彻底学会系列:一、机器学习之线性回归
1.基本概念
线性回归: 有监督学习的一种算法。主要关注多个因变量和一个目标变量之间的关系。
因变量: 影响目标变量的因素: X 1 , X 2 . . . X_1, X_2... X1,X2... ,连续值或离散值。
目标变量: 需要预测的值: target,y
目标变量和自变量之间的关系: 即模型,model
1.1连续值
连续值是可以在一个区间范围内取任意值的变量。例如,身高、体重、温度、时间等都是连续值

1.2离散值
离散值是只能取有限个数值或者可数值的变量。例如,学生人数、家庭成员数、考试分数等都是离散值

1.3简单线性回归
简单线性回归对应的公式: y = w x + b y = wx + b y=wx+b
y 是目标变量即未来要预测的值
x 是影响 y 的因素
w,b 是公式上的参数即要求的模型,w就是斜率,b就是截距
一元一次方程:
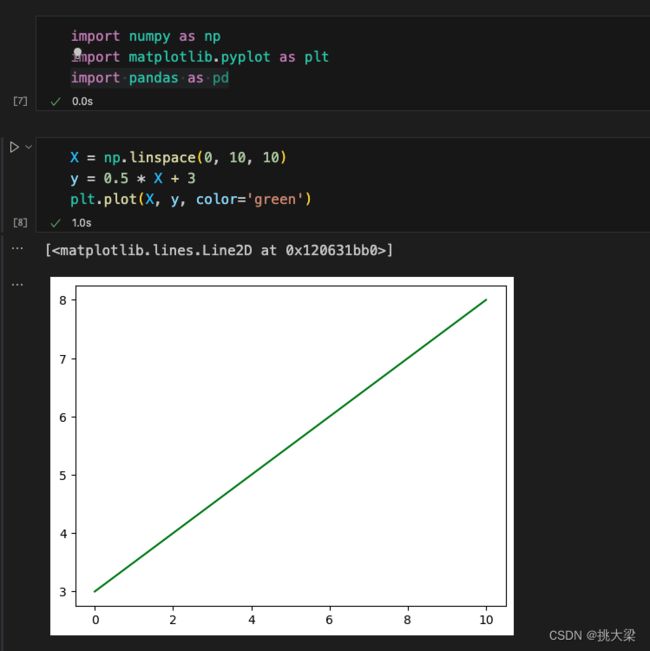
一元二次方程:

1.4最优解
y: 真实值(actual value)
y ^ \hat y y^: 预测值(predicted value), 根据因变量 X 1 , X 2 . . . X_1,X_2... X1,X2...和计算出来的参数w,b得到
error: 误差,预测值和真实值的差距( ε \varepsilon ε)
最优解: 尽可能的找到一个模型使得整体的误差最小,通常叫做损失 Loss,通过损失函数Loss Function计算得到。
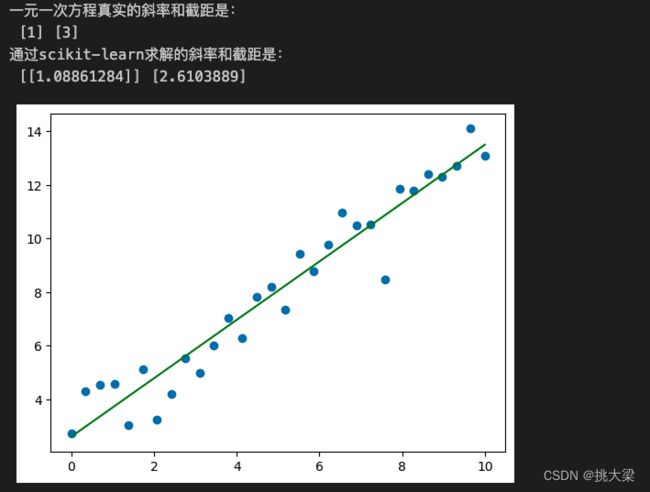
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = np.linspace(0, 10, num=30).reshape(-1, 1)
w = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=1)
b = np.random.randint(1, 10, size=1)
y = X * w + b + np.random.randn(30, 1)
plt.scatter(X, y)
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
w_ = model.coef_
b_ = model.intercept_
print('一元一次方程真实的斜率和截距是:\n', w, b)
print('通过scikit-learn求解的斜率和截距是:\n', w_, b_)
plt.plot(X, X.dot(w_) + b_, color='green')
plt.show()
1.5多元线性回归
现实生活中,往往影响结果 y 的因素不止一个,有可能是 n 个, X 1 , X 2 , X n . . . X_1,X_2,X_n... X1,X2,Xn...
多元线性回归公式:
![]()
b是截距,也可以表示成:
![]()
使用向量来表示:
![]()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# 转化矩阵
x1 = np.random.randint(-150, 150, size=(300, 1))
x2 = np.random.randint(0, 300, size=(300, 1))
# 斜率和截距,随机生成
w = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=2)
b = np.random.randint(1, 10, size=1)
# 根据二元一次方程计算目标值y,并加上"噪声"
y = x1 * w[0] + x2 * w[1] + b + np.random.randn(300, 1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x1, x2, y) # 三维散点图
ax.view_init(elev=10, azim=-20) # 调整视角
#
X = np.concatenate([x1, x2], axis=1)
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
w_ = model.coef_.reshape(-1)
b_ = model.intercept_
print('一元一次方程真实的斜率和截距是:\n', w, b)
print('通过scikit-learn求解的斜率和截距是:\n', w_, b_)
x = np.linspace(-150, 150, 100)
y = np.linspace(0, 300, 100)
z = x * w_[0] + y * w_[1] + b_
ax.plot(x, y, z, color='green')
plt.show()
2.正归方程
2.1最小二乘法矩阵
最小二乘法(Least Squares Method): 将误差方程转化为有确定解的代数方程组(其方程式数目正好等于未知数的个数),从而可求解出这些未知参数。

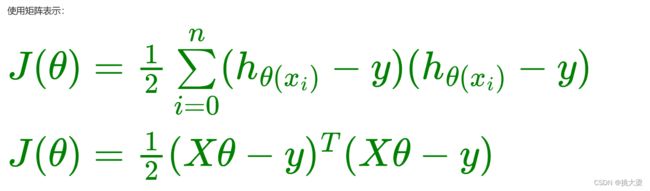
正规方程: 是解决最小二乘问题的一种方法,特别适用于线性回归问题。
![]()
2.2多元一次方程
import numpy as np
X = np.array([[1, 1], [2, -1]])
y = np.array([14, 10])
# linalg 线性代数,solve计算线性回归问题
r = np.linalg.solve(X, y)
print('方程的解: \n ', r)
print('f(x, y) = 8*x + 6*y')
# W = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
W = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
print('正规方程求解二元一次: \n ', W)
X = np.array([[1, -1, 1], [2, 1, -1], [3, -2, 6]])
y = np.array([100, 80, 256])
W = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
print('正规方程求解三元一次: \n ', W)