非对称重加权惩罚最小二乘平滑的基线校正修订版-2
基于惩罚最小二乘法的基线校正方法已成功地应用于各种光谱分析中。该方法通过估计基线来迭代地改变权重。如果信号低于先前拟合的基线,则给予大权重。另一方面,当信号高于拟合基线时,不给出权重或给出小权重,因为它可以被假设为峰值的一部分。
然而,由于噪声分布在基线之上以及基线之下,因此希望在任一情况下给予给予相同或相似的权重。为此,文章提出了一种新的加权方案的基础上广义逻辑函数。所提出的方法迭代地估计噪声水平,并相应地调整权重。
往期内容:
CSDN
优化内存版
def baseline_als_optimized(y, lam, p, niter=10):
L = len(y)
D = sparse.diags([1,-2,1],[0,-1,-2], shape=(L,L-2))
D = lam * D.dot(D.transpose()) # Precompute this term since it does not depend on `w`
w = np.ones(L)
W = sparse.spdiags(w, 0, L, L)
for i in range(niter):
W.setdiag(w) # Do not create a new matrix, just update diagonal values
Z = W + D
z = spsolve(Z, w*y)
w = p * (y > z) + (1-p) * (y < z)
return z根据基准测试,它的速度也快了大约 1,5 倍。
%timeit -n 1000 -r 10 baseline_als(spectra_base, 10000, 0.05)
%timeit -n 1000 -r 10 baseline_als_optimized(spectra_base, 10000, 0.05)模拟光谱
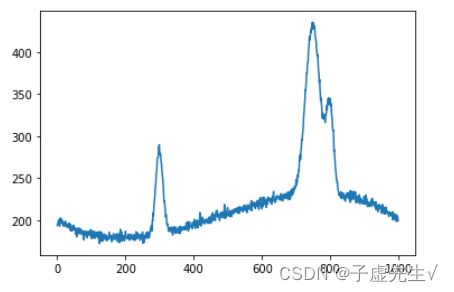
为了测试该算法,我首先生成了一个由多个高斯峰组成的模拟光谱,
从而创建了一个类似于论文图3所示的光谱:
def spectra_model(x):
coeff = np.array([100, 200, 100])
mean = np.array([300, 750, 800])
stdv = np.array([15, 30, 15])
terms = []
for ind in range(len(coeff)):
term = coeff[ind] * np.exp(-((x - mean[ind]) / stdv[ind])**2)
terms.append(term)
spectra = sum(terms)
return spectra
x_vals = np.arange(1, 1001)
spectra_sim = spectra_model(x_vals)使用直接从论文中获取的 4 个点创建了一个三阶插值多项式
from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline
x_poly = np.array([0, 250, 700, 1000])
y_poly = np.array([200, 180, 230, 200])
poly = CubicSpline(x_poly, y_poly)
baseline = poly(x_vals)
noise = np.random.randn(len(x_vals)) * 3
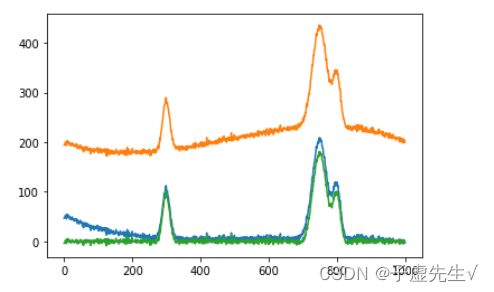
spectra_base = spectra_sim + baseline + noise惩罚加权线性平方方法的改进
from scipy import sparse
from scipy.sparse import linalg
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import norm
def baseline_arPLS(y, ratio=1e-6, lam=100, niter=10, full_output=False):
L = len(y)
diag = np.ones(L - 2)
D = sparse.spdiags([diag, -2*diag, diag], [0, -1, -2], L, L - 2)
H = lam * D.dot(D.T) # The transposes are flipped w.r.t the Algorithm on pg. 252
w = np.ones(L)
W = sparse.spdiags(w, 0, L, L)
crit = 1
count = 0
while crit > ratio:
z = linalg.spsolve(W + H, W * y)
d = y - z
dn = d[d < 0]
m = np.mean(dn)
s = np.std(dn)
w_new = 1 / (1 + np.exp(2 * (d - (2*s - m))/s))
crit = norm(w_new - w) / norm(w)
w = w_new
W.setdiag(w) # Do not create a new matrix, just update diagonal values
count += 1
if count > niter:
print('Maximum number of iterations exceeded')
break
if full_output:
info = {'num_iter': count, 'stop_criterion': crit}
return z, d, info
else:
return z