线程池核心之ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
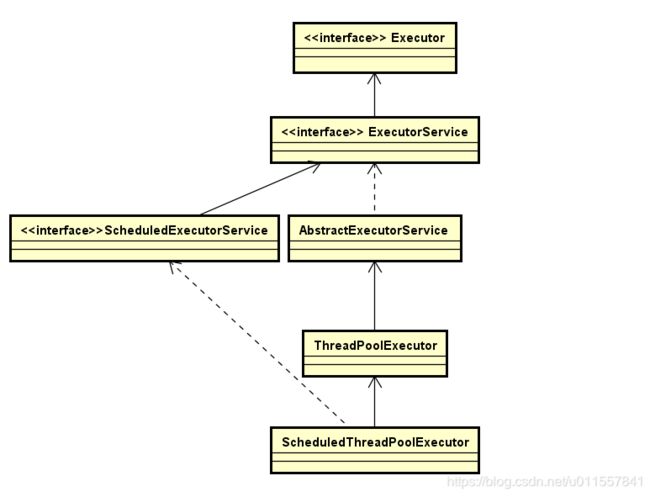
从线程池的UML类图可以看到,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是ThreadPoolExecutor的子类,所以它拥有ThreadPoolExecutor的所有功能,同时它又实现了ScheduledExecutorService接口,所以,这个接口的实现又赋予它新的功能,那就是定时任务的功能。
ScheduledExecutorService
/**
* Creates and executes a one-shot action that becomes enabled
* after the given delay.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @param delay the time from now to delay execution
* @param unit the time unit of the delay parameter
* @return a ScheduledFuture representing pending completion of
* the task and whose {@code get()} method will return
* {@code null} upon completion
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Creates and executes a ScheduledFuture that becomes enabled after the
* given delay.
*
* @param callable the function to execute
* @param delay the time from now to delay execution
* @param unit the time unit of the delay parameter
* @param the type of the callable's result
* @return a ScheduledFuture that can be used to extract result or cancel
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if callable is null
*/
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Creates and executes a periodic action that becomes enabled first
* after the given initial delay, and subsequently with the given
* period; that is executions will commence after
* {@code initialDelay} then {@code initialDelay+period}, then
* {@code initialDelay + 2 * period}, and so on.
* If any execution of the task
* encounters an exception, subsequent executions are suppressed.
* Otherwise, the task will only terminate via cancellation or
* termination of the executor. If any execution of this task
* takes longer than its period, then subsequent executions
* may start late, but will not concurrently execute.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @param initialDelay the time to delay first execution
* @param period the period between successive executions
* @param unit the time unit of the initialDelay and period parameters
* @return a ScheduledFuture representing pending completion of
* the task, and whose {@code get()} method will throw an
* exception upon cancellation
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if period less than or equal to zero
*/
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Creates and executes a periodic action that becomes enabled first
* after the given initial delay, and subsequently with the
* given delay between the termination of one execution and the
* commencement of the next. If any execution of the task
* encounters an exception, subsequent executions are suppressed.
* Otherwise, the task will only terminate via cancellation or
* termination of the executor.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @param initialDelay the time to delay first execution
* @param delay the delay between the termination of one
* execution and the commencement of the next
* @param unit the time unit of the initialDelay and delay parameters
* @return a ScheduledFuture representing pending completion of
* the task, and whose {@code get()} method will throw an
* exception upon cancellation
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if delay less than or equal to zero
*/
public ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
接口ScheduledExecutorService有四个方法:
1、ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit),延迟执行一个线程
2、ScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit),延迟执行一个有结果回调的线程
3、ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay,long period,TimeUnit unit),定时执行一个线程,下一次开始的时间是从上一个任务开始时间算起+period
4、ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long delay,TimeUnit unit),定时执行一个任务,下一次开始的时间从上一个任务执行结束的时间+delay的时间算起
scheduleAtFixedRate
public class MyThreadPool {
static ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("StartTime" + (formatDate(System.currentTimeMillis())));
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Thread(new MyThread()), 0, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private static class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run:" + (formatDate(System.currentTimeMillis())));
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("sleep:" + (formatDate(System.currentTimeMillis())));
}
}
public static String formatDate(long timeLong) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("mm-ss");
return sdf.format(timeLong);
}
}
运行结果
1、任务执行完成延迟2秒

