ggkegg帮助文档 | 译文一
一、前言
本文来自ggkegg使用手册,译文为机器翻译。译文可能与原文有所出入,请查看以原文为主,译文仅提供参考意义。
公众号原文链接:
1. ggkegg | 对KEGG数据进行可视化
2. ggkegg帮助文档 | 译文
译文:小杜的生信笔记
原文链接:https://noriakis.github.io/software/ggkegg/index.html
时间:2023.12.26
三、ggkegg使用说明
1. About
ggkegg从 KEGG 获取信息并进行解析,使用 ggplot2和 ggraph 对其进行分析和可视化,结合使用 KEGG 调查生物功能的其他软件包。该软件包旨在使用图形文法可视化 KEGG 的复杂组件。对于 Python,请使用 plotine 的 pykegg,它提供了与 ggkegg 几乎相同的功能,与 gseapy 和 PyDESeq2以及单细胞转录组学分析库扫描软件包一起使用。
# devtools::install_github("noriakis/ggkegg")
library(ggkegg)
ggkegg的主要目标之一是使用整齐图形以整齐的方式处理 KEGG 信息,并提供 KEGG 信息的定制可视化,包括 KEGG 路径、模块和网络。
library(dplyr)
library(tidygraph)
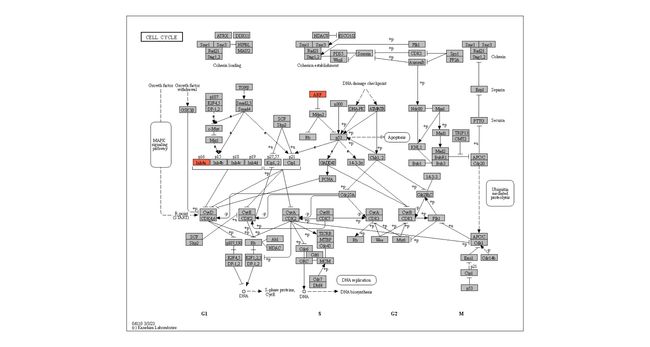
pathway("hsa04110") |> ## Obtain and parse the KEGG pathway
activate(nodes) |> ## node manipulation
mutate(convert_hsa=convert_id("hsa"),
convert_map=convert_id("pathway")) |> ## convert IDs for organism hsa and pathway
ggraph(x=x, y=y)+ ## ggraph plot
geom_edge_parallel(arrow=arrow(length=unit(1,"mm")),
aes(linetype=subtype_name),
end_cap=circle(7.5,"mm"))+ ## Parallel edges
geom_node_rect(aes(filter=type=="gene",
fill=I(bgcolor)),
color="black")+ ## rectangular nodes
geom_node_text(aes(label=convert_hsa),
size=2, family="serif")+ ## text
geom_node_text(aes(label=convert_hsa,
filter=!is.na(convert_hsa) & convert_hsa=="TP53"),
size=2, color="red", family="serif")+ ## highlight text
theme_void()
一些方便的功能准备,如突出的基因在途径。
## Highlight genes in the pathway, and overlay raw map.
highlight_entities("hsa04110", "CDKN2A")
如果提供了命名的数值向量,则将使用连续缩放。
## Highlight genes in the pathway, and overlay raw map.
vecs <- c(-2,2) |> setNames(c("CDKN2A", "CDC45"))
highlight_entities("hsa04110", vecs) +
scale_fill_viridis(name="LFC")
2. Pathway
提供 ggkegg 一个路径 ID,它获取信息,解析信息并生成 ggraph 对象。在内部,parse _ kgml 或 path 函数用于返回 igraph 或 tbl _ graph 对象。它可以用于所有的途径跨生物列在 KEGG 路径数据库。Path 函数是下载和解析 KGML 文件的核心函数。如果该文件已经存在于当前工作目录中,则不会再次下载。该功能还提取反应,包括在途径作为边缘。如果有用 type = line 表示的节点,函数将根据它们的坐标将这些节点转换为边。此转换由 process _ line 函数执行。
library(ggkegg)
library(ggfx)
library(ggraph)
library(igraph)
library(clusterProfiler)
library(dplyr)
library(tidygraph)
2.1示例可视化
该示例首先获取 eco00270并解析信息,转换路径和 eco 标识符,删除零度节点并返回图形对象。
g <- ggkegg(pid="eco00270",
convert_org = c("pathway","eco"),
delete_zero_degree = TRUE,
return_igraph = TRUE)
gg <- ggraph(g, layout="stress")
gg$data$type |> unique()
#> [1] "map" "compound" "gene"
gg + geom_edge_diagonal(
aes(color=subtype_name,
filter=type!="maplink"))+
geom_node_point(
aes(filter= !type%in%c("map","compound")),
fill=gg$data[!gg$data$type%in%c("map","compound"),]$bgcolor,
color="black",
shape=21, size=4
)+
geom_node_point(
aes(filter= !type%in%c("map","gene")),
fill=gg$data[!gg$data$type%in%c("map","gene"),]$bgcolor,
color="black",
shape=21, size=6
)+
geom_node_text(
aes(label=converted_name,
filter=type=="gene"),
repel=TRUE,
bg.colour="white")+
theme_void()
KGML 中描述的 x 坐标、 y 坐标、宽度和高度列为 x、 y、 width 和 height。根据这些信息,计算 xmin、 xmax、 ymin 和 ymax 并将其存储在节点表中。
2.2 geom_node_rect
该包还提供了 geom_node_rect 函数,该函数允许基于 xmin、 xmax、 ymin 和 ymax 的映射在指定位置绘制矩形。
2.2.1为节点分配颜色
可以使用 geom _ node _ rect 在节点上设置不同的多种颜色。当可视化诸如 log2倍数在多个条件之间变化的因素时,此应用程序非常有用。
g <- pathway("ko00520")
V(g)$color_one <- colorRampPalette(RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(5,"Set1"))(length(V(g)))
V(g)$color_two <- colorRampPalette(RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(5,"Set2"))(length(V(g)))
ggraph(g, x=x, y=y) +
geom_node_rect(aes(xmin=xmin, xmax=x, fill=I(color_one)), alpha=0.5)+
geom_node_rect(aes(xmin=x, xmax=xmax, fill=I(color_two)), alpha=0.5)+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(geom_node_text(aes(label=name |>
strsplit(":") |>
sapply("[", 2) |>
strsplit(" ") |>
sapply("[", 1),
filter=type=="ortholog"),
size=2), colour="white", expand=1)
可以指定任意数量的组。
V(g)$color_one <- colorRampPalette(RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(5,"Set1"))(length(V(g)))
V(g)$color_two <- colorRampPalette(RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(5,"Set2"))(length(V(g)))
