大厂面试题-为什么ConcurrentHashMap不允许插入null值
目录
概述
一、探寻源码
二、歧义问题
三、作者回复
四、总结
蜗牛学苑-重构IT职业教育新生态
概述
在Java语言中,给ConcurrentHashMap和Hashtable这些线程安全的集合中的Key或者Value插入null(空)值的会报空指针异常,但是单线程操作的HashMap又允许Key或者Value插入null(空)值。这到底是为什么呢?
一、探寻源码
为了找到原因,我们先来看这样一段源码片段,打开ConcurrentHashMap的putVal()方法,源码中第一句就非常明确地做了判断,如果Key或者Value为null(空)值,就直接抛出空指针异常。
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
} 我们在源码中似乎已经找到了原因,你可以这样回答面试官,说JDK源码就是这么规定的。然而,这个原因是不能说服面试官的,虽然,源码是这样设计的,我们要思考的是,这样设计背后更深层次的原因。
那到底为什么ConcurrentHashMap不允许插入null值,HashMap又允许插入呢?
二、歧义问题
因为给ConcurrentHashMap中插入null(空)值会存在歧义。我们可以假设ConcurrentHashMap允许插入null(空)值,那么,我们取值的时候会出现两种结果:
1、值没有在集合中,所以返回的结果就是null(空);
2、值就是null(空),所以返回的结果就是它原本的null(空)值。
这就产生了歧义问题。
那HashMap允许插入null(空)值,难道它就不担心出现歧义吗?这是因为HashMap的设计是给单线程使用的,所以如果取到null(空)值,我们可以通过HashMap的containsKey(key)方法来区分这个null(空)值到底是插入值是null(空),还是本就没有才返回的null(空)值。
而ConcurrentHashMap就不一样了,因为ConcurrentHashMap是在多线程场景下使用的,它的情况更加复杂。
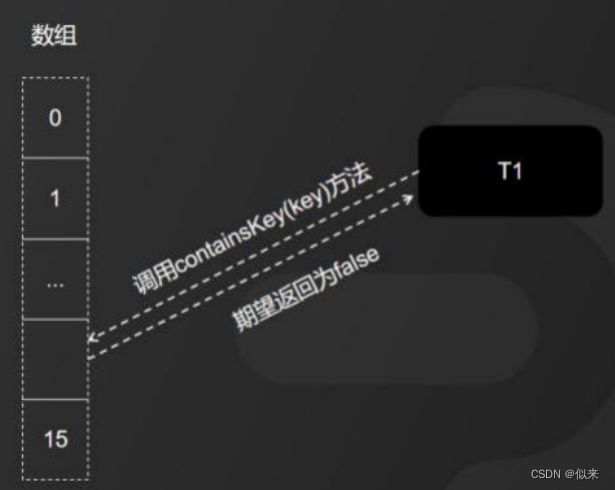
举个例子:现在有线程T1调用了ConcurrentHashMap的containsKey(key)方法,我们期望返回的结果是false,也就是说,T1并没有往ConcurrentHashMap中put null(空)值。
但是,恰恰出了个意外,在线程T1还没有得到返回结果之前,线程T2又调用了ConcurrentHashMap的put()方法,插入了一个Key,并且存入的Value是null(空)值。那么,线程T1最终得到的返回结果就变成true了。
显然,这个结果和我们之前期望的false完全不一致。
也就是说,在多线程的复杂情况下,我们多线程的复杂情况下,到底是插入的null(空)值,还是本就没有才返回的null(空)值。也就是说,产生的歧义不能被证伪。
三、作者回复
对于ConcurrentHashMap不允许插入null值的问题,有人问过ConcurrentHashMap的作者Doug Lea,以下是他回复的邮件内容:
The main reason that nulls aren't allowed in ConcurrentMaps(ConcurrentHashMaps, ConcurrentSkipListMaps) is that ambiguities that may be just barely tolerable in non-concurrent maps can't be accommodated. The main one is that if map.get(key) returns null, you can't detect whether the key explicitly maps to null vs the key isn't mapped.In a non-concurrent map, you can check this via map.contains(key),but in a concurrent one, the map might have changed between calls.
Further digressing: I personally think that allowingnulls in Maps (also Sets) is an open invitation for programsto contain errors that remain undetected untilthey break at just the wrong time. (Whether to allow nulls evenin non-concurrent Maps/Sets is one of the few design issues surroundingCollections that Josh Bloch and I have long disagreed about.)
It is very difficult to check for null keys and valuesin my entire application . Would it be easier to declare somewherestatic final Object NULL = new Object();and replace all use of nulls in uses of maps with NULL?
-Doug
以上信件的主要意思是,Doug Lea认为这样设计最主要的原因是:不容忍在并发场景下出现歧义!
四、总结
ConcurrentHashMap在源码中加入不允许插入null(空)值的设计,主要目的是为了防止并发场景下的歧义问题。
蜗牛学苑-重构IT职业教育新生态