手敲Mybatis(17章)-二级缓存功能,感受装饰器的魅力
1.目的
本节主要是讲Mybatis的二级缓存,一级缓存是会话SqlSession级别的,二级缓存是Mapper级别的这个大家都知道,一级缓存主要是同一个SqlSession实例才可以缓存,那么出现commit等其他情况可能清除缓存,我想要再发起的会话还是相同的查询操作,最好也是可以把数据从缓存中获取出来。这个时候该如何实现呢?
这时候引出来二级缓存,以一个 Mapper 为生命周期,在这个 Mapper 内的同一个操作,无论发起几次会话都可以使用缓存来处理数据。叫二级缓存,是因为要在一级缓存基础上额外添加缓存操作,(也就是要引出来设计模式-装饰器模式),当会话发生 close、commit 操作时则把数据刷新到二级缓存中进行保存,直到执行器发生 update 操作时清空缓存。
本节最重点主要就是装饰器模式,所以先提装饰器模式的思路,就是不改变原有的类和方法,在其上包装了一成自己的功能,是现有类的包装。
二级缓存需要在设置中开启全局缓存,如图,开启了缓存,关闭了一级缓存,然后需要在XMLConfigBuilder中解析,解析完毕将全局缓存设置到Configuration中的cacheEnabled中,true和false代表是否开启。
由于下图在Mapper中设置了cache标签的一些属性,所以需要在XMLMapperBuilder类中需要解析一下,解析一级缓存类,二级缓存类,缓存间隔时间,队列大小以及属性等等,最后将属性构建到缓存构建器中,接着将缓存放入到当前类MapperBuilderAssistant的Cache变量赋值,然后将MapperBuilderAssistant存入的缓存变量存入到MappedStatement的cache里。到此构建结束。
执行时则是构建Executor时判断是否全局缓存,如果全局缓存则在DefaultSqlSession中给的Executor就是CachingExecutor,如果不是则是SimpleExecutor,这里相当于CachingExecutor做了一层SimpleExecutor包装,因为CachingExecutor里有一个Executor变量,这个变量传的就是SimpleExecutor,那么真正执行操作时,我们就可以执行SimpleExecutor的业务,而CachingExecutor主要执行缓存业务,这就是扩展其功能,却又不改变其功能,这里就是装饰器的设计精髓和思想。
CachingExecutor类里实现Executor类,所以还是实现query、update等等的方法,执行query方法前先查看是否有缓存,此时进入事务缓存管理器TransactionalCacheManager,主要是事务缓存TransactionalCache
的装饰器,调用事务缓存里的获取缓存以及存入缓存操作,事务缓存是二级缓存FifoCache(本节二级缓存实现方式是先进先出的队列缓存)的装饰器,也就是说这里最终会调用二级缓存的存储获取缓存操作,事务缓存生命周期是在提交回滚将事务缓存中的变量数据缓存清空,放入到FifoCache缓存中。
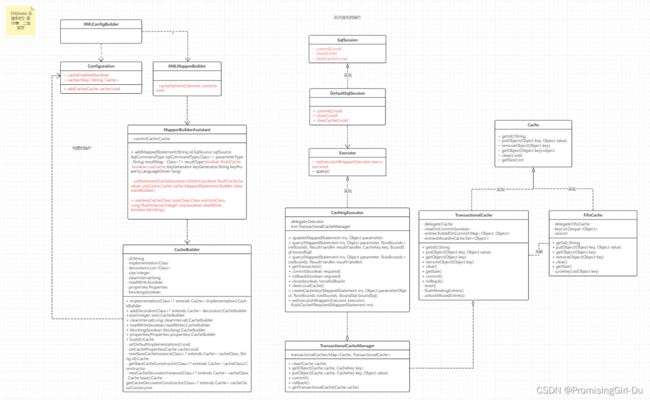
2.uml类图
看类图UML就可以知道整个过程,
1.构建时由XMLConfigBuilder开始解析然后放入到Configration中,然后进入到XMLMapperBuilder解析图二的cache标签,然后进入MapperBuilderAssistant去存储相关内容,处理完后放入Configuration中和MappedStatement中。
2.执行时操作,由SqlSession开始进入到Executor中,首先进入第一个装饰器,CachingExecutor,然后进入事务缓存管理器TransactionalCacheManager,依赖事务缓存TransactionalCache,事务缓存又是二级缓存FifoCache的包装器,二级缓存又是一级缓存的PerpetualCache包装器,最终调度到最底层返回。大致就是UML的这个类图的过程
3.代码
3.1 全局缓存解析
3.1.1 XMLConfigBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder中添加解析全局缓存操作,解析setting标签的name和value,解析完毕放入configuration中的cacheEnabled变量里。
/**
* 解析配置在 XML 文件中的缓存机制。并把解析出来的内容存放到 Configuration 配置项中。
*
*
*
*/
private void settingsElement(Element context) {
if (context == null) return;
List elements = context.elements();
Properties props = new Properties();
for (Element element : elements) {
props.setProperty(element.attributeValue("name"), element.attributeValue("value"));
}
// 设置全局缓存 step-18加
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
// 设置缓存级别
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope")));
} Configuration中的更改就比较简单了,主要是将是否是全局缓存以及将当前的缓存放入到Map中的操作处理,Configuration构造方法中则往类型处理器中注册一级缓存(PerpetualCache)和二级缓存(FiFoCache,本节二级缓存暂时实现先进先出)
public class Configuration {
// 省略其他
// 缓存,存在Map里
protected final Map caches = new HashMap<>();
// 默认启用缓存,cacheEnabled = true/false
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
public Configuration() {
// 省略其他
// step-18-添加
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
}
public boolean isCacheEnabled() {
return cacheEnabled;
}
public void setCacheEnabled(boolean cacheEnabled) {
this.cacheEnabled = cacheEnabled;
}
public void addCache(Cache cache) {
caches.put(cache.getId(), cache);
}
public Cache getCache(String id) {
return caches.get(id);
}
} 3.1.2 XMLMapperBuilder
XMLMapperBuilder类:
因为二级缓存是Mapper级别的,所以会有一些配置操作放入到mapper里需要去解析,如