V(g)$color_three <- colorRampPalette(RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(5,"PuOr"))(length(V(g)))
V(g)$color_four <- colorRampPalette(RColorBrewer::brewer.pal(5,"Paired"))(length(V(g)))
V(g)$space <- V(g)$width/4
ggraph(g, x=x, y=y) +
geom_node_rect(aes(xmin=xmin, xmax=xmin+space, fill=I(color_one), filter=type=="ortholog"))+
geom_node_rect(aes(xmin=xmin+space, xmax=xmin+2*space, fill=I(color_two), filter=type=="ortholog"))+
geom_node_rect(aes(xmin=xmin+2*space, xmax=xmin+3*space, fill=I(color_three), filter=type=="ortholog"))+
geom_node_rect(aes(xmin=xmin+3*space, xmax=xmin+4*space, fill=I(color_four), filter=type=="ortholog"))+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(geom_node_text(aes(label=name |>
strsplit(":") |>
sapply("[", 2) |>
strsplit(" ") |>
sapply("[", 1),
filter=type=="ortholog"),
size=2), colour="white", expand=1)+
theme_void()
2.3 geom_node_shadowtext
在 geom_node_text 中,在 x 和 y 位置绘制阴影文本,但不启用 repl = TRUE。
2.4 Global maps
对于Global maps,编写了 process _ line 函数,该函数根据 KGML 中的坐标属性生成节点和边。然而,我们不能获得和解析定向关系(基板到产品,可逆或不可逆)的基础上坐标。如果您希望保留这些关系,那么就准备好 process_response 函数。
pathway("ko01200") |>
process_reaction() |>
activate(nodes) |>
mutate(x=NULL, y=NULL,
comp=convert_id("compound")) |>
mutate(degree=centrality_degree(mode="all")) |>
ggraph(layout="kk")+
geom_node_point(aes(color=degree,
filter=type=="compound"))+
geom_edge_parallel(
color="grey",
end_cap=circle(1,"mm"),
start_cap=circle(1,"mm"),
arrow=arrow(length=unit(1,"mm"),type="closed"))+
geom_node_text(aes(label=comp,filter=degree>15),
repel=TRUE, bg.colour="white")+
theme_graph()
2.5 Highlighting set of nodes and edges
如果希望获得 ko01230,并突出显示 M00002中涉及的组件,并在映射中显示相应的复合名称,我们可以使用 highhigh _ set _ edge 和 highigh _ set _ node 编写如下代码。
pathway("ko01230") |>
process_line() |>
activate(nodes) |>
mutate(
compound=convert_id("compound"),
M00002=highlight_set_nodes(attr(module("M00002"), "reaction_components"))
) |>
activate(edges) |>
mutate(
M00002=highlight_set_edges(attr(module("M00002"), "definition_components"))
) |>
ggraph(x=x, y=y)+
geom_edge_link()+
with_outer_glow(
geom_edge_link(aes(color=M00002, filter=M00002)),
colour="pink")+
geom_node_point(shape=21,aes(filter=type!="line"))+
with_outer_glow(
geom_node_point(shape=21, aes(filter=M00002, color=M00002)),
colour="pink")+
geom_node_text(aes(label=compound, filter=M00002), repel=TRUE,
bg.colour="white", size=2)+
theme_void()
我们显示了突出代谢途径(ko01100)的例子,使用 M00021定义。哪些边参与了模块内部的反应,哪些节点是参与反应的化合物。请注意,这不会产生与 KEGG 映射器完全相同的输出。对于满足相应条件的节点和边,这将使用TRUE 向tbl_graph添加新列。
g <- pathway("ko01100") |>
process_line() |>
highlight_module(module("M00021")) |>
mutate(compound=convert_id("compound"))
g |> ggraph(x=x, y=y) +
geom_node_point(size=1, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & type!="line"))+
geom_edge_link(width=0.1, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=type=="line"& fgcolor!="none"))+
with_outer_glow(
geom_edge_link(width=1,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
with_outer_glow(
geom_node_point(size=2,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
theme_void()
多个模块涉及半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢,突出 M00017由 ggforce。
list_of_modules <- c("M00021","M00338","M00609","M00017","M00034","M00035","M00368")
for (mm in list_of_modules) {
g <- g |> highlight_module(module(mm))
}
ggraph(g,x=x,y=y,layout="manual") +
geom_edge_link0(width=0.5, color="grey")+
geom_edge_link(color="red",aes(filter=M00017|M00021|M00338|M00609|M00034|M00035|M00368))+
geom_node_point(size=2, color="red",aes(filter=M00017|M00021|M00338|M00609|M00034|M00035|M00368))+
ggforce::geom_mark_rect(aes(fill=M00017,
label=attr(module("M00017"), "name"),
x=x, y=y,
group=M00017,
filter=M00017),
label.fill = "transparent",
label.fontsize = 10,
expand=unit(1,"mm"))+
theme_void()
在可视化有关化合物的信息时,建议使用geom_node_text、ggrepel和 Shadowtext。
