【深蓝学院】移动机器人运动规划--第2章 基于搜索的路径规划--作业
1. Assignment
#include "Astar_searcher.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
//初始化grid map
void AstarPathFinder::initGridMap(double _resolution, Vector3d global_xyz_l, Vector3d global_xyz_u, int max_x_id, int max_y_id, int max_z_id)
{
gl_xl = global_xyz_l(0);//这个应该是左下边界
gl_yl = global_xyz_l(1);
gl_zl = global_xyz_l(2);
gl_xu = global_xyz_u(0);
gl_yu = global_xyz_u(1);
gl_zu = global_xyz_u(2);
GLX_SIZE = max_x_id;
GLY_SIZE = max_y_id;
GLZ_SIZE = max_z_id;
GLYZ_SIZE = GLY_SIZE * GLZ_SIZE;
GLXYZ_SIZE = GLX_SIZE * GLYZ_SIZE;//计算出整个map的最大index
resolution = _resolution;
inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution;
data = new uint8_t[GLXYZ_SIZE];
memset(data, 0, GLXYZ_SIZE * sizeof(uint8_t));
//二重指针数组,这样理解:
// int[5]是一个一维数组元素是int数,是一条线,
// int*[5]是一个二维数组,元素是一维数组指针,首地址是第1条线的地址,+1访问下一条线,
// int**[5]是3维数组,元素是2维数组指针,是一个矩形空间,首地址是第一个平面的地址,+1访问下一个平面
GridNodeMap = new GridNodePtr ** [GLX_SIZE];//存放所有grid node 的数组
for(int i = 0; i < GLX_SIZE; i++){
GridNodeMap[i] = new GridNodePtr * [GLY_SIZE];
for(int j = 0; j < GLY_SIZE; j++){
GridNodeMap[i][j] = new GridNodePtr [GLZ_SIZE];
for( int k = 0; k < GLZ_SIZE;k++){
Vector3i tmpIdx(i,j,k);
Vector3d pos = gridIndex2coord(tmpIdx);
GridNodeMap[i][j][k] = new GridNode(tmpIdx, pos);
}
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("\nheuristic: %d, tie breaker: %d", heu_, tie_breaker_);
}
void AstarPathFinder::resetGrid(GridNodePtr ptr)
{
ptr->id = 0;
ptr->cameFrom = NULL;
ptr->gScore = inf;
ptr->fScore = inf;
}
void AstarPathFinder::resetUsedGrids()
{
for(int i=0; i < GLX_SIZE ; i++)
for(int j=0; j < GLY_SIZE ; j++)
for(int k=0; k < GLZ_SIZE ; k++)
resetGrid(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]);
}
void AstarPathFinder::setObs(const double coord_x, const double coord_y, const double coord_z)
{
if( coord_x < gl_xl || coord_y < gl_yl || coord_z < gl_zl ||
coord_x >= gl_xu || coord_y >= gl_yu || coord_z >= gl_zu )
return;
int idx_x = static_cast<int>( (coord_x - gl_xl) * inv_resolution);
int idx_y = static_cast<int>( (coord_y - gl_yl) * inv_resolution);
int idx_z = static_cast<int>( (coord_z - gl_zl) * inv_resolution);
data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] = 1;
}
vector<Vector3d> AstarPathFinder::getVisitedNodes()
{
vector<Vector3d> visited_nodes;
for(int i = 0; i < GLX_SIZE; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < GLY_SIZE; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < GLZ_SIZE; k++){
//if(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]->id != 0) // visualize all nodes in open and close list
if(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]->id == -1) // visualize nodes in close list only
visited_nodes.push_back(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]->coord);
}
ROS_WARN("visited_nodes size : %d", visited_nodes.size());
return visited_nodes;
}
//idx to coord
Vector3d AstarPathFinder::gridIndex2coord(const Vector3i & index)
{
Vector3d pt;
pt(0) = ((double)index(0) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_xl;
pt(1) = ((double)index(1) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_yl;
pt(2) = ((double)index(2) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_zl;
