Python算法题集_从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
Python算法题集_从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 题105:从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 1. 示例说明
- 2. 题目解析
-
- - 题意分解
- - 优化思路
- - 测量工具
- 3. 代码展开
-
- 1) 标准求解【先序生成+中序定位+递归】
- 2) 改进版一【先序队列+中序队列+递归】
- 3) 改进版二【先序堆栈+中序堆栈+递归】
- 4) 改进版三【迭代+先序循环+辅助堆栈】
- 4. 最优算法
本文为Python算法题集之一的代码示例
题105:从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
1. 示例说明
- 给定两个整数数组
preorder和inorder,其中preorder是二叉树的先序遍历,inorder是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
输出: [-1]
提示:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorder和inorder均 无重复 元素inorder均出现在preorder
preorder保证 为二叉树的前序遍历序列inorder保证 为二叉树的中序遍历序列
2. 题目解析
- 题意分解
- 先序遍历(Preorder Traversal)是常见的二叉树遍历方式,其顺序为:根节点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树【根|左|右】
- 中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)是另一种二叉树遍历方式,其顺序为:左子树 -> 根节点 -> 右子树【左|根|右】
- 本题有两个核心部分,1为
preorder、inorder数组的根节点区分和左子树|右子树节点分离,2是生成链表 - 基本的设计思路在于
preorder次序为根|左|右,可以分离出根节点,然后依据inorder次序为左|根|右的特点,拆分出左子树、右子树
- 优化思路
-
通常优化:减少循环层次
-
通常优化:增加分支,减少计算集
-
通常优化:采用内置算法来提升计算速度
-
分析题目特点,分析最优解
-
可以考虑使用递归、迭代分别实现
-
先序遍历的第一个节点为二叉树的根节点
-
先序遍历根节点向左子树到底,中序遍历最左下节点为第一个,因此先序遍历列表递归左子树,遇到中序遍历的第一个节点截止,可依此解题
-
- 测量工具
- 本地化测试说明:LeetCode网站测试运行时数据波动很大【可把页面视为功能测试】,因此需要本地化测试解决数据波动问题
CheckFuncPerf(本地化函数用时和内存占用测试模块)已上传到CSDN,地址:Python算法题集_检测函数用时和内存占用的模块- 本题本地化超时测试用例自己生成,详见【最优算法章节】
3. 代码展开
1) 标准求解【先序生成+中序定位+递归】
使用先序列表生成根节点,用中序列表定位左右子树,递归展开
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
def buildTree_base(self, preorder, inorder):
if not preorder and not inorder:
return
root=TreeNode(preorder[0])
irootidx=inorder.index(preorder[0])
root.left=self.buildTree_base(preorder[1:irootidx+1],inorder[:irootidx])
root.right=self.buildTree_base(preorder[irootidx+1:],inorder[irootidx+1:])
return root
aSolution = Solution()
aroot = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(idepth, icountlist)
prelist = preorderTraversal(aroot)
inlist = inorderTraversal(aroot)
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_base, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
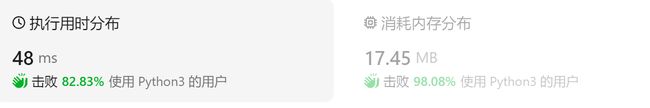
函数 buildTree_base 的运行时间为 137.60 ms;内存使用量为 10036.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
2) 改进版一【先序队列+中序队列+递归】
使用先序列表和中序列表作为队列,利用先序最左节点为中序第一个节点的特点,递归展开
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
def buildTree_ext1(self, preorder, inorder):
def build(rootval):
if inorder and inorder[0] != rootval:
root = TreeNode(preorder.pop(0))
root.left = build(root.val)
inorder.pop(0)
root.right = build(rootval)
return root
return build(None)
aSolution = Solution()
aroot = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(idepth, icountlist)
prelist = preorderTraversal(aroot)
inlist = inorderTraversal(aroot)
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_ext1, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
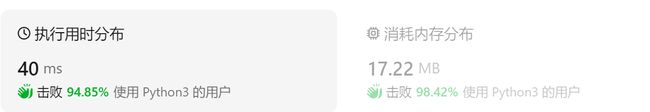
函数 buildTree_ext1 的运行时间为 791.85 ms;内存使用量为 10332.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
3) 改进版二【先序堆栈+中序堆栈+递归】
还是利用先序最左节点为中序第一个节点的特点进行递归展开,但是由于list的pop(0)【队列】性能远远低于pop(-1)【堆栈】,因此先将先序列表和中序列表反转,然后使用堆栈方式实现
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
def buildTree_ext2(self, preorder, inorder):
preorder.reverse()
inorder.reverse()
def build(rootval):
if inorder and inorder[-1] != rootval:
root = TreeNode(preorder.pop())
root.left = build(root.val)
inorder.pop()
root.right = build(rootval)
return root
return build(None)
aSolution = Solution()
aroot = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(idepth, icountlist)
prelist = preorderTraversal(aroot)
inlist = inorderTraversal(aroot)
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_ext2, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
函数 buildTree_ext2 的运行时间为 147.61 ms;内存使用量为 8196.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
4) 改进版三【迭代+先序循环+辅助堆栈】
使用辅助堆栈实现迭代算法,以先序列表为主循环,堆栈和中序列表定位右子树的根节点
import CheckFuncPerf as cfp
class Solution:
def buildTree_ext3(self, preorder, inorder):
if not preorder:
return None
root = TreeNode(preorder[0])
stack = [root]
inorderIndex = 0
for iIdx in range(1, len(preorder)):
preorderVal = preorder[iIdx]
tmpnode = stack[-1]
if tmpnode.val != inorder[inorderIndex]:
tmpnode.left = TreeNode(preorderVal)
stack.append(tmpnode.left)
else:
while stack and stack[-1].val == inorder[inorderIndex]:
tmpnode = stack.pop()
inorderIndex += 1
tmpnode.right = TreeNode(preorderVal)
stack.append(tmpnode.right)
return root
aSolution = Solution()
aroot = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(idepth, icountlist)
prelist = preorderTraversal(aroot)
inlist = inorderTraversal(aroot)
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_ext2, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 运行结果
函数 buildTree_ext3 的运行时间为 113.70 ms;内存使用量为 8196.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
4. 最优算法
根据本地日志分析,最优算法为第4种方式【迭代+先序循环+辅助堆栈】buildTree_ext3
def inorderTraversal(root):
if not root:
return []
list_stack = []
list_node = []
while root or list_stack:
if root:
list_stack.append(root)
root = root.left
else:
curnode = list_stack.pop()
list_node.append(curnode.val)
root = curnode.right
return list_node
def preorderTraversal(root):
if root is None:
return []
list_node = []
stack = [root]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
list_node.append(node.val)
if node.right:
stack.append(node.right)
if node.left:
stack.append(node.left)
return list_node
def generate_symmetry_binary_tree(ilevel, icountlist):
if ilevel <= 0:
return None
root = TreeNode(icountlist[0])
icountlist[0] += 1
left = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(ilevel - 1, icountlist)
right = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(ilevel - 1, icountlist)
root.left = left
root.right = right
return root
idepth, icountlist = 16, []
icountlist.append(1)
aroot = generate_symmetry_binary_tree(idepth, icountlist)
aSolution = Solution()
prelist = preorderTraversal(aroot)
inlist = inorderTraversal(aroot)
print(f'length of list = {len(prelist)}')
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_base, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_ext1, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_ext2, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
result = cfp.getTimeMemoryStr(Solution.buildTree_ext3, aSolution, prelist.copy(), inlist.copy())
print(result['msg'], '执行结果 = {}'.format(result['result'].val))
# 算法本地速度实测比较
length of list = 65535
函数 buildTree_base 的运行时间为 137.60 ms;内存使用量为 10036.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
函数 buildTree_ext1 的运行时间为 791.85 ms;内存使用量为 10332.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
函数 buildTree_ext2 的运行时间为 147.61 ms;内存使用量为 8196.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
函数 buildTree_ext3 的运行时间为 113.70 ms;内存使用量为 8196.00 KB 执行结果 = 1
一日练,一日功,一日不练十日空
may the odds be ever in your favor ~