QT+VS实现Kmeans聚类算法
1、Kmeans的定义
聚类是一个将数据集中在某些方面相似的数据成员进行分类组织的过程,聚类就是一种发现这种内在结构的技术,聚类技术经常被称为无监督学习。k均值聚类是最著名的划分聚类算法,由于简洁和效率使得他成为所有聚类算法中最广泛使用的。
无监督学习通常用于聚类,通过样本件的相似性对数据集进行聚类,使类内差距最小化,类间差距最大化。
2、原理
首先需要弄清楚两个概念:簇和质心
簇: 直观上来看,簇是一组聚在一起的数据,在一个簇中的数据就认为是同一类。
质心: 簇中所有数据的均值通常被称为这个簇的质心。
如何求取质心:
在一个二维平面中,一簇数据点的质心的横坐标就是这一簇数据点的横坐标的均值,质心的纵坐标就是这一簇数据点的纵坐标的均值。同理可推广至高维空间。
欧式距离计算公式:
二维平面上的欧式距离:
假设待求两点的二维平面坐标为a![]() (
(![]() ,
,![]() )和b
)和b![]() (
(![]() ,
,![]() ),则其距离公式为:
),则其距离公式为:
![]() =
=![]() =
=![]()
3、实现的流程步骤
- 首先随机选取样本中的K个点作为初始聚类中心(质心);
- 分别算出样本中其他数据点距离这K个聚类中心的距离,以最近距离的质心缩在的簇作为该数据点分类后的簇;
- 对上述分类完的样本再进行每个簇求平均值,求解出新的聚类质心;
- 与前一次计算得到的K个聚类质心比较,如果聚类质心发生变化,转过程b,否则转过程e;
- 当质心不再发生变化时,停止并输出聚类结果。
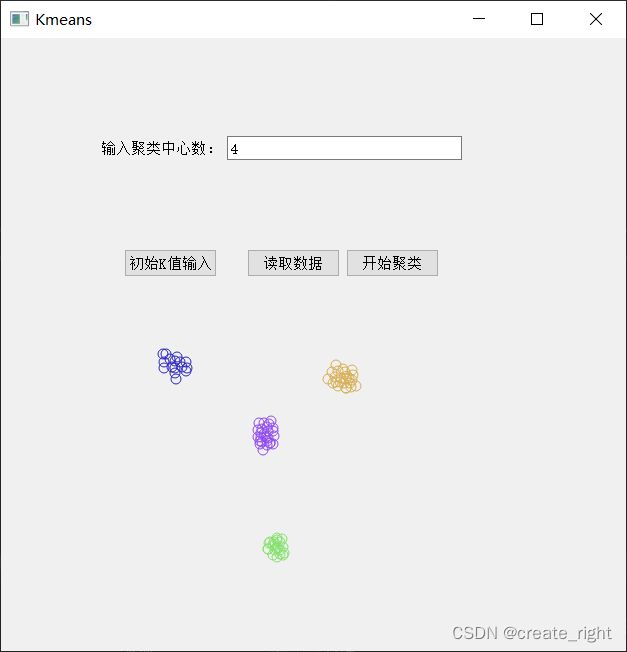
4、实现结果
5、部分代码解析
(1)首先,为了提高分类精度,K个质心初始值的选取,采用人工确定的方法。先人为的选取K个初值,并写成txt格式,如下:
格式:点号-X坐标-Y坐标
读取K值数据的函数如下:
void Kmeans::onBtReadK()
{
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("打开"));
QFile file(fileName);
bool isOpen = 1;
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text))
{
isOpen = 0;
QMessageBox::StandardButton btnValue = QMessageBox::information(this, tr("提示"), tr("打开失败!"));
}
QTextStream stream(&file);
while (!stream.atEnd())
{
QString str = stream.readLine();
QStringList list = str.split(",");
Pointp k1;
k1.no = list.at(0);
k1.x = list.at(1).toDouble();
k1.y = list.at(2).toDouble();
k.push_back(k1);
}
//判断是否读取完毕
if (stream.atEnd() && isOpen)
{
QMessageBox box;
box.setText("数据读取完毕");
box.exec();
}
dd = readK;
}(2)读取K个初始值之后,需要读取整个样本的数据(样本数据格式同K值格式一致),读取函数如下:
void Kmeans::onBtReadData()
{
K = ui.lineEdit->text().toInt();
p.clear();
//打开文件对话框
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("打开"));
QFile file(fileName);
bool isOpen = 1;
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text))
{
isOpen = 0;
QMessageBox::StandardButton btnValue = QMessageBox::information(this, tr("提示"), tr("打开失败!"));
}
//逐行读取文本文件
QTextStream stream(&file);
while (!stream.atEnd())
{
Pointp pt;
QString str = stream.readLine();
QStringList list = str.split(",");
pt.no = list.at(0);
pt.x = list.at(1).toDouble();
pt.y = list.at(2).toDouble();
p.push_back(pt);
}
file.close();
//判断是否读取完毕
if (stream.atEnd()&&isOpen)
{
QMessageBox box;
box.setText("数据读取完毕");
box.exec();
}
}(3)在对话框中输入簇个数,然后点击“开始聚类”按钮,开始进行聚类。首先是计算每个样本到K个聚类中心的距离,并找出最小值,作为该样本点的聚类结果。代码如下:
//计算每个对象至聚类中心的距离
void Kmeans::CalDis()
{
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++)
{
double s0 = 0; QString no; Dis ss; int t = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
double x1 = p.at(i).x;
double y1 = p.at(i).y;