2、任务执行完成延迟11秒,大于period时间

run是任务开始执行的时间,sleep是为了演示耗时的任务操作,由结果可以得出一个结论:scheduleAtFixedRate下次开始的时间是以上个任务开始时间算起的,并且要等到上个任务执行结束,下个任务才开始执行。
scheduleWithFixedDelay
public class MyThreadPool {
static ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("StartTime" + (formatDate(System.currentTimeMillis())));
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Thread(new MyThread()), 0, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private static class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run:" + (formatDate(System.currentTimeMillis())));
try {
Thread.sleep(11000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("sleep:" + (formatDate(System.currentTimeMillis())));
}
}
public static String formatDate(long timeLong) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("mm-ss");
return sdf.format(timeLong);
}
}
任务延迟2秒:

任务延迟11秒:

run是任务开始执行的时间,sleep是为了演示耗时的任务操作,由结果可以得出一个结论:scheduleWithFixedDelay下次开始的时间是以上个任务完成时间算起的。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的运行机制

ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的执行示意图(本文基于JDK8)如上图。
DelayedWorkQueue是一个无界队列,所以ThreadPoolExecutor的maximumPoolSize在ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor中是没有任何意义的(设置maximumPoolSize的大小是没有任何效果的)
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的执行主要包含两部分:
1)当调用ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的scheduledAtFixedRate()或者scheduledWithFixedDelay()方法时,会向ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的DelayWorkQueue中的数组中添加一个RunnableScheduledFuture。
2)线程池中的线程从数组中获取一个RunnableScheduledFuture,然后执行任务。
源码求证
scheduleAtFixedRate
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t); @1
return t;
}
@1 延迟执行
delayedExecute(t)
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture task) {
if (isShutdown())
reject(task);
else {
super.getQueue().add(task); @2
if (isShutdown() &&
!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&
remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
ensurePrestart();
}
}
@2 在队列中加入该任务,而该队列就是DelayedWorkQueue,所以,进入DelayedWorkQueue的add() 方法
public boolean add(Runnable e) {
return offer(e); @3
}
@3 最终调用的是队列的offer() 方法
offer(Runnable x)
public boolean offer(Runnable x) {
if (x == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture e = (RunnableScheduledFuture)x;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(); @4
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0) { @5
queue[0] = e;
setIndex(e, 0);
} else {
siftUp(i, e); @6
}
if (queue[0] == e) {
leader = null;
available.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
@4 如果此时的数据大小大于或等于当前队列的大小,则进行扩容操作
@5 如果此时的数据大小为0,则直接放在队首
@6 如果此时数据大小不为0,则进行小顶堆调整
siftUp(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture key)
private void siftUp(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture key) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; @7
RunnableScheduledFuture e = queue[parent]; @8
if (key.compareTo(e) >= 0) @9
break;
queue[k] = e;
setIndex(e, k);
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
setIndex(key, k);
}
@7 获取父类的下标(在二叉树表示数组的时候,父子节点的下标关系如下:parentNo=(childNo-1)/2)
@8 获取到父类节点
@9 进行子节点和父节点的大小比较
compareTo(Delayed other)
public int compareTo(Delayed other) {
if (other == this) // compare zero if same object
return 0;
if (other instanceof ScheduledFutureTask) {
ScheduledFutureTask x = (ScheduledFutureTask)other;
long diff = time - x.time; @10
if (diff < 0)
return -1;
else if (diff > 0)
return 1;
else if (sequenceNumber < x.sequenceNumber) @11
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
long diff = getDelay(NANOSECONDS) - other.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
return (diff < 0) ? -1 : (diff > 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
@10@11 先比较时间,时间小的排在前面(时间早的任务将先被执行)。如果两个ScheduledFutureTask的time相同,就比较sequenceNumber,sequenceNumber小的排在前面。
以上内容从源码了解了在任务队列中添加一个任务,接下来将从源码了解线程池从任务队列中获取一个任务并执行任务的流程
take()
public RunnableScheduledFuture take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (;;) {
RunnableScheduledFuture first = queue[0];
if (first == null)
available.await();
else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
return finishPoll(first); @1
first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting
if (leader != null)
available.await();
else {
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;
try {
available.awaitNanos(delay);
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && queue[0] != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
@1 忽略其它,直接进入核心代码,当延迟时间小于会等于0的时候,从任务队列的队首取出一个任务
finishPoll(first)
private RunnableScheduledFuture finishPoll(RunnableScheduledFuture f) {
int s = --size;
RunnableScheduledFuture x = queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
setIndex(f, -1);
return f;
}
到此,就分析完了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。