g |> ggraph(x=x, y=y) +
geom_node_point(size=1, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & type!="line"))+
geom_edge_link(width=0.1, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=type=="line"& fgcolor!="none"))+
with_outer_glow(
geom_edge_link(width=1,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
with_outer_glow(
geom_node_point(size=2,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
geom_node_text(aes(label=compound, filter=M00021),
repel=TRUE, bg.colour="white", size=5)+
theme_void()
如果有必要,可以使突出显示的路径中包含的信息可视化,并使用 notation _ custom函数将其放置在原始映射中。在本例中,首先创建一个注释 ggplot,然后使用 ggplotify 将其转换为 grob。然后,在任何需要的位置绘制探头。
annot <- g |> ggraph(x=x, y=y)+
with_outer_glow(
geom_edge_link(width=1,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
with_outer_glow(
geom_node_point(size=2,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
geom_node_text(aes(label=compound, filter=M00021),
repel=TRUE, bg.colour="white", size=5)
g |>
ggraph(x=x, y=y) +
geom_node_point(size=1, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & type!="line"))+
geom_edge_link(width=0.1, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=type=="line"& fgcolor!="none"))+
with_outer_glow(
geom_edge_link(width=1,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
with_outer_glow(
geom_node_point(size=2,
aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=fgcolor!="none" & M00021)),
colour="red", expand=3
)+
annotation_custom(ggplotify::as.grob(annot),
ymin=-1500, ymax=0, xmin=0, xmax=1500)+ ## your desired position
theme_void()
还可以突出显示所需的任何边或节点。在这种情况下,在 mutate 中使用highlight_set_edges 和highlight_set_nodes 函数来生成一个新列,该列包含一个布尔值,指示是否包含指定的 ID。我们可以在所需的 geoms 中突出显示这些节点或边。当如何设置为所有时,仅当查询中包含的所有 ID 都包含在节点中时,才返回 TRUE。如果在节点中包含查询中包含的任何 ID,则如何设置为 TRUE 将返回 TRUE。
gg <- g |> activate(edges) |>
mutate(highlight=highlight_set_edges(c("ko:K00790","ko:K00789")))
gg |>
ggraph(x=x, y=y) + geom_edge_link(width=0.1, aes(filter=fgcolor!="none",
color=I(fgcolor))) +
with_outer_glow(geom_edge_link(width=1, aes(filter=highlight,
color=I(fgcolor))), colour="red", expand=3) + theme_graph()
突出显示与图形突出显示相结合的例子:
library(graphhighlight)
g |> ggraph(x=x, y=y) +
geom_edge_link(width=0.5, aes(color=I(fgcolor), filter=fgcolor!="none")) +
geom_node_point(size=1, aes(color=I(fgcolor), filter=fgcolor!="none" & type!="line"))+
highlight_node(glow=TRUE, filter=fgcolor!='none' & type!='line',
glow_base_size=TRUE,glow_size=0.5)+
theme_void()
在可视化大型映射(如全局映射和概览映射)时,最好使用 geom_edge_link0,如 ggraph geom_edge_* 的文档所述。此外,对于节点,将 scattermore `包的 geom _ scattermore 与 ggraph的 StatFilter 相结合可以实现更快的呈现。
st <- Sys.time()
ggraph(g, x=x, y=y) +geom_edge_link0(aes(color=I(fgcolor)))+
scattermore::geom_scattermore(pointsize=1, stat=StatFilter,
aes(x=x, y=y, color=I(fgcolor),
filter=type!="map"))+theme_void()
ed <- Sys.time()
ed-st
#> Time difference of 0.4859622 secs
st <- Sys.time()
ggraph(g, x=x, y=y) +geom_edge_link(aes(color=I(fgcolor)))+
geom_node_point(size=2, aes(color=I(fgcolor),
filter=type!="map"))+theme_void()
ed <- Sys.time()
ed-st
#> Time difference of 19.0965 secs
2.6在图形上叠加原始 KEGG 路径图像
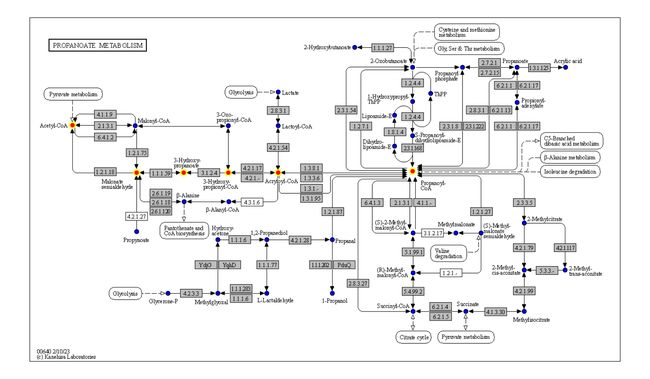
g <- pathway("ko00640",group_rect_nudge=0) ## Obtain pathway graph (don't show grouping rect)
gg <- ggraph(g, layout="manual", x=x, y=y)+
geom_node_point(aes(filter=type=="compound"), color="blue", size=2)+
geom_node_rect(fill="red",aes(filter=type=="ortholog"))+
overlay_raw_map("ko00640")+
theme_void()
gg
您可以使用您喜欢的 geoms 来注释 KEGG 映射组合的函数。
m <- module("M00013")
reactions_in_module <- attr(m, "reaction_components")
g <- g |> mutate(mod=highlight_set_nodes(reactions_in_module, how="all"))
gg <- ggraph(g, layout="manual", x=x, y=y)+
geom_node_rect(fill="grey",aes(filter=type=="ortholog"))+
geom_node_point(aes(filter=type=="compound"), color="blue", size=2)+
overlay_raw_map("ko00640")+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(
geom_node_point(aes(filter=mod, x=x, y=y), color="red",size=2),
