【Pixel Shader】SDF建模和Raymarching算法
参考
Ray Marching and Signed Distance Functions
IQ博客:Distance Functions
ShaderToy Combination SDF
GLSL ES 语言—矢量和矩阵的赋值构造函数
SDF(Signed Distance Functions)是使用距离方程来表示几何体的方式,配合raymarching方法可以仅在pixel shader中渲染出建模效果的画面,而不需要真正的模型输入,这也是shadertoy网站上大部分建模效果的作品使用的方法。关于SDF和raymarching的基础知识可以看第一篇参考文章。
这篇博客在Unity Shader中初步实现了基础的SDF + raymarching算法。
效果
踩坑
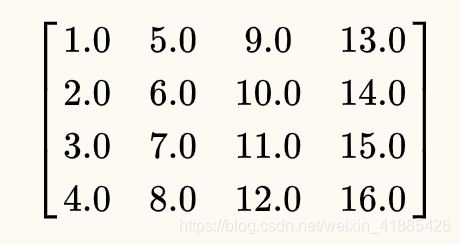
过程中遇到最大的坑是在计算view2world matrix时,由于参考代码都是GLSL写的,GLSL的矩阵构造函数是列主序排列的,即当你在GLSL里写:
mat4 m = mat4(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0,
5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0,
9.0, 10.0, 11.0, 12.0,
13.0, 14.0, 15.0, 16.0);
mat4 m = mat4(v1, v2, v3, v4); //v1 v2 v3 v4均为vec4类型变量
构造出的4x4矩阵m为依次将v1 v2 v3 v4按列从左到右放置的结果。
而在移植到Unity Shader中时,由于ShaderLab使用CG语言,矩阵的构造函数为行主序。如果不注意这个细节,直接使用GLSL代码中的构造顺序,如以下代码:
fixed3x3 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up) {
fixed3 f = normalize(center - eye);
fixed3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
fixed3 u = cross(s, f);
return fixed3x3 (s, u, -f);
}
通过这样的代码,我们得到的将是正确矩阵的转置。
因此正确的写法应该是:
fixed3x3 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up) {
// Based on gluLookAt man page
fixed3 f = normalize(center - eye);
fixed3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
fixed3 u = cross(s, f);
return fixed3x3(s.x, u.x, -f.x, s.y, u.y, -f.y, s.z, u.z, -f.z);
}
这个问题在构造围绕XYZ轴旋转矩阵的时候同样需要注意。
Unity Shader代码
Shader "Custom/SDFTest"
{
Properties
{
}
SubShader{
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct v2f {
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float4 scrPos : TEXCOORD0;
};
v2f vert(appdata_full v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.scrPos = ComputeScreenPos(o.pos);
return o;
}
// 常量定义
#define MAX_MARCHING_STEPS 255// 最大raymarching次数
#define MIN_DIST 0.0// 起始raymarching距离
#define MAX_DIST 100.0// 最远raymarching距离
#define EPSILON 0.0001// 极小量
float opUnion(float d1, float d2)
{
return min(d1, d2);
}
float opSubtraction(float d1, float d2)
{
return max(-d1, d2);
}
float opIntersection(float d1, float d2)
{
return max(d1, d2);
}
float opSmoothUnion(float d1, float d2, float k)
{
float h = max(k - abs(d1 - d2), 0.0);
return min(d1, d2) - h * h * 0.25 / k;
//float h = clamp( 0.5 + 0.5*(d2-d1)/k, 0.0, 1.0 );
//return mix( d2, d1, h ) - k*h*(1.0-h);
}
float opSmoothSubtraction(float d1, float d2, float k)
{
float h = max(k - abs(-d1 - d2), 0.0);
return max(-d1, d2) + h * h * 0.25 / k;
//float h = clamp( 0.5 - 0.5*(d2+d1)/k, 0.0, 1.0 );
//return mix( d2, -d1, h ) + k*h*(1.0-h);
}
float opSmoothIntersection(float d1, float d2, float k)
{
float h = max(k - abs(d1 - d2), 0.0);
return max(d1, d2) + h * h * 0.25 / k;
//float h = clamp( 0.5 - 0.5*(d2-d1)/k, 0.0, 1.0 );
//return mix( d2, d1, h ) + k*h*(1.0-h);
}
/**
* Rotation matrix around the X axis.
