Issues Uploading Large Files To SharePoint
To begin with, the Support for Large Files was one of the enhancements made in Windows SharePoint Services SP 1. By default, the maximum size for uploading files is set to 50 MB. The maximum file size that it can go up to is 2,047 megabytes.
Now it is obvious that any cap on the maximum file size will stop the users from trying to upload larger files (including me!). Though SharePoint is meant to handle files that are up to 2 gigs in size, it is not practically feasible and not recommended as well.
However, there are circumstances where files of much smaller size fail to upload which makes one wonder as to what could be the reason. Hence I decided to write this post for all those who have come across this issue and are looking for some options to work around it.
On a SharePoint server (WSS 3.0, MOSS 2007, SharePoint Server 2010 or SharePoint Server 2013) when we upload any document larger that 50 megs on any document library, we can encounter the following error messages
- "An unexpected error has occurred"
- "The page cannot be displayed”
- "An unknown error occurred"
- "HTTP 404 – Page Not Found”
- “Request timed Out’
If you are using explorer view, the error message would be similar to
Could not find this item --> This is no longer located \\Servername\DavWWWRoot\team. Verify the item's location and try again".
Before we begin, I would like to mention that SharePoint is not really designed to handle huge files > 300 Mb). It stores all files in the content databases and that's where these large files are going. So I strongly recommend using file shares instead.
Going ahead, this can occur due to various reasons and I have listed a few of the possible causes and the workarounds for them
WORKAROUND(s)
Method 1 Increase the maximum upload size for the web application
Note : The default max single file upload size is 50 megs by default for a web application (in IIS 6.0) and 28 megs for IIS 7.0.
- Go to 'Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > SharePoint Central Administration > Application Management'.
- Under SharePoint Web Application Management, click 'Web application general settings’.
- On the Web Application General Settings page, choose the appropriate web application.
- Under Maximum upload size, type the file size which you want to upload and click on OK. You can specify a maximum
file size up to 2,047 megabytes.
Note:
Any upload size which is below 50 megs is enforced directly through web app settings. Above 50 megs, you need to make a some small change to the web.config file to allow larger uploads. Repeat the steps listed below for all zones for your web app all the servers which host the web application role.
- Open the web.config from 'C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\wss\VirtualDirectories\<Virtual Directory>' folder and modify it as follows
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="51200" /> with <httpRuntime executionTimeout="999999" maxRequestLength="51200" />
- Perform an IISReset and you should be good to go.
See <httpRuntime> element in web.config for more information.
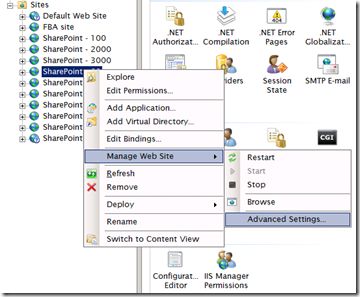
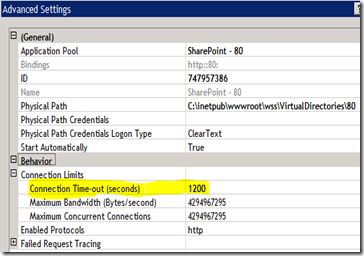
Method 2 Increase the connection time-out setting in IIS
While uploading large files, there are chances that the request will timeout. By default, the IIS connection time-out setting is 120 seconds. Follow these steps to increase the connection time-out setting,
- Click Start, point to All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
- Right-click the virtual server that you want to configure, and then click Properties.
- Click the Web Site tab. Under Connections, type the number of seconds that you want in the Connection time-out box,
and then click OK.
Method 3 Increase the maximum upload size in the web.config file of web application
By default, the web.config file is located in the 'C:\Inetpub\Wwwroot\Wss\Virtual Directories\<Virtual Directory>' folder. Add the following configuration to the web.config, just before the <configuration> section closes out.
Here’s a screenshot of the web.config file after the change:
This sets the value of the maxAllowedContentLength property to 52428800 (in bytes) for the web application only.
See KB944981 - You cannot upload files that are larger than 28 MB on a Windows Server 2008-based computer that is running Windows SharePoint Services 3.0.
Note:
The following information is applicable to IIS 7.0 and suggests making a change to the ‘applicationhost.config’ file which is a core configuration file for IIS. For more information, see
The maxAllowedContentLength property specifies the maximum length of content in a request in bytes and it needs to be set on a Windows Server 2008 computer that has IIS 7.0-only installations. To change the value of the property, do the following
- Open command prompt and go to 'C:\windows\system32\inetsrv' directory
- Run the below command
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxallowedcontentlength:unit
where the variable "requestlimits.maxallowedcontentlength" unit specifies the maximum length of content.
For example, to specify 2000000000 as the maximum length of content, type the following at the command prompt, and then press ENTER:
appcmd set config /section:requestfiltering /requestlimits.maxallowedcontentlength:2000000000
- Perform an IISreset /noforce.
- More info is available at
Method 4 Increase the default chunk size for large files
The large-file-chunk-size property sets the amount of data that can be read from server running SQL Server at one time.
- If you have a file that is greater than your chunk size (such as 70 MB when the chunk size is set to 5 MB), the file would be read in 14 chunks (70 / 5).
- The chunk size is not related to the maximum upload file size.
- The chunk size simply specifies the amount of data that can be read from a file at one time. By default, the large-file-chunk-size property is set to 5 MB.
- Check if the 'large-file-chunk-size' property is set or not
Stsadm -o getproperty -propertyname large-file-chunk-size
- In order to set the large–file–chunk–size property, we need to use the command line. This property is configured for a server or server farm, and cannot be configured for an individual web app server. To set this property, use the following syntax:
Stsadm.exe –o setproperty –pn large–file–chunk–size –pv <size in bytes>
More on this command is available at Large-file-chunk-size: Stsadm property (Office SharePoint Server)
- After making a change to this property, perform an IISreset /noforce.
See What is the maximum value one can set for the Large-file-chunk-size ?
Method 5 Add the executionTimeout value
Increase the execution timeout for the upload page (upload.aspx) to prevent timeouts on the page. The default timeout for ASP.NET 2.0 is 110 seconds, so any uploads that are taking longer than that will result in a request failure. Add the executionTimeout value to web.config in the 'C:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\web server extensions\12\TEMPLATE\LAYOUTS' folder and the ‘C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\wss\VirtualDirectories\<Virtual Directory>' folder.
- Navigate to 'C:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web Server Extensions\12\TEMPLATE\LAYOUTS' folder on the SharePoint server.
- Open the 'web.config' file in notepad or any other text editor and add the executionTimeoutparameter. For example, replace the value as follows
Existing code
<location path="upload.aspx">
<system.web>
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="2097151" />
</system.web>
</location>
Replacement code
<location path="upload.aspx">
<system.web>
<httpRuntime executionTimeout="999999" maxRequestLength="2097151" />
</system.web>
</location>
- Open the 'web.config' file from the 'C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\wss\Virtual Directories\<Virtual Directory>'folder and modify it as follows
Existing line : <httpRuntime maxRequestLength="51200" />
Replacement line : <httpRuntime executionTimeout="999999" maxRequestLength="51200" />
Modify the web.config located in "12\CONFIG" folder
- Navigate to 'C:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web Server Extensions\12\TEMPLATE\CONFIG' folder on the SharePoint server and modify the 'maxRequestLength' property which by default is set to the following
<httpRuntime
maxRequestLength="51200"
/> - Open the 'web.config' file in notepad or any other text editor and modify the value to match the other web.config files
- Save the file and perform an 'IISreset /noforce'.
Antivirus Exclusions
Make sure you have added Antivirus exclusions as per http://support.microsoft.com/kb/952167
ASP.Net Session State
- Open IIS manager, expand the 'Sites' node and select the SharePoint site
- Click on 'Session State' under 'Application Development' and verify that the 'Timeout' value is set to '120' minutes
You can also verify this from the web.config file
What is ASP.Net Session
ASP.NET session state enables you to store and retrieve values for a user as the user navigates the different ASP.NET pages that make up a Web application. HTTP is a stateless protocol, meaning that your Web server treats each HTTP request for a page as an independent request; by default, the server retains no knowledge of variable values used during previous requests. ASP.NET session state identifies requests received from the same browser during a limited period of time as a session, and provides the ability to persist variable values for the duration of that session.
See ASP.NET Session State for more information
Explorer view or Web client issues
While trying to use the explorer view, you may see the following error despite making the aforementioned changes
“Error 0x800700DF: The file size exceeds the limit allowed and cannot be saved” message
If this is the case then the issue is most likely caused by a local restriction set on Web Client service. By default, Web Client file size limit is set to around 47 Mb. To increase this limit:
- Click Start, click Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
- In Registry Editor, locate the following registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WebClientParameters - Right click on the FileSizeLimitInBytes and then click Modify.
- In the Value data box, click on Decimal, and type 4294967295 and then click OK.
- Quit Registry Editor
- Restart Web Client service from Services.msc
Large file Support Limitations
The following features do not support files larger than 50 MB
- Virus checking
- Streaming files
- Client-side restoration of smigrate backup files (limited to 2 GB). The manifest files for an smigrate backup cannot be larger than 2 GB (SPS)
- Site templates (limit of 10 MB per site template, including content).
NOTE:
- As mentioned earlier, I would like to mention that SharePoint is not really designed to handle huge files > 300 Mb). It stores all files in the content databases and that's where these large files are going. So Istrongly recommend using file shares instead.
- Also be aware that increasing you upload file size to 2 GB has performance ramifications so it a user uploads a file and there is no memory available no new requests can be handled until the memory is available again.
Additional Info
- Error message when you try to upload a large file to a document library on a Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 site: "Request timed out"
- Error message when you visit a Web site that is hosted on a server that is running IIS 7.0: "HTTP Error 404.13 - CONTENT_LENGTH_TOO_LARGE"
SharePoint 2010, SharePoint, MOSS 2007, WSS 3.0, Large File Upload, HTTP 404, An unexpected error has occurred, the page cannot be displayed, request time out