UE4通过C++代码实现蓝图方法(UFUNTION暴露代码接口)
学习了一段时间Unreal engine 4,UE4里的蓝图提供了非常便捷的方式,可以让非软件开发人员很轻松地调用方法函数,在零代码的情况下实现游戏逻辑。
蓝图之所以那么方便,是因为软件开发工程师预先把很多方法函数封装成了蓝图方法,有了这些蓝图方法,非软件人员就需要通过简单的拖拽接线就能写逻辑了。有时候我们也可以把一些复杂的逻辑通过c++代码的方式实现,封装成蓝图函数,提供给非软件人员使用。
下面就是讲述UFUNCTION的用法:
暴露C++方法
我们可以通过定义UFUNCTION() 宏和一些自定义来暴露C++方法到蓝图
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
void RandomizeActorSize(float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale) const;
如Actor 类
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "GameFramework/Actor.h"
#include "ActorWithCustomNodes.generated.h"
UCLASS()
class BLOG_API AActorWithCustomNodes : public AActor
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
// Sets default values for this actor's properties
AActorWithCustomNodes(const FObjectInitializer& ObjectInitializer);
protected:
// Called when the game starts or when spawned
virtual void BeginPlay() override;
UPROPERTY(EditAnywhere)
class UStaticMeshComponent* StaticMesh;
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
void RandomizeActorSize(float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale) const;
public:
// Called every frame
virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override;
};
BlueprintCallable,如字面描述,就是一个可以在蓝图里调用的方法。
当然,我们还需要写方法的实现,就像下面所示:
void AActorWithCustomNodes::RandomizeActorSize(const float MinimumScale, const float MaximumScale) const
{
const float Scale = MinimumScale + FGenericPlatformMath::FRand() * (MaximumScale - MinimumScale);
StaticMesh->SetWorldScale3D(FVector(Scale, Scale, Scale));
}
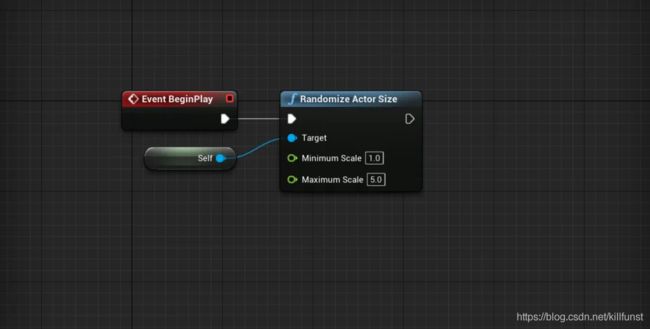
编译代码后,我们可以在该蓝图类里找到这个方法
这么简单的操作就能暴露C++方法到蓝图里了。
但上述方式暴露出来的方法,仅能在该蓝图类或者继承该类的蓝图里调用,很多时候,像一些数学运算的方法,需要在任意蓝图里调用,上诉方式不能满足了。
所以我们还需要做点改动,请往下看…
让我们的方法可以在其他蓝图里调用
这是我们新的方法申明:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
static void RandomizeActorSize(AActor * Target, float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale);
还有方法定义:
void AActorWithCustomNodes::RandomizeActorSize(AActor* Target, const float MinimumScale, const float MaximumScale)
{
// If the target is not valid, stop.
if(!Target || !IsValid(Target)) return;
// Get the target's mesh components.
TArray MeshPointers;
Target->GetComponents(MeshPointers, true);
// If the target actor has no mesh components, stop.
if(!MeshPointers.Num()) return;
// Get the first mesh component that is initialized and not marked for kill.
UStaticMeshComponent * ValidMeshComponent = nullptr;
for(int32 i = 0; i < MeshPointers.Num(); i++)
if(IsValid(MeshPointers[i]))
{
ValidMeshComponent = MeshPointers[i];
break;
}
// If there isn't one, stop.
if(!ValidMeshComponent) return;
// Set the size of the mesh component.