*/
fixed3x3 rotateX(float theta) {
fixed c = cos(theta);
fixed s = sin(theta);
return fixed3x3(
fixed3(1, 0, 0),
fixed3(0, c, s),
fixed3(0, -s, c)
);
}
/**
* Rotation matrix around the Y axis.
*/
fixed3x3 rotateY(float theta) {
fixed c = cos(theta);
fixed s = sin(theta);
return fixed3x3(
fixed3(c, 0, -s),
fixed3(0, 1, 0),
fixed3(s, 0, c)
);
}
/**
* Rotation matrix around the Z axis.
*/
fixed3x3 rotateZ(float theta) {
fixed c = cos(theta);
fixed s = sin(theta);
return fixed3x3(
fixed3(c, s, 0),
fixed3(-s, c, 0),
fixed3(0, 0, 1)
);
}
// 圆角长方体SDF
float sdRoundBox(float3 p, float3 b, float r)
{
float3 q = abs(p) - b;
return length(max(q, 0.0)) + min(max(q.x, max(q.y, q.z)), 0.0) - r;
}
// 球体SDF
float sdSphere(float3 p, float r)
{
return length(p) - r;
}
// 场景SDF
float sdScene(float3 p) {
p /= 0.8;// 全场景uniform scale为0.8倍
p = mul(rotateY(_Time[1]*0.5), p);// 全场景绕Y轴旋转
float d1 = sdRoundBox(p, float3(2.0, 1.0, 2.0), 0.1);
float d2 = sdSphere(p - float3(0.0, 1.0 + 1.0 * sin(_Time[1]), 0.0), 1.0);// 球体平移
return opSmoothUnion(d1, d2, 0.5) * 0.8;// 取平滑交集,*0.8表示第一步uniform scale的补偿
}
/**
* Return the shortest distance from the eyepoint to the scene surface along
* the marching direction. If no part of the surface is found between start and end,
* return end.
*
* eye: the eye point, acting as the origin of the ray
* marchingDirection: the normalized direction to march in
* start: the starting distance away from the eye
* end: the max distance away from the ey to march before giving up
*/
float shortestDistanceToSurface(float3 eye, float3 marchingDirection, float start, float end) {
float depth = start;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_MARCHING_STEPS; i++) {
float dist = sdScene(eye + depth * marchingDirection);
if (dist < EPSILON) {
return depth;
}
depth += dist;
if (depth >= end) {
return end;
}
}
return end;
}
/**
* Return the normalized direction to march in from the eye point for a single pixel.
*
* fieldOfView: vertical field of view in degrees
* size: resolution of the output image
* fragCoord: the x,y coordinate of the pixel in the output image
*/
fixed3 rayDirection(float fieldOfView, float2 size, float2 fragCoord) {
float2 xy = fragCoord - size / 2.0;
float z = size.y / tan(radians(fieldOfView) / 2.0);
return normalize(float3(xy, -z));
}
/**
* Return a transform matrix that will transform a ray from view space
* to world coordinates, given the eye point, the camera target, and an up vector.
*
* This assumes that the center of the camera is aligned with the negative z axis in
* view space when calculating the ray marching direction. See rayDirection.
*/
fixed3x3 viewMatrix(float3 eye, float3 center, float3 up) {
// Based on gluLookAt man page
fixed3 f = normalize(center - eye);
fixed3 s = normalize(cross(f, up));
fixed3 u = cross(s, f);
return fixed3x3(s.x, u.x, -f.x, s.y, u.y, -f.y, s.z, u.z, -f.z);
}
/**
* Using the gradient of the SDF, estimate the normal on the surface at point p.