colour="yellow",expand=5)+
theme_void()
gg
2.7 Group of nodes
这些组在 KGML 中用 type = “ group”指定。Path 函数添加了连接组 ID 和组件 ID 的边缘,允许在布局中显示 KGML 中指定的组以外的组。提到的边用 in _ group 类型指定。
g <- pathway("hsa03460") |> mutate(conv=convert_id("hsa"))
g <- delete_vertex_attr(g, "x")
g <- delete_vertex_attr(g, "y")
ggraph(g, layout = "nicely") +
geom_node_point(aes(filter=type=="gene" | type=="group"), color="black") +
geom_edge_link(aes(color=subtype_name),end_cap=circle(2,"mm"),
start_cap=circle(2,"mm"),
label_dodge = unit(2,"mm"))+
geom_node_text(aes(label=conv), repel=TRUE, bg.colour="white")+
theme_void()
2.8在本地布局中结合多条路径
通过改变节点的位置或收缩多个图形,可以使用本机布局组合多个路径。
## Mutate X position for the first graph
g1 <-pathway("ko00640")
pos <- g1 |> activate(nodes) |> data.frame() |> summarise(min=min(y))
g1_mut <- g1 |> activate(nodes) |> mutate(x=x/max(x))
## Mutate Y position and x position for the second graph
g2 <-pathway("ko00620")
g2_mut <- g2 |> activate(nodes) |> mutate(y=y+pos$min, x=x/max(x))
joined_raw <- graph_join(g1_mut, g2_mut)
joined_name <- graph_join(g1_mut, g2_mut, by=c("name","x","y"))
## Group by node names and take attribute of first rows
## For edges, combine reaction
newg <- joined_raw |>
convert(to_contracted, name) |>
activate(nodes) |>
mutate(purrr::map_vec(.orig_data, function(x) x[1,]))|>
activate(edges) |>
mutate(reaction=purrr::map_vec(.orig_data,
function(x) paste0(unique(x$reaction),
collapse=",")),
subtype_name=purrr::map_vec(.orig_data,
function(x) unique(x$subtype_name)))
## Highlight the cpd:C00024 node for normal-joined, and contracted graph by name
## Blue color indicates occurrence in both pathway
## Normal joined
joined_name |> morph(to_contracted, name) |>
activate(nodes) |>
mutate(occ=purrr::map_vec(.orig_data, function(x) dim(x)[1])) |>
unmorph() |>
ggraph(layout="manual", x=x, y=y) +
geom_edge_link0(width=0.1, aes(color=subtype_name,
filter=subtype_name %in% c("substrate","product")))+
geom_node_point() +
geom_node_point(color="blue", aes(filter=occ>1))+
graphhighlight::highlight_node(filter=name=="cpd:C00024", glow=TRUE,
highlight_color = "red")+
theme_void()
## Contracted
newg |>
activate(nodes) |> mutate(
ko=convert_id("ko"),
occ=purrr::map_vec(.orig_data, function(x) dim(x)[1])) |>
ggraph(layout="manual", x=x, y=y) +
geom_edge_link0(width=0.1, aes(color=subtype_name,
filter=subtype_name %in% c("substrate","product")))+
geom_node_point()+
geom_node_point(color="blue", aes(filter=occ>1)) +
geom_node_point(color="red", aes(filter=name=="cpd:C00024"))+
graphhighlight::highlight_node(filter=name=="cpd:C00024", glow=TRUE,
highlight_color = "red")+
geom_node_text(size=1.5, family="serif", repel=TRUE, bg.colour="white",
aes(label=ko, filter=type=="ortholog"))+
theme_void()
2.8.1 multi _ path _ national
通过使用 multi _ path _ national 函数,可以在一个面板上排列多个本机 KGML 布局。结合 to 收缩,研究不同途径中基因之间的关系变得可行。
通过使用 multi path national 函数,可以在一个面板上排列多个本机 KGML 布局。结合 to 收缩,研究不同途径中基因之间的关系变得可行。
pathways <- c("hsa04110","hsa03460")
multig <- multi_pathway_native(pathways, row_num=2)
multig |>
ggraph(layout="manual", x=x, y=y)+
geom_edge_parallel(alpha=0.2,
arrow=arrow(length=unit(1,"mm")),
start_cap=circle(5,"mm"),
end_cap=circle(5,"mm"))+
geom_node_point(aes(color=pathway_id))+
theme_void()
2.9 可视化丰富 KEGG 和 gseKEGG 的结果
该文库可以直观地显示功能富集分析结果。不管所研究的基因是否在途径中,rich _ 属性都具有布尔值。通过管道化一个 rich _ Result 类对象和 path _ number 到 ggkegg,rich _ Attribute 将包含在生成的图中。突出显示结果图中的 rich _ tribute。为了快速检查,可以使用 rawMap 函数简单地生成覆盖 KEGG 原始映射的突出显示图。
data(geneList, package='DOSE')
de <- names(geneList)[1:100]
enrichKEGG(de, pvalueCutoff=0.01) |>
ggkegg(convert_org = "hsa",
pathway_number=1) +
geom_edge_link(
aes(color=subtype_name),
arrow = arrow(length = unit(1, 'mm')),
start_cap = square(1, 'cm'),
end_cap = square(1.5, 'cm')) +
geom_node_rect(aes(filter=.data$undefined & !.data$type=="gene"),
fill="transparent", color="red")+
geom_node_rect(aes(filter=!.data$undefined &