const float Scale = MinimumScale + FGenericPlatformMath::FRand() * (MaximumScale - MinimumScale);
ValidMeshComponent->SetWorldScale3D(FVector(Scale, Scale, Scale));
}
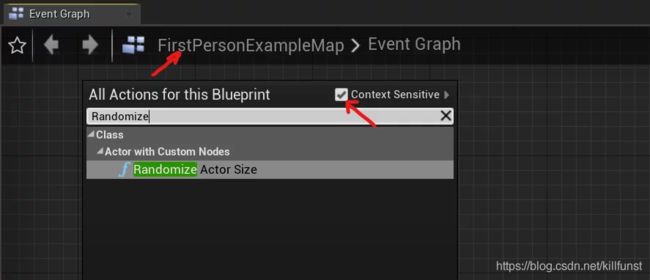
这种方式就更方便调用了。
使用这种方式,我们的蓝图方法就可以在每个蓝图图纸里显示了,比如在关卡蓝图里。
BlueprintCallable vs. BlueprintPure
这是比较常见的两个UFUNCTION的描述。
定义了BlueprintCallable,会有一个输入执行引脚和一个输出执行引脚,用于控制顺序执行。当然我们也可以定义多个输出执行引脚。
而定义了BlueprintPure,这种方法有输入输出引脚,但没有输入输出的执行引脚(白色三角形的引脚)。
多个输出引脚
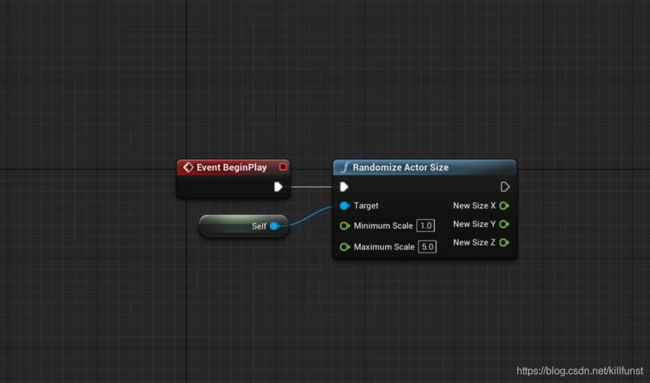
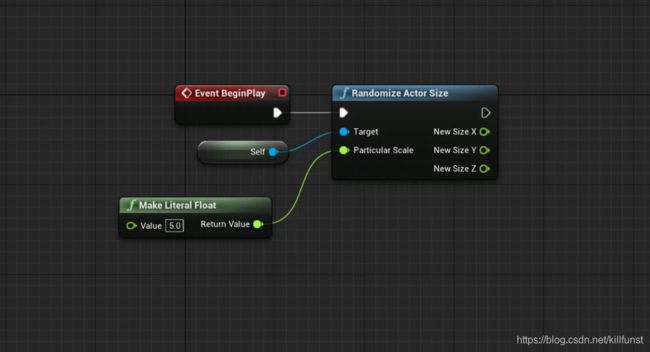
简单的C++方法一般只有一个输出值,但我们可以通过传递引用变量的方式,实现多个输出的效果。
蓝图方法就是应用这种方法来实现多个输出引脚,在C++方法里,声明为引用参数的参数会默认作为蓝图方法的输出引脚。
还是用最初的例子来讲述,申明了NewSizeX、NewSizeY、NewSizeZ三个引用参数,蓝图方法就可以输出这三个值,表示bounding box 的尺寸。
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
static void RandomizeActorSize(AActor * Target, float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale, float & NewSizeX, float & NewSizeY, float & NewSizeZ);
方法实现如下(可以跳过不看):
void AActorWithCustomNodes::RandomizeActorSize(AActor* Target, float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale, float& NewSizeX,
float& NewSizeY, float& NewSizeZ)
{
// If the target is not valid, stop.
if(!Target || !IsValid(Target)) return;
// Get the target's mesh components.
TArray MeshPointers;
Target->GetComponents(MeshPointers, true);
// If the target actor has no mesh components, stop.
if(!MeshPointers.Num()) return;
// Get the first mesh component that is initialized and not marked for kill.
UStaticMeshComponent * ValidMeshComponent = nullptr;
for(int32 i = 0; i < MeshPointers.Num(); i++)
if(IsValid(MeshPointers[i]))
{
ValidMeshComponent = MeshPointers[i];
break;
}
// If there isn't one, stop.
if(!ValidMeshComponent) return;
// Set the size of the mesh component.
const float Scale = MinimumScale + FGenericPlatformMath::FRand() * (MaximumScale - MinimumScale);
ValidMeshComponent->SetWorldScale3D(FVector(Scale, Scale, Scale));
// Get the new size
const FVector Bounds = ValidMeshComponent->GetStaticMesh()->GetBoundingBox().GetSize() * Scale;
NewSizeX = Bounds.X;
NewSizeY = Bounds.Y;
NewSizeZ = Bounds.Z;
}
但如果我们真的需要传递引用参数到引用引脚呢?这也是可以的,需要在参数声明前加上UPARAM(ref)
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
static void RandomizeActorSize(AActor * Target, UPARAM(ref) const float & ParticularScale, float & NewSizeX,
float & NewSizeY, float & NewSizeZ);
多个输出执行引脚
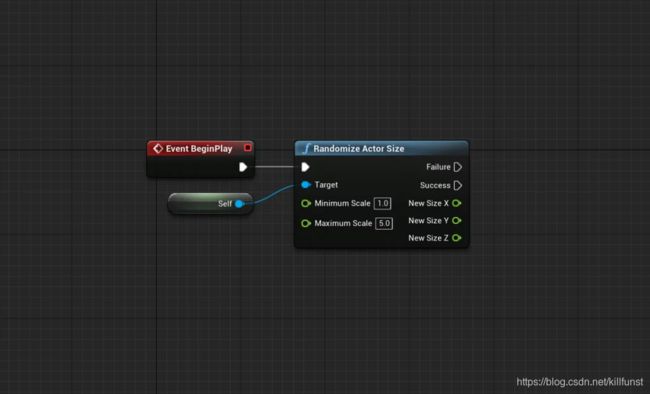
有时候我们需要多个输出执行引脚,比如经过方法里的逻辑,当逻辑输出True时,走成功的执行引脚;逻辑输出False时,走失败的执行引脚。
首先要在头文件里定义枚举
UENUM(BlueprintType)
enum EOutcomePins
{
Failure,
Success
};
然后像下面例子那样改写我们的方法声明
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, meta = (ExpandEnumAsExecs = "Outcome"))
static void RandomizeActorSize(AActor * Target, float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale, float & NewSizeX,
float & NewSizeY, float & NewSizeZ, TEnumAsByte & Outcome);
方法实现如下:
void AActorWithCustomNodes::RandomizeActorSize(AActor* Target, float MinimumScale, float MaximumScale, float& NewSizeX,
float& NewSizeY, float& NewSizeZ, TEnumAsByte & Outcome)
{
// By default, set the outcome to failure, and only change if everything else executed successfully
Outcome = EOutcomePins::Failure;
// If the target is not valid, stop.
if(!Target || !IsValid(Target)) return;
// Get the target's mesh components.
TArray MeshPointers;
Target->GetComponents(MeshPointers, true);
// If the target actor has no mesh components, stop.
if(!MeshPointers.Num()) return;
// Get the first mesh component that is initialized and not marked for kill.
UStaticMeshComponent * ValidMeshComponent = nullptr;
for(int32 i = 0; i < MeshPointers.Num(); i++)
if(IsValid(MeshPointers[i]))
{
ValidMeshComponent = MeshPointers[i];
break;
}
// If there isn't one, stop.
if(!ValidMeshComponent) return;
// Set the size of the mesh component.
const float Scale = MinimumScale + FGenericPlatformMath::FRand() * (MaximumScale - MinimumScale);
ValidMeshComponent->SetWorldScale3D(FVector(Scale, Scale, Scale));
// Get the new size
const FVector Bounds = ValidMeshComponent->GetStaticMesh()->GetBoundingBox().GetSize() * Scale;
NewSizeX = Bounds.X;
NewSizeY = Bounds.Y;
NewSizeZ = Bounds.Z;
// Everything has finished executing, let's set Outcome to success.
Outcome = EOutcomePins::Success;
}
Categories、Tooltips
通过添加Categories描述来给蓝图方法放置在列表的指定的分类中,多层分类用“|”隔开。
而Tooltips是给这个蓝图方法添加使用提示。
如:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, meta = (ExpandEnumAsExecs = "Outcome", Category="Actor|Mesh|Scale", ToolTip = "Try to ranomize the size of actor's static mesh component.\n\nNewSizeX, Y, Z - bounding box for the new actor's scale.", DeprecatedFunction, DeprecationMessage="Please switch to the new and improved Set Actor Scale Neue node."))
原文地址:https://mikelis.net/designing-blueprint-nodes-through-c/