*/
fixed3 estimateNormal(float3 p) {
return normalize(float3(
sdScene(float3(p.x + EPSILON, p.y, p.z)) - sdScene(float3(p.x - EPSILON, p.y, p.z)),
sdScene(float3(p.x, p.y + EPSILON, p.z)) - sdScene(float3(p.x, p.y - EPSILON, p.z)),
sdScene(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z + EPSILON)) - sdScene(float3(p.x, p.y, p.z - EPSILON))
));
}
/**
* Lighting contribution of a single point light source via Phong illumination.
*
* The vec3 returned is the RGB color of the light's contribution.
*
* k_a: Ambient color
* k_d: Diffuse color
* k_s: Specular color
* alpha: Shininess coefficient
* p: position of point being lit
* eye: the position of the camera
* lightPos: the position of the light
* lightIntensity: color/intensity of the light
*
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phong_reflection_model#Description
*/
fixed3 phongContribForLight(fixed3 k_d, fixed3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye,
float3 lightPos, fixed3 lightIntensity) {
fixed3 N = estimateNormal(p);
fixed3 L = normalize(lightPos - p);
fixed3 V = normalize(eye - p);
fixed3 R = normalize(reflect(-L, N));
fixed dotLN = dot(L, N);
fixed dotRV = dot(R, V);
if (dotLN < 0.0) {
// Light not visible from this point on the surface
return fixed3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if (dotRV < 0.0) {
// Light reflection in opposite direction as viewer, apply only diffuse
// component
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN);
}
return lightIntensity * (k_d * dotLN + k_s * pow(dotRV, alpha));
}
/**
* Lighting via Phong illumination.
*
* The vec3 returned is the RGB color of that point after lighting is applied.
* k_a: Ambient color
* k_d: Diffuse color
* k_s: Specular color
* alpha: Shininess coefficient
* p: position of point being lit
* eye: the position of the camera
*
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phong_reflection_model#Description
*/
float3 phongIllumination(fixed3 k_a, fixed3 k_d, fixed3 k_s, float alpha, float3 p, float3 eye) {
const fixed3 ambientLight = 0.5 * fixed3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
fixed3 color = ambientLight * k_a;
float3 lightPos = float3(4.0, 5.0, 4.0);
fixed3 lightIntensity = fixed3(0.4, 0.4, 0.4);
color += phongContribForLight(k_d, k_s, alpha, p, eye,
lightPos,
lightIntensity);
return color;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target{
float2 scr_coords = (i.scrPos.xy / i.scrPos.w) * _ScreenParams.xy;//片元的屏幕坐标
// 相机参数
float3 eyePos = float3(5.0, 7.0, 6.0);
float3 centerPos = float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
float3 up = float3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
float fov = 60.0;
fixed3 dir = rayDirection(fov, _ScreenParams.xy, scr_coords);// 计算该像素的raymarching方向(view空间)
fixed3x3 view2world = viewMatrix(eyePos, centerPos, up);// 计算view to world向量变换矩阵
fixed3 worldDir = mul(view2world, dir);// 将view空间的raymarching方向转化至world空间
float dist = shortestDistanceToSurface(eyePos, worldDir, MIN_DIST, MAX_DIST);
if (dist > MAX_DIST - EPSILON) {
// Didn't hit anything
return fixed4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}
float3 p = eyePos + dist * worldDir;// 计算raymarching与场景相交的点坐标
// phong shading params
fixed3 K_a = fixed3(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);// ambient color
fixed3 K_d = fixed3(0.7, 0.2, 0.2);// diffuse color
fixed3 K_s = fixed3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);// specular color
float shininess = 10.0;
fixed3 color = phongIllumination(K_a, K_d, K_s, shininess, p, eyePos);
return fixed4(color, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}