.data$type=="gene"), fill="white", color="black")+
geom_node_text(aes(label=converted_name,
filter=.data$type == "gene"),
size=2.5,
color="black",family="serif")+
with_outer_glow(geom_node_text(aes(label=converted_name,
filter=.data$enrich_attribute),
size=2.5, color="red"),
colour="white",
expand=4)+
theme_void()
## Quick inspection
res <- enrichKEGG(de, pvalueCutoff=0.01) |> rawMap()
res

RawMap 可以接受由 list 给出的多个 rich-Result 类对象。在这种情况下,用户可以通过在 fill _ color 中指定多种颜色来选择突出显示列表中的组件的颜色。此外,您应该为多重富集结果指定路径 ID。
deres <- enrichKEGG(de, pvalueCutoff=0.01)
res <- rawMap(list(deres, deres, deres), fill_color=c("red","green","blue"), pid="hsa04110")
res
RawMap 也接受 gseResult 类,尽管它可能有助于直接分配诸如 log2倍数变化之类的数值。
data(geneList, package="DOSE")
kk <- gseKEGG(geneList)
res <- rawMap(kk)
res
对于使用 rawValue 的数值也可以这样做。您可以使用 scale _ fill _ gradient2控制您喜欢的颜色渐变。注意,如果一个列表传递了多个命名向量,则使用相同的比例。它可以通过使用 ggh4x 这样的软件包添加额外的音阶来进行定制。
res <- rawValue(geneList[1:100], "hsa04110", auto_add=TRUE)
res
2.10 Using multiple scales when highlighting multiple values in pathwa
使用 ggh4x,您可以使用 scale _ fill _ multi ()按照自己的比例绘制多个值。它被用于包 PlotKEGGPathway 在包 Stana 进行物种内多样性分析。在函数中的使用,请参考 ggh4x 站点和代码。
library(ggh4x)
test <- geneList[1:100]
names(test) <- paste0("hsa:",names(test))
g <- pathway("hsa04110") |>
mutate(value1=node_numeric(test),
value2=node_numeric(test),
value3=node_numeric(test),
value4=node_numeric(test))
res <- ggraph(g) +
geom_node_rect(aes(value1=value1)) +
geom_node_rect(aes(value2=value2, xmin=xmin+width/4))+
geom_node_rect(aes(value3=value3, xmin=xmin+2*width/4))+
geom_node_rect(aes(value4=value4, xmin=xmin+3*width/4))+
overlay_raw_map() + theme_void() +
scale_fill_multi(aesthetics = c("value1", "value2",
"value3", "value4"),
name = list("Condition1",
"Condition2",
"Condition3",
"Condition4"),
colours = list(
scales::brewer_pal(palette = "YlGnBu")(6),
scales::brewer_pal(palette = "RdPu")(6),
scales::brewer_pal(palette = "PuOr")(6),
scales::brewer_pal(palette = "RdBu")(6)
),
guide = guide_colorbar(barheight = unit(50, "pt")))
res
3. Module
可以获取和解析模块信息。支持解析定义和反应。对于定义,函数首先将定义分解为块,并使用 ggraph 和 tbl_graph 或使用 geom_text 和 geom_rect 的文本本身进行图形表示。通过调用 module 函数,创建了 kegg _ module 类对象。
library(ggkegg)
library(tidygraph)
library(dplyr)
mod <- module("M00004")
mod
#> M00004
#> Pentose phosphate pathway (Pentose phosphate cycle)
Module 函数创建 kegg_module 类的一个对象,该对象将反应和定义的解析信息存储在其内部槽中。通过向各种函数提供这个 kegg _ module 对象,可以执行与该模块相关的各种操作。
library(igraph)
mod <- module("M00004")
## Obtain reaction graph
reacg <- attr(mod, "reaction_graph") # or, get_module_attribute()
## Some edges are duplicate and have different reactions,
## so simplify
reacg |>
convert(to_simple) |>
activate(edges) |>
mutate(reaction=lapply(.orig_data,
function(x)
paste0(unique(x[["reaction"]]),
collapse=","))) |>
ggraph()+
geom_node_point()+
geom_edge_parallel(
aes(label=reaction), angle_calc = "along",
label_dodge = unit(5,"mm"),
label_colour = "tomato",
arrow = arrow(length = unit(1, 'mm')),
end_cap = circle(5, 'mm'),
start_cap = circle(5, "mm"))+
geom_node_text(aes(label=name), repel=TRUE,
bg.colour="white", size=4)+
theme_void()
3.1图形中的模块定义
我们可以在图中可视化模块定义。这将对节点进行分组,并将节点连接到与 AND 参数连接的节点(‘ +’和‘’) ,并连接定义。在下面的例子中,包装函式 plot _ module _ block ()显示了每个模块的定义。红色表示 AND 关系,而其他关系(如复合或 OR)表示为边缘标签。
module("M00009") |>
obtain_sequential_module_definition() |> ## return tbl_graph
plot_module_blocks() ## wrapper function
3.2模块文本定义
我们还可以在文本中可视化模块定义。
module("M00004") |>
module_text() |> ## return data.frame
plot_module_text() ## wrapper function
3.3 Module completeness
给定一个有趣的 KO 向量,可以使用布尔表达式计算模块完整性。
mod <- module("M00009")
query <- sample(attr(mod, "definition_components"), 5) |>
strsplit(":") |>
sapply("[",2)
query
#> [1] "K01677" "K00164" "K00247" "K00240" "K00246"
mod |>
module_completeness(query) |>
kableExtra::kable()
3.3.1 跨多个微生物基因组评估模块完整性
例如,我们可以评估从多个物种基因组中推断出的 KO 的完整性。在这里,我们将从 PATRIC 服务器获得的 MIDAS 流水线注释文件中可用的 EC 编号映射到 KO,并计算随机获得的物种的完整性。
