2024/1/5
作业1:有参无返函数练习
1.1在主函数定义二维数组,在有参无返函数中实现杨慧三角
#include
#include
#include
void fun(int n,int arr[n][n]);//声明定义的有参无反函数
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int n;//定义一个变量n
printf("please enter n:");//提示输入n
scanf("%d",&n);
int arr[n][n];//定义一个n行n列的二维数组
fun(n,arr);//将n和数组传给fun函数
return 0;
}
void fun(int n,int arr[n][n])//定义一个有参无反函数fun
{
int i,j;//定义两个循环变量i,j
for(i=0;i 效果图:
1.2在主函数中定义两个字符串并输入,在有参无返函数中实现字符串拷贝
#include
#include
#include
void fun(char dest[20],char src[20]);//声明定义的fun函数
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char dest[20]="";//定义目标字符串数组dest
char src[20]="";//定义源字符串数组src
printf("please enter dest:");//提示输入
gets(dest);//输入字符串dest
printf("please enter src:");//提示输入
gets(src);//输入字符串src
fun(dest,src);//将字符串dest与src传给fun函数
return 0;
}
void fun(char dest[20],char src[20])//定义一个fun函数
{
int i;
for(i=0;src[i]!='\0';i++)
{
dest[i]=src[i];//将src字符串中的内容拷贝到dest字符串中
}
puts(dest);//输出拷贝后的字符串dest
}
效果图:
1.3在主函数中定义两个字符串并输入,在有参无返函数中实现字符串链接
#include
#include
#include
void fun(char dest[20],char src[20]);//声明定义的fun函数
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char dest[20]="";//定义dest字符串数组
char src[20]="";//定义src字符串数组
printf("please enter dest:");//提示输入
gets(dest);//输入字符串dest
printf("please enter src:");//提示输入
gets(src);//输入字符串src
fun(dest,src);//将两个字符串传给fun函数
return 0;
}
void fun(char dest[20],char src[20])//定义有参无返的fun函数
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;dest[i]!=0;i++);//求dest字符串长度
for(j=0;src[j]!='\0';j++)
{
dest[i+j]=src[j];//将src字符串连接到dest字符串后面
}
dest[i+j]='\0';
puts(dest);//输出dest字符串
}
效果图:
1.4在主函数定义二维数组并输入,在有参无返函数中实现二维数组转置
1 2 3 1 4
4 5 6 2 5
3 6
#include
#include
#include
void fun(int a[2][3],int b[3][2]);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a[2][3];//定义两个二维数组
int b[3][2];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)//输入二维数组
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
fun(a,b);//传参
return 0;
}
void fun(int a[2][3],int b[3][2])//定义fun函数
{
int i,j;
printf("\n");
//转置过程中将两个数组行列的值互换
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
b[j][i]=a[i][j];
}
}
//输出转置后的数组
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf("%d ",b[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
效果图:
作业2:有参有返函数练习
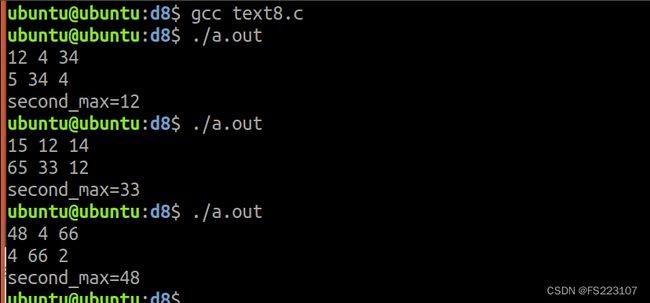
2.1在主函数定义二维数组并输入,在有参有返函数中计算二维数组的第二大值
eg: 数组元素是 12 4 34 5 34 4
则第二大值是12
返回第二大值
#include
#include
#include
int fun(int arr[2][3]);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int arr[2][3];//定义一个2行3列的二维数组
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);//输入二维数组的值
}
}
int s=fun(arr);//传参并接收返回值
printf("second_max=%d\n",s);//输出数组元素中的第二大值
return 0;
}
int fun(int arr[2][3])//定义一个有参有返的fun函数
{
int i,j;
int max=arr[0][0],second_max=arr[0][0];//分别让第一第二大值等于数组中的首元素
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(maxarr[i][j]){//找出数组中的最小值作为第二大值
second_max=arr[i][j];
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<2;i++)//再次遍历数组
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
if(arr[i][j]==max){//如果遍历的元素值与最大值相等,则跳过本次循环
continue;
}
if(second_max 效果图:
2.2在主函数中定义一个字符串并输入,在有参有返函数中实现atoi
返回:最终转换的整数
eg:输入-123sdf3 返回-123
#include
#include
#include
int fun(char str[20]);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char str[20]="";//定义一个字符串数组
printf("please enter str:");//提示输入
gets(str);//输入字符串数组
int s=fun(str);//传参并接收fun函数的返回值
printf("%d\n",s);
return 0;
}
int fun(char str[20])
{
int i,sum=0;
while(str[i]==' ')//让下标i过滤空格
{
i++;
}
int j=i;//用j保存此时i所指的单字符(因为可能是'-'或'+')
if(str[i]=='+' || str[i]=='-'){//跳过正负符号位
i++;
}
while(str[i]!='\0')//遍历剩下字符
{
if(str[i]>='0' && str[i]<='9')//如果为数字
{
sum=sum*10+(str[i]-'0');//用sum来保存数字
}else{
break;//如果是字母或其他字符则跳过
}
i++;
}
if(str[j]=='-')//此时判断存的j是否为'-',是sum取负数
{
sum=-sum;
}
return sum;//将sum返回到main函数
}
效果图:
2.3在主函数定义一维数组并输入,在有参有返函数中计算一维数组的第二小值
eg: 输入元素是 12 4 32 5 34 4
则第二小值是5
返回:第二小值
#include
#include
#include
int fun(int n,int arr[n]);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
// int arr[6]={34,12,32,4,5,3};
// int n=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int n;
printf("please enter n:");
scanf("%d",&n);
int arr[n];//定义一个一维数组并输入
for(int i=0;iarr[j+1])//将数组中的元素升序排列
{
t=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=t;
}
}
}
int second_min=arr[0];//令第二小值为排序后的最小值
for(i=0;i 效果图:
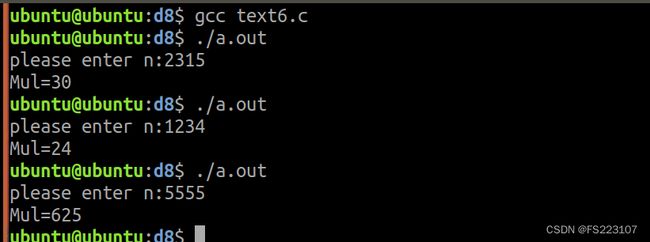
作业3:递归计算各个位数字的乘积。
eg:2315--->2*3*1*5-->30
#include
#include
#include
int fun(int n);
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int n;
printf("please enter n:");//提示输入一个数
scanf("%d",&n);//输入n的值
int Mul=fun(n);//传参并用Mul接收返回值
printf("Mul=%d\n",Mul);
return 0;
}
int fun(int n)
{
if(n==0)
{
return 1;//n==0时,返回1,不改变乘积的结果
}else{
return (n%10)*fun(n/10);//求输入的n各个位的乘积
}
}
效果图: