SpringMVC源码解析——DispatcherServlet初始化
在Spring中,ContextLoaderListener只是辅助功能,用于创建WebApplicationContext类型的实例,而真正的逻辑实现其实是在DispatcherServlet中进行的,DispatcherServlet是实现Servlet接口的实现类。Servlet是一个JAVA编写的程序,此程序是基于HTTP协议的,在服务端运行的(如Tomcat),是按照Servlet规范编写的一个JAVA类。主要是处理客户端的请求并将其结果发送到客户端。Servlet的生命周期是由Servlet的容器来控制的,它可以分为三个阶段:初始化、运行和销毁。
1、初始化阶段
- Servlet容器加载Servlet类,把Servlet类的.class文件中的数据读入到内存中。
- Servlet容器创建一个ServletConfig对象,ServletConfig对象包含了Servlet的初始化配置信息。
- Servlet容器创建一个Servlet对象。
- Servlet容器调用Servlet对象的init方法进行初始化。
2、运行阶段
当Servlet容器收到一个请求时,Servlet容器会针对这个请求创建ServletRequest和ServletResponse对象,然后调用service方法。并把这两个参数传递给service方法,service方法通过ServletRequest对象获取请求的信息,并处理该请求。再通过ServletResponse对象生成这个请求的响应结果。然后销毁ServletRequest和ServletResponse对象,不管这个请求时GET还是POST提交的,最终这个请求都会由service来处理。
3、销毁阶段
当web应用被终止时,Servlet容器会先调用Servlet对象的destroy方法,然后再销毁Servlet对象,同时也会销毁与Servlet对象相关联的ServletConfig对象。我们可以在destroy方法的实现中,释放Servlet所占用的资源,如关闭数据库连接,关闭文件输入输出流等。
Servlet的框架是由两个JAVA包组成:javax.servlet和javax.servlet.http。在javax.servlet包中定义了所有的servlet类都必须实现或扩展的通用接口和类,在javax.servlet.http包中定义了采用HTTP通信协议的HttpServlet类。
servlet被设计成请求驱动,servlet的请求可能包含多个数据项,当web容器接受到某个servlet请求时,servlet把请求封装成一个HttpServletRequest对象,然后把对象传给servlet的对应的服务方法。
HTTP的请求方式包括delete、get、options、post、put和trace,在HttpServlet类中分别提供了相应的服务方法,它们是doDelete、doGet、doOptions、doPost、doPut和doTrace。
DispatcherServlet的初始化
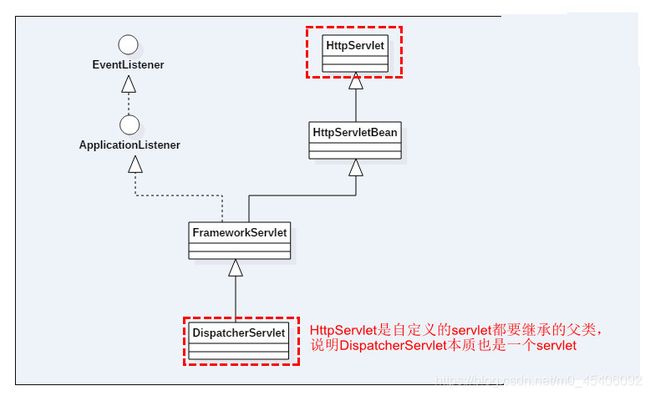
在servlet初始化阶段会调用其init方法,所以我们首先要查看DispatcherServlet中是否重写了init方法。DispatcherServlet类相关的结构图如下:
我们在HttpServletBean中找到了该方法:
/**
* 将配置参数映射到这个servlet的bean属性,并调用子类的初始化方法。
* @throws ServletException 如果bean属性无效(或缺少必需的属性),或者子类的初始化失败。
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 从初始化参数设置bean属性。
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 将当前的这个Servlet类转换为一个BeanWrapper,从而能够以Spring的方式来对init-param的值进行注入。
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
// 注册自定义属性编辑器,一旦遇到Resource类型的属性将会使用ResourceEditor进行解析
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
// 空实现,留给子类覆盖
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("无法设置 servlet '" + getServletName() + "' 的 bean 属性", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 允许子类执行它们喜欢的任何初始化操作。
initServletBean();
}
函数DispatcherServlet的初始化过程主要是通过将当前的Servlet类型实例转换为BeanWapper类型实例,以便使用Spring中提供的注入功能进行对应属性的注入。这些属性如contextAttribute、contextClass、nameSpace、contextConfigLocation等,都可以在web.xml文件中以初始化参数的方式配置在Servlet的声明中。DispatcherServlet继承自FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet类上包含对应的同名属性,Spring会保证这些参数被注入到对应的值中。属性注入主要是包含以下几个步骤。
1、封装及验证初始化参数
ServletConfigPropertyValues除了封装属性外还有对属性验证的功能。
/**
* 创建新的ServletConfigPropertyValues。
* @param config 我们将使用它从ServletConfig中获取属性值
* @param requiredProperties 我们需要的属性集合,对于这些我们不能使用默认值
* @throws ServletException 如果缺少任何必需的属性
*/
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set missingProps = (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requiredProperties) ?