## Load pre-computed KOs, and recursively perform completeness calculation.
mf <- list.files("../")
mf <- mf[startsWith(mf, "M")]
annos <- list()
candspid <- list.files("../species_dir")
candspid <- sample(candspid, 10)
## Obtain EC to KO mapping file from KEGG REST API
mapper <- data.table::fread("https://rest.kegg.jp/link/ec/ko", header=FALSE)
suppressMessages(
for (i in candspid) {
mcs <- NULL
df <- read.table(paste0("../species_dir/",i), sep="\t", header=1)
fid <- paste0("ec:",df[df$ontology=="ec",]$function_id)
kos <- mapper[mapper$V2 %in% fid,]$V1 |> strsplit(":") |> sapply("[",2) |> unique()
for (mid in mf) {
mc <- module_completeness(module(mid, directory="../"),
query = kos)
mcs <- c(mcs, mc$complete |> mean()) ## Mean of blocks
}
annos[[as.character(i)]] <- mcs
}
)
接下来,我们将使用 ComplexHeatmap 和 simple yEnrich 来可视化结果。我们将通过简化 Enrich 将模块描述的单词云与热图一起绘制,用于确定的集群
library(ComplexHeatmap)
## Make data.frame
hdf <- data.frame(annos, check.names=FALSE)
row.names(hdf) <- mf
hdf[is.na(hdf)] <- 0
hdf <- hdf[apply(hdf, 1, sum)!=0,]
## Prepare for word cloud annotation
moddesc <- data.table::fread("https://rest.kegg.jp/list/module", header=FALSE)
## Obtain K-means clustering
km = kmeans(hdf, centers = 10)$cluster
gene_list <- split(row.names(hdf), km)
gene_list <- lapply(gene_list, function(x) {
x[!is.na(x)]
})
annotList <- list()
for (i in names(gene_list)) {
maps <- (moddesc |> dplyr::filter(V1 %in% gene_list[[i]]))$V2
annotList[[i]] <- maps
}
col_fun = circlize::colorRamp2(c(0, 0.5, 1),
c(scales::muted("blue"), "white", scales::muted("red")))
ht1 <- Heatmap(hdf, show_column_names = TRUE,
col=col_fun, row_split=km,
heatmap_legend_param = list(
legend_direction = "horizontal",
legend_width = unit(5, "cm")
),
rect_gp = gpar(col = "white", lwd = 2),
name="Module completeness", border=TRUE,
column_names_max_height =unit(10,"cm"))+
rowAnnotation(
keywords = simplifyEnrichment::anno_word_cloud(align_to = km,
term=annotList,
exclude_words=c("pathway","degradation",
"biosynthesis"),
max_words = 40,fontsize_range = c(5,20))
)
ht1
3.4 模块丰度和路径丰度计算
vec <- c(0.1, 0.5)
names(vec) <- c("K00234","K01676")
module_abundance("M00009", vec)
#> [1] 0.3947368
3.5 Visualize the result of enricher
如果您进行了一些涉及 KEGG Orthology 的实验,并对 KO 到模块关系进行了富集分析,ggkegg 函数将接受结果并绘制基于文本或基于网络的图,其中 KO 被突出显示。
library(BiocFileCache)
#> Loading required package: dbplyr
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dbplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:dplyr':
#>
#> ident, sql
library(clusterProfiler)
#> clusterProfiler v4.9.5 For help: https://yulab-smu.top/biomedical-knowledge-mining-book/
#>
#> If you use clusterProfiler in published research, please cite:
#> T Wu, E Hu, S Xu, M Chen, P Guo, Z Dai, T Feng, L Zhou, W Tang, L Zhan, X Fu, S Liu, X Bo, and G Yu. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. The Innovation. 2021, 2(3):100141
#>
#> Attaching package: 'clusterProfiler'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:igraph':
#>
#> simplify
#> The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter
## Download and cache KO to module relationship
url <- paste0("https://rest.kegg.jp/link/ko/module")
bfc <- BiocFileCache()
path <- bfcrpath(bfc, url)
module.bg <- apply(data.table::fread(path), 2, function(x) sapply(strsplit(x, ":"), "[",2))|> data.frame()|>`colnames<-`(c("term","gene"))
## Using the table, perform enrichment analysis.
mod.enrich <- enricher(c("K00431","K00832"), TERM2GENE=module.bg)
## Visualize using ggkegg
dd <- ggkegg(mod.enrich)
dd
4 Network
library(ggkegg)
library(tidygraph)
library(dplyr)
kne <- network("N00002")
kne
#> N00002
#> BCR-ABL fusion kinase to RAS-ERK signaling pathway
4.1 组合多个网络
下面是一个获取多个网络的示例,将它们与 graph _ join 合并,然后使用 plot _ kegg _ network 包装函式绘制它们。Network _ graph 函数是一个从字符串生成图形的函数。可以指定定义或展开为生成图形的类型。
kne <- network("N00385") ## HCMV
kne2 <- network("N00366") ## HPV
one <- kne |> network_graph()
two <- kne2 |> network_graph()
two
#> # A tbl_graph: 6 nodes and 5 edges
#> #
#> # A rooted tree
#> #
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> name network_name network_ID
#>
#> 1 E5 HPV E5 to EGFR-PI3K signaling pathway N00366
#> 2 V-ATPase HPV E5 to EGFR-PI3K signaling pathway N00366
#> 3 EGFR HPV E5 to EGFR-PI3K signaling pathway N00366
#> 4 PI3K HPV E5 to EGFR-PI3K signaling pathway N00366
#> 5 PIP3 HPV E5 to EGFR-PI3K signaling pathway N00366
#> 6 AKT HPV E5 to EGFR-PI3K signaling pathway N00366
#> #
#> # A tibble: 5 × 4
#> from to type subtype
#>
#> 1 1 2 -| reference
#> 2 2 3 -| reference
#> 3 3 4 -> reference
#> # ℹ 2 more rows
graph_join(one, two, by="name") |> plot_kegg_network()
通过使用 ggforce,可以绘制多个图表来显示哪些基因属于哪个网络。
kne3 <- network("N00485") ## EBV
kne4 <- network("N00030") ## EGF-EGFR-RAS-PI3K
three <- kne3 |> network_graph()
four <- kne4 |> network_graph()
gg <- Reduce(function(x,y) graph_join(x,y, by="name"), list(one, two, three, four))
coln <- gg |> activate(nodes) |> data.frame() |> colnames()
nids <- coln[grepl("network_ID",coln)]
net <- plot_kegg_network(gg)
for (i in nids) {
net <- net + ggforce::geom_mark_hull(alpha=0.2, aes(group=.data[[i]],
fill=.data[[i]], x=x, y=y, filter=!is.na(.data[[i]])))
}
net + scale_fill_manual(values=viridis::plasma(4), name="ID")
5. Usecases (实例)
5.1 从 DESeq2可视化数值属性
通过提供经常用于转录组分析的 DESeq2包的结果,可以在图的节点中反映数值结果。可以使用 sign _ deseq2函数实现此目的。通过指定希望在图中作为列参数反映的数值(例如 log2FoldChange) ,可以将该值赋给节点。如果命中多个基因,numeric _ merge 参数指定如何组合多个值(默认值为 mean)。
在这里,我们使用 RNA-Seq 数据集分析感染 BK 多瘤病毒的人尿路上皮细胞的转录组变化(Baker 等,2022)。从序列读档案中获得的原始序列用 nf-core 处理,随后使用 tximport、salmon和 DESeq2进行分析。
library(ggkegg)
library(DESeq2)
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
library(dplyr)