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
// 省略其他。。。
private void configurationElement(Element element) {
// 省略其他。。。
// 2. 配置cache
cacheElement(element.element("cache"));
}
// 新添加的方法
/**
* elements = context.elements();
Properties props = new Properties();
for (Element element : elements) {
props.setProperty(element.attributeValue("name"), element.attributeValue("value"));
}
// 构建缓存
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
} 3.1.3 MapperBuilderAssistant
MapperBuilderAssistant:mapper助手类,由XMLMapperBuilder的cacheElement方法调用到此类的useNewCache方法里,useNewCache方法最主要的就是构建缓存实体类CacheBuilder,往里边放入一级缓存实现类,二级缓存实现类以及二级缓存的一些必要参数,构建缓存实体完毕就会放入到configuration的缓存变量下。
关于缓存还有另一个地方需要更改,就是addMappedStatement方法中,构建MappedStatement需要添加是否刷新缓存(flushCache)以及是否开启了二级缓存(useCache),当前使用的缓存实现等等的需要构建到MappedStatement,由后期执行Sql时使用。
public class MapperBuilderAssistant extends BaseBuilder {
private Cache currentCache;
// step-18 添加
public Cache useNewCache(Class typeClass,
Class evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
// 判断为null,则用默认值
typeClass = valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class);
evictionClass = valueOrDefault(evictionClass, FifoCache.class);
// 建造者模式构建Cache [currentNamespace=cn.bugstack.mybatis.test.dao.IActivityDao]
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(typeClass)
.addDecorator(evictionClass)
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
// 添加缓存
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
/**
* 添加映射器语句,最新版添加了flushCache,useCache,是否刷新缓存和是否使用缓存字段
*/
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Class parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class resultType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
LanguageDriver lang
) {
// 给id加上namespace前缀:cn.bugstack.mybatis.test.dao.IUserDao.queryUserInfoById
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
//step-18添加,是否是select语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlCommandType, sqlSource, resultType);
// step-14新增/添加三个属性
statementBuilder.resource(resource);
statementBuilder.keyGenerator(keyGenerator);
statementBuilder.keyProperty(keyProperty);
// 结果映射,给 MappedStatement#resultMaps
setStatementResultMap(resultMap, resultType, statementBuilder);
// step-18添加
setStatementCache(isSelect, flushCache, useCache, currentCache, statementBuilder);
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// 映射语句信息,建造完存放到配置项中
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
// 设置语句缓存,主要是构建到MappedStatement中
private void setStatementCache(
boolean isSelect,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
Cache cache,
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder) {
flushCache = valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect);
useCache = valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect);
statementBuilder.flushCacheRequired(flushCache);
statementBuilder.useCache(useCache);
statementBuilder.cache(cache);
}
}3.1.4 XMLStatementBuilder
XMLStatementBuilder中,也主要是关于缓存的操作,在parseStatementNode方法中获取是否是Select标签,如果是代表是要使用缓存,如果不是Select标签代表刷新缓存, 因为会发生更改,所以这里这样处理,并把处理好的这两个字段传给MapperBuilderAssistant的addMappedStatement方法中(也就是上面3.1.3的目录说的代码中)。
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 省略其他...
