【C++入门】C++ STL中string常用函数用法总结
目录
前言
1. string使用
2. string的常见构造
3. string类对象的访问及遍历
迭代器遍历:
访问:
4. string类对象的容量操作
4.1 size和length
4.2 clear、empty和capacity
4.3 reserve和resize
reserve
resize
5. string类对象的修改操作
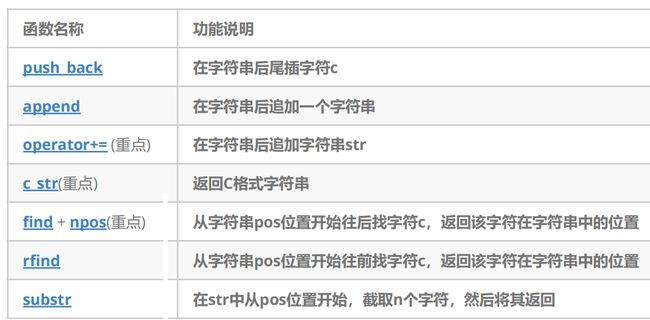
push_back
operator+=
c_str
find
substr
6. insert和erase
insert
erase
总结
前言
STL(standard template libaray-标准模板库):是C++标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复用的组件库,而且是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架,主要包含:算法、仿函数、迭代器、空间适配器、容器、适配器;六大组件,本无主要介绍的是STL容器中string常用函数的用法。
![]()
1. string使用
string是表示字符串的字符串类,它的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,并且添加了一些专门用来操作string的常用接口,在刷题时也经常使用。
使用string类时,必须包含#include
头文件以及using namespace std;
2. string的常见构造
C++的标准库版本不同,string构造方法也会有所不同
详细可查阅:https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/
无参构造:
string s1;字符构造:
//string str('x'); //这样不行
string s;
s = 'x'; // 也就是赋值运算符重载字符串常量构造:
string s2("hello world!");
string s2 = "hello world!";
拷贝构造:
string s3 = s2; // 两种方法等价
string s4(s2);指定n个相同字符进行初始化:
// 接口原型:string (size_t n, char c)
string s6(10, 'x');//10个x初始化迭代器区间构造:
string s7 = "Hello World!";
// 创建一个迭代器区间,从第2个字符开始,到第11个字符结束
string s8(s7.begin() + 1, s7.begin() + 11); // ello World3. string类对象的访问及遍历
迭代器遍历:
begin和end:
- begin返回指向字符串的第一个字符的迭代器
- end返回指向字符串末尾的迭代器
string s1 = "Hello world!";
//迭代器
// iterator用法像指针
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}反向遍历rbegin和rend:
- rbegin返回指向字符串最后一个字符(即其反向开头)的反向迭代器
- rend 返回一个反向迭代器,该迭代器指向字符串第一个字符(被视为其反向末尾)
auto it1 = str.rbegin();
while (it1 != str.rend())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
++it1;
}范围for遍历:
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e;
}访问:
[ ]下标访问:
s1[1] = 'x';
cout << s1[1];4. string类对象的容量操作
string类对象支持直接获取字符串长度,length和size都可以返回有效字符长度,size更通用;
4.1 size和length
string s = "Hello world!";// 12个字符
cout << s.size() << endl; // 12
cout << s.length() << endl;// 124.2 clear、empty和capacity
注意:
- clear后,使用empty会返回true
- clear函数只将size清零
- clear函数不会改变capacity
使用非常简单便捷:
string s = "Hello world!";
//VS环境下,扩容为1.5倍扩容,环境不同capacity结果可能不同
cout << s.capacity() << endl; // 15
cout << s.empty() << endl; // 0 ->false
s.clear();
cout << s.empty() << endl; // 1 ->true
cout << s.capacity() << endl; // 154.3 reserve和resize
reserve和resize有些相似都具有扩容的功能。
reserve
reserve的主要功能就是开空间,为string对象预留空间,提前开好空间,减少扩容,提高效率
环境不同开空间规则也不同
- 在VS环境下为1.5倍扩容,初始容量是15
- g++环境下,从0开始二倍扩容
string s1 ;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 15
s1.reserve(30);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; // 31reserve在一般的编译器中不具备缩容的功能(C++没有严格的去规定)
resize
resize功能是改变字符串的size
string s = "Hello world!";
cout << s << endl; // 输出:Hello world!
cout << s.size() << endl; // 12
cout << s.capacity() << endl; // 15
s.resize(40);
cout << s << endl; // 输出:Hello world!
cout << s.size() << endl; // 40
cout << s.capacity() << endl; // 47在没有给字符时,resize默认补的是\0.
string s = "Hello world!";
s.resize(15,'x'); // 输出:Hello world!xxx这个功能也可以让它用来初始化string对象。
resize值小于字符串的size会删除字符串中的有效字符:
string s = "Hello world!";
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl; // 12
cout << s.capacity() << endl; // 15
s.resize(5);
cout << s << endl; //输出:Hello
cout << s.size() << endl; // 5
cout << s.capacity() << endl; // 155. string类对象的修改操作
push_back
string s("abcde");
s.push_back('f');
s.push_back('g');operator+=
append使用的频率不高,主要使用+=;
string str1 = "Hello";
string str2 = "World";
str1 += str2; // 现在 str1 的值为 "HelloWorld"
c_str
string str = "Hello";
const char* cstr = str.c_str(); // cstr 指向包含 "Hello" 的C风格字符串c_str() 是C++中string 类的成员函数,它返回一个指向以空字符结尾的C风格字符串的指针,以便与需要C风格字符串作为参数的函数进行交互。
注意:
返回的指针指向的字符串是只读的,不能用于修改
find
find用于在字符串中查找子字符串的位置,如果找不到则返回 string::npos
string str = "Hello, World!";
size_t pos = str.find("World"); // pos 的值为 7
substr
substr用于从字符串中提取子字符串
//函数原型
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
pos 是要提取的子字符串的起始位置,len 是要提取的子字符串的长度,默认值为 npos,表示提取从起始位置到字符串末尾的所有字符
string str = "Hello, World!";
string sub = str.substr(7, 5); // sub 的值为 "World"
6. insert和erase
insert
insert的函数原型种类很多,但最长用的也就是在指定位置插入单个字符、字符串、 一个string类对象等感兴趣可以去了解一下;
string str = "Hello!";
str.insert(5, " World"); // 现在 str 的值为 "Hello World!"
当然它也支持使用迭代器插入数据
erase
erase 函数用于从指定位置开始删除指定长度的字符函数原型:
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
它也支持使用迭代器区间删除数据
示例:
string str = "Hello, World!";
str.erase(7, 7); // 现在 str 的值为 "Hello, "
总结
本文主要是string类常用接口的总结,string发布时间早于STL,在最初设计时实现的功能丰富,接口繁多也较为复杂,STL库函数中很多接口都十分相似,学习了string后会对vector和list等等容器的学习有帮助,以上便是本文全部内容,希望对你有所帮助,感谢阅读!