## The file stores DESeq() result on transcriptomic dataset deposited by Baker et al. 2022.
load("uro.deseq.res.rda")
res
#> class: DESeqDataSet
#> dim: 29744 26
#> metadata(1): version
#> assays(8): counts avgTxLength ... replaceCounts
#> replaceCooks
#> rownames(29744): A1BG A1BG-AS1 ... ZZEF1 ZZZ3
#> rowData names(27): baseMean baseVar ... maxCooks
#> replace
#> colnames(26): SRR14509882 SRR14509883 ... SRR14509906
#> SRR14509907
#> colData names(27): Assay.Type AvgSpotLen ...
#> viral_infection replaceable
vinf <- results(res, contrast=c("viral_infection","BKPyV (Dunlop) MOI=1","No infection"))
## LFC
g <- pathway("hsa04110") |> mutate(deseq2=assign_deseq2(vinf),
padj=assign_deseq2(vinf, column="padj"),
converted_name=convert_id("hsa"))
ggraph(g, layout="manual", x=x, y=y) +
geom_edge_parallel(width=0.5, arrow = arrow(length = unit(1, 'mm')),
start_cap = square(1, 'cm'),
end_cap = square(1.5, 'cm'), aes(color=subtype_name))+
geom_node_rect(aes(fill=deseq2, filter=type=="gene"), color="black")+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(geom_node_text(aes(label=converted_name, filter=type!="group"), size=2.5), colour="white", expand=1)+
scale_fill_gradient(low="blue",high="red", name="LFC")+
theme_void()
## Adjusted p-values
ggraph(g, layout="manual", x=x, y=y) +
geom_edge_parallel(width=0.5, arrow = arrow(length = unit(1, 'mm')),
start_cap = square(1, 'cm'),
end_cap = square(1.5, 'cm'), aes(color=subtype_name))+
geom_node_rect(aes(fill=padj, filter=type=="gene"), color="black")+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(geom_node_text(aes(label=converted_name, filter=type!="group"), size=2.5), colour="white", expand=1)+
scale_fill_gradient(name="padj")+
theme_void()
5.1.1使用 ggfx 进一步定制可视化
## Highlighting differentially expressed genes at adjusted p-values < 0.05 with coloring of adjusted p-values on raw KEGG map
gg <- ggraph(g, layout="manual", x=x, y=y)+
geom_node_rect(aes(fill=padj, filter=type=="gene"))+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(geom_node_rect(aes(fill=padj, filter=!is.na(padj) & padj<0.05)),
colour="yellow", expand=2)+
overlay_raw_map("hsa04110", transparent_colors = c("#cccccc","#FFFFFF","#BFBFFF","#BFFFBF"))+
scale_fill_gradient(low="pink",high="steelblue") + theme_void()
gg
5.1.2 使用多个 geoms 来添加信息
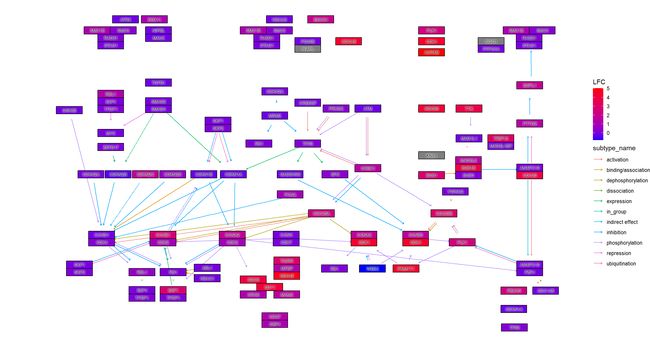
您可以使用 ggplot2中您喜欢的 geom 及其扩展来添加信息。在本例中,我们使用 geomtextpath 添加 log2折叠变化作为轮廓,并使用 Monocraft 定制字体。
g <- g |> mutate(lfc=assign_deseq2(vinf, column="log2FoldChange"))
## Make contour data
df <- g |> data.frame()
df <- df[!is.na(df$lfc),]
cont <- akima::interp2xyz(interp::interp(df$x, df$y, df$lfc)) |>
data.frame() |> `colnames<-`(c("x","y","z"))
##
sysfonts::font_add(family="monocraft",regular="Monocraft.ttf")
gg <- ggraph(g, layout="manual", x=x, y=y)+
geom_edge_parallel(arrow=arrow(length=unit(1,"mm")),
aes(color=subtype_name),
end_cap=circle(7.5,"mm"),
alpha=0.5)+
geomtextpath::geom_textcontour(aes(x=x, y=y, z=z,color=after_stat(level)),
size=3, linetype=2,
linewidth=0.1, data=cont)+
geom_node_rect(aes(fill=padj, filter=type=="gene"))+
ggfx::with_outer_glow(geom_node_rect(aes(fill=padj, filter=!is.na(padj) & padj<0.05)),
colour="yellow", expand=2)+
geom_node_text(aes(label=converted_name), family="monocraft")+
scale_color_gradient2(low=scales::muted("blue"),
high=scales::muted("red"),
name="LFC")+
scale_edge_color_manual(values=viridis::viridis(11), name="Edge type")+
scale_fill_gradient(low="pink",high="steelblue") +
theme_void()
gg
5.2将数值集成到 tbl_graph
5.2.1 Integrating numeric vector to tbl_graph
利用 node_numeric 或 edge_numeric 函数,数值可以反映在节点表或边表中。输入可以是一个命名向量,也可以是一个包含 id 和 value 列的 tibble。
vec <- 1
names(vec) <- c("hsa:51343")
new_g <- g |> mutate(num=node_numeric(vec))
new_g
#> # A tbl_graph: 134 nodes and 157 edges
