Matplotlib 05-样式色彩秀芳华
Matplotlib 05-样式色彩秀芳华
一、matplotlib的绘图样式(style)
在matplotlib中,要想设置绘制样式,最简单的方法是在绘制元素时单独设置样式。
但是有时候,当用户在做专题报告时,往往会希望保持整体风格的统一而不用对每张图一张张修改,因此matplotlib库还提供了四种批量修改全局样式的方式
1.matplotlib预先定义样式
matplotlib贴心地提供了许多内置的样式供用户使用,使用方法很简单,只需在python脚本的最开始输入想使用style的名称即可调用,尝试调用不同内置样式,比较区别
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.style.use('default')
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
plt.style.use('ggplot')
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
那么matplotlib究竟内置了那些样式供使用呢?总共以下26种丰富的样式可供选择。
print(plt.style.available)
['Solarize_Light2', '_classic_test_patch', 'bmh', 'classic', 'dark_background', 'fast', 'fivethirtyeight', 'ggplot', 'grayscale', 'seaborn', 'seaborn-bright', 'seaborn-colorblind', 'seaborn-dark', 'seaborn-dark-palette', 'seaborn-darkgrid', 'seaborn-deep', 'seaborn-muted', 'seaborn-notebook', 'seaborn-paper', 'seaborn-pastel', 'seaborn-poster', 'seaborn-talk', 'seaborn-ticks', 'seaborn-white', 'seaborn-whitegrid', 'tableau-colorblind10']
2.用户自定义stylesheet
在任意路径下创建一个后缀名为mplstyle的样式清单,编辑文件添加以下样式内容
axes.titlesize : 24
axes.labelsize : 20
lines.linewidth : 3
lines.markersize : 10
xtick.labelsize : 16
ytick.labelsize : 16
引用自定义stylesheet后观察图表变化。
plt.style.use('mystyle.mplstyle')
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
值得特别注意的是,matplotlib支持混合样式的引用,只需在引用时输入一个样式列表,若是几个样式中涉及到同一个参数,右边的样式表会覆盖左边的值。
plt.style.use(['dark_background', 'mystyle.mplstyle'])
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
3.设置rcparams
我们还可以通过修改默认rc设置的方式改变样式,所有rc设置都保存在一个叫做 matplotlib.rcParams的变量中。
修改过后再绘图,可以看到绘图样式发生了变化。
plt.style.use('default') # 恢复到默认样式
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
mpl.rcParams['lines.linewidth'] = 2
mpl.rcParams['lines.linestyle'] = '--'
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
另外matplotlib也还提供了了一种更便捷的修改样式方式,可以一次性修改多个样式。
mpl.rc('lines', linewidth=4, linestyle='-.')
plt.plot([1,2,3,4],[5,4,3,2])
plt.show()
4.修改matplotlibrc文件
由于matplotlib是使用matplotlibrc文件来控制样式的,也就是上一节提到的rc setting,所以我们还可以通过修改matplotlibrc文件的方式改变样式。
# 查找matplotlibrc文件的路径
mpl.matplotlib_fname()
找到路径后,就可以直接编辑样式文件了,打开后看到的文件格式大致是这样的,文件中列举了所有的样式参数,找到想要修改的参数,比如lines.linewidth: 8,并将前面的注释符号去掉,此时再绘图发现样式以及生效了。
二、matplotlib的色彩设置(color)
在可视化中,如何选择合适的颜色和搭配组合也是需要仔细考虑的,色彩选择要能够反映出可视化图像的主旨。
从可视化编码的角度对颜色进行分析,可以将颜色分为色相、亮度和饱和度三个视觉通道。通常来说:
色相: 没有明显的顺序性、一般不用来表达数据量的高低,而是用来表达数据列的类别。
明度和饱和度: 在视觉上很容易区分出优先级的高低、被用作表达顺序或者表达数据量视觉通道。
具体关于色彩理论部分的知识,不属于本教程的重点,请参阅有关拓展材料学习。
ECharts数据可视化实验室
学会这6个可视化配色基本技巧,还原数据本身的意义
在matplotlib中,设置颜色有以下几种方式:
1.RGB或RGBA
plt.style.use('default')
# 颜色用[0,1]之间的浮点数表示,四个分量按顺序分别为(red, green, blue, alpha),其中alpha透明度可省略
plt.plot([1,2,3],[3,2,1],color=(0.5, 0.2, 0.1))
plt.plot([4,5,6],[6,5,4],color=(0.5, 0.5, 0.2, 0.7))
plt.show()
2.HEX RGB 或 RGBA
