激活函数整理
sigmoid函数
![]()
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
%matplotlib inline
x=torch.arange(-10,10,0.1,requires_grad=True)
sigmoid=torch.nn.Sigmoid()
y=sigmoid(x)
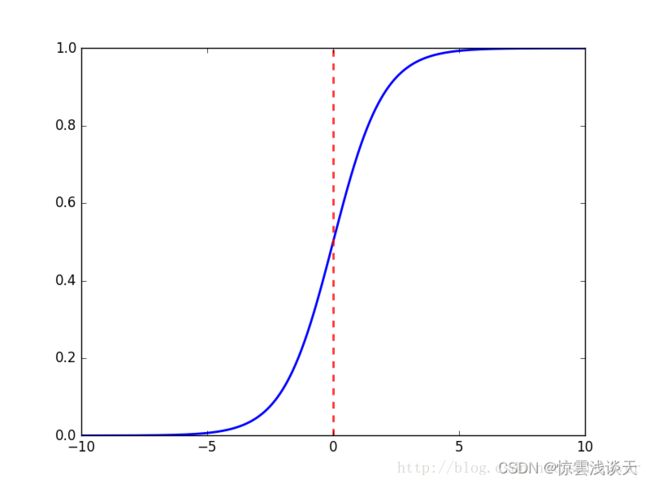
d2l.plot(x.detach(),y.detach(),'x','sigmoid(x)',figsize=(5,2.5))sigmoid函数连续、光滑、单调递增,以 (0,0.5) 中心对称,是一个良好的阈值函数。在x超出[-6,6]的范围后,函数值基本上没有变化,值非常接近,在应用中一般不考虑。
sigmoid函数的值域范围限制在(0,1)之间,恰巧与概率值的范围相对应,这样Sigmoid函数就能与一个概率分布联系起来了。
存在等式:
![]()
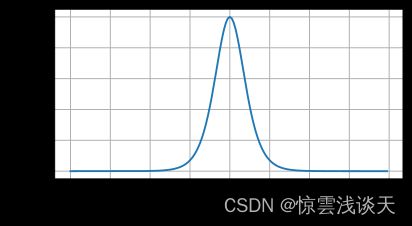
当输入值为0时,sigmoid函数的导数达到最大值0.25;而输入在任一方向上越远离0点时,导数越接近0。
#清除以前的梯度
#retain_graph如果设置为False,计算图中的中间变量在计算完后就会被释放。
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x),retain_graph=True)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),x.grad,'x','grad of sigmoid')sigmoid函数可用作逻辑回归模型的分类器。除此之外还存在其自身的推到特性。
对于分类问题,尤其是二分类问题,都假定服从伯努利分布,
![]()
根据指数分布族的一半表现形式
![]()
伯努利分布可变形为:
![]()
故,伯努利分布也属于指数分布族,
令![]() ,可得
,可得![]()
此为sigmoid函数形式。
tanh函数
与sigmoid类似,tanh函数也会将输入压缩至(-1,1)。
![]()
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
%matplotlib inline
x=torch.arange(-8.0,8.0,0.1,requires_grad=True)
tanh=torch.nn.Tanh()
y=tanh(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),y.detach(),'x','tanh(x)',figsize=(5,2.5))存在等式:
![]()
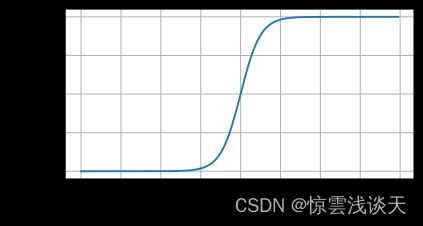
tanh函数的导数如下,当输入接近0时,tanh函数的导数接近最大值1,输入在任一方向上远离0点,导数越接近0。
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x),retain_graph=True)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),x.grad,'x','grad of tanh',figsize=(5,2.5))ReLU函数
ReLU函数的求导表现很好:要么让参数消失,要么让参数通过。
ReLU减轻了神经网络的梯度消失问题。ReLU函数有很多变体,如LeakyReLU,pReLU等。
#原函数
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
%matplotlib inline
x=torch.arange(-8.0,8.0,0.1,requires_grad=True)
relu=torch.nn.ReLU()
y=relu(x)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),y.detach(),'x','relu',figsize=(5,2.5))
#导数
#retain_graph如果设置为False,计算图中的中间变量在计算完后就会被释放。
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x),retain_graph=True)
d2l.plot(x.detach(),x.grad,'x','grad of relu',figsize=(5,2.5))变种:Leaky Relu函数
负区间值非0,为一个斜率相较小的线性函数
softmax函数
在二分类任务时,经常使用sigmoid激活函数。而在处理多分类问题的时候,需要使用softmax函数。它的输出有两条规则。
-
每一项的区间范围的(0,1)
-
所有项相加的和为1
假设有一个数组 V,Vi代表 V 中的第i个元素,那么这个元素的softmax值的计算公式为:
x=torch.Tensor([3.,1.,-3.]) softmax=torch.nn.Softmax(dim=0) y=softmax(x) print(y)