#> #
#> # A directed acyclic multigraph with 40 components
#> #
#> # A tibble: 134 × 23
#> name type reaction graphics_name x y width
#>
#> 1 hsa:1029 gene CDKN2A, ARF,… 532 -218 46
#> 2 hsa:51343 gene FZR1, CDC20C… 981 -630 46
#> 3 hsa:4171 h… gene MCM2, BM28, … 553 -681 46
#> 4 hsa:23594 … gene ORC6, ORC6L.… 494 -681 46
#> 5 hsa:10393 … gene ANAPC10, APC… 981 -392 46
#> 6 hsa:10393 … gene ANAPC10, APC… 981 -613 46
#> # ℹ 128 more rows
#> # ℹ 16 more variables: height , fgcolor ,
#> # bgcolor , graphics_type , coords ,
#> # xmin , xmax , ymin , ymax ,
#> # orig.id , pathway_id , deseq2 ,
#> # padj , converted_name , lfc , num
#> #
#> # A tibble: 157 × 6
#> from to type subtype_name subtype_value pathway_id
#>
#> 1 118 39 GErel expression --> hsa04110
#> 2 50 61 PPrel inhibition --| hsa04110
#> 3 50 61 PPrel phosphorylation +p hsa04110
#> # ℹ 154 more rows
5.2.2 Integrating matrix to tbl_graph
如果希望在图中反映表达式矩阵,则 edge_Matrix 和 node_Matrix 函数可能非常有用。通过指定矩阵和基因 ID,可以将每个样本的数值赋给 tbl _ graph。Edge_Matrix 指定由一条边连接的两个节点的和,忽略组节点。
mat <- assay(vst(res))
new_g <- g |> edge_matrix(mat) |> node_matrix(mat)
new_g
#> # A tbl_graph: 134 nodes and 157 edges
#> #
#> # A directed acyclic multigraph with 40 components
#> #
#> # A tibble: 134 × 48
#> name type reaction graphics_name x y width
#>
#> 1 hsa:1029 gene CDKN2A, ARF,… 532 -218 46
#> 2 hsa:51343 gene FZR1, CDC20C… 981 -630 46
#> 3 hsa:4171 h… gene MCM2, BM28, … 553 -681 46
#> 4 hsa:23594 … gene ORC6, ORC6L.… 494 -681 46
#> 5 hsa:10393 … gene ANAPC10, APC… 981 -392 46
#> 6 hsa:10393 … gene ANAPC10, APC… 981 -613 46
#> # ℹ 128 more rows
#> # ℹ 41 more variables: height , fgcolor ,
#> # bgcolor , graphics_type , coords ,
#> # xmin , xmax , ymin , ymax ,
#> # orig.id , pathway_id , deseq2 ,
#> # padj , converted_name , lfc ,
#> # SRR14509882 , SRR14509883 , …
#> #
#> # A tibble: 157 × 34
#> from to type subtype_name subtype_value pathway_id
#>
#> 1 118 39 GErel expression --> hsa04110
#> 2 50 61 PPrel inhibition --| hsa04110
#> 3 50 61 PPrel phosphorylation +p hsa04110
#> # ℹ 154 more rows
#> # ℹ 28 more variables: from_nd , to_nd ,
#> # SRR14509882 , SRR14509883 ,
#> # SRR14509884 , SRR14509885 ,
#> # SRR14509886 , SRR14509887 ,
#> # SRR14509888 , SRR14509889 ,
#> # SRR14509890 , SRR14509891 , …
5.2.2.1 Values to edge
以命名的数值向量作为输入,可以得到相同的边矩阵效应。此函数根据节点值添加边缘值。下面的示例显示了如何将 LFC 与边缘相结合。这与 edge _ numeric 的行为不同。
## Numeric vector (name is SYMBOL)
vinflfc <- vinf$log2FoldChange |> setNames(row.names(vinf))
g |>
## Use graphics_name to merge
mutate(grname=strsplit(graphics_name, ",") |> vapply("[", 1, FUN.VALUE="a")) |>
activate(edges) |>
mutate(summed = edge_numeric_sum(vinflfc, name="grname")) |>
filter(!is.na(summed)) |>
activate(nodes) |>
mutate(x=NULL, y=NULL, deg=centrality_degree(mode="all")) |>
filter(deg>0) |>
ggraph(layout="nicely")+
geom_edge_parallel(aes(color=summed, width=summed,
linetype=subtype_name),
arrow=arrow(length=unit(1,"mm")),
start_cap=circle(2,"mm"),
end_cap=circle(2,"mm"))+
geom_node_point(aes(fill=I(bgcolor)))+
geom_node_text(aes(label=grname,
filter=type=="gene"),
repel=TRUE, bg.colour="white")+
scale_edge_width(range=c(0.1,2))+
scale_edge_color_gradient(low="blue", high="red", name="Edge")+
theme_void()
往期文章:
1. 复现SCI文章系列专栏
2. 《生信知识库订阅须知》,同步更新,易于搜索与管理。
3. 最全WGCNA教程(替换数据即可出全部结果与图形)
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码一
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码二
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程代码分享 | 代码三
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码四
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码五(最新版本)
4. 精美图形绘制教程
- 精美图形绘制教程
5. 转录组分析教程
转录组上游分析教程[零基础]
一个转录组上游分析流程 | Hisat2-Stringtie
小杜的生信筆記 ,主要发表或收录生物信息学的教程,以及基于R的分析和可视化(包括数据分析,图形绘制等);分享感兴趣的文献和学习资料!!