Class resultTypeClass = resolveAlias(resultType);
// 获取命令类型(select|insert|update|delete)
String nodeName = element.getName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// step-18添加
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = Boolean.parseBoolean(element.attributeValue("flushCache", String.valueOf(!isSelect)));
boolean useCache = Boolean.parseBoolean(element.attributeValue("useCache", String.valueOf(isSelect)));
// 调用助手类【本节新添加,便于统一处理参数的包装】
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id,
sqlSource,
sqlCommandType,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMap,
resultTypeClass,
flushCache,
useCache,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
langDriver);
}
}3.1.5 MapperAnnotationBuilder
当然注解也需要上面的更改, MapperAnnotationBuilder类中也需要更改添加是否刷新缓存以及是否使用缓存,注解的话我们就直接先处理false就ok了。
public class MapperAnnotationBuilder {
// 省略其他....
/**
* 解析语句
*/
private void parseStatement(Method method) {
// 省略其他....
// 调用助手类
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
sqlCommandType,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
false,
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
languageDriver
);
}
}
}3.1.6 CacheBuilder
包:package cn.bugstack.mybatis.mapping;
CacheBuilder构建Cache参数,定义了内部的构建器,等等的操作。
/**
* @Author df
* @Description: 缓存构建器,建造者模式
* @Date 2024/1/12 14:45
*/
public class CacheBuilder {
private String id;
private Class implementation;
private List> decorators;
private Integer size;
private Long clearInterval;
private boolean readWrite;
private Properties properties;
private boolean blocking;
public CacheBuilder(String id) {
this.id = id;
this.decorators = new ArrayList<>();
}
public CacheBuilder implementation(Class implementation) {
this.implementation = implementation;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder addDecorator(Class decorator) {
if (decorator != null) {
this.decorators.add(decorator);
}
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder size(Integer size) {
this.size = size;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder clearInterval(Long clearInterval) {
this.clearInterval = clearInterval;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder readWrite(boolean readWrite) {
this.readWrite = readWrite;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder blocking(boolean blocking) {
this.blocking = blocking;
return this;
}
public CacheBuilder properties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
return this;
}
public Cache build() {
setDefaultImplementations();
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class decorator : decorators) {
// 使用装饰者模式包装
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
// 额外属性设置
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
}
return cache;
}
private void setDefaultImplementations() {
if (implementation == null) {
implementation = PerpetualCache.class;
if (decorators.isEmpty()) {
decorators.add(FifoCache.class);
}
}
}
private void setCacheProperties(Cache cache) {
if (properties != null) {
MetaObject metaCache = SystemMetaObject.forObject(cache);
for (Map.Entry entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String name = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
if (metaCache.hasSetter(name)) {
Class type = metaCache.getSetterType(name);
if (String.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, value);
} else if (int.class == type
|| Integer.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if (long.class == type
|| Long.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Long.valueOf(value));
} else if (short.class == type
|| Short.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Short.valueOf(value));
} else if (byte.class == type
|| Byte.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Byte.valueOf(value));
} else if (float.class == type
|| Float.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Float.valueOf(value));
} else if (boolean.class == type
|| Boolean.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Boolean.valueOf(value));
} else if (double.class == type
|| Double.class == type) {
metaCache.setValue(name, Double.valueOf(value));
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unsupported property type for cache: '" + name + "' of type " + type);
}
}
}
}
}
private Cache newBaseCacheInstance(Class cacheClass, String id) {
Constructor cacheConstructor = getBaseCacheConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not instantiate cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Constructor getBaseCacheConstructor(Class cacheClass) {
try {
return cacheClass.getConstructor(String.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Invalid base cache implementation (" + cacheClass + "). " +
"Base cache implementations must have a constructor that takes a String id as a parameter. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Cache newCacheDecoratorInstance(Class cacheClass, Cache base) {
Constructor cacheConstructor = getCacheDecoratorConstructor(cacheClass);
try {
return cacheConstructor.newInstance(base);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not instantiate cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private Constructor getCacheDecoratorConstructor(Class cacheClass) {
try {
return cacheClass.getConstructor(Cache.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Invalid cache decorator (" + cacheClass + "). " +
"Cache decorators must have a constructor that takes a Cache instance as a parameter. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
} 3.2 缓存使用
3.2.1 CachingExecutor
包:package cn.bugstack.mybatis.executor;
我们新建一个类,装饰器模式的CachingExecutor,实现Executor接口,代表有缓存功能的执行器,实现Executor的所有方法,但处理了缓存后最终都会调度到原来的Executor方法上,这个就是装饰器功能。
变量delegate,就是原调度器,这里在运行时会把simpleExecutor方法赋值到delegate,这样执行了update方法以及query方法还有一些事务方法,都是访问的原调度器也就是simpleExecutor的方法,除了在query方法功能时查询了是否有缓存,是否使用缓存,是的话就从缓存出取出,缓存没有就执行simpleExecutor的query方法执行查询,查询完毕放入缓存,留下次使用。
CachingExecutor的缓存操作和事务处理都依赖于TransactionalCacheManager事务缓存管理器,
/**
* @Author df
* @Description: 二级缓存执行器
* 装饰器模式,装饰执行器,装饰SimpleExecutor类,也就是最终调用到BaseExecutor执行Sql查询
* @Date 2024/1/12 11:29
*/
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CachingExecutor.class);
private Executor delegate;
private TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
return delegate.update(ms, parameter);
}
/**
* 缓存执行器,先从缓存拿数据,如果没有则调用原来的执行器执行Sql语句查询,然后存储到缓存里
* 当用户执行commit或者回滚操作就进入到此缓存执行器的commit,我们将事务缓存清空,刷新到FifoCache里
* */
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 是否使用缓存
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
List list = (List) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// cache:缓存队列实现类,FIFO
// key:哈希值 [mappedStatementId + offset + limit + SQL + queryParams + environment]
// list:查询的数据
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && cache.getSize() > 0) {
logger.debug("二级缓存:{}", JSON.toJSONString(list));
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 1. 获取绑定SQL
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 2. 创建缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
return delegate.getTransaction();
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
delegate.clearLocalCache();
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This method should not be called");
}
// 如果需要刷新缓存操作则清除缓存
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
