merge(user) 方法将更新后的实体对象合并到持久化上下文中
entityManager.close();
entityManagerFactory.close();
}
}
XML模式
tx纲要
tx标记处理在Spring对事务的全面支持中配置所有这些bean。这些标签将在题为事务管理的章节中介绍。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
beans>
通常,当您使用tx命名空间中,您还可以使用aop名称空间(因为Spring中的声明式事务支持是通过使用AOP实现的)。前面的XML片段包含引用aop架构,以便aop名称空间可供您使用。
jdbc纲要
jdbc元素允许您快速配置嵌入式数据库或初始化现有数据源。这些元素分别记录在嵌入式数据库支持和初始化数据源中。
要使用jdbc模式中的元素,您需要在Spring XML配置文件的顶部有以下序言。以下代码片段中的文本引用了正确的模式,以便jdbc命名空间中的元素对您可用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" <!--声明的用法jdbc命名空间-->
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
https://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd"> <!--指定位置(使用其他模式位置)-->
<!-- bean definitions here -->
</beans>