new HashSet<>(requiredProperties) : null);
Enumeration paramNames = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = paramNames.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// 如果我们仍然缺少属性,则失败。
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(missingProps)) {
throw new ServletException(
"从ServletConfig初始化Servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"'失败;缺少以下必需的属性:" +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
这个函数创建一个ServletConfigPropertyValues对象,从给定的ServletConfig中获取属性值,并将其添加到PropertyValues中。如果requiredProperties中存在缺失的属性,则抛出ServletException异常。
2、将当前Servlet实例转化成BeanWapper实例
PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess是Spring中提供的工具方法,主要是用于将指定实例转化为Spring中可以处理的BeanWapper类型的实例。
3、注册相对于Resource的属性编辑器
这里使用属性编辑器的目的是在对当前实例(DispatcherServlet)属性注入过程中一旦遇到Resource类型的属性就会使用ResourceEditor去解析。
4、属性注入
BeanWapper为Spring中的方法,支持Spring的自动注入。其实我们最常用的属性注入无非是contextAttribute、contextClass、nameSpace、contextConfigLocation等。
5、ServletBean的初始化
在ContextLoaderListener加载的时候已经创建了WebApplicationContext实例,而在这个函数中最重要的就是对这个实例进行进一步的补充初始化。
继续查看initServletBean(),父类覆盖了HttpServletBean中的initServletBean函数,源码如下:
/**
* 重写HttpServletBean类的方法,在设置完所有bean属性后调用。创建该Servlet的Web应用上下文。
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("初始化Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("上下文初始化失败", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"可能导致潜在敏感数据的不安全记录显示" :
"已掩盖以防止对潜在敏感数据的不安全记录";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': 请求参数和标头将被 " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("完成初始化需要 " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
这个函数会调用initWebApplicationContext用于创建并初始化WebApplicationContext实例,initFrameworkServlet()函数不做任何实现,可以在子类中进行扩展。
WebApplicationContext的初始化
initWebApplicationContext函数的主要工作就是创建并刷新WebApplicationContext实例并对Servlet功能所使用的变量进行初始化。initWebApplicationContext函数的源码如下:
/**
* 初始化并发布该servlet的WebApplicationContext。
* 实际创建上下文的工作委托给{@link #createWebApplicationContext}方法。
* 子类可以重写该方法。
* @return WebApplicationContext实例
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 在构造函数中注入了上下文实例 -> 使用它
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac && !cwac.isActive()) {
// 上下文尚未刷新 -> 提供服务,如设置父上下文、设置applicationContextId等
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// 注入父上下文时未指定明确的父上下文 -> 将根application上下文(如果有的话)设置为父上下文
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 配置并刷新WebApplicationContext实例
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// 在构造函数中没有注入上下文实例 -> 检查servlet context中是否存在一个注册的上下文。
// 如果存在,则假定父上下文(如果有的话)已经设置,并且用户已经进行了任何初始化,例如设置上下文id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// 为这个servlet没有定义上下文实例 -> 创建一个本地上下文
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// 该上下文不是支持刷新的ConfigurableApplicationContext或者在构造函数中注入的上下文已经刷新 ->
// 在这里手动触发onRefresh方法。
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// 将上下文发布为servlet context attribute。
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
这个函数用于初始化和发布WebApplicationContext。它首先从servlet上下文中获取根应用程序上下文,然后根据需要创建和配置应用程序上下文实例。如果已经存在一个应用程序上下文实例,则直接使用它。如果没有,则根据需要创建一个本地应用程序上下文。最后,将应用程序上下文发布为servlet上下文属性,并返回该上下文实例。
对于initWebApplicationContext函数中的初始化工作主要包含几个部分。
1、通过构造函数的注入对WebApplicationContext进行初始化
当进入initWebApplicationContext函数后通过判断this.webApplicationContext !=null后,便可以确定this.webApplicationContext是否是通过构造函数来初始化的。
2、通过contextAttribute进行初始化
通过在web.xml文件中配置的servlet参数contextAttribute来查找ServletContext中对应的属性,默认为WebApplicationContext.class .getName()+".ROOT"。也就是在ContextLoaderListener加载时会创建WebApplicationContext实例,并将实例以WebApplicationContext.class.getName()+".ROOT"为key放入ServletContext中,当然我们也可以重写初始化逻辑使用自己创建的WebApplicationContext,并在servlet的配置中通过初始化参数contextAttribute指定key。
/**
* 从配置了名称的`ServletContext`属性中获取一个`WebApplicationContext`。
* 在该 servlet 初始化(或调用)之前,`WebApplicationContext`必须已经加载并存储在 `ServletContext` 中。
* 子类可以覆盖此方法以提供不同的`WebApplicationContext`检索策略。
* @return 该 servlet 的`WebApplicationContext`,如果未找到则返回`null`
* @see #getContextAttribute()
