Netty通信中的粘包半包问题(一)
前言
我们在日常开发过程中,客户端和服务端的连接大多使用的是TCP协议,因为我们要保证数据的可靠传输,
当网络中出现丢包时要求,要求数据包的发送端重传给接收端。而TCP是一种面向连接的传输层协议,
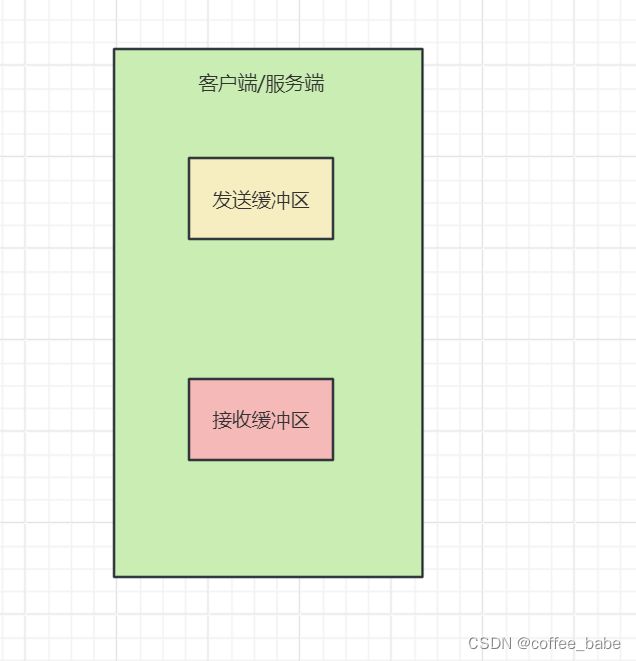
当使用TCP进行传输时,客户端和服务端会各自维护两个缓冲区,它们分别是发送缓冲区、接收缓冲区,如图所示
在网络传输过程中,虽然对要发送的数据包大小没有要求,但是TCP又不可能一次性的把数据全部加载到
发送缓冲区中,这样会有可能撑爆TCP的发送缓冲区,比如说你要发送个1G的数据给服务端,TCP本身是不会
每次根据你要发送的数据包大小划定缓冲区大小的。但是它会收数据链路层的协议限制,
因为数据链路层是服务于传输层协议的,我们需要了解数据链路层当中传输的最大单元
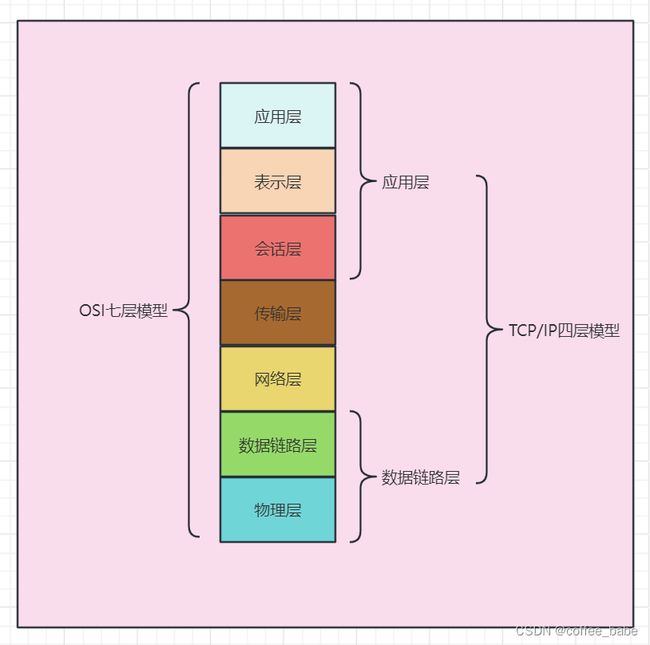
MTU(Maximum Transmission Unit)最大传输单元,用来通知对方所能接受数据服务单元的最大尺寸,说明发送方能能够接受的有效载荷大小,另外传输层还会进行一个MSS大小的TCP分段。MSS是最大报文长度的缩写,MSS是TCP报文段中的数据字段的最大长度。数据字段加上TCP首部才等于整个的TCP报文段,所以MSS并不是TCP报文的最大长度,而是MSS=TCP报文长度 - TCP首部长度,在以太网中MTU是1500个字节,其中TCP报头占20个字节,IP包头占20个字节,剩下的大小才是我们能在发送的有效数据包大小,也就是1500-20-20=1460个字节,
也就是说,如果没有进行过调整,当你发送的数据包小于1460个字节的时候,客户端在发送缓冲区里放下你的报文时还会有空余,但是不会立马发送,而是会等待缓冲区达到一个阈值时再发送,这个时候就会出现粘包现象,因为TCP在发送缓冲区会存在其他报文的数据,看着就像粘在一起一样。反过来讲,当你要发送的数据包大于这个发送缓冲区的大小时,将会留到下一次发送缓冲区填充,相当于一个报文被拆分了多次进行发送.这两种现象会导致服务端必须要等待接收到完整数据报文才可以进行处理,不然就得现将数据暂存到内存中,影响处理效率,会影响服务端整体的吞吐量,因为服务端需要维持报文的中间状态,维护报文之间的顺序关系,增加了服务端的工作量
下面我以代码的形式复现一下:
1.Client
package splicing.demo;
import constant.Constant;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class EchoCliStickyHalf {
private final int port;
private final String host;
public EchoCliStickyHalf(int port, String host) {
this.port = port;
this.host = host;
}
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
// 线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 客户端启动必备, 和服务器的不同点
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
// 指定使用NIO的通信模式
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
// 指定服务器的IP地址和端口,和服务器的不同点
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
// 和服务器的不同点
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoCliStickyHalfHandler());
}
});
// 异步连接到服务器,sync()会阻塞到完成,和服务器的不同点
ChannelFuture f = b.connect().sync();
// 阻塞当前进程,直到客户端的channel被关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new EchoCliStickyHalf(Constant.DEFAULT_PORT, Constant.DEFAULT_SERVER_IP).start();
}
}
package splicing.demo;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class EchoCliStickyHalfHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 客户端读取到网络数据后的处理
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client Accept[" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8) +
"] and the counter is :" + counter.incrementAndGet());
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
String request = "Mark,Zhuge,Fox,Zhouyu,Loulan"
+ System.getProperty("line.separator");
ByteBufAllocator alloc = ctx.alloc();
ByteBuf msg = null;
// 我们希望服务器接收到100个这样的报文
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
ByteBuf byteBuf = alloc.buffer();
msg = alloc.buffer(request.length());
msg.writeBytes(request.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
// super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
// super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
}
}
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 常量
*/
public class Constant {
public static final Integer DEFAULT_PORT = 7777;
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVER_IP= "127.0.0.1";
// 根据输入信息拼接出一个应答信息
public static String response(String msg) {
return "Hello, " + msg + ", Now is" + new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString();
}
}
2.Server
package splicing.demo;
import constant.Constant;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
public class EchoSvrStickyHalf {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EchoSvrStickyHalf.class);
private final int port;
public EchoSvrStickyHalf(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EchoSvrStickyHalf echoSvrStickyHalf =
new EchoSvrStickyHalf(Constant.DEFAULT_PORT);
LOG.info("服务器即将启动");
echoSvrStickyHalf.start();
LOG.info("服务器关闭");
}
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
// 线程组
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 服务端启动必备
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoSvrStickyHalfHandler());
}
});
// 异步绑定到服务器,sync()会阻塞到完成
ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync();
LOG.info("服务器启动完成。");
// 阻塞当前线程,直到服务器的ServerChannel被关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}
package splicing.demo;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class EchoSvrStickyHalfHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf)msg;
String request = in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Server Accept[" + request + "] and the counter is :" + counter.incrementAndGet() );
String resp = "Hello, " +request + ". Welcome to Netty World" + System.getProperty("line.separator");
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(resp.getBytes()));
// super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
/**
* 发生异常后的处理
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
3.分析
代码中明明发送了100个报文,结果服务端收到的报文个数,却是两个报文,中间的某一个报文还发生了半包,
下期我们再来讨论如何解决这种现象