double x2 = k.at(j).x;
double y2 = k.at(j).y;
double s1 = sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
t++;
if (t == 1)
{
s0 = s1;
no = k.at(j).no;
}
if (s1 < s0)
{
s0 = s1;
no = k.at(j).no;
}
}
ss.s = s0;
ss.no = p.at(i).no;
ss.x = p.at(i).x;
ss.y = p.at(i).y;
ss.noK = no;
S.push_back(ss);
}
}(4)根据分类后的样本计算新的质心,如下:
//计算质心
void Kmeans::Calcentroid()
{
centroid s;
for (int i = 0; i < k.size(); i++)
{
s.sx = 0; s.sy = 0; int iCt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < S.size(); j++)
{
if (k.at(i).no == S.at(j).noK)
{
s.sx = s.sx + S.at(j).x;
s.sy = s.sy + S.at(j).y;
iCt++;
}
}
s.noK = k.at(i).no;
s.sx = s.sx / iCt;
s.sy = s.sy / iCt;
dis.push_back(s);
}
}(5)然后判断新质心与旧质心之间的距离,若为0,则停止重新计算。
6、整体代码如下(输入的数据中不能包含负数,因为控件范围是从0开始的)
//Kmeans.cpp文件
#include "Kmeans.h"
Kmeans::Kmeans(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
start = false;
dd = to2K;
ui.setupUi(this);
connect(ui.pushButton, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(onBtReadData()));
connect(ui.pushButton_2, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(onBtCalKmeans()));
connect(ui.pushButton_3, SIGNAL(clicked()), this, SLOT(onBtReadK()));
}
void Kmeans::onBtReadData()
{
K = ui.lineEdit->text().toInt();
p.clear();
//打开文件对话框
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("打开"));
QFile file(fileName);
bool isOpen = 1;
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text))
{
isOpen = 0;
QMessageBox::StandardButton btnValue = QMessageBox::information(this, tr("提示"), tr("打开失败!"));
}
//逐行读取文本文件
QTextStream stream(&file);
while (!stream.atEnd())
{
Pointp pt;
QString str = stream.readLine();
QStringList list = str.split(",");
pt.no = list.at(0);
pt.x = list.at(1).toDouble();
pt.y = list.at(2).toDouble();
p.push_back(pt);
}
file.close();
//判断是否读取完毕
if (stream.atEnd()&&isOpen)
{
QMessageBox box;
box.setText("数据读取完毕");
box.exec();
}
}
void Kmeans::onBtReadK()
{
QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("打开"));
QFile file(fileName);
bool isOpen = 1;
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text))
{
isOpen = 0;
QMessageBox::StandardButton btnValue = QMessageBox::information(this, tr("提示"), tr("打开失败!"));
}
QTextStream stream(&file);
while (!stream.atEnd())
{
QString str = stream.readLine();
QStringList list = str.split(",");
Pointp k1;
k1.no = list.at(0);
k1.x = list.at(1).toDouble();
k1.y = list.at(2).toDouble();
k.push_back(k1);
}
//判断是否读取完毕
if (stream.atEnd() && isOpen)
{
QMessageBox box;
box.setText("数据读取完毕");
box.exec();
}
dd = readK;
}
void Kmeans::toK()
{
//随机选取k个初始聚类中心
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
Pointp k1;
k1.no = i + 1;
k1.x = p.at(i).x;
k1.y = p.at(i).y;
k.push_back(k1);
}
}
int Kmeans::onBtCalKmeans()
{
K = ui.lineEdit->text().toInt();
if (S.size()&&p.size()==S.size())
{
QMessageBox box;
box.setText("已经计算完成");
box.exec();
return 0;
}
if (dd == to2K)
{
toK();
}
CalDis();//S
Calcentroid();//用到S,得dis
//CKmeans();//用到dis,得new k.
int iCount = 0;
while (iCount < K)
{
if (dis.size())
{
for (int i = 0; i < k.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dis.size(); j++)
{
if (k.at(i).no == dis.at(j).noK)
{
//qDebug() <<"k:" <rect());
QPainter painterP(&pp);
QPen pen;
painterP.setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing, true);
Pointp p1;
p1.no = p.at(0).no;
p1.x = p.at(0).x;
p1.y = p.at(0).y;
for (int i = 1; i < p.size(); i++)
{
if (p1.x > p.at(i).x)
{
p1.x = p.at(i).x;
}
if (p1.y > p.at(i).y)
{
p1.y = p.at(i).y;
}
}
double xmin = p1.x;
double ymin = p1.y;
for (int i = 1; i < p.size(); i++)
{
if (p1.x < p.at(i).x)
{
p1.x = p.at(i).x;
}
if (p1.y < p.at(i).y)
{
p1.y = p.at(i).y;
}
}
double xmax = p1.x;
double ymax = p1.y;
int w=ui.label_2->width();
int h=ui.label_2->height();
double a = w/(xmax -xmin);
double b1 = h/(ymax -ymin);
for (int i = 0; i < k.size(); i++)
{
int r = qrand() % 256;
int g = qrand() % 256;
int b = qrand() % 256;
QColor color = QColor(r, g, b);
for (int j = 0; j < S.size(); j++)
{
if (k.at(i).no == S.at(j).noK)
{
pen.setColor(color);
painterP.setPen(pen);
int radius = 5;
double x = S.at(j).x;
double y = S.at(j).y;
x = (x - xmin)*a;
y = (y - ymin)*b1;
painterP.drawEllipse(x - radius, y - radius, radius * 2, radius * 2);
}
}
}
ui.label_2->setPicture(pp);
} //Kmeans.h文件
#pragma once
#include
#include "ui_Kmeans.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#pragma execution_character_set("UTF-8")
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
struct Pointp
{
double x;
double y;
QString no;
};
struct Dis
{
double x;
double y;
QString no;
QString noK;
double s;
};
struct centroid
{
QString noK;
double sx;
double sy;
};
enum Pd
{
readK,
to2K,
blank
};
class Kmeans : public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Kmeans(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~Kmeans();
public slots:
void onBtReadData();
int onBtCalKmeans();
void onBtReadK();
void toK();
public:
std::vector p;//原始数据点
std::vector k;//各簇质心坐标
int K;
std::vector S;
std::vector dis;
bool start;
Pd dd;
public:
void Calcentroid();
void CKmeans();
void CalDis();
void drawPoint();
private:
Ui::KmeansClass ui;
};