return pt;
}
Vector3i AstarPathFinder::coord2gridIndex(const Vector3d & pt)
{
Vector3i idx;
idx << min( max( int( (pt(0) - gl_xl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLX_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (pt(1) - gl_yl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLY_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (pt(2) - gl_zl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLZ_SIZE - 1);
return idx;
}
Eigen::Vector3d AstarPathFinder::coordRounding(const Eigen::Vector3d & coord)
{
return gridIndex2coord(coord2gridIndex(coord));
}
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isOccupied(const Eigen::Vector3i & index) const
{
return isOccupied(index(0), index(1), index(2));
}
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isFree(const Eigen::Vector3i & index) const
{
return isFree(index(0), index(1), index(2));
}
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isOccupied(const int & idx_x, const int & idx_y, const int & idx_z) const
{
return (idx_x >= 0 && idx_x < GLX_SIZE && idx_y >= 0 && idx_y < GLY_SIZE && idx_z >= 0 && idx_z < GLZ_SIZE &&
(data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] == 1));
}
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isFree(const int & idx_x, const int & idx_y, const int & idx_z) const
{
return (idx_x >= 0 && idx_x < GLX_SIZE && idx_y >= 0 && idx_y < GLY_SIZE && idx_z >= 0 && idx_z < GLZ_SIZE &&
(data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] < 1));
}
inline void AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc(GridNodePtr currentPtr, vector<GridNodePtr> & neighborPtrSets, vector<double> & edgeCostSets)
{
neighborPtrSets.clear();
edgeCostSets.clear();
/*
*
STEP 4: finish AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc yourself
please write your code below
*
*
*/
//A*每次找26个neighbor node,判断是否occupied,如果不是,计算edge cost(g),并加入到open list中
Eigen::Vector3i tmp_index = currentPtr->index;
Eigen::Vector3i tmp_lower, tmp_upper;
tmp_lower << min( max( int( (tmp_index(0) - 1) ), 0), GLX_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (tmp_index(1) - 1) ), 0), GLY_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (tmp_index(2) - 1) ), 0), GLZ_SIZE - 1);
tmp_upper << min( max( int( (tmp_index(0) + 1) ), 0), GLX_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (tmp_index(1) + 1) ), 0), GLY_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (tmp_index(2) + 1) ), 0), GLZ_SIZE - 1);
for(int i = tmp_lower(0); i <= tmp_upper(0); i++){
for(int j = tmp_lower(1); j <= tmp_upper(1); j++){
for(int k = tmp_lower(2); k <= tmp_upper(2); k++){
//free节点才加入扩展
Eigen::Vector3i neighbor_idx(i,j,k);
if(isFree(neighbor_idx) && neighbor_idx != tmp_index) {//只加入free node,且自己不加
neighborPtrSets.emplace_back(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]);
edgeCostSets.emplace_back(
sqrt(
std::pow((i - currentPtr->index(0)), 2)
+ std::pow((j - currentPtr->index(1)), 2)
+ std::pow((k - currentPtr->index(2)), 2))
);
}
}
}
}
}
double AstarPathFinder::getHeu(GridNodePtr node1, GridNodePtr node2)
{
/*
choose possible heuristic function you want
Manhattan, Euclidean, Diagonal, or 0 (Dijkstra)
Remember tie_breaker learned in lecture, add it here ?
*
*
*
STEP 1: finish the AstarPathFinder::getHeu , which is the heuristic function
please write your code below
*
*
*/
if(!node1 || !node2) {
ROS_ERROR("Invalid node pointer");
return std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); // 或其他错误处理方式
}
double heuristic_value;
if( heu_ == ZERO ) {
return 0;
} else if ( heu_ == L1 ) {
heuristic_value = (node1->coord-node2->coord).lpNorm<1>();
} else if ( heu_ == L2 ) {
heuristic_value = (node1->coord-node2->coord).lpNorm<2>();
} else if ( heu_ == DIAGONAL ) {//对角diagonal暂时先返回2D的diagonal的结果
double dx = fabs(node1->coord.x() - node2->coord.x());
double dy = fabs(node1->coord.y() - node2->coord.y());
double dz = fabs(node1->coord.z() - node2->coord.z());
double tmp_min = std::min(min(dx, dy), dz);
heuristic_value = (dx + dy + dz) + (sqrt3_ - 3) * tmp_min;//助教给的答案公式
}
switch( tie_breaker_ ){
case RULE_1:
if(heu_== L1)
tb_rule1_p_ = 1.0 / (Eigen::Vector3d(GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE, GLZ_SIZE)).lpNorm<1>();// 1.0/可能path的最大cost
else if(heu_== L2) {
tb_rule1_p_ = 1.0 / (Eigen::Vector3d(GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE, GLZ_SIZE)).lpNorm<2>();
} else if(heu_== DIAGONAL) {
tb_rule1_p_ = 1.0 / (GLX_SIZE + GLY_SIZE + GLZ_SIZE) + (sqrt3_ - 3) * std::min(min(GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE), GLZ_SIZE);
}
heuristic_value = heuristic_value * (1 + tb_rule1_p_);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("tie breaker RULE_0 p: " << tb_rule1_p_);//L2 tb_rule1_p_=0.0133333
break;
case RULE_2://未来可能的实现
break;
case RULE_3:
break;
case RULE_4:
break;
case RULE_NONE: default:
break;
}
return heuristic_value;
}
void AstarPathFinder::AstarGraphSearch(Vector3d start_pt, Vector3d end_pt)
{
ros::Time time_1 = ros::Time::now();
//index of start_point and end_point
Vector3i start_idx = coord2gridIndex(start_pt);
Vector3i end_idx = coord2gridIndex(end_pt);
goalIdx = end_idx;
//position of start_point and end_point
start_pt = gridIndex2coord(start_idx);
end_pt = gridIndex2coord(end_idx);
//Initialize the pointers of struct GridNode which represent start node and goal node
GridNodePtr startPtr = new GridNode(start_idx, start_pt);
GridNodePtr endPtr = new GridNode(end_idx, end_pt);
//openSet is the open_list implemented through multimap in STL library
openSet.clear();
// currentPtr represents the node with lowest f(n) in the open_list
GridNodePtr currentPtr = NULL;
GridNodePtr neighborPtr = NULL;
//put start node in open set
startPtr -> gScore = 0;
startPtr -> fScore = startPtr -> gScore + getHeu(startPtr,endPtr);
//STEP 1: finish the AstarPathFinder::getHeu , which is the heuristic function
startPtr -> id = 1;
startPtr -> coord = start_pt;
openSet.insert( make_pair(startPtr -> fScore, startPtr) );//默认按照key升序排序
/*
*
STEP 2 : some else preparatory works which should be done before while loop
please write your code below
*
*
*/
double tentative_gScore;
vector<GridNodePtr> neighborPtrSets;
vector<double> edgeCostSets;
//计算graph中所有的node到start_pt的heuristic
//将start node赋予地图(因为是刚才new出来的,不是直接从地图里面取出来的)
GridNodeMap[start_idx(0)][start_idx(1)][start_idx(2)] = startPtr;
// this is the main loop
while ( !openSet.empty() ){
/*
*
*
step 3: Remove the node with lowest cost function from open set to closed set
please write your code below
IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
This part you should use the C++ STL: multimap, more details can be find in Homework description
*
*
*/
//弹出一个就要找到他所有的未被扩展的邻居
// ROS_DEBUG("\nhere3");
currentPtr = openSet.begin()->second;
openSet.erase(openSet.begin());
currentPtr->id = -1;//mark as visited
// if the current node is the goal
if( currentPtr->index == goalIdx ){
ros::Time time_2 = ros::Time::now();
terminatePtr = currentPtr;
ROS_WARN("[A*]{sucess} Time in A* is %f ms, path cost if %f m", (time_2 - time_1).toSec() * 1000.0, currentPtr->gScore * resolution );
return;
}
//get the succetion(找到currentPtr的neighbor nodes)
AstarGetSucc(currentPtr, neighborPtrSets, edgeCostSets); //STEP 4: finish AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc yourself
/*
*
*
STEP 5: For all unexpanded neigbors "m" of node "n", please finish this for loop
please write your code below
*
*/
//在这个循环里面,id只会为0/1,为-1的都是遍历完之后被erase掉了
for(int i = 0; i < (int)neighborPtrSets.size(); i++){
neighborPtr = neighborPtrSets[i];
tentative_gScore = currentPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
// ROS_DEBUG("\nneighborPtr->id: %d", neighborPtr->id);
/*
*
*
Judge if the neigbors have been expanded
please write your code below
IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
neighborPtrSets[i]->id = -1 : expanded, equal to this node is in close set
neighborPtrSets[i]->id = 1 : unexpanded, equal to this node is in open set
*
*/
if(neighborPtr -> id == 0 ){ //discover a new node, which is not in the closed set and open set
/*
*
*
STEP 6: As for a new node, do what you need do ,and then put neighbor in open set and record it
please write your code below
*
*/
if(neighborPtr -> gScore == inf) {
neighborPtr->cameFrom = currentPtr;
neighborPtr -> gScore = tentative_gScore;
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr, endPtr); //getHeu(startPtr,neighborPtr);
neighborPtr -> id = 1;//标记为expanded
openSet.insert( make_pair(neighborPtr->fScore, neighborPtr) );//加入到open list中,注意,这里需要使用fscore,而不是gscore,如果是gscore,就成了Dijkstra了
// ROS_DEBUG("\nneighborPtr -> gScore is inf");
continue;//这里可以直接退出本轮循环,因为下面的条件不会满足
} else {
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nA* here neighborPtr -> gScore is not inf");
}
}
//这里不能取等,去等了如果前面在找neighbors时没有去掉本身,就会陷入自己来自于自己的bug
if(tentative_gScore < neighborPtr-> gScore){ //this node is in open set and need to judge if it needs to update, the "0" should be deleted when you are coding
/*
*
*
STEP 7: As for a node in open set, update it , maintain the openset ,and then put neighbor in open set and record it
please write your code below
*
*/
neighborPtr -> cameFrom = currentPtr;
neighborPtr -> gScore = tentative_gScore;
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr, endPtr);
}
//不满足条件的就是在close set中,不用处理,在下次的while循环中会被erase掉
}
}
//if search fails
ros::Time time_2 = ros::Time::now();
if((time_2 - time_1).toSec() > 0.1)
ROS_WARN("Time consume in Astar path finding is %f", (time_2 - time_1).toSec() );
}
vector<Vector3d> AstarPathFinder::getPath()
{
vector<Vector3d> path;
vector<GridNodePtr> gridPath;
/*
*
*
STEP 8: trace back from the curretnt nodePtr to get all nodes along the path
please write your code below
*
*/
Vector3d end_pt = gridIndex2coord(goalIdx);
GridNodePtr tmpPtr = terminatePtr;
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("terminatePtr->gscore: " << tmpPtr->gScore);
while(tmpPtr->cameFrom != nullptr) { //这两种判断方式都可以,gscore为0或者cameFrome为空
// while(tmpPtr->gScore != 0) {
gridPath.emplace_back(tmpPtr);
tmpPtr = tmpPtr->cameFrom;
}
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\nhas found start goal, coord: " << tmpPtr->coord.transpose());
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("\ninverse path:, gridPath.size()" << gridPath.size() );
for (auto ptr: gridPath) {
path.push_back(ptr->coord);
ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("" << ptr->coord.transpose());
}
reverse(path.begin(),path.end());
return path;
}
2. 解
2.1 A* 不同heuristic的对比
一些设置:
- 在
random_complex_generator.cpp固定随机种子固定生成的地图
void RandomMapGenerate()
{
// random_device rd;
// default_random_engine eng(rd());
default_random_engine eng(40); // 使用42作为种子(unsigned int类型),使得每次生成的地图是固定的
...
}
- 由于每次手动点击设置goal会存在偏差,于是在
demo_node.cpp中固定goal
void rcvWaypointsCallback(const nav_msgs::Path & wp)
{
if( wp.poses[0].pose.position.z < 0.0 || _has_map == false )
return;
Vector3d target_pt;
// target_pt << wp.poses[0].pose.position.x,
// wp.poses[0].pose.position.y,
// wp.poses[0].pose.position.z;
target_pt << 4.90,4.90,0; //设为固定的用于对比
ROS_INFO("\n[node] receive the planning target, start is: (%f, %f, %f), target is: (%f, %f, %f)",
_start_pt(0), _start_pt(1), _start_pt(2), target_pt(0), target_pt(1), target_pt(2));
pathFinding(_start_pt, target_pt);
}
- 设置:无tie breaker,heuristic有四个:0,L1,L2,Diagonal
2D Diagonal heuristic: h = ( d x + d y ) + D ∗ ( 2 − 2 ) ∗ m i n ( d x , d y ) h=(dx +dy) +D* (\sqrt2-2)*min(dx,dy) h=(dx+dy)+D∗(2−2)∗min(dx,dy)
3D Diagonal heuristic: h = ( d x + d y + d z ) + D ∗ ( 3 − 3 ) ∗ m i n ( d x , d y , d z ) h=(dx +dy+dz) +D* (\sqrt3-3)*min(dx,dy,dz) h=(dx+dy+dz)+D∗(3−3)∗min(dx,dy,dz)
其中
D D D为沿着一个轴移动的成本(通常设为1),
d x = ∣ x n o d e 1 − x n o d e 2 ∣ d y = ∣ y n o d e 1 − y n o d e 2 ∣ d z = ∣ z n o d e 1 − z n o d e 2 ∣ dx=|x_{node1} - x_{node2}| \\dy=|y_{node1} - y_{node2}|\\ dz=|z_{node1} - z_{node2}| dx=∣xnode1−xnode2∣dy=∣ynode1−ynode2∣dz=∣znode1−znode2∣
运行结果实例截图:
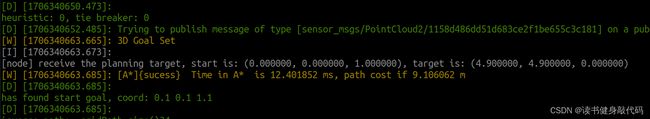
结果:
虽然做了上述设置,但每次运行时间还是不同,所以多做几次取平均值: - 0 heuristic
| 组号 | Heuristic | time(ms) | path cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 12.401852 | 9.106062 |
| 2 | 0 | 12.944236 | 9.106062 |
| 3 | 0 | 12.540016 | 9.106062 |
| 4 | 0 | 12.005185 | 9.106062 |
| avg | 0 | 12.47282225 | 9.106062 |
- L1 heuristic
| 组号 | Heuristic | time(ms) | path cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L1 | 11.930942 | 9.106062 |
| 2 | 0 | 12.116784 | 9.106062 |
| 3 | 0 | 11.759542 | 9.106062 |
| 4 | 0 | 11.780423 | 9.106062 |
| avg | 0 | 11.89692275 | 9.106062 |
- L2 heuristic
| 组号 | Heuristic | time(ms) | path cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L1 | 12.830061 | 9.106062 |
| 2 | 0 | 13.720000 | 9.106062 |
| 3 | 0 | 13.756997 | 9.106062 |
| 4 | 0 | 13.889060 | 9.106062 |
| avg | 0 | 13.5490295 | 9.106062 |
- Diagonal heuristic
| 组号 | Heuristic | time(ms) | path cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L1 | 12.651738 | 9.106062 |
| 2 | 0 | 12.741407 | 9.106062 |
| 3 | 0 | 14.569988 | 9.106062 |
| 4 | 0 | 12.993555 | 9.106062 |
| avg | 0 | 13.239172 | 9.106062 |
- avg对比
path cost相同,都是最优,只比较时间:
| Heuristic | time(ms) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 12.47282225 |
| L1 | 11.89692275 |
| L2 | 13.5490295 |
| Diagonal | 13.239172 |
在这张地图和goal的设置中,使用L1 heuristic相较0 heuristic来说搜索时间有所缩短,L2和Diagonal都使搜索时间增加,这里仅作参考,具体heuristic的作用针对不同goal和地图可能不同。
2.2 Tie breaker对A* 的影响
同样按照2.1中的设置,heuristic固定为Diagonal,对A* 施加RULE_1的tie breaker:
在计算Heuristic时加入一个系数p,计算 h ′ = h ∗ ( 1 + p ) h^\prime=h*(1+p) h′=h∗(1+p) p = 一步的最小 c o s t 可能的 p a t h 的最大 c o s t ( 比如矩形地图的斜对角线 c o s t ) p=\frac{一步的最小cost}{可能的path的最大cost(比如矩形地图的斜对角线cost)} p=可能的path的最大cost(比如矩形地图的斜对角线cost)一步的最小cost
该部分代码如下:
double AstarPathFinder::getHeu(GridNodePtr node1, GridNodePtr node2)
{
if(!node1 || !node2) {
ROS_ERROR("Invalid node pointer");
return std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); // 或其他错误处理方式
}
double heuristic_value;
if( heu_ == ZERO ) {
return 0;
} else if ( heu_ == L1 ) {
heuristic_value = (node1->coord-node2->coord).lpNorm<1>();
} else if ( heu_ == L2 ) {
heuristic_value = (node1->coord-node2->coord).lpNorm<2>();
} else if ( heu_ == DIAGONAL ) {//对角diagonal暂时先返回2D的diagonal的结果
double dx = fabs(node1->coord.x() - node2->coord.x());
double dy = fabs(node1->coord.y() - node2->coord.y());
double dz = fabs(node1->coord.z() - node2->coord.z());
double tmp_min = std::min(min(dx, dy), dz);
heuristic_value = (dx + dy + dz) + (sqrt3_ - 3) * tmp_min;
}
switch( tie_breaker_ ){
case RULE_1:
if(heu_== L1)
tb_rule1_p_ = 1.0 / (Eigen::Vector3d(GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE, GLZ_SIZE)).lpNorm<1>();// 1.0/可能path的最大cost
else if(heu_== L2) {
tb_rule1_p_ = 1.0 / (Eigen::Vector3d(GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE, GLZ_SIZE)).lpNorm<2>();
} else if(heu_== DIAGONAL) {
tb_rule1_p_ = 1.0 / (GLX_SIZE + GLY_SIZE + GLZ_SIZE) + (sqrt3_ - 3) * std::min(min(GLX_SIZE, GLY_SIZE), GLZ_SIZE);
}
heuristic_value = heuristic_value * (1 + tb_rule1_p_);
// ROS_DEBUG_STREAM("tie breaker RULE_0 p: " << tb_rule1_p_);//L2 tb_rule1_p_=0.0133333
break;
case RULE_2://未来可能的实现
break;
case RULE_3:
break;
case RULE_4:
break;
case RULE_NONE: default:
break;
}
return heuristic_value;
}
- 无tie breaker
| 组号 | tie breaker | time(ms) | path cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NO | 13.050096 | 9.106062 |
| 2 | NO | 12.888861 | 9.106062 |
| 3 | NO | 13.205173 | 9.106062 |
| 4 | NO | 13.281006 | 9.106062 |
| 5 | NO | 12.602840 | 9.106062 |
| 6 | NO | 13.001383 | 9.106062 |
| 7 | NO | 12.626246 | 9.106062 |
| 8 | NO | 13.128497 | 9.106062 |
| avg | NO | 12.97301275 | 9.106062 |
- RULE_1 tie breaker
| 组号 | tie breaker | time(ms) | path cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RULE_1 | 14.896261 | 9.106062 |
| 2 | RULE_1 | 16.362376 | 9.106062 |
| 3 | RULE_1 | 15.170169 | 9.106062 |
| 4 | RULE_1 | 15.184500 | 9.106062 |
| 5 | RULE_1 | 15.019135 | 9.106062 |
| 6 | RULE_1 | 14.946042 | 9.106062 |
| 7 | RULE_1 | 15.375405 | 9.106062 |
| 8 | RULE_1 | 15.038559 | 9.106062 |
| avg | RULE_1 | 15.249055875 | 9.106062 |
- avg对比
path cost同样都是最优。
| tie breaker | time(ms) |
|---|---|
| NO | 12.97301275 |
| RULE_1 | 15.249055875 |
从本组实验中可以看出,加入tie breaker使A* 的搜索时间增加,但仍是最优路径,结果仅做参考。
2.3 A*与JPS对比
由于JPS部分比较复杂,课程作业给出了rules,主要是在JPSGetSucc()函数中判断是否jump成功以及使用Look ahead rules和Jumping rules,根据A的实现方法,我实现了JPS,但是在对比过程中经常发现JPS搜索耗时比A长,且path cost经常比A*稍微大一点,所以JPS可能是存在问题,但是由于最核心的rules不是自己实现的,所以debug起来有些困难,所以JPS部分实验没办法开展,贴个图:
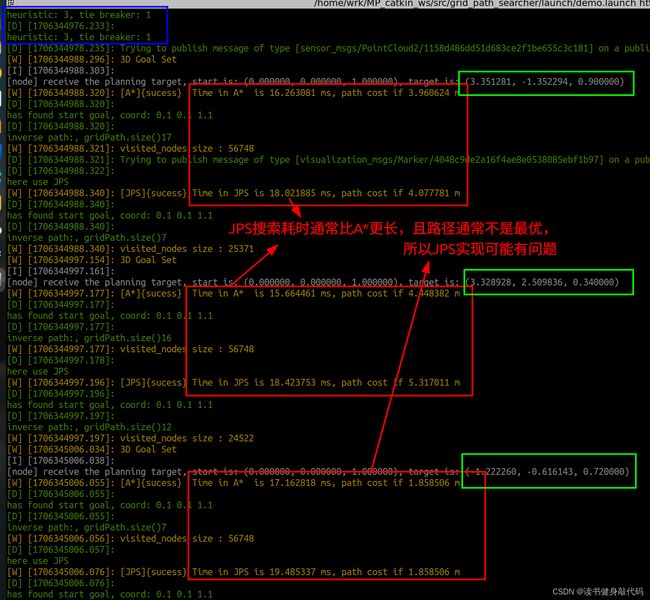
总结:
- 空旷场景JPS可坑更快,障碍物多;地形复杂时A* 可能更好,此时JPS优势可能不明显。
- JPS只能在D相同的grid map中使用,其他map无法使用,但是A*可以使用。
2.4 过程中遇到的问题
2.4.1 地图分辨率
motion planning中对于地图有分辨率(resolution)的概念
nh.param("map/resolution", _resolution, 0.2);
_inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution;//分辨率0.2,逆分辨率即5
_max_x_id = (int)(_x_size * _inv_resolution);
_max_y_id = (int)(_y_size * _inv_resolution);
_max_z_id = (int)(_z_size * _inv_resolution);

降低分辨率会导致空间开销进一步减小,算法速度加快,但精度会降低,例如,如果将 _resolution 的值从0.2降低到0.1,那么每个栅格代表的实际世界空间的大小就从5格降低到10格。修改分辨率是精度与效率的trade-off。
2.4.2 JPS粗略理解
JPSGetSucc函数用于进行jump,并判断是否jump成功。
其中,JPS3DNeib是重要的数据结构,
ns总会被add的nodef1:可能是force neighbor的节点f2:这个应该是straight recall的要被扩展的节点nsz:4种L1 norm对应的{always added, neighbors to add if forced}
jump函数是递归函数,如果发现存在isOccupied的neighbor,则jump返回true,
num_neib + num_fneib = always added+ neighbors to add if forced是一次扩展最多query的node个数
先query所有always added node,再query所有neighbors to add if forced。
在过程中如果发现了forced neighbor(即jump返回true,即发现了occupied),则记录扩展的方向(从currentPtr的index三个方向上个增加了多少,这个增加量就是expandDir扩展方向),并且将这个存在force neighbor的node(index为neighborIdx)加到open list中,并计算edgeCostSets(当前节点indexcurrentPtr->index和存在forced node的indexneighborIdx的欧氏距离),即g。
2.4.3 some bugs
四个错误:
- openSet.insert( make_pair(neighborPtr->fScore, neighborPtr) )这里我用的是gscore,应该用fscore
- 算hscore的时候,应该是当前node到end node,而不是start node到当前node
我的错误代码:
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(startPtr,neighborPtr); //getHeu(startPtr,neighborPtr);
正确代码:
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr, endPtr); //getHeu(startPtr,neighborPtr);
- 计算gscore进行更新时计算错误,要从curPtr加上edgeCost与之前的neighborPtr中保存的从别的路径到的cost相比,意思是:从curPtr到neighborPtr有不止一条路,现在尝试的这条路与之前保存的进行相比,不要比错了。我用了下面的错误的代码
tentative_gScore = neighborPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
if(tentative_gScore < neighborPtr-> gScore){
neighborPtr -> cameFrom = currentPtr;
neighborPtr -> gScore = tentative_gScore;
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr, endPtr);
}
我这样写,下面那个if永远进不去。
上面第一句应该改为
tentative_gScore = currentPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
对算法理解不深入。
- 一个bug,在main中,忘了对JPS设置heuristic。