*/
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
WebApplicationContext wac = WebApplicationContextUtils
.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("未找到WebApplicationContext:初始化器未注册?");
}
return wac;
}
3、重写创建WebApplicationContext实例
如果以上两种方式都没有获取到WebApplicationContext实例,只能重写创建新的实例了。
/**
* 创建用于该servlet的WebApplicationContext,可以是默认的
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext}
* 或者如果设置了的话,可以是一个自定义的上下文类(通过
* {@link #setContextClass 设置})。
* 代理到#createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext)方法。
* @param parent 要使用的父WebApplicationContext,如果无,则传入{@code null}
* @return 用于该servlet的WebApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
* @see #createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext)
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable WebApplicationContext parent) {
return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent);
}
/**
* 创建本servlet的WebApplicationContext,可以是一个默认的XmlWebApplicationContext或者是一个自定义的上下文类(通过setContextClass方法设置)。
* 此实现期望自定义上下文实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口。可以在子类中重写。
*
请不要忘记将此servlet实例作为创建的上下文的应用监听器注册(以便触发它的onRefresh回调),并在返回上下文实例之前调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的refresh方法。
* @param parent 要使用的父级ApplicationContext,如果无父级则为null
* @return 本servlet的WebApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
// 读取servlet的初始化参数contextClass,如果没有配置默认为XmlWebApplicationContext.class
Class contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"在名称为'" + getServletName() +
"'的servlet中发生致命的初始化错误:自定义WebApplicationContext类[" + contextClass.getName() +
"]不是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类型的");
}
// 通过反射方式实例化contextClass
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// parent为在ContextLoaderListener中创建的实例
// 在ContextLoaderListener加载的时候初始化的WebApplicationContext类型的实例
wac.setParent(parent);
// 获取contextConfigLocation属性,配置在servlet初始化参数中
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
//初始化Spring环境,包括加载配置文件等
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
4、configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
无论是通过构造函数注入还是单独创建,都会调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法来对已经创建的WebApplicationContext实例进行配置及刷新,源码如下:
/**
* 配置并刷新Web应用上下文
*
* @param wac 可配置的Web应用上下文
*/
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// 应用上下文id仍然设置为其默认值
// -> 基于可用信息分配一个更有用的id
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
} else {
// 生成默认id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// 当上下文刷新时,wac环境的#initPropertySources方法将被调用;这里提前调用以确保servlet属性源在以下下方的post-processing或初始化之前可用
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment cwe) {
cwe.initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
个函数用于配置和刷新Web应用上下文。首先根据上下文的id是否与默认值相同来为其设置一个更有用的id。然后设置上下文的servletContext、servletConfig和命名空间,并添加一个监听器。接下来,通过调用wac环境的initPropertySources方法来初始化属性源。最后,调用postProcessWebApplicationContext和applyInitializers方法对上下文进行后处理和初始化,并刷新上下文。
5、刷新WebApplicationContext
onRefresh是FrameworkServlet类中提供的模板方法,在其子类DispatcherServlet中进行了重写,主要用于刷新Spring在Web功能实现中所必须使用的全局变量。DispatcherServlet中onRefresh函数的源码如下:
/**
* 这个方法调用了 {@link #initStrategies} 方法。
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* 初始化这个 servlet 使用的策略对象。
* 对于需要初始化更多策略对象的情况,可以被子类重写。
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
初始化MultipartResolver
在Spring中,MultipartResolver主要是处理文件上传。默认情况下,Spring是没有Multipart处理的,因为很多开发者想要自己处理它们。如果想使用Spring的Multipart,则需要在Web应用的上下文中添加Multipart解析器。这样,每个请求就会被检查是否包含Multipart。然而如果请求中包含Multipart,那么上下文中定义的MultipartResolver就会解析它,这样请求中的Multipart属性就会想其他属性一样被处理。常用配置如下:
100000
那么MultipartResolver就是在initMultipartResolver中被加入到DispatcherServlet中的。
/**
* 初始化用于此类的 MultipartResolver。
* 如果在 BeanFactory 中未定义给定名称的 bean,则不提供多部分处理。
*/
private void initMultipartResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.multipartResolver = context.getBean(MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, MultipartResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("检测到 " + this.multipartResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("检测到 " + this.multipartResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 默认情况下没有 multipart 解析器。
this.multipartResolver = null;
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("未声明 '" + MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "' multipart 解析器");
}
}
}
因为之前的步骤已经完成了Spring中配置文件的解析,所以在这里只要在配置文件注册过都可以通过ApplicationContext提供的getBean方法来直接获取对应的bean,进而初始化MultipartResolver中的multipartResolver变量。
初始化LocaleResolver
在Spring的国际化配置中一共有三种使用方式。
- 基于URL参数的配置。通过URL参数来控制国际化,而提供这个功能的就是AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver,默认的参数名为local,注意大小写。
- 基于session的配置。它通过检验用户会话中预置的属性来解析区域。最常用的是根据用户本次会话过程中的语言设定决定语言中来。
- 基于cookie的国际配置。CookieLocaleResolver用于通过浏览器的cookie设置Locale对象。这种策略在应用程序中不支持会话或者状态必须保存在客户端有用。
这三种方式都可以解决国际化问题,但是对于LocaleResolver的使用基础是在DispatcherServlet中的初始化。
/**
* 初始化该类使用的LocaleResolver。
* 如果BeanFactory中没有给定名称的bean,将默认使用AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver。
*/
private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.localeResolver = context.getBean(LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("检测到 " + this.localeResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("检测到 " + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 需要使用默认的LocaleResolver
this.localeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("没有LocaleResolver '" + LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME +
"': 使用默认 [" + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
提取配置文件中设置的LocaleResolver来初始化DispatcherServlet中的localeResolver属性。
初始化ThemeResolver
initThemeResolver未来会被遗弃,这里不做详细介绍,只是简单的展示源码。
/**
* 初始化由该类使用的ThemeResolver。
* 如果BeanFactory中没有给定名称的bean定义此命名空间,默认为FixedThemeResolver。
*/
@Deprecated
private void initThemeResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.themeResolver = context.getBean(THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ThemeResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("检测到 " + this.themeResolver);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("检测到 " + this.themeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 需要使用默认策略
this.themeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, ThemeResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("没有ThemeResolver '" + THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME +
"': 使用默认 [" + this.themeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
初始化HandlerMappings
当客户端发出Request时DispatcherServlet会将Request提交给,然后HandlerMapping根据WebApplicationContext的配置来回传给DispatcherServlet相应的Controller。
在基于SpringMVC的Web应用中,可以为DispatcherServlet提供多个HandlerMapping供其应用。DispatcherServlet在选用HandlerMapping的过程中,将根据我们所指定的一些列HandlerMapping的优先级进行排序,然后优先使用优先级在前的HandlerMapping。如果当前的HandlerMapping能够返回可用的Handler,DispatcherServlet则使用当前返回的Handler来进行Web请求的处理,而不再继续询问其他的HandlerMapping。否则,DispatcherServlet将继续按照各个HandlerMapping的优先级进行询问,直到获取一个可用的Handler为止。初始化配置的源码如下:
/**
* 初始化用于此类的HandlerMappings。
* 如果BeanFactory中未定义此命名空间的HandlerMapping bean,默认为BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping。
*/
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// 在ApplicationContext中查找所有HandlerMappings,包括祖先上下文。
Map matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// 我们保持HandlerMappings的排序。
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 忽略,之后我们将添加一个默认HandlerMapping。
}
}
// 如果找不到其他HandlerMapping,则通过注册默认HandlerMapping来确保至少有一个HandlerMapping。
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("未声明servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': 使用DispatcherServlet.properties中的默认策略");
}
}
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
}
这个Java函数用于初始化HandlerMappings,根据配置从ApplicationContext中获取所有的HandlerMapping实例,并按照指定的顺序排序。如果没有定义HandlerMapping,则使用默认的BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping。最后,根据找到的HandlerMapping实例设置一些属性值。如果只期望SpringMVC加载指定的HandlerMapping时,可以修改web.xml中的DispatcherServlet的初始参数,将detectAllHandlerMappings设置为false,此时SpringMVC将会查找名为“handlerMapping”的bean,并作为当前系统中唯一的HandlerMapping。
初始化HandlerAdapters
该步骤适用于初始化适配器,源码如下:
/**
* 初始化该类使用的HandlerAdapters。
* 如果该命名空间的BeanFactory中没有定义HandlerAdapter Bean,则默认使用SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter。
*/
private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerAdapters = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {
// 在ApplicationContext中,包括祖先上下文,查找所有的HandlerAdapters。
Map matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// 我们按排序顺序保存HandlerAdapters。
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
}
} else {
try {
HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha);
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 忽略,稍后添加默认HandlerAdapter。
}
}
// 确保我们至少有一些HandlerAdapters,如果找不到其他HandlerAdapters,则注册默认HandlerAdapters。
if (this.handlerAdapters == null) {
this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("对于servlet '" + getServletName() + "'没有声明HandlerAdapters:使用DispatcherServlet.properties中的默认策略");
}
}
}
同样在初始化的过程中涉及了一个变量detectAllHandlerAdapters,和detectAllHandlerMappings作用很相似,只不过作用对象是HandlerAdapter。可以通过修改web.xml中的DispatcherServlet的初始参数,将detectAllHandlerAdapters设置为false,使得SpringMVC查找bean名称为“handlerAdapter”的HandlerAdapter实例。
作为总控制器的派遣servlet通过处理器映射得到处理器后,会轮询处理器适配器模板,查找能够处理当前HTTP请求的处理器适配器的实现,处理器适配器模块根据处理器映射返回的处理器类型,例如简单的适配器类型、注解控制器类型或者远程调用处理器类型,来选择一个适当的处理器适配器的实现,从而适配当前的HTTP请求。
- HTTP请求处理器适配器(HttpRequestHandlerAdapter),仅支持对HTTP请求处理器的适配,它简单地将HTTP请求对象和相应对象传递给HTTP请求处理器的实现,它并不需要返回值,它主要是基于HTTP的远程调用的实现上。
- 简单控制处理器适配器(SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter),这个实现类将HTTP请求适配到一个控制器的实现进行处理。这里控制器的实现是一个简单的控制器接口的实现。简单控制处理器适配器被设计成一个框架类的实现,不需要被改写,客户化的业务逻辑通常是在控制器接口的实现类中实现的。
- 注解方式处理器适配器(AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter),这个类的实现是基于注解的实现,它需要结合注解的方式映射和注解方法处理器协同工作。它通过解析声明在注解控制器的请求映射信息来解析相应的处理器方法来处理当前的HTTP请求。在处理的过程中,它通过反射来发现探测处理器方法的参数,调用处理器方法,并且映射返回值到模型和控制器对象,最后返回模型和控制器对象给作为主控制器的派遣器servlet。
初始化HandlerExceptionResolvers
基于HandlerExceptionResolver接口的异常处理,使用这种方法只需要实现resolveException方法,该方法返回一个ModelAndView对象,在方法内部对异常的类型进行判断,然后尝试生成对应的ModelAndView对象,如果该方法返回了null,则Spring会继续寻找其他实现了HandlerExceptionResolver接口的bean。换句话说,Spring会搜索所有注册在其环境中实现了HandlerExceptionResolver接口bean,逐个执行,直到返回一个ModelAndView对象。
public class DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver extends AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver {
/**
* 检查是否应该应用此解析器(即,如果提供的处理器与配置的
* {@linkplain #setMappedHandlers 处理器} 或 {@linkplain #setMappedHandlerClasses 处理器类} 中的任何一个匹配)
* 然后委托给 {@link #doResolveException} 模板方法。
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
if (shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) {
prepareResponse(ex, response);
ModelAndView result = doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (result != null) {
// 在 warn 日志启用时打印调试消息。
if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && (this.warnLogger == null || !this.warnLogger.isWarnEnabled())) {
logger.debug(buildLogMessage(ex, request) + (result.isEmpty() ? "" : " to " + result));
}
// 在 logException 方法中显式配置的 warn 日志器。
logException(ex, request);
}
return result;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView doResolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
// ErrorResponse exceptions that expose HTTP response details
if (ex instanceof ErrorResponse errorResponse) {
ModelAndView mav = null;
if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException theEx) {
mav = handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException theEx) {
mav = handleHttpMediaTypeNotSupported(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException theEx) {
mav = handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingPathVariableException theEx) {
mav = handleMissingPathVariable(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException theEx) {
mav = handleMissingServletRequestParameter(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException theEx) {
mav = handleMissingServletRequestPartException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof ServletRequestBindingException theEx) {
mav = handleServletRequestBindingException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException theEx) {
mav = handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HandlerMethodValidationException theEx) {
mav = handleHandlerMethodValidationException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof NoHandlerFoundException theEx) {
mav = handleNoHandlerFoundException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof NoResourceFoundException theEx) {
mav = handleNoResourceFoundException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof AsyncRequestTimeoutException theEx) {
mav = handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
return (mav != null ? mav :
handleErrorResponse(errorResponse, request, response, handler));
}
// Other, lower level exceptions
if (ex instanceof ConversionNotSupportedException theEx) {
return handleConversionNotSupported(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof TypeMismatchException theEx) {
return handleTypeMismatch(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException theEx) {
return handleHttpMessageNotReadable(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException theEx) {
return handleHttpMessageNotWritable(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof MethodValidationException theEx) {
return handleMethodValidationException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
else if (ex instanceof BindException theEx) {
return handleBindException(theEx, request, response, handler);
}
}
catch (Exception handlerEx) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failure while trying to resolve exception [" + ex.getClass().getName() + "]", handlerEx);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 处理 {@link ErrorResponse} 异常。
* 默认实现将状态和头信息设置为从 {@code ErrorResponse} 获取到的值。
* 如果可用,{@link ProblemDetail#getDetail()} 将用作
* {@link HttpServletResponse#sendError(int, String)} 的消息。
* @param errorResponse 需要处理的异常
* @param request 当前的 HTTP 请求
* @param response 当前的 HTTP 响应
* @param handler 执行的处理器
* @return 一个空的 {@code ModelAndView},表示异常已处理
* @throws IOException 可能从 {@link HttpServletResponse#sendError} 抛出
* @since 6.0
*/
protected ModelAndView handleErrorResponse(ErrorResponse errorResponse,
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler) throws IOException {
if (!response.isCommitted()) {
HttpHeaders headers = errorResponse.getHeaders();
headers.forEach((name, values) -> values.forEach(value -> response.addHeader(name, value)));
int status = errorResponse.getStatusCode().value();
String message = errorResponse.getBody().getDetail();
if (message != null) {
response.sendError(status, message);
}
else {
response.sendError(status);
}
}
else {
logger.warn("忽略异常,响应已提交。: " + errorResponse);
}
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
初始化RequestToViewNameTranslator
当Controller处理器方法没有返回一个View对象或逻辑视图名称,并且在该方法中没有直接往Response的输出流里面写数据的时候,Spring就会采用约定好的方式提供一个逻辑视图名称。这个逻辑视图名称是通过Spring定义的RequestToViewNameTranslator接口的getViewName方法来实现的。首先看一下初始化RequestToViewNameTranslator的源码如下:
/**
* 初始化该servlet实例使用的RequestToViewNameTranslator。
* 如果没有配置实现,则默认使用DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator。
*/
private void initRequestToViewNameTranslator(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.viewNameTranslator = context.getBean(REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("检测到 " + this.viewNameTranslator.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("检测到 " + this.viewNameTranslator);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 需要使用默认实现
this.viewNameTranslator = getDefaultStrategy(context, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("未检测到RequestToViewNameTranslator '" + REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME +
"': 使用默认 [" + this.viewNameTranslator.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
Spring已经给我们提供了一个它自己的实现,就是DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator,源码如下:
public class DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator implements RequestToViewNameTranslator {
private static final String SLASH = "/";
private String prefix = "";
private String suffix = "";
private String separator = SLASH;
private boolean stripLeadingSlash = true;
private boolean stripTrailingSlash = true;
private boolean stripExtension = true;
/**
* Translates the request URI of the incoming {@link HttpServletRequest}
* into the view name based on the configured parameters.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if neither a parsed RequestPath, nor a
* String lookupPath have been resolved and cached as a request attribute.
* @see ServletRequestPathUtils#getCachedPath(ServletRequest)
* @see #transformPath
*/
@Override
public String getViewName(HttpServletRequest request) {
String path = ServletRequestPathUtils.getCachedPathValue(request);
return (this.prefix + transformPath(path) + this.suffix);
}
/**
* Transform the request URI (in the context of the webapp) stripping
* slashes and extensions, and replacing the separator as required.
* @param lookupPath the lookup path for the current request,
* as determined by the UrlPathHelper
* @return the transformed path, with slashes and extensions stripped
* if desired
*/
@Nullable
protected String transformPath(String lookupPath) {
String path = lookupPath;
if (this.stripLeadingSlash && path.startsWith(SLASH)) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
if (this.stripTrailingSlash && path.endsWith(SLASH)) {
path = path.substring(0, path.length() - 1);
}
if (this.stripExtension) {
path = StringUtils.stripFilenameExtension(path);
}
if (!SLASH.equals(this.separator)) {
path = StringUtils.replace(path, SLASH, this.separator);
}
return path;
}
}初始化ViewResolvers
在SpringMVC中,当Controller将请求处理结果放入到ModelAndView中以后,DispatcherServlet会根据ModelAndView选择合适的视图进行渲染。ViewResolver接口定义了resolveViewName方法,根据viewName创建合适类型的View实现。初始化ViewResolvers的源码如下:
/**
* 初始化用于此类的 ViewResolvers。
* matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, ViewResolver.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// 我们按升序排列 ViewResolvers。
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.viewResolvers);
}
} else {
try {
ViewResolver vr = context.getBean(VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ViewResolver.class);
this.viewResolvers = Collections.singletonList(vr);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 忽略,后面我们会添加一个默认的 ViewResolver。
}
}
// 如果没有找到其他 ViewResolver,则通过从 DispatcherServlet.properties 中注册一个默认的 ViewResolver 来确保至少有一个 ViewResolver。
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, ViewResolver.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("未为 servlet '" + getServletName() +
" 声明 ViewResolvers:使用默认的 ViewResolver 策略");
}
}
}
初始化FlashMapManager
SpringMVC Flush提供了一个请求存储属性,可供其他请求使用。在使用重定向的时候非常必要,例如POST/GET/DELETE。初始化FlashMapManager的源码如下:
/**
* 初始化由此servlet实例使用的FlashMapManager。
* 如果未配置实现,则默认为{@code org.springframework.web.servlet.support.DefaultFlashMapManager}。
*/
private void initFlashMapManager(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.flashMapManager = context.getBean(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME, FlashMapManager.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Detected " + this.flashMapManager.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + this.flashMapManager);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// 需要使用默认实现
this.flashMapManager = getDefaultStrategy(context, FlashMapManager.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No FlashMapManager '" + FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.flashMapManager.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}