# 用十六进制颜色码表示,同样最后两位表示透明度,可省略
plt.plot([1,2,3],[3,2,1],color='#0b0904')
plt.plot([4,5,6],[6,5,4],color='#030c0e77')
plt.show()
3.灰度色阶
# 当只有一个位于[0,1]的值时,表示灰度色阶
plt.plot([1,2,3],[6,5,4],color='0.6')
plt.show()
4.单字符基本颜色
# matplotlib有八个基本颜色,可以用单字符串来表示,分别是'b', 'g', 'r', 'c', 'm', 'y', 'k', 'w',对应的是blue, green, red, cyan, magenta, yellow, black, and white的英文缩写
plt.plot([1,2,3],[6,5,4],color='c')
plt.show()
5.颜色名称
# matplotlib提供了颜色对照表,可供查询颜色对应的名称
plt.plot([1,2,3],[6,5,4],color='crimson')
plt.show()
6.使用colormap设置一组颜色
有些图表支持使用colormap的方式配置一组颜色,从而在可视化中通过色彩的变化表达更多信息。
在matplotlib中,colormap共有五种类型:
- 顺序(Sequential)。通常使用单一色调,逐渐改变亮度和颜色渐渐增加,用于表示有顺序的信息
- 发散(Diverging)。改变两种不同颜色的亮度和饱和度,这些颜色在中间以不饱和的颜色相遇;当绘制的信息具有关键中间值(例如地形)或数据偏离零时,应使用此值。
- 循环(Cyclic)。改变两种不同颜色的亮度,在中间和开始/结束时以不饱和的颜色相遇。用于在端点处环绕的值,例如相角,风向或一天中的时间。
- 定性(Qualitative)。常是杂色,用来表示没有排序或关系的信息。
- 杂色(Miscellaneous)。一些在特定场景使用的杂色组合,如彩虹,海洋,地形等。
x = np.random.randn(50)
y = np.random.randn(50)
plt.scatter(x,y,c=x,cmap='spring')
plt.show()
作业
1)查阅matplotlib官网,列举出Sequential,Diverging,Cyclic,Qualitative,Miscellaneous分别有哪些内置的colormap,并以代码绘图的形式展现出来
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from colorspacious import cspace_converter
from collections import OrderedDict
cmaps = OrderedDict()
cmaps={'Perceptually Uniform Sequential':['viridis', 'plasma', 'inferno', 'magma', 'cividis'],
'Sequential':['Greys', 'Purples', 'Blues', 'Greens', 'Oranges', 'Reds','YlOrBr', 'YlOrRd', 'OrRd', 'PuRd', 'RdPu', 'BuPu','GnBu', 'PuBu', 'YlGnBu', 'PuBuGn', 'BuGn', 'YlGn'],
'Sequential (2)':['binary', 'gist_yarg', 'gist_gray', 'gray', 'bone', 'pink','spring', 'summer', 'autumn', 'winter', 'cool', 'Wistia','hot', 'afmhot', 'gist_heat', 'copper'],
'Diverging':['PiYG', 'PRGn', 'BrBG', 'PuOr', 'RdGy', 'RdBu','RdYlBu', 'RdYlGn', 'Spectral', 'coolwarm', 'bwr', 'seismic'],
'Cyclic':['twilight', 'twilight_shifted', 'hsv'],
'Qualitative':['Pastel1', 'Pastel2', 'Paired', 'Accent','Dark2', 'Set1', 'Set2', 'Set3','tab10', 'tab20', 'tab20b', 'tab20c'],
'Miscellaneous':['flag', 'prism', 'ocean', 'gist_earth', 'terrain', 'gist_stern','gnuplot', 'gnuplot2', 'CMRmap', 'cubehelix', 'brg','gist_rainbow', 'rainbow', 'jet', 'turbo', 'nipy_spectral','gist_ncar']}
gradient = np.vstack((np.linspace(0, 1, 256), np.linspace(0, 1, 256)))
def plot_color_gradients(cmap_category, cmap_list):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=len(cmap_list),figsize=(8,len(cmap_list)/4))
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0.01, left=0.2, right=0.99)
axes[0].set_title(cmap_category + ' colormaps', fontsize=14)
for ax, name in zip(axes, cmap_list):
ax.imshow(gradient, aspect='auto', cmap=plt.get_cmap(name))
pos = list(ax.get_position().bounds)
x_text = pos[0] - 0.01
y_text = pos[1] + pos[3]/2.