} 3.2.2 TransactionalCacheManager
事务缓存管理器,也是使用了装饰器模式,是对事务缓存的包装操作,用于在缓存执行器创建期间实例化,包装执行期内的所有事务缓存操作,做批量的提交和回滚时缓存数据刷新的处理。
/**
* @Author df
* @Description: 事务缓存,管理器
* 装饰器,是对事务缓存的包装操作,用于在缓存执行器创建期间实例化,包装执行期内的所有事务缓存操作,做批量的提交和回滚时缓存数据刷新的处理。
* @Date 2024/1/12 11:15
*/
public class TransactionalCacheManager {
private Map transactionalCaches = new HashMap<>();
public void clear(Cache cache) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).clear();
}
/**
* 得到某个TransactionalCache的值
*/
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
/**
* 将key和值放入TransactionalCache中
*/
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
/**
* 提交时全部提交
*/
public void commit() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.commit();
}
}
/**
* 回滚时全部回滚
*/
public void rollback() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.rollback();
}
}
// 获取事务缓存或初始化事务缓存
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) {
TransactionalCache txCache = transactionalCaches.get(cache);
if (txCache == null) {
txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache);
transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache);
}
return txCache;
}
}
3.2.3 TransactionalCache
事务缓存操作,是对二级缓存的包装,也就是装饰器模式,事务的提交回滚等最终会到此处,进行TransactionalCache全局变量的刷新操作,将缓存存储到二级缓存中。
事务回滚或提交时,此时清除TransactionalCache里的缓存变量信息,如果是提交操作,则把当前缓存信息刷新到二级缓存里。
/**
* @Author df
* @Description: The 2nd level cache transactional buffer. 事务缓存
* 包装二级缓存,事务的提交回滚等最终会到此处,进行TransactionalCache全局变量的刷新操作,将缓存存储到二级缓存中
* 也就是装饰器模式。
* @Date 2024/1/12 11:07
*/
public class TransactionalCache implements Cache {
// 二级缓存
private Cache delegate;
// commit 时要不要清缓存
private boolean clearOnCommit;
// commit 时要添加的元素
private Map entriesToAddOnCommit;
private Set 3.2.3 FifoCache
二级缓存,此次实现先入先出缓存,也是装饰器模式,包装一级缓存,由于是先入先出,所以定义了队列,存储缓存时会存储到keyList这个队列里,存储时会判断这个队列是否达到了队列数,如果是则移除最早进来的数据。
/**
* @Author df
* @Description: FIFO (first in, first out) cache decorator
* 装饰器模式,其余的操作都包装给Cache去完成。
* 包装一级缓存PerpetualCache,调用到对应方法就会调用到一级缓存的存储数据,移除数据等方法。
* @Date 2024/1/12 10:51
*/
public class FifoCache implements Cache {
private final Cache delegate;
private Deque我们知道,DefaultSqlSessionFactory开启会话时创建执行器,所以这时我们可以判断是否使用带有缓存的执行器还是普通的执行器SimpleExecutor,Configuration中添加如下代码,用来判断用cacheEnabled如果是则代表缓存处理器,不是就用SimpleExecutor。
然后将这个执行器存入到DefaultSqlSession变量中,然后执行update或query方法时就直接执行已经处理好的执行器就可以。
/**
* 生产执行器
*/
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
Executor executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
// 配置开启缓存,创建 CachingExecutor(默认就是有缓存)装饰者模式
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
return executor;
}
4.单元测试
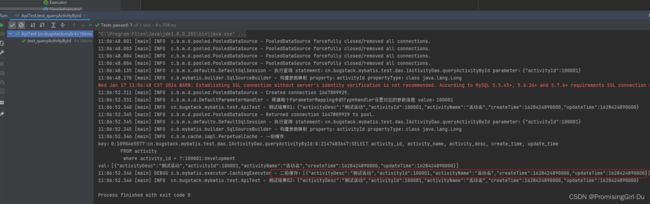
执行两个SqlSession看是否能查询到缓存处理。
public class ApiTest {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ApiTest.class);
@Test
public void test_queryActivityById() throws IOException {
// 1. 从SqlSessionFactory中获取SqlSession
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config-datasource.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
// 2. 请求对象
Activity req = new Activity();
req.setActivityId(100001L);
// 3. 第一组:SqlSession
// 3.1 开启 Session
SqlSession sqlSession01 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 3.2 获取映射器对象
IActivityDao dao01 = sqlSession01.getMapper(IActivityDao.class);
logger.info("测试结果01:{}", JSON.toJSONString(dao01.queryActivityById(req)));
sqlSession01.close();
// 4. 第一组:SqlSession
// 4.1 开启 Session
SqlSession sqlSession02 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4.2 获取映射器对象
IActivityDao dao02 = sqlSession02.getMapper(IActivityDao.class);
logger.info("测试结果02:{}", JSON.toJSONString(dao02.queryActivityById(req)));
sqlSession02.close();
}
}测试结果: