Elasticsearch:构建自定义分析器指南
在本博客中,我们将介绍不同的内置字符过滤器、分词器和分词过滤器,以及如何创建适合我们需求的自定义分析器。更多关于分析器的知识,请详细阅读文章:
-
开始使用 Elasticsearch (3)
-
Elasticsearch: analyzer
为什么我们需要定制分析器?
你可以通过以所需的方式组合字符过滤器、分词器和分词过滤器来创建自定义分析器来满足您的特定需求。 这使得文本处理具有高度的灵活性和定制性。
正如我们所见,Elasticsearch 中的分析器由三部分组成,我们将看到不同的内置组件:
安装
为了方便今天的测试,我们将安装无安全配置的 Elasticsearch 及 Kibana。我们可以参考文章 “Elasticsearch:如何在 Docker 上运行 Elasticsearch 8.x 进行本地开发”。
我们还需要安装 Python 所需要的包:
pip3 install elasticsearch$ pip3 list | grep elasticsearch
elasticsearch 8.12.0
rag-elasticsearch 0.0.1 /Users/liuxg/python/rag-elasticsearch/my-app/packages/rag-elasticsearch测试
我们创建一个连接到 Elasticsearch 的客户端:
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
es = Elasticsearch("http://localhost:9200")
print(es.info())更多关于如何连接到 Elasticsearch 的代码,请参考 “Elasticsearch:关于在 Python 中使用 Elasticsearch 你需要知道的一切 - 8.x”。
Char map filters
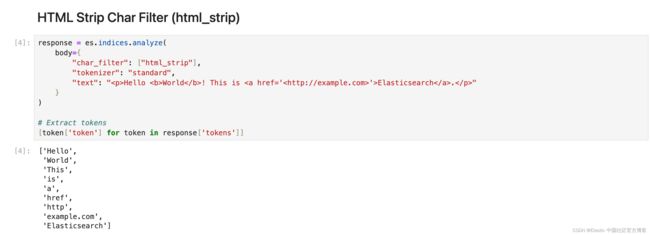
HTML Strip Char Filter (html_strip)
从文本中删除 HTML 元素并解码 HTML 实体。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"char_filter": ["html_strip"],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text": "Hello World! This is Elasticsearch.
"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Pattern Replace Char Filter (pattern_replace)
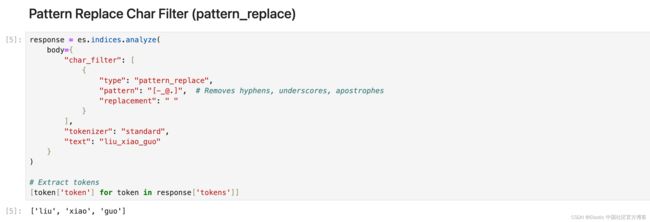
使用正则表达式来匹配字符或字符序列并替换它们。 在下面的示例中,我们从用户名中提取名称:
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"char_filter": [
{
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "[-_@.]", # Removes hyphens, underscores, apostrophes
"replacement": " "
}
],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text": "liu_xiao_guo"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Mapping Char Filter (mapping)
允许自定义定义的字符或字符序列映射。 示例:你可以定义一个映射,将 “&” 替换为 “and”,或将 “€” 替换为 “euro”。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
{
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": [
"@gmail.com=>", # Replace @gmail.com with nothing
"$=>dollar", # Replace $ with dollar
]
}
],
"text": "xiaoguo.liu@gmail.com gives me $"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Tokenizers
Standard Tokenizer (standard)
Standard 分词器将文本按照单词边界划分为术语,如 Unicode 文本分段算法所定义。 它删除了大多数标点符号。 它是大多数语言的最佳选择。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Letter Tokenizer (letter)
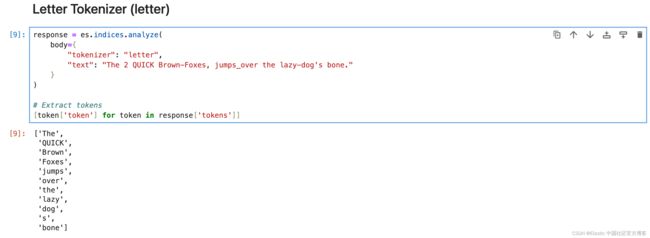
每当遇到非字母的字符时,letter 分词器就会将文本分成术语。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "letter",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Lowercase Tokenizer (lowercase)
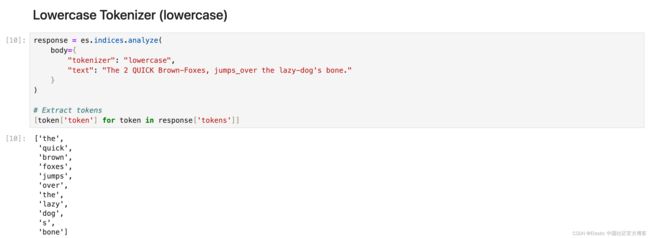
小写分词器类似于字母分词器,但它也将所有术语小写。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "lowercase",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Whitespace Tokenizer (whitespace)
每当遇到任何空白字符时,whitespace 分词器都会将文本划分为术语。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
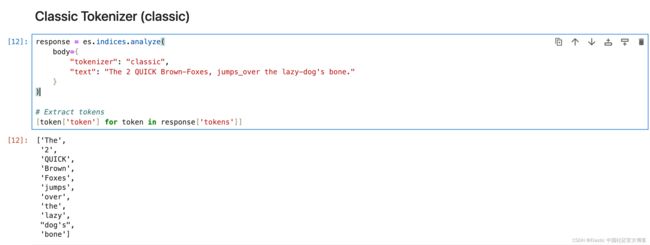
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Classic Tokenizer (classic)
classic 分词器是一种基于语法的英语分词器。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "classic",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]UAX URL Email Tokenizer (uax_url_email)
uax_url_email 标记生成器类似于标准标记生成器,只不过它将 URL 和电子邮件地址识别为单个标记。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "classic",
"text": "visit https://elasticstack.blog.csdn.net to get the best materials to learn Elastic Stack"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]N-Gram Tokenizer (ngram)
当 ngram 分词器遇到任何指定字符(例如空格或标点符号)列表时,它可以将文本分解为单词,然后返回每个单词的 n-grams:连续字母的滑动窗口,例如 Quick → [qu, ui, ic, ck]。Elasticsearch 中的 N-Gram 分词器在术语部分匹配很重要的场景中特别有用。 最适合自动完成和键入时搜索功能以及处理拼写错误或匹配单词中的子字符串。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": {
"type": "ngram",
"min_gram": 3,
"max_gram": 4
},
"text": "Hello Xiaoguo"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Edge N-Gram Tokenizer (edge_ngram)
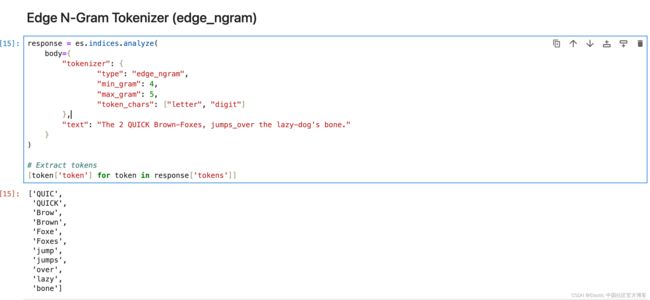
Elasticsearch 中的 edge_ngram 分词器用于从单词的开头或 “边缘” 开始将单词分解为更小的块或 “n-gram”。 它生成指定长度范围的标记,提供单词从开头到给定大小的一部分。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": {
"type": "edge_ngram",
"min_gram": 4,
"max_gram": 5,
"token_chars": ["letter", "digit"]
},
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Keyword Tokenizer (keyword)
关键字分词器接受给定的任何文本,并将完全相同的文本输出为单个术语。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Pattern Tokenizer (pattern)
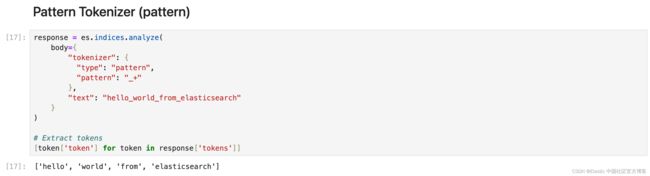
Pattern 分词器使用正则表达式,在文本与单词分隔符匹配时将其拆分为术语,或者将匹配的文本捕获为术语。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": {
"type": "pattern",
"pattern": "_+"
},
"text": "hello_world_from_elasticsearch"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Path Tokenizer (path_hierarchy)
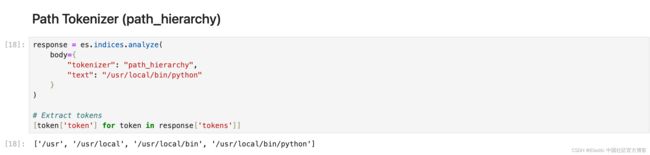
它将路径在每个路径分隔符处分解为分词。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "path_hierarchy",
"text": "/usr/local/bin/python"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Token filters
确保你始终传递列表中的过滤器,即使它只有一个,并且你应用的过滤器的顺序非常重要。
Apostrophe
删除撇号后面的所有字符,包括撇号本身。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"filter": ["apostrophe"],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
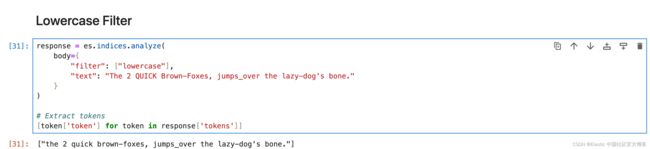
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Lowercase Filter
将所有分词转换为小写。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"filter": ["lowercase"],
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Uppercase Filter
将所有分词转换为大写。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"filter": ["uppercase"],
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
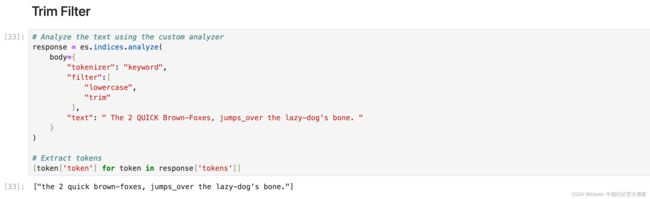
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Trim Filter
删除流中每个分词的前导和尾随空格。
# Analyze the text using the custom analyzer
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"filter":[
"lowercase",
"trim"
],
"text": " The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone. "
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]ASCII Folding Filter (asciifolding)
asciifolding 过滤器会删除标记中的变音标记。比如,Türkiye 将成为 Turkiye。
# Analyze the text using the custom analyzer
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"filter": ["asciifolding"],
"text": "Türkiye"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Synonym Filter
synonym 分词过滤器允许在分析过程中轻松处理同义词。
# Analyze the text using the custom analyzer
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter":[
"lowercase",
{
"type": "synonym",
"synonyms": ["jumps_over => leap"]
}
],
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
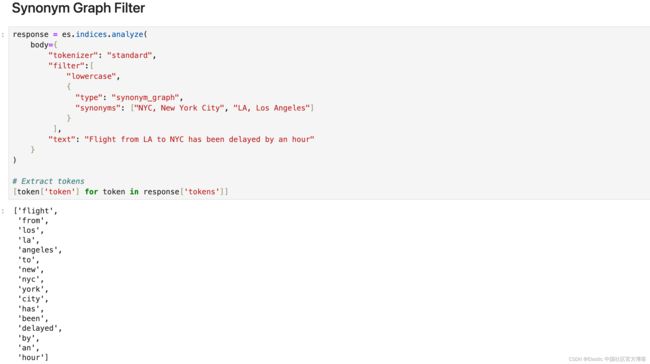
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Synonym Graph Filter
最适合多词同义词。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter":[
"lowercase",
{
"type": "synonym_graph",
"synonyms": ["NYC, New York City", "LA, Los Angeles"]
}
],
"text": "Flight from LA to NYC has been delayed by an hour"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]请记住,输出并不直观地表示内部图形结构,但 Elasticsearch 在搜索查询期间使用此结构。
与通常同义词不匹配的匹配短语查询将与同义词图完美配合。
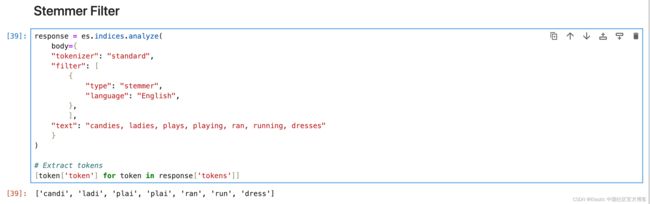
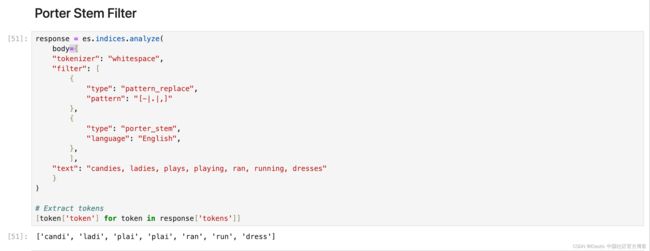
Stemmer Filter
词干过滤器,支持多种语言的词干提取。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
{
"type": "stemmer",
"language": "English",
},
],
"text": "candies, ladies, plays, playing, ran, running, dresses"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]KStem Filter
kstem 过滤器将算法词干提取与内置字典相结合。 与其他英语词干分析器(例如 porter_stem 过滤器)相比,kstem 过滤器的词干提取力度较小。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
'kstem',
],
"text": "candies, ladies, plays, playing, ran, running"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Porter Stem Filter
与其他英语词干过滤器(例如 kstem 过滤器)相比,倾向于更积极地进行词干提取。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": [
{
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "[-|.|,]"
},
{
"type": "porter_stem",
"language": "English",
},
],
"text": "candies, ladies, plays, playing, ran, running, dresses"
}
)
# Extract tokens
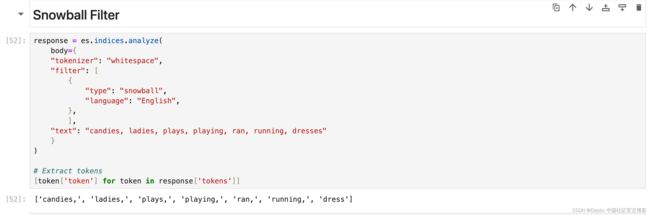
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Snowball Filter
使用 Snowball 生成的词干分析器对单词进行词干分析的过滤器。 适用于法语、德语、俄语、西班牙语等不同语言。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": [
{
"type": "snowball",
"language": "English",
},
],
"text": "candies, ladies, plays, playing, ran, running, dresses"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Stemmer Override
通过应用自定义映射来覆盖词干算法,然后保护这些术语不被词干分析器修改。 必须放置在任何阻塞过滤器之前。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": [
{
"type": "stemmer_override",
"language": "English",
"rules": [
"running, runs => run",
"stemmer => stemmer"
]
},
],
"text": "candies, ladies, plays, playing, ran, running, dresses"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]更多使用方法,请参考 Stemmer override token filter | Elasticsearch Guide [8.12] | Elastic
Keyword Marker Filter
将某些术语标记为关键字,防止它们被其他过滤器(如词干分析器)修改。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": [
{
"type": "keyword_marker",
"keywords": ["running"] # Mark 'running' as a keyword
},
{
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "[-|.|,]"
},
{
"type": "porter_stem",
"language": "English",
},
],
"text": "candies, ladies, plays, playing, runs, running"
}
)
# Extract tokens
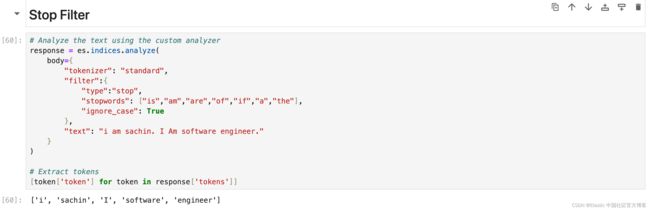
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Stop Filter
从分词流中删除停用词(经常被忽略的常用词)。 示例 — if、of、is、am、are、the。可以使用默认或自定义的停用词列表。
# Analyze the text using the custom analyzer
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter":{
"type":"stop",
"stopwords": ["is","am","are","of","if","a","the"],
"ignore_case": True
},
"text": "i am sachin. I Am software engineer."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Unique Filter
从流中删除重复的分词。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter":[
"lowercase", "unique",
],
"text": "Happy happy joy joy"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Length Filter
删除比指定字符长度更短或更长的分词。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter":[
"lowercase",
{
"type": "length",
"min": 1,
"max": 4
}
],
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]NGram Token Filter
从分词形成指定长度的 ngram。 最适合在键入时自动完成或搜索。 或者用于用户可能会犯错或拼写错误的搜索。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter":[
{
"type": "ngram",
"min_gram": 3,
"max_gram": 4
}
],
"text": "Skinny blue jeans by levis"
}
)
# Extract tokens
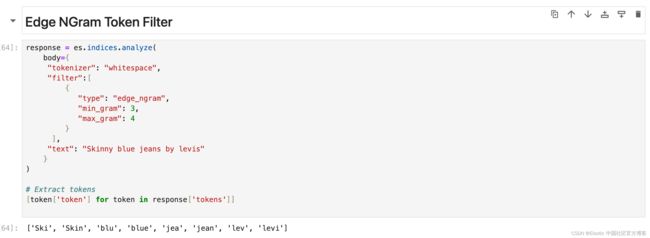
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Edge NGram Token Filter
从分词的开头形成指定长度的 ngram。 最适合在键入时自动完成或搜索。 它对于搜索建议中常见的部分单词匹配非常有效。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter":[
{
"type": "edge_ngram",
"min_gram": 3,
"max_gram": 4
}
],
"text": "Skinny blue jeans by levis"
}
)
# Extract tokens
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]
Shingle Filter
通过连接相邻的标记,将 shingles 或单词 ngram 添加到分词流中。 默认情况下,shingle 分词过滤器输出两个字的 shingles。 最适用于提高搜索短语查询性能。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter":[
{
"type": "shingle",
"min_shingle_size": 2,
"max_shingle_size": 3
}
],
"text": "Welcome to use Elastic Stack"
}
)
[token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]Creating a custom analyzer
以下是文本,下面是所需的输出:
text = "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
# Desired output
['2', 'quick', 'brown', 'fox', 'jump', 'over', 'lazy', 'dog', 'bone']分析器应完成的事情列表:
- 删除所有符号 - 连字符和下划线。
- 删除停用词。
- 将所有文本小写。
- 删除撇号。
- 词干。
response = es.indices.analyze(
body={
"char_filter": [
{
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": [
"- => ' '", # replacing hyphens with blank space
"_ => ' '", # replacing underscore with blank space
]
}
],
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["apostrophe", "lowercase", "stop", "porter_stem"],
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes, jumps_over the lazy-dog's bone."
}
)
# Extract and print tokens
tokens = [token['token'] for token in response['tokens']]
tokens现在需要注意的一件事是顺序,无论你在内部处理时给 Elasticsearch 什么顺序,总是使用相同的顺序 char_filter > tokenizer > token_filter 但 char_filter 或 token filter 块内的顺序会有所不同。
将自定义分析器添加到索引
为了避免复杂化,最好创建一个新的索引并根据你的要求设置分析器。 以下是设置分析器的方法。
settings = {
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_custom_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": {
"type": "mapping",
"mappings": [
"- => ' '",
"_ => ' '",
]
},
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase", "apostrophe", "stop", "porter_stem"],
}
}
},
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 0,
"routing.allocation.include._tier_preference": "data_hot"
},
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {"type":"text", "analyzer":"my_custom_analyzer"},
"brand": {"type": "text", "analyzer":"my_custom_analyzer", "fields": {"raw": {"type": "keyword"}}},
"updated_time": {"type": "date"}
}`
}
}
response = es.indices.create(index="trial_index", body=index_settings)你可以在地址找到所有的代码:https://github.com/liu-xiao-guo/analyzers-python