fig.text(x_text, y_text, name, va='center', ha='right', fontsize=10)
for ax in axes:
ax.set_axis_off()
for cmap_category, cmap_list in cmaps.items():
plot_color_gradients(cmap_category, cmap_list)
plt.show()
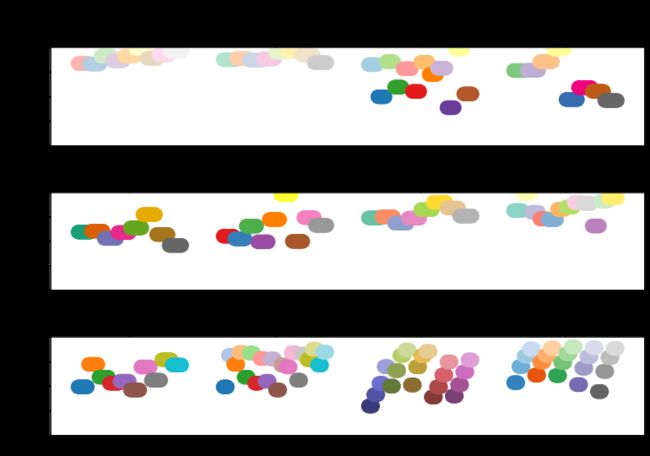
2)学习如何自定义colormap,并将其应用到任意一个数据集中,绘制一幅图像,注意colormap的类型要和数据集的特性相匹配,并做简单解释
mpl.rcParams.update({'font.size': 12})
_DSUBS = {'Perceptually Uniform Sequential': 5, 'Sequential': 6,'Sequential (2)': 6, 'Diverging': 6, 'Cyclic': 3,'Qualitative': 4, 'Miscellaneous': 6}
_DC = {'Perceptually Uniform Sequential': 1.4, 'Sequential': 0.7,'Sequential (2)': 1.4, 'Diverging': 1.4, 'Cyclic': 1.4,'Qualitative': 1.4, 'Miscellaneous': 1.4}
x = np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, 100)
for cmap_category, cmap_list in cmaps.items():
dsub = _DSUBS.get(cmap_category, 6)
nsubplots = int(np.ceil(len(cmap_list) / dsub))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=nsubplots, squeeze=False,figsize=(11, 2.6*nsubplots))
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
locs = []
for j, cmap in enumerate(cmap_list[i*dsub:(i+1)*dsub]):
rgb = cm.get_cmap(cmap)(x)[np.newaxis, :, :3]
lab = cspace_converter("sRGB1", "CAM02-UCS")(rgb)
if cmap_category == 'Sequential':
y_ = lab[0, ::-1, 0]
c_ = x[::-1]
else:
y_ = lab[0, :, 0]
c_ = x
dc = _DC.get(cmap_category, 1.4)
ax.scatter(x + j*dc, y_, c=c_, cmap=cmap, s=300, linewidths=0.0)
if cmap_category in ('Perceptually Uniform Sequential','Sequential'):
locs.append(x[-1] + j*dc)
elif cmap_category in ('Diverging', 'Qualitative', 'Cyclic','Miscellaneous', 'Sequential (2)'):
locs.append(x[int(x.size/2.)] + j*dc)
ax.set_xlim(axes[0, 0].get_xlim())
ax.set_ylim(0.0, 100.0)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')
ticker = mpl.ticker.FixedLocator(locs)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker)
formatter = mpl.ticker.FixedFormatter(cmap_list[i*dsub:(i+1)*dsub])
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(rotation=50)
ax.set_ylabel('Lightness $L^*$', fontsize=12)
ax.set_xlabel(cmap_category + ' colormaps', fontsize=14)
fig.tight_layout(h_pad=0.0, pad=1.5)
plt.show()